Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Microscope Parts and Functions
Загружено:
Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Microscope Parts and Functions
Загружено:
Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
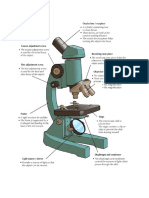
Ocular Lens - The ocular lens, or eyepiece, magnifies the image.
It contains
a measuring scale called and ocular micrometer. The ocular micrometer has
no units. Revolving Nose Piece - Several objective lenses of varying
magnification and numerical aperture are mounted on the revolving
nosepiece.
Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so
as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes. Body tube
(Head): The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. ...
Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus
Nosepiece: The upper part of a compound microscope that holds the
objective lens. Also called a revolving nosepiece or turret. ... Objective Lens:
The lens closest to the specimen that first receives the rays from the
specimen (the object) and forms the image in the focal plane of the eyepiece.
The objective lens is the lens closest to the slide or object you are viewing.
The purpose of the objective lens is to gather light and enhance
magnification. A typical compound microscope will have four objective
lenses: one scanning lens, low-power lens, high-power lens, and an oil-
immersion lens.
Stage clips: Metal clips that hold the slide in place.
Aperture: The hole in the middle of the stage that allows light from the
illuminator to reach the specimen. On/off switch: This switch on the base of
the microscope turns the illuminator off and on. Illumination: The light source
for a microscope. ... Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches
the specimen.
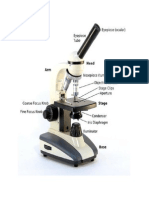
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the
specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an
iris diaphragm. Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the
specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage.
Microscopic illuminator – This is the microscopes light source, located at
the base. It is used instead of a mirror. it captures light from an external
source of a low voltage of about 100v. Condenser – These are lenses that are
used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen
Head: Often referred to as the body, it is the upper part of
the microscope that includes the eyepiece tubes and prisms. Illumination
System: The light source on light microscopes, typically mounted under the
stage except on inverted microscopes.
Diaphragm or Iris: Many microscopes have a rotating disk under the stage.
This diaphragm has different sized holes and is used to vary the intensity and
size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide.
Arm: The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope.
A mechanical stage of a microscope refers to the mechanism that has been
mounted on the stage for holding and moving the microscope slide. It is an
important part of the microscope that enhances the function of the stage.
Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus.
Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the
specimen.
Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed. Stage clips: Metal clips that
hold the slide in place. Stage height adjustment (Stage Control): These
knobs move the stage left and right or up and down. Aperture: The hole in the
middle of the stage that allows light from the illuminator to reach the
specimen.
Base: The bottom of the microscope, used for support.
On/off switch: This switch on the base of the microscope turns the
illuminator off and on. Illumination: The light source for a microscope
Вам также может понравиться
- Microscope Parts and Functions GuideДокумент3 страницыMicroscope Parts and Functions GuideJhonLloyd DomingoОценок пока нет
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыMicroscope Parts and FunctionsAntonov VodkaОценок пока нет
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsДокумент3 страницыCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsRonalee PeralesОценок пока нет
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsДокумент3 страницыParts of Microscope and Their Functionsiammiiie0150% (2)
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsДокумент9 страницCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCIОценок пока нет
- Ekaterina 6b MicroscopesДокумент19 страницEkaterina 6b Microscopesapi-269598196Оценок пока нет
- Compound Microscopes:: Parts of A Compound MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыCompound Microscopes:: Parts of A Compound MicroscopeJade SamonteОценок пока нет
