Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH 2 Study Guide
Загружено:
Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH 2 Study Guide
Загружено:
Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name________________________________Class____________________Date____________________
Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A
Answer Key
SECTION 1. ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES
SECTION 3. CARBON-BASED MOLECULES
1. nucleus: dense center of an atom
1. true
2. neutron: particle with no electrical charge
2. false
3. proton: particle with positive electrical charge
3. true
4. electron: particle with negative electrical charge
4. false
5. compounds
5. Students should sketch one of the following, based on
6. elements
Figure 3.1 in the student text: straight chain, branched
7. false
chain, or ring.
8. false
6. Provide energy
9. true
7. starches, sugar
10. true
8. Store energy
11. outermost
9. fat, oils
12. strong
10. source of amino acids
13. electrons
11. beans, meat, nuts
14. covalent
12. map for making proteins
15. compound
13. DNA, RNA
16. element
14. polymer
17. ionic bond
18. covalent bond SECTION 4. CHEMICAL REACTIONS
19. atom 1. reactants, products; reactants, products
20. molecule 2. chemical bonds
3. reactants
SECTION 2. PROPERTIES OF WATER
4. atoms
1. false
5. same rate
2. true
6. false
3. true
7. true
4. a
8. true
5. b
9. false
6. c
10. false
7. evenly
11. chemical reaction that absorbs more energy than it
8. solvent
releases
9. nonpolar
12. chemical reaction that releases more energy than it
10. more acidic, neutral, more basic
absorbs
11. solute
13. amount of energy that needs to be absorbed for a
chemical reaction to start
14. substances changed during a chemical reaction
15. substances made by a chemical reaction
16. state reached when reactants and products are made at
the same rate
17. amount of energy that will break a bond between two
atoms
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology i Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A
Name________________________________Class____________________Date____________________
Study Guide A continued
SECTION 5. ENZYMES
1. b
2. c
3. a
4. (starting in upper left box and moving clockwise) in
living things, temperature and pH, by speeding them
up, by binding to the enzyme, making it possible for
the reaction to take place
5. decrease
6. enzymes
7. Enzymes
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology ii Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A
Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
Study Guide A
KEY CONCEPT
All living things are based on atoms and their interactions.
MAIN IDEA: LIVING THINGS CONSIST OF ATOMS OF DIFFERENT ELEMENTS.
Draw lines to connect the parts of an atom with their descriptions.
1. nucleus particle with a positive electrical charge
2. neutron particle with a negative electrical charge
3. proton particle with no electrical charge
4. electron dense center of an atom
Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
5. Water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2), are examples of
compounds / elements.
6. Elements / Compounds are made up of only one type of atom.
MAIN IDEA: IONS FORM WHEN ATOMS GAIN OR LOSE ELECTRONS.
Choose whether the statement is true or false.
7. true / false An atom becomes an ion when its number of protons changes.
8. true / false Some ions are positively charged, and some ions have no charge.
9. true / false The formation of an ion results in a full outermost energy level.
10.true / false Ions usually form when electrons are transferred from one
atom to another.
Study Guide A continued
MAIN IDEA: ATOMS SHARE PAIRS OF ELECTRONS IN COVALENT BONDS.
Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
11. Shared pairs of electrons fill the innermost / outermost energy levels of
bonded atoms.
12. Covalent bonds are generally very strong / weak.
13. Two atoms may form several covalent bonds to share several pairs of
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 1 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
protons / electrons.
14. A molecule is held together by ionic / covalent bonds.
Vocabulary Check
element compound ion molecule
ionic bond covalent bond atom
Write each word or phrase next to its definition.
____________________ 15. a substance made of atoms of different elements
bonded together in a certain ratio
____________________ 16. a particular type of atom
____________________ 17. a bond formed by the electrical force between two
ions of opposite charge
____________________ 18. a bond formed when two atoms share a pair
of electrons
____________________ 19. the smallest basic unit of matter
____________________ 20. two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Section 2: Properties of Water
KEY CONCEPT
Water’s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth.
Main Idea: LIFE DEPENDS ON HYDROGEN BONDS IN WATER.
Choose whether the statement is true or false.
1. true / false Polar molecules have two regions with a slight positive charge.
2. true / false Water is a polar molecule.
