Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Heart Failure: Dysfunction)
Загружено:
Christine Pialan Salimbagat0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров5 страницThis document discusses heart failure, including its causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and management. Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It may or may not involve congestion. Common causes include coronary atherosclerosis. Pathophysiologically, it involves impaired contractility and filling of the heart. Signs and symptoms depend on whether the left or right side of the heart is more affected. Diagnostic tests include echocardiogram, chest x-ray, ECG, and blood tests. A Swan-Ganz catheter can measure pressures in the heart chambers and pulmonary arteries. Management focuses on returning the heart to normal function using medications like di
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Cardio-G
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses heart failure, including its causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and management. Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It may or may not involve congestion. Common causes include coronary atherosclerosis. Pathophysiologically, it involves impaired contractility and filling of the heart. Signs and symptoms depend on whether the left or right side of the heart is more affected. Diagnostic tests include echocardiogram, chest x-ray, ECG, and blood tests. A Swan-Ganz catheter can measure pressures in the heart chambers and pulmonary arteries. Management focuses on returning the heart to normal function using medications like di
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров5 страницHeart Failure: Dysfunction)
Загружено:
Christine Pialan SalimbagatThis document discusses heart failure, including its causes, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and management. Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It may or may not involve congestion. Common causes include coronary atherosclerosis. Pathophysiologically, it involves impaired contractility and filling of the heart. Signs and symptoms depend on whether the left or right side of the heart is more affected. Diagnostic tests include echocardiogram, chest x-ray, ECG, and blood tests. A Swan-Ganz catheter can measure pressures in the heart chambers and pulmonary arteries. Management focuses on returning the heart to normal function using medications like di
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 5
Cardio G in most blood vessels in the body,
primarily in the lungs, to angiotensin 2
Heart Failure which is a potent vasoconstrictor.
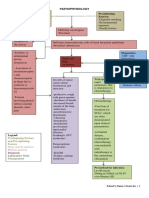
- Is the inability of the heart to pump Angiotensin 2 further stimulates the
sufficient blood to meet the needs of release in the adrenal cortex of
the tissues for oxygen and nutrients aldosterone, which causes sodium
- May or may not be congestion retention in the kidneys, further
- If (+) congestion = congestive heart increasing blood pressure. Only
failure normally released when there’s
reduced in blood flow to the kidneys. In
Causes heart failure, they are stimulated
because of the reduced blood flow to
1. Coronary atherosclerosis
the kidneys but not because of trauma
- Condition wherein the blood vessel
like stab wound, but because of the
supplying oxygenated blood to the
heart’s inability to pump blood
heart is obstructed by fats or atheroma,
throughout the organs. As a resultthe
clot, thrombus or by embolus
BP is increased, worsening the heart
Pathophysiology failure of client)
- sympathetic nervous system stimulation
Impaired contractile properties of the (organs receiving reduced blood flow
heart which (systolic dysfunction) secondary to heart failure)
Impaired filling of the heart (diastolic increases workload on the heart
dysfunction) if there’s decompensation: no
contraction, resistance to filling further
Result
worsening of heart failure
Lower than normal cardiac output
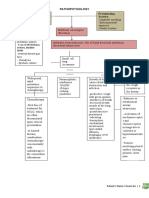
Signs and symptoms
Compensatory mechanisms of the body
- ventricular hypertrophy (enlargement a. Left sided heart failure
of ventricle muscles) - most often fails earlier than the right
- renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system sided heart failure (Because left heart
(activated normally when there’s does more work)
insufficient blood flow to the kidneys. - Pulmonary congestion
The insufficient blood flow to the - #1 pathognomonic sign: pulsus aternans
kidneys and decreased sodium to the (alternating strong and weak pulse)
kidneys, if detected by the b. Right sided heart failure
juxtaglomerular cells , releases enzyme - Systemic congestion: edema, ascites
Renin. Renin splits Angiotensinogen, (abnormal buildup of fluid in the
