Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Animal Cell
Загружено:
Lu XxОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Animal Cell
Загружено:
Lu XxАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Animal Cell:
Platelets: The smallest cell type within your blood, platelets play a key role in
blood clot formation. Once platelets sense damage or torn tissue, they start to clump
together, forming a blood clot to slow or stop the bleeding.
Glia are the supporting cells that help your nerves function properly.
There are a few major types of glia, and all play a role in helping your
brain, spinal cord and other nerves communicate efficiently. Some glial
cells produce myelin, a waxy substance that "insulates" your neurons for
better communication. Others act as the immune cells of the brain,
helping fight off infections that would otherwise harm your nerves. And
still others help keep your neurons supplied with nutrients so that your
nervous system has the energy to work properly.
skeletal muscle cells – the cells that make up virtually all of the muscles
in your body. Skeletal muscle is the kind of muscle that – surprise – is
anchored to your skeleton. It contracts to move your bones. So, say,
when you contract your bicep, you'll bend your elbow. Skeletal muscle
cells are, in part, voluntarily controlled by your brain. That means you can
decide to move your leg, for instance, and your brain will send a signal
that corresponds with that movement
cardiac muscle cells. These are the cells that make up your heart and
contract to pump blood through your body. Cardiac muscle cell
contraction is not voluntarily controlled – instead, your body maintains a
steady heart rhythm without you having to think about it.
smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle makes up the linings of certain
blood vessels, as well as some organs, like your stomach. Smooth
muscle is important for helping your organs move. For example, smooth
muscle contraction helps move food through your digestive tract to allow
for proper digestion. Like cardiac muscle, smooth muscle contraction is
not voluntarily controlled. So, for instance, you don't need to think about
moving food from your stomach into your intestines because your body
just does it for you.
The Bottom Line: Cell Specialization
Still with us? Here's the gist of what you need to know about cell specialization.
Cells develop from immature stem cells into mature, highly functional cells by a
process called differentiation.
Differentiation allows developing cells to take on unique structures, and it allows
the cell to carry out specialized functions.
The process of differentiation is triggered by signals from the environment and
results in changes in gene expression that guide the cell's development.
Differentiation allows cells to develop into the four major tissue types: epithelial
tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue and muscle tissue.
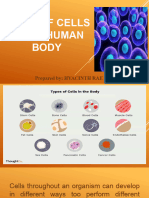
There are at least 200 different cell types in the human body. Some that you'll
need to know best include specialized blood cells, specialized nerve cells and
specialized muscle cells.
Вам также может понравиться
- Video Recap of Mutations by Amoeba SistersДокумент2 страницыVideo Recap of Mutations by Amoeba Sistersapi-233187566Оценок пока нет
- The Musculoskeletal SystemДокумент27 страницThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.Оценок пока нет
- Assignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionДокумент8 страницAssignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionJefferОценок пока нет
- Types of Cells in The BodyДокумент27 страницTypes of Cells in The BodyGulali KhanОценок пока нет
- Types of Cells in The Human BodyДокумент24 страницыTypes of Cells in The Human BodyHyacinth RaeОценок пока нет
- Cell Modifications and TissuesДокумент4 страницыCell Modifications and TissuesElla PascuaОценок пока нет
- MusclesДокумент1 страницаMusclesRHEYAN EDRISОценок пока нет
- Types of Cells in The Body1Документ29 страницTypes of Cells in The Body1aldrin braganzaОценок пока нет
- Immune SystemДокумент12 страницImmune SystemCasper Irra Marcos100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41Документ16 страницChapter 2 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41PiereОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41Документ16 страницChapter 2 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41Cathy GuantsОценок пока нет
- From Cells To Organ SystemsДокумент19 страницFrom Cells To Organ SystemsLori LorenzОценок пока нет
- From Cells To Organ SystemsДокумент19 страницFrom Cells To Organ SystemsLori LorenzОценок пока нет
- Cell Organization Grade 7Документ21 страницаCell Organization Grade 7Christine Henry-SterlingОценок пока нет
- GEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureДокумент4 страницыGEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDonnalyn Mae EscrupoloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41Документ16 страницChapter 3 Lesson 2 Pages 38 - 41PiereОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine SystemДокумент19 страницThe Endocrine Systemmuhammad aslamОценок пока нет