3. true / false Slightly charged regions of water molecules form hydrogen bonds.
Choose the best answer for the question.
4. Which property allows water to resist changes in temperature?
a. high specific heat
b. cohesion
c. adhesion
d. polarity
5. Which property causes water to form beads?
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 2 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
a. high specific heat
b. cohesion
c. adhesion
d. polarity
6. Which property of water helps plants to transport water from their roots to their leaves?
a. high specific heat
b. cohesion
c. adhesion
d. polarity
Study Guide A continued
MAIN IDEA: MANY COMPOUNDS DISSOLVE IN WATER.
Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
7. A solution is a mixture of substances that is evenly / unevenly distributed throughout the
entire mixture.
8. Blood plasma is an example of a solvent / solute.
9. “Oil and water don’t mix” because a polar / nonpolar molecule can’t easily dissolve in a
polar solvent.
MAIN IDEA: SOME COMPOUNDS FORM ACIDS OR BASES.
10. In the pH table below, add labels to show which side of the table shows pHs that are
more acidic, and which side shows pHs that are more basic. Then add a label to show
which pH is neutral.
_____________________________________________________________________
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Vocabulary Check
Fill in the blank with either solvent or solute.
11. A __________ dissolves in a solution.
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 3 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
Section 3: Carbon-Based Molecules
Study Guide A
MAIN IDEA: CARBON ATOMS HAVE UNIQUE BONDING PROPERTIES.
Choose whether the statement is true or false.
1. true / false Carbon atoms form the building blocks of most living things.
2. true / false Carbon’s outer energy level is full.
3. true / false Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with up to four other atoms.
4. true / false The three basic structures of carbon-based molecules are straight chain, bent
chain, and ring.
MAIN IDEA: FOUR MAIN TYPES OF CARBON-BASED MOLECULES ARE FOUND IN
LIVING THINGS.
Complete the table with the functions and examples provided for each type of
carbon-based molecule.
Functions Examples
Provide energy meat fat oils
Building blocks of proteins sugar beans DNA
Map for making proteins RNA starches nuts
Store energy
Molecule Type Functions Examples
Carbohydrate 6. 7.
Lipid 8. 9.
Protein 10. 11.
Nucleic acid 12. 13.
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 4 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 5: Enzymes
Vocabulary Check
14. The prefix mono- means “one,” and the prefix poly- means “many.”
Which contains more molecules, a monomer or a polymer? _____________________
Section 4: Chemical Reactions
KEY CONCEPT
Life depends on chemical reactions.
Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
2. During a chemical reaction, chemical bonds / solutes break and reform.
3. Reactants / products are the substances changed during a chemical reaction.
4. Bond energy is the amount of energy it takes to break a bond between two
atoms / ions.
5. Equilibrium occurs when reactants and products are made at the same rate / different
rates.
MAIN IDEA: CHEMICAL REACTIONS RELEASE OR ABSORB ENERGY.
Choose whether the statement is true or false.
6. true / false Not all chemical reactions involve changes in energy.
7. true / false Activation energy is required for a chemical reaction to start.
8. true / false Some chemical reactions release more energy than they absorb, while others
absorb more energy than they release.
9. true / false Chemical reactions can occur whether or not energy is added to the reactants.
10. true / false An exothermic chemical reaction absorbs more energy than it releases.
Vocabulary Check
Draw lines to connect the words or phrases that mean the same thing.
11. endothermic reaction substances changed during a
chemical reaction
12. exothermic reaction substances made by a chemical reaction
13. activation energy chemical reaction that releases more energy
than it absorbs
14. reactants chemical reaction that absorbs more energy
than it releases
15. products amount of energy that needs to be absorbed
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 5 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 5: Enzymes
for a chemical reaction to start
16. equilibrium amount of energy that will break a bond
between two atoms
17. bond energy state reached when reactants and products are
made at the same rate
MAIN IDEA: A CATALYST LOWERS ACTIVATION ENERGY.
Choose the best answer to the question.
1. Activation energy is the energy required to
a. complete a chemical reaction.
b. start a chemical reaction.
c. produce a catalyst.
d. produce the reactants.
2. Which of the following can reduce the amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction
to take place?
a. reactant
b. product
c. catalyst
d. hydrogen bond
3. What happens to the speed of a chemical reaction when a catalyst is present?
a. It speeds up.
b. It slows down.
c. It stays the same.
d. It becomes erratic.