- The Microscope GuideДокумент9 страницThe Microscope GuideSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- Compound Microscop EДокумент26 страницCompound Microscop EDixie MerinОценок пока нет
- สี่โมงเย็น si-mong-yen วันอาทิตย์ wan-atit: Objective lensesДокумент3 страницыสี่โมงเย็น si-mong-yen วันอาทิตย์ wan-atit: Objective lenseskim myungyОценок пока нет
- 1 MicroscopeДокумент4 страницы1 MicroscopeYasin Haq KhanjadaОценок пока нет
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsДокумент2 страницыMicroscope Parts and FunctionsKenneth P PablicoОценок пока нет
- Demonstration of Microscope and Its PartsДокумент5 страницDemonstration of Microscope and Its PartsSujoy Tontubay100% (1)
- COMPOUND-MICROSCOPEДокумент2 страницыCOMPOUND-MICROSCOPEgonaticejerome25Оценок пока нет
- Eyepiece: The Lens The Viewer Looks Through To See TheДокумент4 страницыEyepiece: The Lens The Viewer Looks Through To See TheKemuel LozadaОценок пока нет
- MicroscopeДокумент4 страницыMicroscopeAlibabaОценок пока нет
- Layka M. SabdaniДокумент4 страницыLayka M. SabdaniRaniaОценок пока нет
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeДокумент4 страницыParts and Function of A MicroscopeFria mae AbellanoОценок пока нет
- Compound Microscope PartsДокумент3 страницыCompound Microscope PartsMimi MonteОценок пока нет
- The Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)Документ11 страницThe Compund Microscope (Hardcopy)JheanAlphonsineT.MeansОценок пока нет
- Parts and Functions of a Compound MicroscopeДокумент3 страницыParts and Functions of a Compound MicroscopeTheresa LambayonОценок пока нет
- MicroscopeДокумент3 страницыMicroscopeJoun Erica TalinguezОценок пока нет
- Parts of MicroscopeДокумент4 страницыParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Compound MicroscopeДокумент5 страницParts of A Compound MicroscopeKim Ashley BallesterosОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsДокумент1 страницаParts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsThess Tecla Zerauc Azodnem0% (1)
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsДокумент2 страницыMicroscope Parts and FunctionsIrish Mejia100% (1)
- Parts of A MicroscopeДокумент5 страницParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaОценок пока нет
- Eyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeДокумент4 страницыEyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeChristine Joy ArisgarОценок пока нет
- Parts and Functions of a Compound MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыParts and Functions of a Compound MicroscopeNuñez, Eliza G.Оценок пока нет
- Microscope Parts GuideДокумент2 страницыMicroscope Parts GuideSamiracomputerstation Kuya MarvsОценок пока нет
- There Are Three Structural Parts of The Microscope IДокумент3 страницыThere Are Three Structural Parts of The Microscope Ijoshladac94Оценок пока нет
- COMPOUND Microscope-Parts & Functions: Structural ComponentsДокумент3 страницыCOMPOUND Microscope-Parts & Functions: Structural Componentssmart_dudeОценок пока нет
- Sections MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыSections MicroscopeZennОценок пока нет
- Microscope Parts GuideДокумент3 страницыMicroscope Parts GuideJanuary Pentinio AbarentosОценок пока нет
- The MicroscopeДокумент3 страницыThe MicroscopethereseОценок пока нет
- Compound MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыCompound MicroscopeditucalanshanmichaelvОценок пока нет
- Give Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыGive Detail Function of Parts of The MicroscopeLiam GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Microscopes Parts and FunctionДокумент3 страницыMicroscopes Parts and Functionweng100% (6)
- Compound Microscope Parts GuideДокумент2 страницыCompound Microscope Parts GuideBRENT TRISTAN RIVADAОценок пока нет
- Functions of The MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыFunctions of The MicroscopefralphzenОценок пока нет
- Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece:: MirrorДокумент1 страницаEyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece:: MirrorJny An AparenteОценок пока нет
- MICROSCOPEДокумент26 страницMICROSCOPE09ANKIT MISHRAОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Instrumentation: Optical Components of A Microscope. CondenserДокумент2 страницыLaboratory Instrumentation: Optical Components of A Microscope. CondenserrlatjorlukОценок пока нет
- Biology Microscope PartsДокумент3 страницыBiology Microscope Partsaguilarrovic56Оценок пока нет
- Microscope: A Stage: - A Foot, or BaseДокумент3 страницыMicroscope: A Stage: - A Foot, or Baseabdirahiim ahmedОценок пока нет
- PracticalДокумент2 страницыPracticalNim RaОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент1 страницаReviewerAnne MalabananОценок пока нет
- Structural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Документ4 страницыStructural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Nemie VelascoОценок пока нет