- Types of CellsДокумент9 страницTypes of CellsJacqueline MarilaoОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory and Types of CellsДокумент6 страницCell Theory and Types of CellsLance Afraim MortelОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueДокумент10 страницCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalОценок пока нет
- Muscles EngДокумент3 страницыMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710Оценок пока нет
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 03Документ8 страницExp SC 5 - Chapter 03megamind publicationОценок пока нет
- Types of CellsДокумент7 страницTypes of CellsRishikesh BhintadeОценок пока нет
- Science 4 Lesson 2.1 FinalДокумент34 страницыScience 4 Lesson 2.1 FinalAlicia PerezОценок пока нет
- The Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsДокумент4 страницыThe Muscular System: Parts & FunctionsNeil AdelanОценок пока нет
- Cell Types Human and AnimalsДокумент2 страницыCell Types Human and AnimalsBianca GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Is Cell Important For HumansДокумент2 страницыIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaОценок пока нет
- 05 - 1.3 - Specialized Plant and Animal CellsДокумент18 страниц05 - 1.3 - Specialized Plant and Animal CellsfabishchikutsaОценок пока нет
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionДокумент27 страниц10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىОценок пока нет
- What Is AnatomyДокумент14 страницWhat Is AnatomyRina Hayatun NufusОценок пока нет
- Body Systems OrganizationДокумент12 страницBody Systems Organizationmegha139Оценок пока нет
- Cell TypesДокумент19 страницCell TypesRhea GulayОценок пока нет
- 1 Cell Biology IntroductionДокумент2 страницы1 Cell Biology IntroductionMariam AymanОценок пока нет
- CellsДокумент2 страницыCellsPartyland El Pais de la FiestaОценок пока нет
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticДокумент11 страницCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornОценок пока нет
- Skeletal SystemsДокумент3 страницыSkeletal Systemsemmanuel richardОценок пока нет
- Muscles and BloodДокумент13 страницMuscles and BloodMaria IezhitsaОценок пока нет
- 1 Class The Human CellДокумент16 страниц1 Class The Human Cellapi-248015505Оценок пока нет
- Organs Systems of The BodyДокумент12 страницOrgans Systems of The BodyJan Michael SalomonОценок пока нет
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Документ37 страницWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalДокумент22 страницыSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Skeletal and Muscular SystemДокумент12 страницSkeletal and Muscular Systemapi-296946092100% (1)
- 2nd - Human Organ SystemsДокумент26 страниц2nd - Human Organ SystemsJaeshelle Florendo100% (1)
- Submitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2Документ3 страницыSubmitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2John Benedict VocalesОценок пока нет
- Written Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBДокумент23 страницыWritten Report Group 1 HSHSHSHSJSJDNXNXBNoronisa PendalidayОценок пока нет
- Body SystemsДокумент13 страницBody SystemsDarshema isduriОценок пока нет
- What Is The Skeletal System?Документ21 страницаWhat Is The Skeletal System?Ezekiel A. NavarroОценок пока нет
- The Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoДокумент5 страницThe Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoRed DemonОценок пока нет
- HUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Документ19 страницHUMAN-ORGAN-SYSTEM, RR11Am (LEC) 2021-NCMC101 (Pelausa, Joel C.)Joel PelausaОценок пока нет
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreДокумент9 страницExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaОценок пока нет
- Bones Muscles and SkinДокумент17 страницBones Muscles and SkinThene Truthe NoweОценок пока нет
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionДокумент24 страницыBrain Anatomy and FunctionAdamu GudinaОценок пока нет
- Linguistic Assignment 3Документ9 страницLinguistic Assignment 3Miya LoveОценок пока нет
- Muscular SystemДокумент41 страницаMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaОценок пока нет
- 3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodyДокумент5 страниц3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodySabrina PorcoОценок пока нет
- Do Now: Read The Article On Crazy Man-Made Jellyfish On My Desk and Answer The Questions!Документ17 страницDo Now: Read The Article On Crazy Man-Made Jellyfish On My Desk and Answer The Questions!oomphaloomphaОценок пока нет
- Human Body Systems Final Project 03-04 Draft 5Документ80 страницHuman Body Systems Final Project 03-04 Draft 5mDapiosenОценок пока нет
- Textos I Medicina Level I 2020Документ18 страницTextos I Medicina Level I 2020Valeria DonzelliОценок пока нет
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesДокумент3 страницыAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesОценок пока нет
