Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Red Spectrum White Light Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo
Загружено:
Sanifer PlayzОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Red Spectrum White Light Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo
Загружено:
Sanifer PlayzАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Answers to end-of-chapter questions
Chapter 15
1 a red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet 8 White light is dispersed because it is a
mixture of different colours/wavelengths, [1]
b red = lowest frequency, longest wavelength
which travel at different speeds in glass. [1]
violet = highest frequency, shortest wavelength
Laser light is a single wavelength
2 a radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible (monochromatic) and so cannot
light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays be dispersed. [1]
b radio waves = lowest frequency, longest 9 a i refraction [1]
wavelength
ii dispersion [1]
gamma rays = highest frequency, shortest
wavelength b i A (red, at top) [1]
ii C (yellow, third from top) [1]
3 300 000 000 m/s or 3.0 × 108 m/s
c any two from:
4 monochromatic; frequency (or wavelength)
gamma, cosmic, X-rays, UV, IR,
5 a microwaves, radio, TV [2]
spectrum
10 a electromagnetic [1]
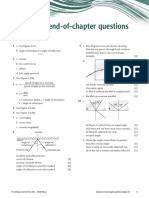
red orange short [1]
white light yellow
green b film or photographic film or electronic
prism blue detector or charge-coupled device (CCD) [1]
violet indigo
ray broadens on entering prism, c absorbed/stopped by bone (not deflected/
and again on leaving [1] reflected) [1]
red and violet ends of spectrum less absorption by flesh or penetrates/passes
correctly indicated [1] through flesh [1]
b violet [1] d any one of:
photographic film badges, behind screen
c Different colours travel at different when operating X-ray machine, protective
speeds in glass. [1] clothing, minimise exposure [1]
The slowest colour is the most
strongly dispersed. [1]
6 a false
b true
c true
7 300 000 000 m/s = 3.0 × 108 m/s [1]
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE Physics Answers to end-of-chapter questions: Chapter 15 1
Вам также может понравиться
- 14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveДокумент4 страницы14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveNolawitОценок пока нет
- Microphone WorksheetДокумент3 страницыMicrophone WorksheetMarg Lawless0% (1)
- 14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveДокумент4 страницы14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveMahad AsimОценок пока нет
- Pearsons Et Al. - 1977 - Speech Levels in Various Noise EnvironmentsДокумент82 страницыPearsons Et Al. - 1977 - Speech Levels in Various Noise EnvironmentsRalph MuehleisenОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 14Документ4 страницыWorksheet 14b972xmny46Оценок пока нет
- Answers To End of Chapter Questions CambДокумент2 страницыAnswers To End of Chapter Questions CambMoi MoiОценок пока нет
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDuy TôОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 14Документ4 страницыWorksheet 14JunLi CaiОценок пока нет
- Exam Style Answers 30 Asal Physics CBДокумент2 страницыExam Style Answers 30 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahОценок пока нет
- Em WavesДокумент3 страницыEm WavesLisandra SantosОценок пока нет
- Light WorksheetДокумент2 страницыLight WorksheetTom GROCOTTОценок пока нет
- Materi - 1 - SpectrosДокумент49 страницMateri - 1 - SpectrosSalwa KamiliaОценок пока нет
- SpectrometryДокумент33 страницыSpectrometryilyas taufikОценок пока нет
- Unit 15 Electromagentic SpectrumДокумент3 страницыUnit 15 Electromagentic SpectrumGhazala SajjadОценок пока нет
- E01 Handbook IntroductionДокумент12 страницE01 Handbook IntroductionAlexander Quebra Madeira NemchinovОценок пока нет
- P15 SpectraДокумент18 страницP15 SpectraAlice NgaОценок пока нет
- R1 Part 1 TWIДокумент56 страницR1 Part 1 TWIYasir NassrullahОценок пока нет
- SpectrumДокумент13 страницSpectrumNimmi NimsОценок пока нет
- A-Level Medical Physics Question PackДокумент18 страницA-Level Medical Physics Question Packxinasad710Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet 15Документ5 страницWorksheet 15Aliya RizviОценок пока нет
- Radiography InterpretationДокумент56 страницRadiography InterpretationFongJeremyОценок пока нет
- FTA ReportДокумент20 страницFTA Reportzen AlkaffОценок пока нет
