Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Module 1a (Introduction)
Загружено:
Rowell D. Sinsay0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров2 страницыModule 1
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документModule 1
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров2 страницыModule 1a (Introduction)
Загружено:
Rowell D. SinsayModule 1
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Bataan Heroes College
1.1 What is surveying?
Surveying is the art of determining, with respect to one another, the positions of points on the
earth’s surface. This end is accomplished by measurements in the three dimensions of space:
distance, direction and elevation.
1.2 Types of Surveys
1. Topographic surveys are those which are made for the purpose of representing the three-
dimensional relations of the earth’s surface on maps or models.
2. Land surveys are those which are made incident to fixing of property lines, the calculation of
land areas, or the transfer of real property from one owner to another.
3. Route surveys are made for the purpose of the location and construction of engineering
projects which are built along fixed routes and gradients.
4. Hydrographic surveys comprise the operations necessary to map the shore lines of bodies of
water; to chart the bottom areas of streams, lakes, etc.; to measure the flow of streams
5. Mine surveys are made to determine the position of all underground workings and surface
structures of mines, to fix the position and directions of tunnels, shafts, etc.
6. Cadastral surveys are made to fix the boundaries of municipalities and of state jurisdictions.
7. Aerial surveys are those which make use of photographs taken from airplane.
1.3 Definition of terms
1. Level surface is a curved surface every element of which is normal to a plumb line.
2. Horizontal plane is a plane tangent to a level surface.
3. Horizontal line is a line tangent to a level surface.
4. Horizontal angle is an angle formed by the intersection of two lines in a horizontal plane.
5. Vertical line is a line perpendicular to the horizontal plane.
6. Vertical plane is a plane in which a vertical line is an element.
7. Vertical angle is an angle between two intersecting lines in a vertical plane.
8. Elevation of a point is the vertical distance above or below some arbitrarily assumed level
surface or datum.
9. Contour is an imaginary line of constant elevation on the ground surface.
10. Difference in elevation is the vertical distance between two points.
Fundamentals of Surveying: Module 1 Page 1 of 2
Engr. Edgardo L. Lintag, Jr.
Bataan Heroes College
11. Grade or gradient of a line is its slope or rate of ascent or descent.
1.4 Methods of measuring distances
1. Pacing consists of counting the number of steps or paces in a required distance.
2. Odometer reading uses an odometer which converts the number of revolutions of a wheel of
known circumference to a distance.
3. Stadia method is used to quickly determine the horizontal distance to, and elevation of, a
point.
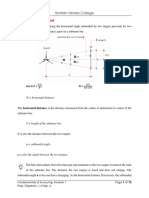
4. Subtense bar method is taking the horizontal angle subtended by two targets precisely spaced
at a fixed distance apart on a subtense bar.
5. Taping involves the direct measurement of a distance using steel tapes.
6. Electronic Distance Measurement uses devices which measure lengths indirectly by
determining the number of waves of transmitted electromagnetic energy in travelling between
the ends of two lines.
Fundamentals of Surveying: Module 1 Page 2 of 2
Engr. Edgardo L. Lintag, Jr.