protein produced by liver causes the abdomen), neck vein distention,
release of angiotensin 1 which is a mild hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
vasoconstrictor, then converted by
angiotensin converting enzyme located
Diagnostic Tests – uses a catheter to measure the pressure
on the pulmonary vein
1. Clinical manifestaions - Indirect measurement of pressure of
Classification of heart failure left side of heart
a. Class 1 (symptomatic with exertion) - Mean 12-16 mmHg
b. Class 2 (symptomatic with less than
Nursing Care
ordinary activities)
a. Patient in Trendelenburg position
c. Class 3 (Symptomatic with less than - To prevent air embolism (trendelenburg
ordinary activities) position helps air embolus be trapped in
d. Class 4 (always symptomatic) the right atrium or right ventricle and
2. Echoocardiogram (assess ejection not be lodged in pulmonary capillaries)
fraction of ventricles) - For venous engorgement prevention
3. Chest radiographs (cardiomegaly) b. Use sterile technique
c. MD thread ballon tipped catheter thru
4. ECG
subclavial vein > right atrium and right
5. Serum levels ventricle > balloon is inflated (1-2ml of
CBC air but never water, water has more
Kidney function weight than air and if touches the wall
- Creatinine clearance: of the atrium might trigger arrythmias)
125ml/min/1.73m2, 25mg/kg/24hrs (balloon acts as buffer between the
hard part of catheter and wall of
- Creatinine: n 0.6-1.2mg/dl (more
ventricle to prevent ventricular
accurate)
arrhythmias) > blood guides balloon to
- BUN: 10-20mg/dl pulmonary capillaries
d. When measuring, make sure that the
*kidneys are assessed because they are very zero mark on the
sensitive to lack of blood flow. If the patient has manometer/transducer or stopcock is
heart failure, first organ to suffer: kidneys at the level of client’s right atrium (level
of 4th ICS, left midaxillary line):
6. Cardiac catheterization – insertion of phlebostatic axis (phlebo [ blood ] +
catheter through artery of the leg, catheter is static)
then driven to the heart to make sure the - Phlebostatic axis: Lowest blood
pressure in the chambers of the heart pressure, set to 0 point (0mmHg) of
manometer or transducer
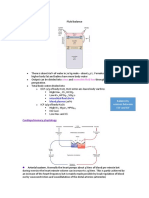
7. Swan-ganz catheter - Normal central venous pressure (CVP):
> 4 lumen catheter 5-10cm H20 or 3-6mmHg
Measures: - Increase: hypervolemia
a. CVP (central venous pressure: the - Decrease: hypovolemia
pressure of the right side of heart) – Proximal Lumen
mean 3-6mmHg - Rests in the vena cava or the right
Disadvantage: late indicator of atrium
increased fluid volume, it takes a while - Reflects the central venous pressure
before increased fluid volume increases Distal Lumen
CVP - Rests in the pulmonary artery
b. Pulmonary artery capillary - Reflects the PACP (pulmonary artery
pressure/pulmonary capillary wedge capillary pressure)/PCWP (pulmonary
pressure capillary wedge pressure)
Thermistor Lumen ballon tip formationing pulmonary wedge
- Measures cardiac output using the pressure
thermal dilution technique
- Fast change indicates increased cardiac
output
- Low change indicates decreased cardiac
output
Inflation lumen and balloon
- Inject 1-2ml of air to inflate balloon
Swan Ganz catheter
Illustration of where phlebostatic axis is, where
the stop cup (?) should be leveled to maintain
adequate measurement
4 lumens of swan ganz catheter, where the
catheter will go through the heart
Management - For fluid retention in heart failure
- Diuretics decreases fluid retention
Goal: To return heart to normal function Loop diuretics
- Furosemide
Medications - Torsemide
1. Inotropic agents (drugs meant to : inhibit the reacsorption of Na, K and CI
increase strength of cardiac in thick ascending limb of loop of henle
contraction) (basic unit of kidney)
a. Dobutamine 5. Vasodilators
- A1, B1, B2 Angiotensin-converting enzyime
- #1 inotropic agent in heart failure inhibitors
- Given as continuous infusion: 1- - ‘pril’
2ug/kg/min - Acts as vasodilators
b. Digoxin - Also diuretics, because they inhibit the
- Action: inhibits the Na-K-pump (Na-K- production of aldosterone that saves
ATPase) > increases influx of calcium sodium from the body and eliminates
into cell > depolarizes cells > creates potassium
action potential > slow HR, inc cardiac - ACE inhibitor increases potassium level
contractility and decreases sodium level
- Therapeutic dose: 0.5 – 2mg/dl - Captopril
- Toxicity: anorexia – earlist sign - Enalapril (s/e: nonproductive cough)
- Digibind: antidote Angiotensin Receptor blocker
- Contraindication - ‘sartan’
*Hypercalcemia – calcium potentiates - Vasodilator
digoxin may lead to arrhythmias - Losartan
*Hypokalemia – less potassium, less - Valsartan
resistance to calcium influx may lead to Beta blockers
arrhythmias - ‘olol’
