Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Order of Operations and Rules of Divisibility
Загружено:
Andrea Nicole Sales0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
123 просмотров4 страницыОригинальное название
Flashcards pg 1-3
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
123 просмотров4 страницыOrder of Operations and Rules of Divisibility
Загружено:
Andrea Nicole SalesАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
Order of Operations Commutative Law
PEMDAS Addition – a + b = b + a
• If same level, start from Multiplication – a x b = b x a
left to right
Associative Law Distributive Law
Addition- (77+2) +3 = 77+(2+3)
= Same answer a(b+c) = (axb) + (axc)
Multiplication – (1x2) X 3 = 1x(2x3)
= Same answer
4(8+3) = 32 + 12
Rules of Divisibility Rules of Divisibility
2 - last digit is EVEN 8 - last three digits are divisible by 8
3 - sum of the digit is DIVISIBLE by 3 9 - sum of the digits is divisible by 9
4 - last two digits of number are divisible by 4 10 - last digit is 0
5 - last digit is 5 or 0 11 - sum every other digit and subtract the
6 - even number and sum of digits is remaining digits. if the result is divisible by 11, so
divisible by 3 is the number
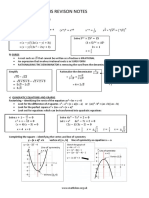
Power, Exponents and Roots
Percent •
•
(xa)(xb) = xa+b
(xa)b = xa x b
• Find the indicated percent
- ( a ) ( % ) ÷ 100 • x0 = 1
• Find the unknown number (percent) • xa ÷ xb = xa-b
- a ÷ % (100) • (xy)a = (xa)(ya)
• Find the percent • √xy = (√x) (√y)
• 1/ a = x-a
- a ÷ b (100) x
Power, Exponents and Roots
Common Factor
ax+ay+az = a(x+y+z)
• x a/b = b√xa
• (-1) n = positive if n is even/ negative
if n is odd Sum and Difference of Two Cubes
(x+y) (x2-xy+y2) and
(x-y) (x2+xy+y2)
Non-Perfect Trinomial Square of Binomials
6x2 - 7x - 3 = (2x-3)(3x+1)
(x+y)2 = x2 + xy + y2
Difference of Two Squares (x-y)2 = x2 - xy + y2
x2 - y2 = (x-y)(x+y)
Square of Multinomials Two Binomials with Like Terms
(x+y+z+m+n)2 = (Expansion)
x2 + y2 + z2 + m2 + n2 + 2xy + 2xz +
2xm + 2xn + 2 yz + 2ym + 2yn + 2zm + (2x-3)(3x+1) = 6x2 + 2x - 9x - 3
2zn + 2mn = 6x2 - 7x - 3
Sum and Difference of Two Numbers Biquadratic Equation
(x+y) (x-y) = x2 - y2
A degree w/o the terms of degree 1 and 3
Cube of Binomials Example: x^4 - 13x^2 + 36 = 0
(x+y)3 = x^3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3 Formula: x = − b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) / 2a
(x-y)3 = x3 - 3x2y + 3xy2 - y3
Quadratic Equation Work Problems
2 methods (1/x + 1/x) x = x
- Factoring
- Quadtratic Formula
Distance Problems
x = − b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) / 2a d = rt
Logarithms Properties Logarithms
Exponent Form: 34 = 3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 81
Log Form: log381 = 4
- loga b + loga c = loga bc
- bloga c = loga(cb) log41 = 0 (Any non-zero number, 1 is always equation)
- loga b - loga c = loga (b/c) Take Note: A logarith w/o base the implicit base is 10
Fibonacci Sequence Harmonic Sequence
sequence such that the reciprocals of the
- first term is 0 and the second term is 1
terms from an arithmetic sequence
- to get the next number, you need to sum Example:
up the previous terms up
-20, -26, -32,-38, - 44 (arithmetic example)
-1/20, -1/26, -1/32, -1/38, -1/44 (harmonic example)
Example: 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13…
Arithmetic Sequence Arithmetic Series
an = a1 + {(n-1) d} sn = n/2 (a1 - an)
- used when first and last term are known
Arithmetic Means sn = n/2 {2a + (n-1) d}
- are the terms between any two given terms
- last term is unknown but the difference is given
Вам также может понравиться
- Factoring and Solving Polynomial EquationsДокумент13 страницFactoring and Solving Polynomial EquationsMark Francis HernandezОценок пока нет
- Math Workshop by SlidesgoДокумент35 страницMath Workshop by SlidesgoAyesha Nayyer100% (1)
- Math SL: Functions, Sequences, Trigonometry & AlgebraДокумент15 страницMath SL: Functions, Sequences, Trigonometry & Algebramikalala1105Оценок пока нет
- POL enДокумент6 страницPOL enPedroОценок пока нет
- Maths Exam Solution for Finance and EconomicsДокумент11 страницMaths Exam Solution for Finance and EconomicsjeanboncruОценок пока нет
- IIT Foundation Class 9 PolynomialsДокумент16 страницIIT Foundation Class 9 PolynomialsAvinash Kumar100% (1)
- AlevelpureДокумент18 страницAlevelpureAlex GoldsmithОценок пока нет
- Equation, Ratio Preparation & Variation: 0 N 1 N 2 N 0 N 1 N 2 N 1/nДокумент5 страницEquation, Ratio Preparation & Variation: 0 N 1 N 2 N 0 N 1 N 2 N 1/nGIRIKОценок пока нет
- IIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEДокумент23 страницыIIT JEE 2008 Paper 1 Solutions by FIITJEEAbhinav100% (43)
- SAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsДокумент11 страницSAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsneenaОценок пока нет