- MICROPARAДокумент8 страницMICROPARALaureen CordovaОценок пока нет
- Parts of a MicroscopeДокумент17 страницParts of a MicroscopedamyangdcsОценок пока нет
- Components of The Microscope: StageДокумент4 страницыComponents of The Microscope: StageRisamy RuzОценок пока нет
- Mirror:: Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece: Objective LensesДокумент1 страницаMirror:: Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece: Objective LensesJny An AparenteОценок пока нет
- Compound Microscope 12 FДокумент38 страницCompound Microscope 12 FDaniell' HeardОценок пока нет
- MICROSCPEДокумент3 страницыMICROSCPEAbrigo JhozhuaОценок пока нет
- Head/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeДокумент2 страницыHead/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeNica Bautista BarsolasoОценок пока нет
- EyepieceДокумент2 страницыEyepieceOzner WanijimaОценок пока нет
- Basic Concept of MicroscopesДокумент22 страницыBasic Concept of MicroscopesShadreck Kachembwe phiriОценок пока нет
- Compound Microscope Parts and Functions GuideДокумент2 страницыCompound Microscope Parts and Functions Guidemydiamondstar17Оценок пока нет
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationОт EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationОценок пока нет
- The Impact of European Currency PDFДокумент14 страницThe Impact of European Currency PDFLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- 20170708225026siemens Bribery Scandal Case AssignmentДокумент1 страница20170708225026siemens Bribery Scandal Case AssignmentRehabUddinОценок пока нет
- Chap 009Документ20 страницChap 009Qasih Izyan100% (2)
- Case Study QuestionsДокумент2 страницыCase Study QuestionsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Case Study 2Документ1 страницаCase Study 2Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Chap 1 International Business PDFДокумент27 страницChap 1 International Business PDFLileth ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Chap 009Документ20 страницChap 009Qasih Izyan100% (2)
- Advantages of Specialization: Lumban, Rosette SДокумент11 страницAdvantages of Specialization: Lumban, Rosette SLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Be Able To Calculate Foreign Exchange RatesДокумент12 страницBe Able To Calculate Foreign Exchange RatesLileth ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Elements of Culture in International BusinessДокумент4 страницыElements of Culture in International BusinessLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Case Study 2Документ1 страницаCase Study 2Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- 20170708225026siemens Bribery Scandal Case AssignmentДокумент1 страница20170708225026siemens Bribery Scandal Case AssignmentRehabUddinОценок пока нет
- Silk Road of Different PeriodsДокумент7 страницSilk Road of Different PeriodsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Elements of Culture in International BusinessДокумент4 страницыElements of Culture in International BusinessLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Case Study QuestionsДокумент2 страницыCase Study QuestionsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Apjmr-2017 5 2 05 PDFДокумент8 страницApjmr-2017 5 2 05 PDFlet's skip thisОценок пока нет
- How the Internet and World Wide Web Affect International BusinessДокумент3 страницыHow the Internet and World Wide Web Affect International BusinessLileth ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Learning Paper Starting International OperationДокумент2 страницыLearning Paper Starting International OperationLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- FFE - Chapter 3 (23-29)Документ7 страницFFE - Chapter 3 (23-29)Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Psychological Process Theory: "The Seven Steps of Criminological Thinking"Документ11 страницPsychological Process Theory: "The Seven Steps of Criminological Thinking"Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Of The Pioneer, They Studied Irritation Based On The Product Category and Consumer Segmentation Indicators Such AsДокумент1 страницаOf The Pioneer, They Studied Irritation Based On The Product Category and Consumer Segmentation Indicators Such AsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Advocacy Campaign Posters Warn PedestriansДокумент1 страницаAdvocacy Campaign Posters Warn PedestriansLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Performance Task FOR Business Finance: Submitted byДокумент6 страницPerformance Task FOR Business Finance: Submitted byLileth Anne Panghulan Viduya100% (1)