Вам также может понравиться
- Engineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsОт EverandEngineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (24)
- Module 1 Surveying ConceptsДокумент14 страницModule 1 Surveying ConceptsGaboОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Land Surveying BasicsДокумент200 страницCivil Engineering Land Surveying BasicsvilmoskaОценок пока нет
- Survey Record Full Merged 1 &2Документ125 страницSurvey Record Full Merged 1 &2oxygen oxygenОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: Introduction To SurveyingДокумент7 страницChapter One: Introduction To SurveyingWelday GebremichaelОценок пока нет
- Introduction To SurveyingДокумент5 страницIntroduction To SurveyingAlone TimeОценок пока нет
- Fundermental Surveying - Theory and Practice PDFДокумент28 страницFundermental Surveying - Theory and Practice PDFSupriya Roy100% (1)
- Fundamentals of SurveyingДокумент28 страницFundamentals of Surveyingim tsoyОценок пока нет
- Module I Chain SurveyingДокумент21 страницаModule I Chain SurveyingSherinIsmailОценок пока нет
- Introduction To SurveyingДокумент17 страницIntroduction To SurveyingBurka DinkaОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 Introduction To SurveyingДокумент9 страницUnit-1 Introduction To SurveyingSaHil ShaRmaОценок пока нет
- Wa0020.Документ38 страницWa0020.Sajjad AhmadОценок пока нет
- Survey Unit 1Документ46 страницSurvey Unit 1Swati ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Engineering SurveyingДокумент12 страницEngineering SurveyingzelalemОценок пока нет
- SurveyingДокумент9 страницSurveyingSreejith VaneryОценок пока нет
- Prof. V. Kanakasabai PHDДокумент16 страницProf. V. Kanakasabai PHDfishnaОценок пока нет
- Principles of Surveying: Location of A Point by Measurement From Two Points of ReferenceДокумент9 страницPrinciples of Surveying: Location of A Point by Measurement From Two Points of ReferenceHari RОценок пока нет
- Subject: Elements of Civil Engineering Topic: SurveyingДокумент43 страницыSubject: Elements of Civil Engineering Topic: SurveyingpappuОценок пока нет
- Surveying (1&2)Документ41 страницаSurveying (1&2)Muhe JsОценок пока нет
- Ce6304 NotesДокумент64 страницыCe6304 NotesMukkannanОценок пока нет
- Ce6304 Surveying1 1Документ64 страницыCe6304 Surveying1 1ဒုကၡ သစၥာОценок пока нет
- SurveyingДокумент33 страницыSurveyingAditya SutarОценок пока нет
- CE2254 SQДокумент99 страницCE2254 SQMigaeaОценок пока нет
- SurveyBook 1Документ27 страницSurveyBook 1Vamshee KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Subject: Elements of Civil Engineering Topic: SurveyingДокумент43 страницыSubject: Elements of Civil Engineering Topic: SurveyingpappuОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - Basic Civil Engineering & Engineering Mechanics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inДокумент16 страницUnit 3 - Basic Civil Engineering & Engineering Mechanics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inNikhil ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of SurveyingДокумент28 страницFundamentals of SurveyingPHEBY MOOGОценок пока нет
- Edit2 PDFДокумент62 страницыEdit2 PDFArun ManneОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Surveying ActivityДокумент5 страницFundamentals of Surveying ActivityHarold BautistaОценок пока нет
- DIMARANAN Assignment1 SurveyingДокумент3 страницыDIMARANAN Assignment1 SurveyingCarlo DimarananОценок пока нет
- Basics of Surveying PDFДокумент115 страницBasics of Surveying PDFraghu prasadОценок пока нет
- Chap 1-1Документ39 страницChap 1-1Mareyam DnglОценок пока нет
- Azimuth MergedДокумент193 страницыAzimuth Mergederwinandal9Оценок пока нет
- Coordinate SystemДокумент25 страницCoordinate SystemJoanna SeproОценок пока нет
- Inbound 877515323206559134Документ4 страницыInbound 877515323206559134Roselyn CantosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 PDFДокумент12 страницChapter 4 PDFJamED ALRubioОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To SurveyingДокумент19 страницCHAPTER 1 - Introduction To SurveyingRemielle Ednilao LaguismaОценок пока нет
- Program: B.Tech Subject Name: Basic Civil Engineering & Mechanics Subject Code: BT-204 Semester: 2ndДокумент32 страницыProgram: B.Tech Subject Name: Basic Civil Engineering & Mechanics Subject Code: BT-204 Semester: 2ndSHASHI RANJANОценок пока нет
- SSC Je Study Materials Civil Surveying EngineeringДокумент9 страницSSC Je Study Materials Civil Surveying EngineeringMr. BeastОценок пока нет