- Give high in potassium foods: apple, - Decrease HR and cardiac demand
banana, carrots - Beta 1 antagonist
- Metoprolol
2. Vasodilators - Propranolol
- If cause if vasoconstriction (e.g - Contraindication: asthmatics (also
myocardial infarction) blocks beta2 receptors that’s
a. Nitroglycerin responsible for bronchodilation, may
b. Nesiritide lead to bronchoconstriction)
c. Na nitroprusside Calcium Channel Blockers
- Amlodipine, nicardipine
3. Vasoconstrictors - s/e: erectile dysfunction
- If cause of vasodilation or lack of fluids
in blood vessels (e.g shock) 6. surgery
a. Dopamine a. PTCA (percutaneous transluminal
- Stimulates A1, B1receptors coronary angioplasty
b. Vasopressin - For 1-2 affected vessels
c. Epinephrine b. Coronary artery bypass graft
- For 3 affected vessels
4. Lower BP c. Carotid endarderectomy
Diuretics d. Mechanical assist device
Intraaortic balloon pump
- Assist heart in pumping sufficient blood Left sided heart failure tends to produce
to the body pulmonary manifestations
- deflates with systole Right sided heart failure tends to
- inflates with diastole produce systemic manifestations
- Increases cardiac output Ultimately, both left sided and right
sided failure tend to occur together
Left ventricular assist device
Heart transplantation
Summary
Вам также может понравиться
- F.SARAWI NCP SIC Drug StudyДокумент30 страницF.SARAWI NCP SIC Drug StudyaldwinОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular System: TH THДокумент2 страницыCardiovascular System: TH THChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermДокумент11 страницChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloОценок пока нет
- Acyanotic Heart Diseases ASD-Atrial Septal DefectДокумент5 страницAcyanotic Heart Diseases ASD-Atrial Septal DefectPrincess LegansonОценок пока нет
- Cardio Notes, Heart FailureДокумент17 страницCardio Notes, Heart FailureJoy DunwanОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsДокумент6 страницHeart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsJessareth Atilano CapacioОценок пока нет
- Cardio Lecture Notes: Congestive Heart FailureДокумент7 страницCardio Lecture Notes: Congestive Heart Failurecolek22100% (5)
- NCMB 418 Hemodynamics Week 7Документ34 страницыNCMB 418 Hemodynamics Week 7Jennifer Ambrosio100% (1)
- MODULE 20 HANDOUTS Cardiovascular SystemДокумент4 страницыMODULE 20 HANDOUTS Cardiovascular SystemMichaela PoОценок пока нет
- ValvularДокумент2 страницыValvularJulia Rae Delos SantosОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Документ8 страницCongestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Michelle Vera GabunОценок пока нет
- Hemodynamics: Ncmb418 - Critical Care Nursing Rle Midterm LectureДокумент7 страницHemodynamics: Ncmb418 - Critical Care Nursing Rle Midterm LectureKyle Saberon100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент20 страницCardiovascular SystemFisco DessereiОценок пока нет
- Study of Illness Condition: Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology AnalysisДокумент9 страницStudy of Illness Condition: Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology AnalysisaldwinОценок пока нет
- 25circulation Part 3Документ15 страниц25circulation Part 3Jaydave PatelОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHAДокумент46 страницHeart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHAYuanita WahyuningsihОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular FunctionДокумент5 страницCardiovascular FunctionJohn Fritz Gerald BascoОценок пока нет
- Patho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Документ91 страницаPatho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Puranjay ChandelОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Tamponade and ManagementДокумент42 страницыCardiac Tamponade and Managementأم حمدОценок пока нет
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemДокумент9 страницLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular DisorderДокумент21 страницаCardiovascular Disorderdanica cordovaОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыCongestive Heart FailureZosmita Shane GalgaoОценок пока нет
- Study of Illness Condition: Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology AnalysisДокумент3 страницыStudy of Illness Condition: Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology AnalysisCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINAОценок пока нет
- Cardio Vascular SystemДокумент26 страницCardio Vascular SystemmayankОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisДокумент6 страницCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHEОценок пока нет
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersДокумент13 страниц1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasОценок пока нет