- FFE - Chapter 3 (21-22)Документ4 страницыFFE - Chapter 3 (21-22)Lileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Evaluation Item Not Demonstrated 0 Does Not Meet Expectations 1-4 Meets Expectations 5-7 Exceeds Expectations 8-10 Earned PointsДокумент1 страницаEvaluation Item Not Demonstrated 0 Does Not Meet Expectations 1-4 Meets Expectations 5-7 Exceeds Expectations 8-10 Earned PointsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Research Instruments For Data CollectionДокумент4 страницыResearch Instruments For Data Collectionizzatie88Оценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент2 страницыQuestionsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Work Immersion Eval SheetДокумент1 страницаWork Immersion Eval SheetLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- InquiriesДокумент1 страницаInquiriesLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Brief Operating Instructions for Liquiline CM42 Two-Wire TransmitterДокумент44 страницыBrief Operating Instructions for Liquiline CM42 Two-Wire TransmitterkurmakkОценок пока нет
- 7E Parts List: USB 7E CARD CAGE - Send 95519 & 94631 WITH ORDER 7E Usb Key Usb To Disk DriveДокумент4 страницы7E Parts List: USB 7E CARD CAGE - Send 95519 & 94631 WITH ORDER 7E Usb Key Usb To Disk DriveJoel MetonОценок пока нет
- E12686-1600-9002-01-09 Consumer List ClientДокумент193 страницыE12686-1600-9002-01-09 Consumer List ClientthanhОценок пока нет
- Bear 2010 CatalogДокумент21 страницаBear 2010 CatalogDaniel Nicolas BriccolaОценок пока нет
- Rcma470ly (Monitor de Corrente Residual)Документ4 страницыRcma470ly (Monitor de Corrente Residual)gilvandroОценок пока нет
- FRS Hardware Manual.V100.enДокумент4 страницыFRS Hardware Manual.V100.enMazen AlhouseenОценок пока нет
- Components, Design, Installation and Maintenance of The Protex Ii Wet Chemical Restaurant Kitchen Fire Suppression SystemДокумент108 страницComponents, Design, Installation and Maintenance of The Protex Ii Wet Chemical Restaurant Kitchen Fire Suppression SystemtalhaОценок пока нет
- Movento: The Sophisticated Runner System Technical Data SheetДокумент26 страницMovento: The Sophisticated Runner System Technical Data SheetMiguel Angel EstevesОценок пока нет
- Newsletter SIMOPRIME 55 2023 en Upcoming Product ChangesДокумент4 страницыNewsletter SIMOPRIME 55 2023 en Upcoming Product Changesabdul ArkadanОценок пока нет
- Install Control ValveДокумент2 страницыInstall Control ValveprasОценок пока нет
- Cinematography FileДокумент13 страницCinematography FileJakovGrdovicОценок пока нет
- How To Wire AH3-3 TimerДокумент7 страницHow To Wire AH3-3 TimerNisar AhmedОценок пока нет
- H1 Axial Piston Pumps: Single and TandemДокумент46 страницH1 Axial Piston Pumps: Single and TandemGilson RodriguesОценок пока нет
- New ChangeДокумент68 страницNew ChangeAnoop Kamla PandeyОценок пока нет
- Fire Alarm System Inspection and Testing FormДокумент4 страницыFire Alarm System Inspection and Testing FormBrahim SemariОценок пока нет
- UD20197B C - Baseline - Multi Lingual - Video Intercom 8 Series Villa Door Station - QSG - V2.2.3Документ4 страницыUD20197B C - Baseline - Multi Lingual - Video Intercom 8 Series Villa Door Station - QSG - V2.2.3Rosa UrquietaОценок пока нет
- k4td AccДокумент14 страницk4td AccAhmos Y MohamedОценок пока нет
- Members of Federation of Indian Plywood & Panel Industry (Fippi)Документ13 страницMembers of Federation of Indian Plywood & Panel Industry (Fippi)Shelly BarrettОценок пока нет
- LT-951SEC MR-2320 Installation and Operation Manual Rev.2 102306Документ92 страницыLT-951SEC MR-2320 Installation and Operation Manual Rev.2 102306Diego CortesОценок пока нет
- Proposal BOQ Estimation ThumbrulesДокумент2 страницыProposal BOQ Estimation ThumbrulesanujbizОценок пока нет
- Harmony XB4 - XB4BA31Документ5 страницHarmony XB4 - XB4BA31Ashby KbОценок пока нет
- TOPCON-CT-80-A-ENGДокумент4 страницыTOPCON-CT-80-A-ENGعباس مطهر الماخذيОценок пока нет
- Vernier Height GuageДокумент3 страницыVernier Height GuageMurtaza NaeemОценок пока нет
- Air Compressor Maintenance - Reciprocating Compressor - SafetyCultureДокумент6 страницAir Compressor Maintenance - Reciprocating Compressor - SafetyCulturematthew kagurabadzaОценок пока нет
- Manual Ais MAIANA™ Assembly Manual (Rev 4)Документ22 страницыManual Ais MAIANA™ Assembly Manual (Rev 4)proiecte6620Оценок пока нет
- PBMU Series Installation Manual 1.0Документ7 страницPBMU Series Installation Manual 1.0Yusuf MudathirОценок пока нет
- 2-NSF Scotch Yoke Type Pneumatic Actuator-ENДокумент60 страниц2-NSF Scotch Yoke Type Pneumatic Actuator-ENLenin Tzul GomezОценок пока нет
- Px4flow Manual v1.3Документ2 страницыPx4flow Manual v1.3Mohamed Atef Abbas ElsahartyОценок пока нет
- Service Manual for MV 300-450-600-800-1000 Modular Cubers/TITLEДокумент32 страницыService Manual for MV 300-450-600-800-1000 Modular Cubers/TITLEjaco12729530% (1)
- HR E577tДокумент6 страницHR E577tSite EngineeringtiaОценок пока нет