- Survey IДокумент58 страницSurvey IPrakash LamaОценок пока нет
- Introductory ClassesДокумент4 страницыIntroductory ClassesCCCCCCCОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ15 страницModule 1GaniОценок пока нет
- I. Definition of SurveyingДокумент10 страницI. Definition of SurveyingJojo VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Surveying Lab ManualДокумент33 страницыSurveying Lab Manualhima sagarОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Surveying Module 1 PrelimДокумент145 страницFundamentals of Surveying Module 1 PrelimAnne LucasОценок пока нет
- Civil Master NotesДокумент11 страницCivil Master NotesGopal kumawatОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Surveying - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inДокумент27 страницUnit 1 - Surveying - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inmadhavi likharОценок пока нет
- Survey PaperДокумент6 страницSurvey PaperAsad WaxierОценок пока нет
- GE211 Lecture 4Документ45 страницGE211 Lecture 4Uriel Marie JabaoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Survey 1Документ35 страницLecture 1 Survey 1m saadullah khanОценок пока нет
- Road ProfieДокумент24 страницыRoad ProfieRamkishor SahuОценок пока нет
- Ce37 Surveying I NotesДокумент49 страницCe37 Surveying I NotesJEAN DE DIEU MUVARAОценок пока нет
- SURVEYING - 1 Short Answers IДокумент5 страницSURVEYING - 1 Short Answers IHarish MerugumalaОценок пока нет
- 1a Introductory ClassesДокумент3 страницы1a Introductory ClassesCCCCCCCОценок пока нет
- Introduction To SurveyingДокумент29 страницIntroduction To SurveyingAjeeth BОценок пока нет
- Triangulation SurveyДокумент21 страницаTriangulation SurveyGTSОценок пока нет
- Lecture Note - ES 1Документ48 страницLecture Note - ES 1Brian SamirgalОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 Name: Rowell D. Sinsay Score/Rating: - Course: BSCE 3A Date: 11-03-21Документ10 страницActivity 4 Name: Rowell D. Sinsay Score/Rating: - Course: BSCE 3A Date: 11-03-21Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Geo Group PresentationДокумент8 страницGeo Group PresentationRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Journal Entry No. 1Документ1 страницаJournal Entry No. 1Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 Name: Rowell D. Sinsay Score/Rating: - Course: BSCE 3A Date: 11-03-21Документ10 страницActivity 4 Name: Rowell D. Sinsay Score/Rating: - Course: BSCE 3A Date: 11-03-21Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Engineering Economics: Module No. 1Документ22 страницыIntroduction To Engineering Economics: Module No. 1Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Module 3c (Traverse Adjustment)Документ11 страницModule 3c (Traverse Adjustment)Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- (Template) Self Inroduction PDFДокумент1 страница(Template) Self Inroduction PDFRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Module 1 The Field of Engineering ManagementДокумент11 страницModule 1 The Field of Engineering ManagementRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- Module 1e (Subtense Bar Method)Документ12 страницModule 1e (Subtense Bar Method)Rowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- ROWELL SINSAY - Self InroductionДокумент1 страницаROWELL SINSAY - Self InroductionRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- ROWELL SINSAY - Rubric 2 Freestyle ActivityДокумент1 страницаROWELL SINSAY - Rubric 2 Freestyle ActivityRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- ROWELL SINSAY - Self InroductionДокумент1 страницаROWELL SINSAY - Self InroductionRowell D. SinsayОценок пока нет
- L202 AU511 Technical DrawingДокумент2 страницыL202 AU511 Technical DrawingghmoralesfОценок пока нет
- Análisis de Estabilidad Del Soil NailДокумент5 страницAnálisis de Estabilidad Del Soil NailAl_catrazОценок пока нет
- Dynamics & Statics: Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992Документ17 страницDynamics & Statics: Previous Year Questions From 2020 To 1992Subhay kumarОценок пока нет
- 5746956Документ21 страница5746956Wajid HussainОценок пока нет
- 2008 Minimum Drawing ChecklistДокумент5 страниц2008 Minimum Drawing Checklisteng_bilalОценок пока нет
- Peter Markli My Profession The Art of BuildingДокумент50 страницPeter Markli My Profession The Art of BuildingEduard MilitaruОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three Levelling (Measuring Vertical Distance)Документ24 страницыChapter Three Levelling (Measuring Vertical Distance)Welday GebremichaelОценок пока нет
