Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 4
Загружено:
abhi029Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
Загружено:
abhi029Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4
29 September 2020 03:55 PM
“Price” is the price at which counterparties agree to transact, while “value” is the value of holding a given
position.
Let’s explore the concepts of price and value in the context of a forward:
■ Forward price: The price at which the long forward is obligated to purchase the underlying asset from the
short forward. The forward price is determined at initiation and does not change.
■ Forward value: The value of holding a position in a forward at a given point in time during the life of the
forward.
A forward is designed to have zero value at initiation. To ensure this, a forward price is chosen that is
agreeable, or “fair,” to both counterparties. It is “fair” because at initiation neither of the counterparties
perceive their position to have positive value (i.e., an asset) or negative value (i.e., a liability).
Instead, the forward value will be one of the following:
■ Asset: The forward value of the counterparty that benefits from changes in the determinants of value will
now be positive (an asset).
■ Liability: The forward value of the counterparty that is harmed by changes in the determinants of value will
now be negative (a liability).
Unlike a forward, an option is not designed to have zero value at initiation. Option value is positive for the long
position (which has the right to exercise) and negative for the short position (which is obligated to transact
should the long position exercise). Hence, option value is an asset for the long position and a liability for the
short position.
The premium should be equal to the option’s value. If differences between the premium and option value
occur, this suggests that the market is mispricing the premium.
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 04:04 PM
New Section 1 Page 1
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 04:06 PM
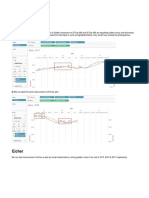
The value of a forward is, by design, zero at initiation. Following initiation, the value of the forward from the
long forward’s perspective is:
where ft = Long forward value F = Forward price t = Valuation date T = Expiration date T − t = Years between
the valuation date and the expiration date St = Underlying asset price on the valuation date rt = Continuously
compounded risk-free interest rate on the valuation date
Hence, the short forward’s value is −ft, the negative of the long forward’s value
The forward price that is set at initiation should be equal to:
where F = Forward price t0 = Initiation date T = Expiration date T − t0 = Years between the initiation date and
the expiration date S0 = Underlying asset price on the initiation date r0 = Continuously compounded risk-free
interest rate on the initiation date
Screen clipping taken: 29-09-2020 04:46 PM
New Section 1 Page 2
New Section 1 Page 3
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Stock AnalysisДокумент8 страницStock Analysisabhi029Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Data Dictionary - Telecom Churn Case StudyДокумент2 страницыData Dictionary - Telecom Churn Case Studyabhi029Оценок пока нет
- Agglomerative Clustering: Point Label X Y Point Label A A B B C C D D E E F FДокумент2 страницыAgglomerative Clustering: Point Label X Y Point Label A A B B C C D D E E F Fabhi029Оценок пока нет
- Blanchard - ch02 A Tour of The BookДокумент24 страницыBlanchard - ch02 A Tour of The BookaljonbudimanОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- G.R. No. 158805 - Valley Golf & Amp Country Club, Inc. v. Vda. deДокумент16 страницG.R. No. 158805 - Valley Golf & Amp Country Club, Inc. v. Vda. deKaren Gina DupraОценок пока нет
- Fact-Sheet 20191230 08 Idxbumn20 PDFДокумент1 страницаFact-Sheet 20191230 08 Idxbumn20 PDFvivafatma92Оценок пока нет
- Emirates Airlines Strategic AnalysisReportДокумент25 страницEmirates Airlines Strategic AnalysisReportkhalda1892% (52)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Summer Vacation Assignment - AccountancyДокумент2 страницыSummer Vacation Assignment - Accountancykrishgupta723Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Update BNP 2023Документ34 страницыUpdate BNP 2023Bill LeeОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Jasmine Loo SwissДокумент10 страницJasmine Loo Swissnrsyzna100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Economics For Today Asia Pacific 5th Edition Layton Test BankДокумент34 страницыEconomics For Today Asia Pacific 5th Edition Layton Test Banklovellednayr984100% (27)
- ENPL To MSIPL-ENPL SiranchowkДокумент1 страницаENPL To MSIPL-ENPL SiranchowkDeepak SinghОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Company Analysis ReportДокумент32 страницыCompany Analysis ReportATREYA NAYAKОценок пока нет
- Ing, Q'Ty, Price:: Say: Us Dollars Two Thousand Three Hundred Seventhy One OnlyДокумент1 страницаIng, Q'Ty, Price:: Say: Us Dollars Two Thousand Three Hundred Seventhy One OnlyNi Komang Ayu Cahya Puja DewiОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- CH 32 A Macroeconomic Theory of The Open EconomyДокумент45 страницCH 32 A Macroeconomic Theory of The Open EconomyveroirenОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Analyzing Managerial Decision: United AirlinesДокумент4 страницыAnalyzing Managerial Decision: United AirlinesCliff KaaraОценок пока нет
- 20 Securities Selection and Portfolio Construction and EvaluationДокумент24 страницы20 Securities Selection and Portfolio Construction and EvaluationShaikh Saifullah KhalidОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Consideration LectureДокумент26 страницConsideration LectureOsamah BakhshОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Impact of Political Instability On EconomyДокумент28 страницImpact of Political Instability On Economyshahrukh AliyaОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Analisis Hukum Terhadap Prinsip Most Favoured Nations Dalam Sengketa Dagang Impor Produk BesiДокумент10 страницAnalisis Hukum Terhadap Prinsip Most Favoured Nations Dalam Sengketa Dagang Impor Produk BesiAdriansyah PutraОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Allocation and Apportionment and Job and Batch Costing Worked Example Question 2Документ2 страницыAllocation and Apportionment and Job and Batch Costing Worked Example Question 2Roshan RamkhalawonОценок пока нет
- R15 Firm and Market Structures - Q BankДокумент12 страницR15 Firm and Market Structures - Q Bankakshay mouryaОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurship DevelopmentДокумент94 страницыEntrepreneurship Developmentashish9dubey-16Оценок пока нет
- Assets Liabilities and EquityДокумент2 страницыAssets Liabilities and EquityArian Amurao50% (2)
- ACCOUNTING 3B Homework 3Документ3 страницыACCOUNTING 3B Homework 3Jasmin Escaño100% (1)
- As Per Request 30 Days: QuotationДокумент2 страницыAs Per Request 30 Days: QuotationAdmin SAF PrintersОценок пока нет
- Benefits & Risks of The Resale Price MethodДокумент2 страницыBenefits & Risks of The Resale Price MethodLJBernardoОценок пока нет
- S No. Name of Bank User Id Remarks: (7 Characters)Документ4 страницыS No. Name of Bank User Id Remarks: (7 Characters)Sudeepa SudeepaОценок пока нет
- Febrero 24Документ12 страницFebrero 24micasacontractors893Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Activity - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeДокумент6 страницActivity - Statement of Comprehensive IncomeGrace HernandezОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ6 страницBook 1Naveen BishtОценок пока нет
- Maths ProjectДокумент22 страницыMaths ProjectAditya GiddeОценок пока нет
- Invoice: Sakvinyl SolutionsДокумент1 страницаInvoice: Sakvinyl SolutionsMEENAKSHI IQCSОценок пока нет
- Porter 5 Forces of Airline Industry in United States of AmericaДокумент1 страницаPorter 5 Forces of Airline Industry in United States of AmericaSOMJEET HOM ROY 1923572Оценок пока нет