Study Guide A continued
Vocabulary Check
Circle the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
5. A catalyst can increase / decrease the amount of energy needed to start a chemical
reaction.
6. Substrates are to catalysts / enzymes as keys are to locks.
7. Enzymes / substrates are catalysts for chemical reactions in living things.
© Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Holt McDougal Biology 6 Chemistry of Life
Study Guide A Section 5: Enzymes
Вам также может понравиться
- C1 1 PDFДокумент114 страницC1 1 PDFVidaurri100% (1)
- Monthly TEST PHYSICAL SCIENCE GRADE 11Документ3 страницыMonthly TEST PHYSICAL SCIENCE GRADE 11GraceEstoleCalo67% (3)
- Dwnload Full Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual PDFalicenhan5bzm2z100% (13)
- General Chemistry 1 and 2 TOPICSДокумент2 страницыGeneral Chemistry 1 and 2 TOPICSEnd ChanОценок пока нет
- 6728286Документ12 страниц6728286johan hicoruОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Revision Crossword 1Документ1 страницаChemistry Revision Crossword 1RishaОценок пока нет
- Chapter2 ReviewДокумент12 страницChapter2 Reviewapi-235052534100% (1)
- F4 Che Definitions ListДокумент5 страницF4 Che Definitions ListAlvin Dang Zhi BinОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Prelim - FinalДокумент10 страницPhysical Science Prelim - FinalrichardsamranoОценок пока нет
- مهمة 2Документ6 страницمهمة 2redahussein20Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry Lecturer Data Sep 2020Документ33 страницыChemistry Lecturer Data Sep 2020BilalHaidarОценок пока нет
- CH 2 Practice TestДокумент4 страницыCH 2 Practice TestLulwa KhaskiehОценок пока нет
- For 3rd Year High School (Chemistry Only)Документ6 страницFor 3rd Year High School (Chemistry Only)sikatlearning1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Practice TestДокумент5 страницChapter 6 Practice TestLogan ParkisonОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Документ2 страницы2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoОценок пока нет
- Document PDFДокумент21 страницаDocument PDFAnnie Bagalacsa Cepe-TeodoroОценок пока нет
- Format, Syllabus & Sample Questions For Secondary Vanda Science 2024Документ10 страницFormat, Syllabus & Sample Questions For Secondary Vanda Science 2024Peggy NgОценок пока нет
- Full Download Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions ManualДокумент36 страницFull Download Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manualnyrupvibys100% (38)
- Resonance and VSEPR Theory NEB Grade 11 NotesДокумент1 страницаResonance and VSEPR Theory NEB Grade 11 Notesrbc2jwjy4qОценок пока нет
- I. Simple Recall. Identify The Following. Write The Answers After The QuestionДокумент2 страницыI. Simple Recall. Identify The Following. Write The Answers After The QuestionTurlingОценок пока нет
- Activity 3 Protein Preiy Julian M. de GuiaДокумент3 страницыActivity 3 Protein Preiy Julian M. de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manual PDFalicenhan5bzm2z100% (13)
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition by Starr Evers ISBN Solution ManualДокумент13 страницBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition by Starr Evers ISBN Solution Manualmichael100% (28)
- DefinitionДокумент3 страницыDefinitionliow junhaoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Active Reading GuideДокумент10 страницChapter 2 Active Reading GuideAnonymous y0j9r8UОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Review: VocabularyДокумент4 страницыChapter 4 Review: VocabularyChristopher HurtОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeДокумент8 страницChapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeJADEN MANNОценок пока нет
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions ManualДокумент26 страницBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions ManualShawnPerezxgat100% (53)
- Biology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions ManualДокумент12 страницBiology Today and Tomorrow Without Physiology 5th Edition Starr Solutions Manualashleebernardgikfndpcxw100% (13)
- Chemistry Practice TestДокумент10 страницChemistry Practice TestCarl Joe EdjanОценок пока нет