- ICSE X Physics - Chap 6 (Spectrum)Документ7 страницICSE X Physics - Chap 6 (Spectrum)mohammedumar7864521Оценок пока нет
- 14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14Документ4 страницы14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14dil19860209Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 - MSДокумент3 страницыChapter 15 - MSAdrián Castillo SantillánОценок пока нет
- Quarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsДокумент16 страницQuarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsadrianquininezaОценок пока нет
- MSC Medical Physics Medical Imaging Exam 1Документ9 страницMSC Medical Physics Medical Imaging Exam 1Andy JohnstoneОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Aerial Photographic Systems: Ies / Cee / For / Gle 301Документ30 страницIntroduction To Aerial Photographic Systems: Ies / Cee / For / Gle 301JJОценок пока нет
- 15 Worksheet (AS) Superposition of WavesДокумент5 страниц15 Worksheet (AS) Superposition of WavesMahad AsimОценок пока нет
- Lecture1 PDFДокумент12 страницLecture1 PDFFredrick AwuduОценок пока нет
- Electromagnet Aand SpectrumДокумент10 страницElectromagnet Aand Spectrumnoxapa5578Оценок пока нет
- Physics Section C - Exam Style QuestionsДокумент3 страницыPhysics Section C - Exam Style QuestionsIbrar MajeedОценок пока нет
- Senior ColorДокумент28 страницSenior ColorRaj GhimireОценок пока нет
- Bushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 11th EditionДокумент2 страницыBushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 11th Editiongasai gasai100% (1)
- Worksheet 15Документ5 страницWorksheet 15JunLi CaiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Spectrum - Lecture 1Документ14 страницElectromagnetic Spectrum - Lecture 1Mvita HenocОценок пока нет
- 4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPДокумент30 страниц4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPwillowchenchenОценок пока нет
- SpectrumaДокумент5 страницSpectrumalisemaОценок пока нет
- Wave Optics NewДокумент13 страницWave Optics Newxejis32200Оценок пока нет
- Q1Документ7 страницQ1Brandon LeoputraОценок пока нет
- Note4 PreClass PDFДокумент27 страницNote4 PreClass PDFSimon SiuОценок пока нет
- SDO Aurora 2nd-Quarter Science 10-FINALДокумент7 страницSDO Aurora 2nd-Quarter Science 10-FINALmarianettemadiz95Оценок пока нет
- EM SpectrumДокумент10 страницEM Spectrumabhinavsingh22012006Оценок пока нет
- Unit2topic3 Examzone Ms PDFДокумент3 страницыUnit2topic3 Examzone Ms PDFNusaiba AminОценок пока нет
- IB Physics Course Companion: Glossary of Terms From Option ChaptersДокумент46 страницIB Physics Course Companion: Glossary of Terms From Option ChaptersGajendraОценок пока нет
- Wave C12Документ9 страницWave C12Wajira Sanjaya PereraОценок пока нет
- Bab 6 C - AnswerДокумент2 страницыBab 6 C - AnswerLiuJiewChuanОценок пока нет
- Wave Optics ExercisesДокумент16 страницWave Optics ExercisesRitesh BОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 EM Waves and UV ProtectionДокумент41 страницаUnit 10 EM Waves and UV Protectiongalaxy113Оценок пока нет
- Q2 Science Long Quiz Module 1 and 2Документ5 страницQ2 Science Long Quiz Module 1 and 2dhanessa condesОценок пока нет
- Mark SchemeДокумент8 страницMark SchemeBrandon LeoputraОценок пока нет
- 6.1 LThe Wave Nature of LightДокумент10 страниц6.1 LThe Wave Nature of LightShallimar AlcarionОценок пока нет
- Jacques Tissue OpticsДокумент60 страницJacques Tissue OpticsrickОценок пока нет
- Invse Square LawДокумент10 страницInvse Square LawBEDELE KNOWLEDGEОценок пока нет
- C-Curve and SenitometryДокумент66 страницC-Curve and Senitometryadhikariaashi2004Оценок пока нет
- 421 821 Chapter 6Документ14 страниц421 821 Chapter 6Marie Kris NogaОценок пока нет
- 3fotografiasj BDJ 2009 558part5Документ6 страниц3fotografiasj BDJ 2009 558part5Lucky ArnandoОценок пока нет
- CH 2 - Electromagnetic Radiation PDFДокумент13 страницCH 2 - Electromagnetic Radiation PDFNidhi PatelОценок пока нет
- Note4 PDFДокумент24 страницыNote4 PDFSimon SiuОценок пока нет
- 7 Electromagnetic WavesДокумент1 страница7 Electromagnetic WavesGajendraОценок пока нет
