Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Positioning 2
Загружено:
le chixИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Positioning 2
Загружено:
le chixАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1-4.
POSITIONING A PATIENT FOR EXAMINATION OR TREATMENT
Patients are put in special positions for examination, for treatment or test, and to obtain specimens. You
should know the positions used, how to assist the patient, and how to adjust the drapes.
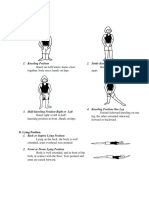
a. Horizontal Recumbent Position. Used for most physical examinations. Patient is on his back with legs
extended. Arms may be above the head, alongside the body or folded on the chest.
b. Dorsal Recumbent Position. Patient is on his back with knees flexed and soles of feet flat on the bed.
Fold sheet once across the chest. Fold a second sheet crosswise over the thighs and legs so that genital
area is easily exposed.
c. Fowler's Position. Used to promote drainage or ease breathing. Head rest is adjusted to desired height
and bed is raised slightly under patient's knees
d. Dorsal Lithotomy Position. Used for examination of pelvic organs. Similar to dorsal recumbent position,
except that the patient's legs are well separated and thighs are acutely flexed. Feet are usually placed in
stirrups. Fold sheet or bath blanket crosswise over thighs and legs so that genital area is easily exposed.
Keep patient covered as much as possible.
e. Prone Position. Used to examine spine and back. Patient lies on abdomen with head turned to one side
for comfort. Arms may be above head or alongside body. Cover with sheet or bath blanket.
NOTE: An unconscious patient, or one with an abdominal incision or breathing difficulty usually cannot lie
in this position.
f. Sim's Position. Used for rectal examination. Patient is on left side with right knee flexed against
abdomen and left knee slightly flexed. Left arm is behind body; right arm is placed comfortably.
NOTE: Patient with leg injuries or arthritis usually cannot assume this position.
g. Knee-Chest Position. Used for rectal and vaginal examinations and as treatment to bring uterus into
normal position. Patient is on knees with chest resting on bed and elbows resting on bed or arms above
head. Head is turned to one side. Thighs are straight and lower legs are flat on bed.
NOTE: Do not leave patient alone; he/she may become dizzy, faint, and fall.
Figure 1-1. Horizontal recumbent position.
Figure 1-3. Fowler's position.
Figure 1-2. Dorsal recumbent position.
Figure 1-4. Dorsal lithotomy position.
Figure 1-5. Prone position.
Figure 1-6. Sim’s position.
Figure 1-7. Knee-chest position.
Figure 4-1. Prone position.
Figure 4-2. Supine position.
Figure 4-3. Sim’s position.
1. Elevate the head of the bed.
o Elevate 60 to 90 degrees for the Fowler's position.
o Elevate 45 to 60 degrees for the semi-Fowler's position.
Figure 4-5. Fowler’s position.
Figure 4-6. Semi-Fowler’s position.
Figure 4-7. Lateral position.
Вам также может понравиться
- 126 Sex Positions Guaranteed to Spice up Your Bedroom: IntimacyОт Everand126 Sex Positions Guaranteed to Spice up Your Bedroom: IntimacyОценок пока нет
- Drugs & PregnancyДокумент385 страницDrugs & Pregnancysanjeevani20100% (3)
- Yoga For Low Back Pain Relief: 21 Restorative Yoga Poses for Back PainОт EverandYoga For Low Back Pain Relief: 21 Restorative Yoga Poses for Back PainРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Patient Positioning Cheat SheetДокумент8 страницPatient Positioning Cheat SheetDENNIS N. MUÑOZОценок пока нет
- Mar ChecklistДокумент18 страницMar ChecklistMin MawОценок пока нет
- Revised Market Potential Estimates for Biopure's Hemopure Based on Competitive LandscapeДокумент4 страницыRevised Market Potential Estimates for Biopure's Hemopure Based on Competitive Landscapeargand_xw9097Оценок пока нет
- Common Patient PositionsДокумент26 страницCommon Patient PositionsRonnel FranciaОценок пока нет
- Advances in Extraction TechniquesДокумент13 страницAdvances in Extraction TechniquesashajangamОценок пока нет
- Patient Positioning (Sims, Orthopneic, Dorsal Recumbent) Guide (2020)Документ28 страницPatient Positioning (Sims, Orthopneic, Dorsal Recumbent) Guide (2020)JOSHUA DICHOSO100% (1)
- Fundamental and Derived PositionsДокумент15 страницFundamental and Derived Positionsrajiv_rao_m75% (20)
- Basic Position Where Most Exercises BeginДокумент9 страницBasic Position Where Most Exercises BeginAgik ParОценок пока нет
- EEG ArtifactsДокумент18 страницEEG ArtifactsNazwan Hassa100% (1)