- Blood VesselsДокумент4 страницыBlood VesselsCrazy StrangerОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemДокумент20 страницPharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemCheryl OrtizОценок пока нет
- PP CardiacДокумент62 страницыPP CardiacMarie Queenly Pagaran100% (1)
- HypertensionДокумент11 страницHypertensionJyoti singhОценок пока нет
- Management of Patientswith Complications From Heart DiseaseДокумент8 страницManagement of Patientswith Complications From Heart Diseasekristine keen buanОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент26 страницCardiovascular SystemJenny Torreda100% (1)
- PulmonarycirculationДокумент34 страницыPulmonarycirculationq2ndzg5rjxОценок пока нет
- مخلص فسيولجيДокумент10 страницمخلص فسيولجيraseel571Оценок пока нет
- Obstruction of Blood FlowДокумент4 страницыObstruction of Blood FlowJessica Carmela CasugaОценок пока нет
- Lec 3 - Circulatory SystemДокумент8 страницLec 3 - Circulatory SystemJewel Jehd AlegriaОценок пока нет
- Cardiology HFДокумент11 страницCardiology HFdhayemaruОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент4 страницыCongestive Heart Failureepoi89Оценок пока нет
- Integrated Therapeutics IiiДокумент160 страницIntegrated Therapeutics IiiSalahadinОценок пока нет
- 3 Heart FailureДокумент8 страниц3 Heart FailureAudrey Ann AcobОценок пока нет
- Heart Rate Blood PressureДокумент128 страницHeart Rate Blood PressureShubhra ShettyОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Heart Disease2Документ61 страницаRheumatic Heart Disease2Puji Yunisyah RahayuОценок пока нет
- The Circulatory SystemДокумент25 страницThe Circulatory SystemEduardson PHОценок пока нет
- CardiovascularДокумент6 страницCardiovascularMabes100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент10 страницCardiovascular Systemsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Heart Failure Lily ModifiedДокумент57 страницHeart Failure Lily ModifiedSabila FatimahОценок пока нет
- Cardiac II Study GuideДокумент6 страницCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnОценок пока нет
- Cardiac FailureДокумент63 страницыCardiac FailureNina OaipОценок пока нет
- Blood PressureДокумент26 страницBlood PressureEniola DaramolaОценок пока нет
- Hemodynamic MonitoringДокумент4 страницыHemodynamic MonitoringHazelGraceОценок пока нет
- CARDIOДокумент10 страницCARDIOMarcel TabucolОценок пока нет
- Anatomy: Cardiac Symptoms Cardiac Examination ECG and X RayДокумент27 страницAnatomy: Cardiac Symptoms Cardiac Examination ECG and X RayEmey AlahmadОценок пока нет
- Leg Swelling Fluid Balance: Urine Insensible Fluid LossДокумент9 страницLeg Swelling Fluid Balance: Urine Insensible Fluid LossDarwithaОценок пока нет
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsДокумент3 страницыPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANOОценок пока нет
- Case 2 SlosДокумент7 страницCase 2 SlosNamarОценок пока нет
- Test 2Документ12 страницTest 2Kat IvyОценок пока нет
- CardioДокумент9 страницCardioAly HannahОценок пока нет
- ch28 Notes Part 2Документ9 страницch28 Notes Part 2Monica JubaneОценок пока нет
- Cardiac TamponadeДокумент10 страницCardiac TamponadevineeshОценок пока нет
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisОт EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Salimbagat - Legal Notes Second BatchДокумент14 страницSalimbagat - Legal Notes Second BatchChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- HTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisДокумент8 страницHTP - Supporting The Patient On DialysisChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Salimbagat - Legal Notes First BatchДокумент8 страницSalimbagat - Legal Notes First BatchChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Case 3 - Anatomy and Physiology - SalimbagatДокумент4 страницыCase 3 - Anatomy and Physiology - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Case 4 - Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresДокумент7 страницCase 4 - Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Assessment 8 - SalimbagatДокумент2 страницыAssessment 8 - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Scrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanДокумент12 страницScrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresДокумент12 страницCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- NCPs - SalimbagatДокумент6 страницNCPs - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Reflection: Opening QuestionsДокумент3 страницыReflection: Opening QuestionsChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Katz Index of I.A.D.L - SalimbagatДокумент1 страницаKatz Index of I.A.D.L - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- LAWTON - BRODY I.A.D.L. - SalimbagatДокумент2 страницыLAWTON - BRODY I.A.D.L. - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Geriatric Depression Scale - SalimbagatДокумент2 