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE PhysicsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: © Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE PhysicsSanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsДокумент2 страницыAnswers To End-Of-Chapter QuestionsSanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: A B C D e F A B A AДокумент2 страницыAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: A B C D e F A B A ASanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Global Indian International School, Uppal, Hyderabad Internal Assessment - 2 Revision Worksheet-1Документ2 страницыGlobal Indian International School, Uppal, Hyderabad Internal Assessment - 2 Revision Worksheet-1Sanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Math Worksheet 1Документ1 страницаMath Worksheet 1Sanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- BST Class X Igcse New PPT - 2 June 2ndДокумент19 страницBST Class X Igcse New PPT - 2 June 2ndSanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Verifying Pythagorn TheoremДокумент6 страницVerifying Pythagorn TheoremSanifer PlayzОценок пока нет
- Remote Sensing PDFДокумент23 страницыRemote Sensing PDFDigital MapperОценок пока нет
- Catalogo AntenasДокумент67 страницCatalogo AntenasCarlos Javier Jimenez SalineroОценок пока нет
- A Survey of Magnetooptic Effects MARVIS J. FREISER 1968Документ10 страницA Survey of Magnetooptic Effects MARVIS J. FREISER 1968Jose MatutesОценок пока нет
- WAVES (Anatomy of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves)Документ6 страницWAVES (Anatomy of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves)Ricabelle Lising100% (1)
- 2022 May ETC Optical CommunicationДокумент2 страницы2022 May ETC Optical CommunicationHussain BarwahwalaОценок пока нет
- Ground Wave Modeling and Simulation Strategies and Path Loss Prediction Virtual ToolsДокумент8 страницGround Wave Modeling and Simulation Strategies and Path Loss Prediction Virtual Toolsedmilsonsilva1Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic WavesДокумент3 страницыElectromagnetic WavesA.BensonОценок пока нет
- SSP 861503 Noise Vibration and HarshnessДокумент84 страницыSSP 861503 Noise Vibration and HarshnessMahmoud S NasereddinОценок пока нет
- Ultra-Long Dual-Sideband BOTDA With Balanced DetectionДокумент5 страницUltra-Long Dual-Sideband BOTDA With Balanced DetectionJoaquín Gómez CarmonaОценок пока нет
- FM ExercisesДокумент5 страницFM ExercisesanililhanОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Speech Science An Integrated Approach To Theory and Clinical Practice 3 e 3rd Edition 0132907119Документ38 страницTest Bank For Speech Science An Integrated Approach To Theory and Clinical Practice 3 e 3rd Edition 0132907119inhoopnebuloseve9nqt100% (10)
- Sound WavesДокумент2 страницыSound Wavesamyshi97Оценок пока нет
- 3544 Im 21455-30Документ58 страниц3544 Im 21455-30grosselloОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Aspirin - Infrared (Ir) Spectroscopy and Melting Point DeterminationДокумент15 страницAnalysis of Aspirin - Infrared (Ir) Spectroscopy and Melting Point DeterminationMahmoud ElshahawyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Wireless Coding and ModulationДокумент35 страницIntroduction To Wireless Coding and ModulationTuấn Đạt Lê XuânОценок пока нет
- 3rd Grading Grade 7 ScienceДокумент3 страницы3rd Grading Grade 7 ScienceJoenard SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice QuizДокумент5 страницMultiple Choice QuizQuoc NguyenОценок пока нет
- Islamic University of Technology: Experiment 5: Planar EM Solution of Quarter Wave Transformer ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыIslamic University of Technology: Experiment 5: Planar EM Solution of Quarter Wave Transformer ObjectivemahabubОценок пока нет
- Attenuation of Sound WavesДокумент2 страницыAttenuation of Sound Wavescal2_uniОценок пока нет
- CH21-3 - Standing Waves: Important IdeasДокумент4 страницыCH21-3 - Standing Waves: Important Ideasمحمد رزقОценок пока нет
- Surface-Wave Method For Near-Surface Characterization: A TutorialДокумент21 страницаSurface-Wave Method For Near-Surface Characterization: A TutorialJavier MtОценок пока нет
- 6 - Light A Wave and A ParticleДокумент21 страница6 - Light A Wave and A ParticleUnshackled ChouОценок пока нет
- Lecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Документ45 страницLecture - Chapter7 2020 Part1Qassem MohaidatОценок пока нет
- Sandeep M.Tech Project PPTQ - PPTMДокумент28 страницSandeep M.Tech Project PPTQ - PPTMSandeepBttnОценок пока нет
- Lecture Phy SoundДокумент51 страницаLecture Phy SoundYi Ying HannieОценок пока нет
- AQA Physics P12 Summary AnswersДокумент3 страницыAQA Physics P12 Summary AnswersjayakantharushanОценок пока нет
- 12 - Interference and Diffraction Slides NopollsДокумент19 страниц12 - Interference and Diffraction Slides NopollsKhoi HuynhОценок пока нет