Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Objective: Learn About It!
Загружено:
Peachy AbelidaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Objective: Learn About It!
Загружено:
Peachy AbelidaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions
Objective
At the end of the lesson, you will be able to describe a solution and its components.
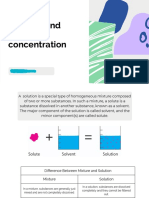
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances that exist in a single
phase.
What are the components of a solution?
Learn about it!
Everything in a solution is evenly spread out and mixed. Hence, the properties of a
solution are the same throughout.
The substance that is being dissolved is the solute and the substance that dissolves the
solute is called the solvent. Usually, the solute is present in smaller amounts than the
solvent. For example, in salt water, salt is the solute and water is the solvent.
"Like dissolves Like"
The general rule of a solution is, 'like dissolves like', which means polar solutes are
soluble in polar solvents while nonpolar solutes are soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Example
Water dissolves salt because water is a polar solvent and salt is a polar solute.The
nonpolar solute dichloromethane is soluble in the nonpolar solvent carbon tetrachloride.
However, dichloromethane will not dissolve in a polar solvent like water.
Learn about it!
Properties of a solution
The particle size of solute is between 0 to 100 nm.
The solute and solvent cannot be separated by filtration.
The solute never settle on standing.
Light will pass through the solution unchanged.
Which are not solutions?
Colloids and suspensions are mixtures, but they are not solutions.
The particle size of solute in a colloid is between 100 and 1000 nm. Like solutions,
these particles do not settle on standing, and they cannot be separated by filtration.
However, colloids exhibit brownian motion, which is the random movement of
particles suspended in liquid or gas. Examples of colloids are shaving cream, fog, and
smoke.
The particle size in a suspension is over 1000 nm. They settle on standing, and they
can be separated by filtration. Their concentration is not uniform throughout. Examples
of suspension include muddy water and paint.
Examples
Solutions are not always solids dissolved in liquids. They can also be formed by any
combination of solids, liquids, and gases.
Gas-Gas: oxygen and nitrogen in air
Gas-Liquid: carbon dioxide in soda
Gas-Solid: hydrogen in palladium
Liquid-Liquid: Acetic acid in water (vinegar)
Liquid-Solid: mercury and silver (dental filling)
Solid-Liquid: sugar in water
Solid-Solid: alloy of copper and zinc
Learn about it!
Solubility is defined as the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of the solution
at any a given temperature. If less than 0.1 g of the solute is dissolved in 100 mL of the
solution, it is said to be insoluble or sparingly soluble.
Unsaturated, Saturated, and Supersaturated Solutions
A solution is said to be unsaturated when more solute can be dissolved in solution.
A solution is said to be saturated when no more solute can be dissolved at the current
temperature. The dissolved solute is in equilibrium with the undissolved solute.
A solution that contains more of the solute than normally exists for a saturated solution
at a particular temperature is said to be supersaturated. Supersaturated solutions can
be formed by adding more solute to a saturated solution and heating it to dissolve all
solute. The resulting supersaturated solution is unstable, and when it is disturbed, the
excess solute crystallizes out and the solution becomes saturated.
What do you think?
What are examples of solutions you use every day?
Key Points
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures that occur in a single phase.
Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar
solutes but polar solvents cannot dissolve nonpolar solutes.