страницыGeriatric Depression Scale - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Skill 12 Learning Feedback - SalimbagatДокумент1 страницаSkill 12 Learning Feedback - SalimbagatChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- NCP ImpairedSkinIntegДокумент2 страницыNCP ImpairedSkinIntegChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Name: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCC Group K Week 2 - Care of Older Adult Clinical RotationДокумент3 страницыName: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCC Group K Week 2 - Care of Older Adult Clinical RotationChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Socio 1 Midterm Exam: Answer. (CAPITAL LETTER)Документ2 страницыSocio 1 Midterm Exam: Answer. (CAPITAL LETTER)Christine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of Nursing: Level II AACUP AccreditedДокумент4 страницыMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology College of Nursing: Level II AACUP AccreditedChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Name: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCCДокумент1 страницаName: Salimbagat, Christine P. BSN Iii - CCCChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- dnd3 Character Sheet STD 105cДокумент2 страницыdnd3 Character Sheet STD 105cGerry MaloneyОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Manufacturer Pt. Bital AsiaДокумент3 страницыMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Manufacturer Pt. Bital AsiaediОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson Plan in HousekeepingДокумент6 страницDetailed Lesson Plan in HousekeepingreyОценок пока нет
- Statistics and Data CollectionДокумент11 страницStatistics and Data CollectionRichimon LicerioОценок пока нет
- Method Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False CeilingsДокумент3 страницыMethod Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False Ceilingsmozartjr22100% (1)
- Ra 9293 Amending Ra 7836Документ2 страницыRa 9293 Amending Ra 7836vonoblesseОценок пока нет
- Curriculum in MalaysiaДокумент37 страницCurriculum in MalaysiaEmily Ling100% (1)
- Living GraceДокумент227 страницLiving GraceÁdám NógrádiОценок пока нет
- III Job Order CostingДокумент66 страницIII Job Order CostingJoshuaGuerrero0% (1)
- Tamang GrammarДокумент12 страницTamang Grammarsoftdina100% (1)
- Global Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualДокумент16 страницGlobal Strategy 3rd Edition Peng Solutions ManualJenniferThompsonxergb100% (13)
- Satellite Motion NotesДокумент23 страницыSatellite Motion NotesVarshLok100% (1)
- 2 Short Summary of English and American GeographyДокумент2 страницы2 Short Summary of English and American GeographyDonna Mendoza ComiaОценок пока нет
- Neighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0Документ1 страницаNeighbor'S Plot - : Sheet No Rev No R0jibeesh cmОценок пока нет
- L-M349 (L1b1a) Kenézy Ancestral JourneyДокумент20 страницL-M349 (L1b1a) Kenézy Ancestral JourneyGábor Balogh100% (2)
- CALDER New Research On Low-Frequency Membrane AbsorbersДокумент11 страницCALDER New Research On Low-Frequency Membrane AbsorbersAndre VareОценок пока нет
- Dossier 015 enДокумент5 страницDossier 015 enAshok KumarОценок пока нет
- Earthquake Lesson Plan 2022Документ5 страницEarthquake Lesson Plan 2022Maylyn Grace Dalumpines-Colon EbonaloОценок пока нет
- Price and Output Determination Under OligopolyДокумент26 страницPrice and Output Determination Under OligopolySangitha Nadar100% (1)
- Settlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Документ11 страницSettlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Arindam RoulОценок пока нет
- Libi Vs IACДокумент1 страницаLibi Vs IACBingoheartОценок пока нет
- Motivation MBAДокумент31 страницаMotivation MBAAkshitaОценок пока нет
- 2016-FL3030说明书50m臂长最后版-2016 11 3 PDFДокумент96 страниц2016-FL3030说明书50m臂长最后版-2016 11 3 PDFMohammed SumerОценок пока нет
- Content Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)Документ6 страницContent Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)AngelaОценок пока нет
- The Magical Diaries of Ethel ArcherДокумент7 страницThe Magical Diaries of Ethel Archerleeghancock100% (1)
- Title Toolbox 1 AДокумент2 страницыTitle Toolbox 1 AGet LiveHelpОценок пока нет
- Of Gods, Glyphs and KingsДокумент24 страницыOf Gods, Glyphs and KingsBraulioОценок пока нет
- Thesis TopicsДокумент9 страницThesis TopicsInayath AliОценок пока нет
- Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions ManualДокумент11 страницEssentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions Manualjeffreyhayesagoisypdfm100% (13)
- Downtown SLO Business Owners Ask City Council To Consider Parking ChangesДокумент4 страницыDowntown SLO Business Owners Ask City Council To Consider Parking ChangesKaytlyn LeslieОценок пока нет