- INGLES MEDICO I - Clase 6 - Cell As Structural and Functional Unit of The Body 2023Документ2 страницыINGLES MEDICO I - Clase 6 - Cell As Structural and Functional Unit of The Body 2023alinelucioalvesОценок пока нет
- The Human Body: The Facts Book for Future Doctors - Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksОт EverandThe Human Body: The Facts Book for Future Doctors - Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksОценок пока нет
- CE Orientation Final ExamДокумент1 страницаCE Orientation Final ExamLu XxОценок пока нет
- A Child of SorrowДокумент1 страницаA Child of SorrowLu XxОценок пока нет
- Bubble Lab - Dish Soap2Документ4 страницыBubble Lab - Dish Soap2Lu XxОценок пока нет
- ORGANIC PESTICIDE FROM BLENDED GARLIC AlДокумент11 страницORGANIC PESTICIDE FROM BLENDED GARLIC AlLu XxОценок пока нет
- Lesson 20: Dominic Angeles, Kane Rosales, John Dennis SyquiДокумент57 страницLesson 20: Dominic Angeles, Kane Rosales, John Dennis SyquiLu XxОценок пока нет
- Trial Sem 3 2017 SMK THREE RIVERSДокумент10 страницTrial Sem 3 2017 SMK THREE RIVERSKeertana SubramaniamОценок пока нет
- M G University M.SC Applied Microbiology SyllabusДокумент52 страницыM G University M.SC Applied Microbiology SyllabusHermann AtangaОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes (Bilingual)Документ349 страницBiology Notes (Bilingual)dipanjan biswasОценок пока нет
- SikaForce 010 Part BДокумент11 страницSikaForce 010 Part BAlexander DpsОценок пока нет
- 22 February 2022 Academic Reading TestДокумент17 страниц22 February 2022 Academic Reading TestMin MaxОценок пока нет
- Emergency Radiology Course - Brain, Not Bleed: 4 Review QuestionsДокумент3 страницыEmergency Radiology Course - Brain, Not Bleed: 4 Review QuestionsEmaardiantariОценок пока нет
- Inhibidores Naturales de La Acetil ColinesterasaДокумент12 страницInhibidores Naturales de La Acetil Colinesterasafsuarez113Оценок пока нет
- Zigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's DiseaseДокумент14 страницZigmond MJ, Burke RE - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Diseaseursula_ursula100% (1)
- Parker Aggleton 2003 StigmaДокумент12 страницParker Aggleton 2003 StigmaGareth Owen100% (2)
- Congenital Muscular TorticollisДокумент5 страницCongenital Muscular TorticollisKevin Paul ZuñigaОценок пока нет
- Cane Sugar PDFДокумент633 страницыCane Sugar PDFbernie_bph50% (2)
- Proteinuria A Guide To Diagnosis and AssДокумент7 страницProteinuria A Guide To Diagnosis and AssMarcelliaОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Nursing Pnle 2022Документ25 страницPsychiatric Nursing Pnle 2022Bariwan FaredaОценок пока нет
- B.inggris Report TextДокумент3 страницыB.inggris Report TextSeryx DoankОценок пока нет
- 2022 09 10NewScientistДокумент60 страниц2022 09 10NewScientistAyala AbishevaОценок пока нет
- Hemophilia and Its Treatment: Brief ReviewДокумент7 страницHemophilia and Its Treatment: Brief ReviewSalsa BillaОценок пока нет
- 7.2 Notes On Apgar and Ballad Scoring SystemДокумент7 страниц7.2 Notes On Apgar and Ballad Scoring SystemPasay Trisha Faye Y.Оценок пока нет
- RCDSO Guidelines Implant Dentistry PDFДокумент16 страницRCDSO Guidelines Implant Dentistry PDFl4j0b9Оценок пока нет
- OsteoarthritisДокумент4 страницыOsteoarthritisDharti PatelОценок пока нет
- Assessment in Science 9Документ2 страницыAssessment in Science 9LanieОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Thorax Lungs Lecture 2019 2020Документ43 страницыAssessment of Thorax Lungs Lecture 2019 2020Dan Floyd FernandezОценок пока нет
- Intellectual Disabilities ScriptДокумент6 страницIntellectual Disabilities Scriptapi-302509341Оценок пока нет
- BPC-157 - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side Effects - ExamineДокумент10 страницBPC-157 - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side Effects - Examineozman blooriОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2021-06-23 at 11.36.48 AMДокумент116 страницScreenshot 2021-06-23 at 11.36.48 AMSmitha ShekarОценок пока нет
- Toxic and Safe Plants PDFДокумент31 страницаToxic and Safe Plants PDFAbad Masoud KittaniОценок пока нет
- Extended Essay Chemistry (HL) - Extraction of Citrus Essential Oil From Citrus Fruit Skin and Determination of Limonene Content and Its Antibacterial Potency: Comparative InvestigationДокумент39 страницExtended Essay Chemistry (HL) - Extraction of Citrus Essential Oil From Citrus Fruit Skin and Determination of Limonene Content and Its Antibacterial Potency: Comparative InvestigationGracielle Jesslyne CahyadiОценок пока нет
- Physiological Reports - 2022 - Mulder - Distinct Morphologies of Arterial Waveforms Reveal Preload Contractility andДокумент18 страницPhysiological Reports - 2022 - Mulder - Distinct Morphologies of Arterial Waveforms Reveal Preload Contractility andMASIEL AMELIA BARRANTES ARCEОценок пока нет
- The Science of Sleep: A Brief Guide On How To Sleep Better Every NightДокумент2 страницыThe Science of Sleep: A Brief Guide On How To Sleep Better Every NightMark Anthony RaymundoОценок пока нет
- Failure of Endoscopic Spine SurgeryДокумент6 страницFailure of Endoscopic Spine SurgeryKaustubh KeskarОценок пока нет