- Neonatal Thrombocytopenia: An Overview of Etiologies and ManagementДокумент21 страницаNeonatal Thrombocytopenia: An Overview of Etiologies and ManagementbidisОценок пока нет
- Good Posture GymnasticsДокумент8 страницGood Posture GymnasticsKaye ViolonОценок пока нет
- Basic Position Where Most Exercises BeginДокумент9 страницBasic Position Where Most Exercises Beginantonettedgreat67% (3)
- Proper Patient Positioning and Draping TechniquesДокумент27 страницProper Patient Positioning and Draping TechniquesJennifer Solano Cruel100% (5)
- Medical MnemonicsДокумент3 страницыMedical Mnemonicsle chix100% (1)
- Functional Re-Education by Kusum-Wps OfficeДокумент19 страницFunctional Re-Education by Kusum-Wps OfficeKusum deep0% (1)
- Body MechanicsДокумент24 страницыBody MechanicsKevin Matthew O. Velasco50% (2)
- Kneeling and lying yoga positionsДокумент3 страницыKneeling and lying yoga positionsMarklein Dumangeng100% (1)
- Basic PositionsДокумент3 страницыBasic PositionsDenielle MarceñoОценок пока нет
- Module in Tumbling GymnasticsДокумент21 страницаModule in Tumbling GymnasticsKARL MICHAEL NAVARETTEОценок пока нет
- Positioning Patients Cheat SheetДокумент7 страницPositioning Patients Cheat SheetUchi Nurul FauziahОценок пока нет
- Positioning DrapingДокумент35 страницPositioning DrapingAbigail Filio Monge60% (5)
- Exercise Basics ReportДокумент10 страницExercise Basics ReportShiela Mae Falsis Sales100% (1)
- Care Study CAESARIAN SECTIONДокумент29 страницCare Study CAESARIAN SECTIONNoreen EndinoОценок пока нет
- 2-Fundamental and Derived PositionsДокумент50 страниц2-Fundamental and Derived Positionsphysical therapy channel ptОценок пока нет
- Positions at a GlanceДокумент18 страницPositions at a GlanceRaquel M. MendozaОценок пока нет
- Positions for Patient CareДокумент26 страницPositions for Patient CaresunielgowdaОценок пока нет
- Positions in NursingДокумент3 страницыPositions in NursingAparna HarshanОценок пока нет
- English LessonДокумент13 страницEnglish LessonNoeroel AlfyОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент8 страницUntitledEric MensahОценок пока нет
- Body Positions For Physical Exam PDFДокумент2 страницыBody Positions For Physical Exam PDFReifonAruseifu100% (2)
- Fowler's Position - Definition of Fowler's Position in The Medical Dictionary - by The Free Online Medical Dictionary, Thesaurus and EncyclopediaДокумент3 страницыFowler's Position - Definition of Fowler's Position in The Medical Dictionary - by The Free Online Medical Dictionary, Thesaurus and EncyclopediaMahesh R RajuОценок пока нет
- Efn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Документ10 страницEfn Topic 10 - Sulfi Nurafifah 1020031181Erdin TriansyahОценок пока нет
- Functional Re EducationДокумент45 страницFunctional Re EducationThopu UmamaheswariОценок пока нет
- FAULTY FETAL DI-WPS OfficeДокумент8 страницFAULTY FETAL DI-WPS OfficeDr. Vinay VijayakumarОценок пока нет
- PositionsДокумент4 страницыPositionsMixsz LlhAdyОценок пока нет
- Positioning Fowler ' S PositionsДокумент4 страницыPositioning Fowler ' S PositionsKristine Cariño FormosoОценок пока нет
- Basic PositionДокумент46 страницBasic Positionnixanty123Оценок пока нет
- Different Kinds of Body PositionДокумент6 страницDifferent Kinds of Body PositionLouieJanesIIОценок пока нет
- Sushibala Assignment 02Документ5 страницSushibala Assignment 02Ananda NgangomОценок пока нет
- Leopold Maneuvers1 1Документ22 страницыLeopold Maneuvers1 1Gladys OdibuОценок пока нет
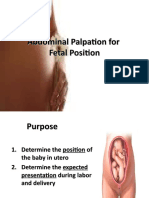
- Abdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionДокумент22 страницыAbdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionSandra Jane AcostaОценок пока нет
- Abdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionДокумент22 страницыAbdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionFerreze AnnОценок пока нет
- Determine Fetal Position and PresentationДокумент22 страницыDetermine Fetal Position and PresentationCharlaine Gripal SudlaОценок пока нет
- Goals of Patient Positioning: Patient Positions in BedДокумент4 страницыGoals of Patient Positioning: Patient Positions in Bedjoanna sheenОценок пока нет
- Leopolds-Maneuver StudentsДокумент40 страницLeopolds-Maneuver StudentsCarlo GacadОценок пока нет
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of NursingДокумент2 страницыLiceo de Cagayan University: College of NursingJAN ELMER L. LABESORESОценок пока нет
- Lie PresentationДокумент31 страницаLie PresentationMichael Anthony ErmitaОценок пока нет
- Motor Development (1year)-1Документ31 страницаMotor Development (1year)-1Ashwini BajajОценок пока нет
- BSN1C Flores Ha (Rle) Ass2 PrelimsДокумент11 страницBSN1C Flores Ha (Rle) Ass2 PrelimsFrances Nicole FloresОценок пока нет
