Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chemical Basis of Life 2
Загружено:
Ian Russ BautistaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chemical Basis of Life 2
Загружено:
Ian Russ BautistaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE 2.
ATOM
-Smallest particle of matter non-divisible by chemical means
-Composed of protons (+) and neutron (neutral) in the nucleus and electrons (-) outside
the nucleus
-The smallest unit of an element to enter into chemical reactions
-all atoms of an element have a particular number of protons(atomic number)
-Electrically neutral because the number of protons equals the number of electrons
-Atomic weight depends on the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
-Chemical properties depend on the number of electrons in the outer shell
MOLECULES
-Form when two or more atoms of the same element react with one another or combine
with atoms of another element.
The smallest part of a compound that still has the properties of that compound
-could be inorganic or organic molecules
Common elements in living things
1. Oxygen (O) – 65% of human body weight
2. Carbon (C) – 18%
3. Hydrogen (H) – 10%
4. Nitrogen (N) – 3%
5. Sodium (Na) – 0.15%
6. Magnesium (Mg) – 0.05%
7. Phosphorus (P) – 1.1%
8. Sulfur (S) – 0.25%
9. Chlorine (Cl) – 0.15%
10. Potassium (K) – 0.35%
11. Calcium (Ca) – 2%
12. Iron (Fe) – 0.0004%
13.Iodine (I) – 0.0004%
Chemical Bonding
-interactions involving atoms of elements combining with one another
-The attractive force that binds atom together to form molecules
-Determined by the electrons the surrounds the nucleus
-An atom may bond with another atom by either gaining, losing or sharing electrons
Type of Chemical Bonds
Covalent Bond – Electrons are shared; characteristic of most chemicals in living things;
smallest particles formed are called molecules
Ionic Bond – An electron is transferred from one atom to another; ions (charge
particles) are formed- cations, when electron is lost; anions, when electron is gained
Hydrogen Bond - When hydrogen combines with oxygen or with another
electronegative atom; weak and can easily be formed or broken; very important in
biological system; important in determining the structure of DNA, and proteins
INORGANIC MOLECULES
-usually contain positive and negative ions
-atoms are usually held together by ionic bond
-usually composed of short chain
-often associated with non-living things
-includes water, acid and bases, salts, and gases
WATER
- The most abundant component of the protoplasm
- Inorganic compound composed of two atoms of hydrogen and an atom of oxygen
Physical Properties of Water
1. Universal Solvent
2. High specific heat and latent heat of vaporization
3. High degree of thermal conductivity
4. Immiscible with lipids
5. Neutral pH
6. Liquid in form at room temperature
7. High surface tension
Physiological Properties of Water
Вам также может понравиться
- Social Skills WorksheetsДокумент26 страницSocial Skills WorksheetsHusaini100% (5)
- Chemical Basis of LifeДокумент38 страницChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonОценок пока нет
- Cell As A Unit of LifeДокумент18 страницCell As A Unit of LifeMohamad Abdul WahabОценок пока нет
- 3 NomenclatureДокумент45 страниц3 Nomenclaturerusnah chungОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic CellsДокумент2 страницыProkaryotic CellsBerch MelendezОценок пока нет
- Lecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2Документ6 страницLecture On Organic Chemistry Part 2ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHOОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент3 страницыIntegumentary SystemPongman92Оценок пока нет
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesДокумент6 страницProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234Оценок пока нет
- The Effects of Cell Structure On Function Lab ExperimentДокумент3 страницыThe Effects of Cell Structure On Function Lab ExperimentRio Ruby LloviaОценок пока нет
- Human Physiology Cell Structure Function I Lecture 31.july .2012Документ112 страницHuman Physiology Cell Structure Function I Lecture 31.july .2012Ít'ž Aàďìĺ SàìfОценок пока нет
- Kingdom AnimaliaДокумент25 страницKingdom AnimaliaBernadette MungcalОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need To Know About AlkanesДокумент2 страницыEverything You Need To Know About AlkanesJohnОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesДокумент21 страницаProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- BiosphereДокумент27 страницBiosphereJamaika Sofia LetimОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент3 страницыLipidsMohd FarhanОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент21 страницаBiochemistryJaymarie ZabateОценок пока нет
- Art and ScienceДокумент1 страницаArt and ScienceAshley AquinoОценок пока нет
- Classification of MatterДокумент17 страницClassification of MatterAshmyra ManaloОценок пока нет
- The Origin and Chemistry of Life: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Sheryl Santa Cruz-BiscochoДокумент25 страницThe Origin and Chemistry of Life: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Sheryl Santa Cruz-Biscochoirish x100% (1)
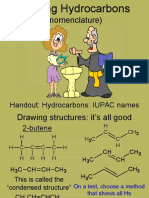
- IUPAC names hydrocarbonsДокумент28 страницIUPAC names hydrocarbonsRigen Alam100% (1)
- EnzymeДокумент16 страницEnzymePrecious DerainОценок пока нет
- BIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDДокумент73 страницыBIOENERGETICS - How The Body Converts Food To Energy - Group 7 (MC 102 - Lecture) EDITEDJowe VarnalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Cell MembraneДокумент6 страницChapter 8 Cell MembranerexartoozОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration 1Документ28 страницCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory and Functions of LifeДокумент1 страницаCell Theory and Functions of LifeLucca PiaggioОценок пока нет
- Activity 02 The Cell CityДокумент4 страницыActivity 02 The Cell Citybernard0% (1)
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliДокумент49 страницCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharОценок пока нет
- Valence and Core ElectronsДокумент19 страницValence and Core Electronsapi-233187566Оценок пока нет
- CH01 BiologyДокумент36 страницCH01 BiologysugisweОценок пока нет
- Nano TechnologyДокумент12 страницNano Technologyrenuka mulaОценок пока нет
- Humans and The Microbial WorldДокумент41 страницаHumans and The Microbial WorldLudyОценок пока нет
- Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsДокумент21 страницаMass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsVince DulayОценок пока нет
- Atoms and The Periodic TableДокумент16 страницAtoms and The Periodic TableRainОценок пока нет
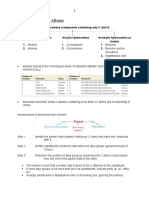
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Документ6 страницOrganic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Jojo LeongОценок пока нет
- Carbon Compounds Student WorksheetДокумент5 страницCarbon Compounds Student WorksheetFiryal Nabilah Q AОценок пока нет
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidДокумент36 страницDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoОценок пока нет
- SCH 102: Organic Chemistry IДокумент152 страницыSCH 102: Organic Chemistry IH to O ChemistryОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Activity SheetДокумент1 страницаPhotosynthesis Activity SheetLae DeeОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeДокумент44 страницыUnit 2 - Biochemistry of Life: Chapter 4: Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of LifeJeremy CorrenОценок пока нет
- A-P Chapter 3 Cell StructureДокумент35 страницA-P Chapter 3 Cell StructureMONIQUE VELASCOОценок пока нет
- Reference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EДокумент11 страницReference: Essentials For Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb, EAnnalei GagnéОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Lipids Lesson 3: The Cell MembraneДокумент12 страницUnit 3 Lipids Lesson 3: The Cell MembraneValenzuela Allene GraceОценок пока нет
- NomenclatureДокумент64 страницыNomenclatureKaushik SenguptaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleДокумент89 страницChapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleAnn BorromeoОценок пока нет
- 3 - Cellular Respiration NotesДокумент22 страницы3 - Cellular Respiration Notesapi-375285021Оценок пока нет
- How cell theory developedДокумент4 страницыHow cell theory developedLourence BajariasОценок пока нет
- Animal CellДокумент11 страницAnimal CellDaryl De LeonОценок пока нет
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateДокумент24 страницыLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashir100% (1)
- Cells Questions and VocabДокумент12 страницCells Questions and VocabFanna Sharma100% (1)
- Bio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsДокумент11 страницBio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsEmo tionsОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis Lecture PowerpointДокумент26 страницProtein Synthesis Lecture PowerpointJames Dauray100% (1)
- 2nd Q CEellДокумент30 страниц2nd Q CEellDeserie ZabalaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Microbiology and ParasitologyДокумент44 страницыChapter 1 Microbiology and ParasitologyGrachel Ann Pariente DayuhaОценок пока нет
- Plant and Animal Cells PuzzleДокумент3 страницыPlant and Animal Cells PuzzleLisa Ellis0% (1)
- Cell Anatomy Notes OutlineДокумент10 страницCell Anatomy Notes Outlinemjamie12345Оценок пока нет
- Study Questions Biology 141 Cellular Respiration, Kreb CycleДокумент3 страницыStudy Questions Biology 141 Cellular Respiration, Kreb CycleMeï QadriОценок пока нет
- Properties of BondsДокумент36 страницProperties of BondsPaulОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Документ6 страницExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Unit 2 BIOL1000 - Chemistry and MacromoleculesДокумент29 страницUnit 2 BIOL1000 - Chemistry and Macromoleculesthatcowman11Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 PartialДокумент11 страницChapter 2 PartialcrystalghayleparrasОценок пока нет
- Editable Gross Motor Skills Match and Move GameДокумент6 страницEditable Gross Motor Skills Match and Move GameIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Theories of Personality and PsychopathologyДокумент68 страницTheories of Personality and PsychopathologyIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleДокумент64 страницыPsychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry: Contributions of The Psychosocial Sciences To Human BehaviorДокумент35 страницPsychiatry: Contributions of The Psychosocial Sciences To Human BehaviorIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Genchemlab Expt. 10 Acids and BasesДокумент5 страницGenchemlab Expt. 10 Acids and BasesIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Psychiatry Tests Guide Intelligence and PersonalityДокумент17 страницPsychiatry Tests Guide Intelligence and PersonalityIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Feeling Worksheet 7Документ1 страницаFeeling Worksheet 7Ian Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Pre Hand WritingДокумент22 страницыPre Hand WritingIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Updated Activity Analysis Using The Occupational Therapy Practice Framework IIIДокумент49 страницUpdated Activity Analysis Using The Occupational Therapy Practice Framework IIIIan Russ Bautista100% (2)