Solutions are different from colloids and suspensions in terms of particle size and
ways of separating the components.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksОт EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksОценок пока нет
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksОт EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksОценок пока нет
- Section 1: Types of SolutionДокумент13 страницSection 1: Types of SolutionAndreaNicoleBanzonОценок пока нет
- Week 7 and 8 Gen ChemДокумент24 страницыWeek 7 and 8 Gen ChemAlice RiveraОценок пока нет
- Solutions Notes TeacherДокумент4 страницыSolutions Notes TeacherSanaanKhanОценок пока нет
- Teaching 2153 35058 1664836521 1Документ3 страницыTeaching 2153 35058 1664836521 1Gök YüzüОценок пока нет
- растворы и концентрация 1Документ21 страницарастворы и концентрация 1Dorama AikaОценок пока нет
- Properties of SolutionsДокумент2 страницыProperties of SolutionspratikОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Science ReviewerДокумент79 страницGrade 7 Science ReviewerNini JimbuuОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Project: Done by - Viral, Manan, Kush, Naitik, Parthiv, VirajДокумент12 страницChemistry Project: Done by - Viral, Manan, Kush, Naitik, Parthiv, VirajViraj PatelОценок пока нет
- SolutionДокумент29 страницSolutionana mae mancillaОценок пока нет
- Properties of SolutionsДокумент11 страницProperties of SolutionsJOHN CHRISTIAN MEMORACIONОценок пока нет
- 41solution MixtureДокумент6 страниц41solution Mixtureapi-269920605Оценок пока нет
- Jaydeep Tadvi Chemistry ProjectДокумент10 страницJaydeep Tadvi Chemistry ProjectNilesh DamorОценок пока нет
- General ChemistryДокумент12 страницGeneral ChemistryJoshua Romea100% (1)
- Solution Chemistry StudentsДокумент4 страницыSolution Chemistry StudentsCiastha Alna C. BarcenaОценок пока нет
- Orange Juice, Alcohol and Detergent Are All Soluble in Water. Orange Juice, Alcohol and Detergent Are All Soluble in WaterДокумент1 страницаOrange Juice, Alcohol and Detergent Are All Soluble in Water. Orange Juice, Alcohol and Detergent Are All Soluble in WaterCherry Clair Andus InsangОценок пока нет
- SolutionsДокумент49 страницSolutionsPeter Jeff LauretaОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 ModuleДокумент74 страницыGrade 9 ModuletabilinОценок пока нет
- Question 1, 2,4Документ5 страницQuestion 1, 2,4escobarchristopherdanielОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - Solutions and Their BehaviorДокумент48 страницChemistry - Solutions and Their BehaviorMohdErwanОценок пока нет
- Oc 4 Jdu 73 PST GL0 ZWДокумент12 страницOc 4 Jdu 73 PST GL0 ZWJoshua RomeaОценок пока нет
- Solutions and SolubilityДокумент9 страницSolutions and SolubilityDarrell W. GarwayОценок пока нет
- SolutionsДокумент47 страницSolutionsblismae genotivaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 SolutionsДокумент92 страницыChapter 16 SolutionsPeter PanОценок пока нет
- 3 2Документ18 страниц3 2tehzeebmohiuddinОценок пока нет
- SolutionsДокумент24 страницыSolutionsAbdulaziz AlamriОценок пока нет
- GLT 121Документ31 страницаGLT 121Benjamen Folarin100% (3)
- Kinds of Mixtures: SolutionsДокумент6 страницKinds of Mixtures: SolutionsHero MirasolОценок пока нет
- CHM ReportingДокумент70 страницCHM ReportingNica Rose GrozenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Solution and SolubilityДокумент63 страницыChapter 3 Solution and Solubility32 Yip Yi Shyan 叶宇轩Оценок пока нет
- General Chemistry 2 Week 4Документ2 страницыGeneral Chemistry 2 Week 4jcjimz259Оценок пока нет
- SC Mixtures W9Документ48 страницSC Mixtures W9faridaahmed.8912Оценок пока нет
- Types of MixturesДокумент17 страницTypes of MixturesMarvin De JonggoyОценок пока нет
- Mixtures and Separations-Lecture#1Документ15 страницMixtures and Separations-Lecture#1victoria0% (1)
- Chemistry 9th CH 6Документ11 страницChemistry 9th CH 6Maheen RajaОценок пока нет
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 07Документ9 страницClass IX Chemistry Chapter 07Sam FisherОценок пока нет
- What Is A Solution - Docx COPY OF OTHERSДокумент3 страницыWhat Is A Solution - Docx COPY OF OTHERSMelanie Lagbo CalinaoОценок пока нет
- Solutions and SolubilityДокумент28 страницSolutions and SolubilityMhimi ViduyaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Properties of MaterialsДокумент75 страницUnit 2 Properties of MaterialsBlopОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chapter 6Документ17 страницChemistry Chapter 6Kashaf fatimaОценок пока нет