- Week 5 and 6 Summative TestДокумент2 страницыWeek 5 and 6 Summative TestJulie Anne Portal - OdascoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineДокумент6 страницLesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineEdgardo VILLASEÑORОценок пока нет
- I. Simple Recall. Identify The Following. Write The Answers After The QuestionДокумент2 страницыI. Simple Recall. Identify The Following. Write The Answers After The QuestionTurlingОценок пока нет
- Bullet Points in ChemistryДокумент2 страницыBullet Points in Chemistrymohd faizzОценок пока нет
- 7.2 Worksheet Ionic Bonds and Ionic CompoundsДокумент4 страницы7.2 Worksheet Ionic Bonds and Ionic CompoundsseiffaisalОценок пока нет
- Honors Unit 2 Biochemistry Study Guide S23Документ6 страницHonors Unit 2 Biochemistry Study Guide S23realsteelwarredОценок пока нет
- Physical ScienceДокумент22 страницыPhysical ScienceMary Joyce Nicolas ClementeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeДокумент5 страницChapter 2 Chemical Context of LifeZoe AposОценок пока нет
- Integrated Science2Документ2 страницыIntegrated Science2Earn8348Оценок пока нет
- Atoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Документ8 страницAtoms, Elements, and Compounds-Chapter 6Araas AraasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ10 страницChapter 2AnonymousОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Chemistry 6th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual PDFДокумент35 страницDwnload Full Chemistry 6th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual PDFrachaelkellerbg5yun100% (12)
- Atomic Structure CrosswordДокумент1 страницаAtomic Structure Crossword吴蔓华Оценок пока нет
- Test - The Science 7 Final Exam ReviewДокумент8 страницTest - The Science 7 Final Exam ReviewAli MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Fat StyupidДокумент17 страницFat StyupidVincent LinОценок пока нет
- Science 9 Final Exam Review KEY: Safety and ChemistryДокумент17 страницScience 9 Final Exam Review KEY: Safety and ChemistryVirna75Оценок пока нет
- Post-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6Документ27 страницPost-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6CloudetteMendozaОценок пока нет
- Biology GuideДокумент8 страницBiology GuideANDREA LUCIA AVILA OCHOAОценок пока нет
- Q2 Hybrid - Module 2Документ18 страницQ2 Hybrid - Module 2ace fuentesОценок пока нет
- BIOL 111 Practice Assignment #1Документ5 страницBIOL 111 Practice Assignment #1Sara FarheenОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: Occurrence of A Chemical Reaction: TPO: RelateДокумент4 страницыLesson 1: Occurrence of A Chemical Reaction: TPO: RelateEdgardo VILLASEÑORОценок пока нет
- Test: "Chemical Bonds" (Chapter 18 Gizmo's: Covalent & Ionic Bonds) - Quizlet PDFДокумент3 страницыTest: "Chemical Bonds" (Chapter 18 Gizmo's: Covalent & Ionic Bonds) - Quizlet PDFMansahib SinghОценок пока нет
- 2020-2021 COT 1 - ScriptДокумент5 страниц2020-2021 COT 1 - ScriptEllimacRoseОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 6th Edition Mcmurry Solutions ManualДокумент35 страницChemistry 6th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manualthrenodyvoxlkio100% (22)
- Psma 1Документ1 страницаPsma 1Rebekah EquizОценок пока нет
- GAMSAT Science ContentДокумент2 страницыGAMSAT Science ContentInez KoОценок пока нет
- Quarter 4 - : Balancing Chemical EquationДокумент15 страницQuarter 4 - : Balancing Chemical EquationKrisha Mae ChaОценок пока нет
- PDF DocumentДокумент15 страницPDF Documentsadam 10Оценок пока нет
- CHEMHACK Inorganic Ebook (XI + XII) - 4771033 - 2022 - 07 - 22 - 11 - 19Документ91 страницаCHEMHACK Inorganic Ebook (XI + XII) - 4771033 - 2022 - 07 - 22 - 11 - 19SurajОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Gene Action and MutationsДокумент2 страницыGene Action and MutationsEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- Great Depress Notes pt2Документ5 страницGreat Depress Notes pt2Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- How To - Live TV ProductionДокумент3 страницыHow To - Live TV ProductionEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- Know How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA SequenceДокумент1 страницаKnow How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA SequenceEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- School Calendar: September October July AugustДокумент2 страницыSchool Calendar: September October July AugustEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- Cells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetEmiliano Arvizu Franco Jr100% (2)