- EN1911 Tut - PDFДокумент20 страницEN1911 Tut - PDFKrsto BatinićОценок пока нет
- American Journal PhysicsДокумент9 страницAmerican Journal PhysicsPutri Syahreni HarahapОценок пока нет
- The Benefits of Using Autodesk Civil 3DДокумент72 страницыThe Benefits of Using Autodesk Civil 3DNtt HươngОценок пока нет
- Engineering Drawing Short QuestionsДокумент11 страницEngineering Drawing Short QuestionsTarish Mittal89% (47)
- How To Draw Kanji of KujiIn enДокумент24 страницыHow To Draw Kanji of KujiIn enWalter HofmannОценок пока нет
- Mini Launcher: Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide For The PASCO Scientific Model ME-6825AДокумент44 страницыMini Launcher: Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide For The PASCO Scientific Model ME-6825AaldrfgОценок пока нет
- Physics - ProjectilesДокумент18 страницPhysics - Projectilesfyeth10Оценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid Bodies PDFДокумент25 страницStatics of Rigid Bodies PDFsalman khanОценок пока нет
- S&L - Lesson 16. Introduction To Setting of CurvesДокумент6 страницS&L - Lesson 16. Introduction To Setting of CurvesEr Jogendra SorenОценок пока нет
- Question 2Документ3 страницыQuestion 2Vishak PuthoorОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Engineering DrawingДокумент15 страницModule 1 Engineering DrawingSK Punta Tabuc97% (39)
- SUT 171 Fundamentals of Surveying Unit # 4 "Measurement of Angles"Документ7 страницSUT 171 Fundamentals of Surveying Unit # 4 "Measurement of Angles"TsegishОценок пока нет
- 06Документ18 страниц06joticahe100% (2)
- Comparision Between AWS D1.1&ASME Sec - IXДокумент33 страницыComparision Between AWS D1.1&ASME Sec - IXStephen RajОценок пока нет
- New Methods of Measuring Marginal Utility 01Документ77 страницNew Methods of Measuring Marginal Utility 01dquartulliarchivos20 QОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Directions and AnglesДокумент45 страницMeasurement of Directions and AnglesXielleОценок пока нет
- Pentaksiran Sumatif Akhir Tahun Tingkatan 3 2020Документ14 страницPentaksiran Sumatif Akhir Tahun Tingkatan 3 2020Sharizad Shaari100% (1)
- All-Round Glass Inspection: How To OptimizeДокумент14 страницAll-Round Glass Inspection: How To OptimizeThomasОценок пока нет
- Projectile and Uniform Circular MotionДокумент20 страницProjectile and Uniform Circular Motionbeenilicious100% (1)
- Différence Et Similitudes Entre ASME Et AWSДокумент63 страницыDifférence Et Similitudes Entre ASME Et AWSImane KhammouriОценок пока нет
- Quasi-3D Modelling of Two-Phase Slug Flow in PipesДокумент12 страницQuasi-3D Modelling of Two-Phase Slug Flow in PipeskumarОценок пока нет
- Perspective: University Spiru Haret BucharestДокумент56 страницPerspective: University Spiru Haret BucharestBrandusa TurlacОценок пока нет
- TO (Struktur Organisasi) PDFДокумент42 страницыTO (Struktur Organisasi) PDFAnisha Charisma PermatasariОценок пока нет
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОт EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОценок пока нет
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsОт EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (65)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (33)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutОт EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (142)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraОт EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (10)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (811)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsОт EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (223)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldОт EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeОт EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (19)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeОт EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (699)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsОт EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (593)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorОт EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (137)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogОт EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeОт EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderОт EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (283)