- Types of SolutionДокумент2 страницыTypes of SolutionLee Mart LumahangОценок пока нет
- 8 - SolutionsДокумент6 страниц8 - SolutionsDeng FajardoОценок пока нет
- Weeks5 7solutionsДокумент27 страницWeeks5 7solutionsEmma LoreinОценок пока нет
- Module 1Q SCI 7 3Документ10 страницModule 1Q SCI 7 3PeterClomaJr.Оценок пока нет
- Module 1Q SCI 7 3Документ10 страницModule 1Q SCI 7 3PeterClomaJr.Оценок пока нет
- Week 2 d1 q1 Science 6Документ32 страницыWeek 2 d1 q1 Science 6karen rose maximoОценок пока нет
- Is Matter Around Us PureДокумент31 страницаIs Matter Around Us Purethinkiit100% (1)
- Analytical SolutionsДокумент5 страницAnalytical SolutionsLaiba ZulfiqarОценок пока нет
- Solution ChemistryДокумент24 страницыSolution ChemistryJisna JaisonОценок пока нет
- Solutions and SolubilityДокумент12 страницSolutions and Solubilityapi-293690555Оценок пока нет
- SolutionДокумент8 страницSolutionTamia ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Saint Ferdinand College Sta - Ana Street, City of Ilagan, Isabela Senior High School DepartmentДокумент6 страницSaint Ferdinand College Sta - Ana Street, City of Ilagan, Isabela Senior High School DepartmentJem SonОценок пока нет
- Solutions: © 2011 Mark H. Rosengarten AE 1Документ21 страницаSolutions: © 2011 Mark H. Rosengarten AE 1Yustinus ErickoОценок пока нет
- Chapter # 06: Solutions (Topic Wise Questions)Документ10 страницChapter # 06: Solutions (Topic Wise Questions)husain aliОценок пока нет
- Solution in ChemistryДокумент7 страницSolution in ChemistrymartsambaludОценок пока нет
- Physical Properties of SolutionДокумент3 страницыPhysical Properties of SolutionRhye Tabaday LopezОценок пока нет
- G6Q1W5 6Документ38 страницG6Q1W5 6Shiella Mariz BinotapaОценок пока нет
- Physical Properties of SolutionsДокумент38 страницPhysical Properties of SolutionsAntonio Exal ColladoОценок пока нет
- Bullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsОт EverandBullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsОценок пока нет
- Tron Blockchain Matrix Project: Unlimited Auto Reinvests. 100% DecentralisedДокумент13 страницTron Blockchain Matrix Project: Unlimited Auto Reinvests. 100% DecentralisedPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Flexibility Is The Ability of A Joint or Series of Joints To Move Through An UnrestrictedДокумент1 страницаFlexibility Is The Ability of A Joint or Series of Joints To Move Through An UnrestrictedPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Starting Over Again LyricsДокумент1 страницаStarting Over Again LyricsPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Cant Figth Is Feeling AnymoreДокумент1 страницаCant Figth Is Feeling AnymorePeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Youth Development Office: Scholarship Contract (Economic Scholarship)Документ3 страницыYouth Development Office: Scholarship Contract (Economic Scholarship)Peachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Concentration of SolutionsДокумент3 страницыConcentration of SolutionsPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Sanguillosa, Angelo Luis: Contact No: 09509434203Документ2 страницыSanguillosa, Angelo Luis: Contact No: 09509434203Peachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Korean Ver:: 1st Mini Album: MAMA (2012)Документ9 страницKorean Ver:: 1st Mini Album: MAMA (2012)Peachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Elements and Their UsesДокумент17 страницElements and Their UsesPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Matter Acids and BasesДокумент6 страницMatter Acids and BasesPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Basic Polvoron RecipeДокумент8 страницBasic Polvoron RecipePeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Branches of ScienceДокумент6 страницBranches of SciencePeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Position PaperДокумент5 страницPosition PaperPeachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- City Address: #03 Republic Ave. Brgy. Holy Spirit, Quezon City Mobile: 09124140078Документ2 страницыCity Address: #03 Republic Ave. Brgy. Holy Spirit, Quezon City Mobile: 09124140078Peachy AbelidaОценок пока нет
- Cefiximum: CefiximeДокумент2 страницыCefiximum: CefiximeaiОценок пока нет
- CHM 3201 Exp6Документ8 страницCHM 3201 Exp6ARMAN AKRAM BIN OMAR / UPMОценок пока нет