- Mat ExerciseДокумент10 страницMat ExercisekinnelparmarОценок пока нет
- Handout - Mapeh4 - GYMNASTICS 2ndqtrДокумент3 страницыHandout - Mapeh4 - GYMNASTICS 2ndqtrELMC MadridianОценок пока нет
- positioningДокумент1 страницаpositioningHannah RizzyОценок пока нет
- Fundamental PositionsДокумент35 страницFundamental PositionsVinod Kumar50% (4)
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantДокумент41 страницаNursing Care of A Family With An InfantDaniela Claire FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Positioning A Client in BedДокумент32 страницыPositioning A Client in BedGrape JuiceОценок пока нет
- Understanding Common Patient PositionsДокумент9 страницUnderstanding Common Patient Positionsrecky ernawanОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Types of Body Movement A. Axial MovementДокумент2 страницы3.2 Types of Body Movement A. Axial MovementAlexandra Nicole IsaacОценок пока нет
- Functional Re EducationДокумент38 страницFunctional Re EducationDhruvОценок пока нет
- Exercises and Movements For Physical ActivitiesДокумент2 страницыExercises and Movements For Physical ActivitiesMylz MendozaОценок пока нет
- Path FitДокумент30 страницPath FitJay Micalyn Umayam MolinaОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Exercises: Fundamental and Derived PositionsДокумент11 страницTherapeutic Exercises: Fundamental and Derived PositionsAnujGuptaОценок пока нет
- TumblingДокумент12 страницTumblingCrystel JazamaeОценок пока нет
- Nurses prayer for guidance, strength and wisdomДокумент1 страницаNurses prayer for guidance, strength and wisdomle chixОценок пока нет
- Del Monte KitchenomicsДокумент16 страницDel Monte Kitchenomicsle chixОценок пока нет
- Medication SuffixesДокумент2 страницыMedication Suffixesle chix100% (1)
- Renal Regulation of Extracellular Fluid Potassium ConcentrationДокумент32 страницыRenal Regulation of Extracellular Fluid Potassium ConcentrationDaniel AdamsОценок пока нет
- JC 7Документ20 страницJC 7Alexander S. Garcia Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsДокумент20 страницLecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsJedoОценок пока нет
- Personal health data for nursing studentДокумент8 страницPersonal health data for nursing studentJenny AjocОценок пока нет
- Reliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric StudyДокумент8 страницReliability of Anatomic Reference Planes in Establishing The Occlusal Plane in Different Jaw Relationships: A Cephalometric Studyedy harahapОценок пока нет
- Community Acquired PneumoniaДокумент63 страницыCommunity Acquired PneumoniaLet BorlagdanОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Care Process NoteДокумент3 страницыNutrition Care Process Noteapi-242497565Оценок пока нет
- PR Menarini PDX Ab RBCДокумент2 страницыPR Menarini PDX Ab RBCvyasakandarpОценок пока нет
- Rosemont Health Center Rev01Документ7 страницRosemont Health Center Rev01Amit VishwakarmaОценок пока нет
- 1413272524world10 15 14 PDFДокумент38 страниц1413272524world10 15 14 PDFCoolerAdsОценок пока нет
- Estradiol Valerate + Dienogest PDFДокумент6 страницEstradiol Valerate + Dienogest PDFJuan FernandezОценок пока нет
- Rectal Cancer Grossing Guide Optimizes Margin AssessmentДокумент18 страницRectal Cancer Grossing Guide Optimizes Margin Assessmentionut216100% (1)
- Past PE Papers Viva TopicsДокумент29 страницPast PE Papers Viva TopicsLouis MasonОценок пока нет
- Organsymbol KartenДокумент24 страницыOrgansymbol KartenMacaio100% (2)
- Drug Study HydrocodoneДокумент1 страницаDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyОценок пока нет
- How I Do CMR Scanning Safely: Elisabeth Burman Research Sister Royal Brompton Hospital, London UKДокумент41 страницаHow I Do CMR Scanning Safely: Elisabeth Burman Research Sister Royal Brompton Hospital, London UKYuda FhunkshyangОценок пока нет
- Concrete MSDS 1 PDFДокумент5 страницConcrete MSDS 1 PDFmanil_5100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease to CardiomegalyДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease to CardiomegalyRj Avila100% (1)
- Symposiumbooklet CareerДокумент36 страницSymposiumbooklet Careerroh009Оценок пока нет
- BurosumabДокумент8 страницBurosumabutamiprakosoОценок пока нет
- ICU HandoverДокумент2 страницыICU HandoverMark 'Mark Douglas' DouglasОценок пока нет
- Resume Massage Therapist NtewДокумент2 страницыResume Massage Therapist NtewPartheebanОценок пока нет
- Pedigree Analysis: (Cf. Chapters 4.4, 5.2, 6.2 of Textbook)Документ11 страницPedigree Analysis: (Cf. Chapters 4.4, 5.2, 6.2 of Textbook)Kristyne OliciaОценок пока нет