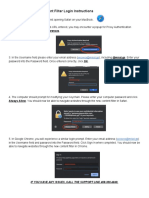
- Content Filter Login InstructionsДокумент1 страницаContent Filter Login InstructionsEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- Test Over 2-6 (V1-Online) (20-21)Документ1 страницаTest Over 2-6 (V1-Online) (20-21)Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- 2-5 Assignment PDFДокумент2 страницы2-5 Assignment PDFEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 VocabДокумент1 страницаUnit 4 VocabEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- The Crucible and Mccarthyism: Reading For InformationДокумент6 страницThe Crucible and Mccarthyism: Reading For InformationEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrОценок пока нет
- CE-401CE 2.0 Network Diagrams 2015Документ83 страницыCE-401CE 2.0 Network Diagrams 2015Shubham BansalОценок пока нет
- 2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommДокумент40 страниц2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommMilic MilicevicОценок пока нет
- Introducing RS: A New 3D Program For Geotechnical AnalysisДокумент4 страницыIntroducing RS: A New 3D Program For Geotechnical AnalysisAriel BustamanteОценок пока нет
- The 5 TibetansДокумент3 страницыThe 5 TibetansValentin100% (2)
- Capsicums - Innovative Uses of An Ancient CropДокумент11 страницCapsicums - Innovative Uses of An Ancient CropMaarioОценок пока нет
- Morris 2Документ22 страницыMorris 2IsmaelLouGomezОценок пока нет
- Q4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseДокумент36 страницQ4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseZenn Tee100% (1)
- Taenia SoliumДокумент40 страницTaenia SoliumBio SciencesОценок пока нет
- Custard The DragonДокумент4 страницыCustard The DragonNilesh NagarОценок пока нет
- Comsol ProfileДокумент4 страницыComsol ProfilePrashant KumarОценок пока нет
- 8484.sensor CEM Diagnostic Tests User Manual v3.1.0Документ28 страниц8484.sensor CEM Diagnostic Tests User Manual v3.1.0Edgar FuentesОценок пока нет
- Alum Rosin SizingДокумент9 страницAlum Rosin SizingAnkit JainОценок пока нет
- Lisca - Lingerie Catalog II Autumn Winter 2013Документ76 страницLisca - Lingerie Catalog II Autumn Winter 2013OvidiuОценок пока нет
- Features and Highlights - : CapableДокумент2 страницыFeatures and Highlights - : CapableaarianОценок пока нет
- Clover by The RiverДокумент24 страницыClover by The RiverE. PoornimaОценок пока нет
- ?????Документ89 страниц?????munglepreeti2Оценок пока нет
- Single Nozzle Air-Jet LoomДокумент7 страницSingle Nozzle Air-Jet LoomRakeahkumarDabkeyaОценок пока нет
- Fluids Mechanics HomeworkДокумент92 страницыFluids Mechanics Homeworkm3994794% (31)
- Ed 4 and 3 North East England - University of SheffieldДокумент23 страницыEd 4 and 3 North East England - University of Sheffieldsaravananr04Оценок пока нет
- DEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EДокумент28 страницDEMU COUP - Leviat - 17 1 EJianhua WuОценок пока нет
- Routes of Medication AdministrationДокумент2 страницыRoutes of Medication AdministrationTracy100% (6)
- STAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesДокумент152 страницыSTAT 713 Mathematical Statistics Ii: Lecture NotesLiban Ali MohamudОценок пока нет
- CPower Product Training.09.2016.EnДокумент70 страницCPower Product Training.09.2016.Enerdinc100% (1)
- C8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1Документ7 страницC8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1SANKET MATHURОценок пока нет
- Grundfosliterature SP A - SP LДокумент104 страницыGrundfosliterature SP A - SP LRizalino BrazilОценок пока нет
- TM 55 1520 400 14 PDFДокумент227 страницTM 55 1520 400 14 PDFOskar DirlewangerОценок пока нет
- Shipping Agents in SGДокумент3 страницыShipping Agents in SGeason insightsОценок пока нет
- André Bakker Modeling Flow Fields in Stirred TanksДокумент40 страницAndré Bakker Modeling Flow Fields in Stirred TanksKhalida BekrentchirОценок пока нет