- Doe Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Volume 2 of 2 Doe-Hdbk-10191-93Документ128 страницDoe Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Volume 2 of 2 Doe-Hdbk-10191-93Titer100% (3)
- The Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Документ8 страницThe Mine Drainage Quality Prediction of Surface Coal Mine Rock Samples With Humidity Column Test-3-10Fanteri Aji DharmaОценок пока нет
- Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Sheet and Strip For Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)Документ4 страницыWrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Sheet and Strip For Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)Angel ChangОценок пока нет
- Galaxy ClassIficationДокумент4 страницыGalaxy ClassIficationkОценок пока нет
- MUCLecture 2023 3140165Документ9 страницMUCLecture 2023 3140165hus khОценок пока нет
- Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Laser Beam ScannerДокумент12 страницElectro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Laser Beam ScannerJános OrbánОценок пока нет
- Article 5.0: Hazardous (Classified) Locations, Classes I, Ii, and Iii, Divisions 1 and 2Документ22 страницыArticle 5.0: Hazardous (Classified) Locations, Classes I, Ii, and Iii, Divisions 1 and 2RodrinerBillonesОценок пока нет
- Materials Today CommunicationsДокумент11 страницMaterials Today CommunicationsNukala PranavarshОценок пока нет
- EXPERIMENT 4 HOOKEs LAW PDFДокумент6 страницEXPERIMENT 4 HOOKEs LAW PDFJabar BazeedОценок пока нет
- Cathodic Arc DepositionДокумент3 страницыCathodic Arc DepositionBrandon DavisОценок пока нет
- (Course Booklet For PG Section) Handbook of Informationv6Документ70 страниц(Course Booklet For PG Section) Handbook of Informationv6Pitambar KunduОценок пока нет
- Birla Instritute of Technology & Science, Pilani, Pilani Campus Chemical Engineering DepartmentДокумент2 страницыBirla Instritute of Technology & Science, Pilani, Pilani Campus Chemical Engineering DepartmentVaibhav SharmaОценок пока нет
- Volvo Oil AnalysisДокумент5 страницVolvo Oil Analysisgilar herliana putraОценок пока нет
- Suzhou Hengda Product CatalogДокумент13 страницSuzhou Hengda Product CatalogFabiola HernandezОценок пока нет
- Crouse Hinds Rs RSM Rss Junction Boxes Catalog PageДокумент1 страницаCrouse Hinds Rs RSM Rss Junction Boxes Catalog Pagejose luisОценок пока нет
- FANR REG 24 English OriginalДокумент54 страницыFANR REG 24 English OriginaljeyalaljОценок пока нет
- Einstein, Perrin, and The Reality of Atoms PDFДокумент4 страницыEinstein, Perrin, and The Reality of Atoms PDFDiego PachecoОценок пока нет
- Mellors Inorganic ChemistryДокумент936 страницMellors Inorganic ChemistryMichael WilliamsОценок пока нет
- TECKA Air Cooled Screw Chiller (Heat Pump) Unit - Brochure TECKA202103Документ10 страницTECKA Air Cooled Screw Chiller (Heat Pump) Unit - Brochure TECKA202103Guvanch MuradowОценок пока нет
- Practical 2 - Determining The Content of Salt in Sea WaterДокумент3 страницыPractical 2 - Determining The Content of Salt in Sea WatersmarakОценок пока нет
- Compressor Technical Data: NJ9232GK 220-240 V 50 HZ 943NA01 A - Application / Limit Working ConditionsДокумент3 страницыCompressor Technical Data: NJ9232GK 220-240 V 50 HZ 943NA01 A - Application / Limit Working ConditionsGeri SulanjakuОценок пока нет
- Physics 25 - Simple Phenomena of MagntismДокумент48 страницPhysics 25 - Simple Phenomena of MagntismHakim AbbasОценок пока нет
- Informational Passages RC - Voyagers 1 and 2Документ1 страницаInformational Passages RC - Voyagers 1 and 2andreidmannnОценок пока нет
- Can Anybody Give Me Syllabus of Allen Enthusiast Course? Do It Cover 11th Syllabus AlsoДокумент1 страницаCan Anybody Give Me Syllabus of Allen Enthusiast Course? Do It Cover 11th Syllabus AlsoG HaОценок пока нет
- Sulzer CPT ANSIДокумент14 страницSulzer CPT ANSIahmed elhamy mohamedОценок пока нет
- Share GEN-CHEM-Q4 - LP2Документ8 страницShare GEN-CHEM-Q4 - LP2Jenny Manzanillo MirabonaОценок пока нет
- The Prieska Experience - Flotation Developments in Copper-Zinc SeparationДокумент9 страницThe Prieska Experience - Flotation Developments in Copper-Zinc Separationmushava nyokaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14a - Viscoelastic Properties of Soft TissueДокумент15 страницLecture 14a - Viscoelastic Properties of Soft TissueYathui LawОценок пока нет