- ANS Disorders, RSD, HypertonicityДокумент41 страницаANS Disorders, RSD, HypertonicityIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- SacramentДокумент38 страницSacramentIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- The Allen Cognitive Level Screen and The Allen BatteryДокумент10 страницThe Allen Cognitive Level Screen and The Allen BatteryIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- ANA1Lab of Shoulder and Scapula - Student GuideДокумент9 страницANA1Lab of Shoulder and Scapula - Student GuideIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Data Extraction Tool Ni AyniДокумент7 страницData Extraction Tool Ni AyniIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- ROL Summary Table EDITED Ni AyniДокумент12 страницROL Summary Table EDITED Ni AyniIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Hello WorldДокумент1 страницаHello WorldIan Russ BautistaОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Quiz | 50 Items QuizДокумент7 страницPhysical Science Quiz | 50 Items QuizDYUN PRANSYA100% (1)
- MODEL PAPERS FOR INSPECTOR FIA BY SIR SYED ACADEMYДокумент113 страницMODEL PAPERS FOR INSPECTOR FIA BY SIR SYED ACADEMYYasir ButtОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructureДокумент8 страницAtomic StructureEllie AbelОценок пока нет
- 01 Properties of Electric Charges PDFДокумент28 страниц01 Properties of Electric Charges PDFSeroKeretaMasaroWidiarОценок пока нет
- Manuscript Quarks and Leptons 2Документ20 страницManuscript Quarks and Leptons 2Nichole AlbaracinОценок пока нет
- Sample Problems Chap 19 CutnellДокумент9 страницSample Problems Chap 19 CutnellJoeОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Chem Test 1Документ3 страницыInorganic Chem Test 1BoopathiMalarОценок пока нет
- CHEM+110+All+Chapters 3Документ465 страницCHEM+110+All+Chapters 3عبدالاله بن رباعОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesДокумент45 страницCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Revision NotesOm KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Basic Electrical Quantities System of Units Circuit Components)Документ75 страницChapter 2 (Basic Electrical Quantities System of Units Circuit Components)jeloserrano60Оценок пока нет
- CH 2 Coulombs Law APEMДокумент3 страницыCH 2 Coulombs Law APEMJames FlaughОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure Lab 3Документ2 страницыAtomic Structure Lab 308090311Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry 14 Outline GuideДокумент52 страницыChemistry 14 Outline GuideMarquee Mae EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Easy Science Quiz Bee Questions on Physics, Chemistry and BiologyДокумент48 страницEasy Science Quiz Bee Questions on Physics, Chemistry and BiologyMelissa A. BernardoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Polytechnic Engineering-Chemistry Semester 1 and 2 Text BooksДокумент272 страницыChemistry Polytechnic Engineering-Chemistry Semester 1 and 2 Text BooksKumar SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Y8 Science Chapter 2Документ36 страницY8 Science Chapter 2shabnam.aurangzaib109100% (1)
- SNC 1D0 Unit Test: Atoms & ElementsДокумент5 страницSNC 1D0 Unit Test: Atoms & ElementsuyenОценок пока нет
- New Concept of GravityДокумент9 страницNew Concept of GravityAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteОценок пока нет
- ChemmovieДокумент6 страницChemmovieapi-269382043Оценок пока нет
- Nuclear Chemistry Final PDFДокумент28 страницNuclear Chemistry Final PDFaljon100% (2)
- NS Grade 8 Revision Papers Booklet June 2020 1587131765Документ37 страницNS Grade 8 Revision Papers Booklet June 2020 1587131765Abutieey TumzaaОценок пока нет
- Test OdtДокумент4 страницыTest OdtkanwaljitsinghchanneyОценок пока нет
- Dating Rocks and Fossils Using Geologic Methods - Learn Science at Scitabl122629Документ7 страницDating Rocks and Fossils Using Geologic Methods - Learn Science at Scitabl122629Malcom Xi Bin HalfanОценок пока нет
- Atoms PDFДокумент5 страницAtoms PDFBea Dacillo BautistaОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table History ActivityДокумент32 страницыPeriodic Table History ActivityJJ FajardoОценок пока нет
- Class 7 ScienceДокумент40 страницClass 7 ScienceQulb e AbbasОценок пока нет
- WS 2 Decay Process 2Документ3 страницыWS 2 Decay Process 2Nyaruko SanОценок пока нет
- Test 2-P2Документ8 страницTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamОценок пока нет
- AQA - GCSE Combined Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsДокумент19 страницAQA - GCSE Combined Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 Predictionsa kamranОценок пока нет
- Technical Physics Lecture Notes on Gauss's Law and Electric PotentialДокумент3 страницыTechnical Physics Lecture Notes on Gauss's Law and Electric PotentialAmir YonanОценок пока нет