- Polynomial Zeros and FactorsДокумент23 страницыPolynomial Zeros and Factorshemal mitreshОценок пока нет
- Lecture Note 3Документ40 страницLecture Note 3Frendick LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Politecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsДокумент10 страницPolitecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsJuan Luis GonzalezОценок пока нет
- 1 Algebra and FunctionsДокумент50 страниц1 Algebra and FunctionsSri Devi NagarjunaОценок пока нет
- LSE MA100 Background CheckДокумент5 страницLSE MA100 Background CheckAlternative EgoОценок пока нет
- CALCULUS Medyo May SagotДокумент11 страницCALCULUS Medyo May SagotANABEL EGOCОценок пока нет
- Model Exam 2022 N.SДокумент10 страницModel Exam 2022 N.STesfamichael FufaОценок пока нет
- 1920F4T2M1MSДокумент11 страниц1920F4T2M1MSLUI ansonОценок пока нет
- Math 100 Finals Samplex - UP DIlimanДокумент2 страницыMath 100 Finals Samplex - UP DIlimanChristelli JaroОценок пока нет
- Algebra and Trigonometry Formulas, Identities, and ConceptsДокумент6 страницAlgebra and Trigonometry Formulas, Identities, and ConceptsKirstie Alley San JoseОценок пока нет
- Solution 1002257Документ12 страницSolution 1002257gulshanprasad510Оценок пока нет
- Algebra+2 FormulasДокумент8 страницAlgebra+2 FormulasYuan AcostaОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Linear FunctionsДокумент28 страниц3.3 Linear Functionsm_armoutiОценок пока нет
- RESONANCE Equations For PreRmoДокумент36 страницRESONANCE Equations For PreRmoAyush KumarОценок пока нет
- Polynomials: Teachers Teaching With TechnologyДокумент9 страницPolynomials: Teachers Teaching With TechnologyAdrian RОценок пока нет
- MAT Paper 2010 SolutionsДокумент8 страницMAT Paper 2010 SolutionsXu SarahОценок пока нет
- Algebra: Use The Factor and Remainder Theorems To WorkДокумент108 страницAlgebra: Use The Factor and Remainder Theorems To WorkKiticat TsatseОценок пока нет
- Advanced AlgebraДокумент11 страницAdvanced Algebracristina gomezОценок пока нет
- Exs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationДокумент3 страницыExs 6-1-60v1 SLHL Further DifferentiationASYA HIZLIОценок пока нет
- Add Math Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыAdd Math Formula SheetjokuxkunОценок пока нет
- Roots of Polynomial Equations: N N N N 1 N 1 1 0Документ7 страницRoots of Polynomial Equations: N N N N 1 N 1 1 0Dahanyakage WickramathungaОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Paper With Solution Maths PDFДокумент16 страницPaper 1 Paper With Solution Maths PDFmehul yoОценок пока нет
- 2nd-Quarter-Math-ReviewerДокумент8 страниц2nd-Quarter-Math-ReviewerSofia Marmel GuevarraОценок пока нет
- Graphing Rational Functions (Worksheet) - AKДокумент2 страницыGraphing Rational Functions (Worksheet) - AKAngelene Madrazo 黄贞文Оценок пока нет
- Algebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKДокумент6 страницAlgebra - Quantitative Aptitude For CAT EBOOKaditya_kumar_me80% (5)
- TANGENT LINESДокумент2 страницыTANGENT LINESTah Ieh100% (1)
- MIT18 01SC Pset3prbДокумент9 страницMIT18 01SC Pset3prbsachin rawatОценок пока нет
- Tagore Public School Term 1 Math Exam 2022Документ5 страницTagore Public School Term 1 Math Exam 2022Shriyanshi GarodiaОценок пока нет
- Integration of Rational Fractions: 4.1 Integration For None Repeated Linear FactorsДокумент6 страницIntegration of Rational Fractions: 4.1 Integration For None Repeated Linear FactorsJamie MedallaОценок пока нет
- 2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 SolutionsДокумент10 страниц2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 Solutionsmiddoka101Оценок пока нет
- TutorialNS1 - With AnswersДокумент2 страницыTutorialNS1 - With AnswersLexОценок пока нет
- ENRICHED/ THEMATIC MELCДокумент8 страницENRICHED/ THEMATIC MELCPatricia TombocОценок пока нет
- Ch8 - More About Equations - EX8CДокумент17 страницCh8 - More About Equations - EX8CWayne TsoiОценок пока нет
- ACT Math Facts & FormulasДокумент8 страницACT Math Facts & Formulaslslisen100% (1)
- Calculus I (MATH 1060 and 1061) Fall 2014 Review For The Final ExamДокумент8 страницCalculus I (MATH 1060 and 1061) Fall 2014 Review For The Final ExamCurtis AngstОценок пока нет
- In MathematicsДокумент2 страницыIn MathematicsRey James Domingo 2nd (Grendrunger)Оценок пока нет
- Week 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)Документ36 страницWeek 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)not funny didn't laughОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Mathematics With Applications To Pharmacy - CompressДокумент12 страницPharmaceutical Mathematics With Applications To Pharmacy - CompressAbhishek SharmaОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Mathematics With Applications To PharmacyДокумент12 страницPharmaceutical Mathematics With Applications To PharmacyAjay Kaundal75% (4)
- Midterm 3 Sample A SolutionsДокумент2 страницыMidterm 3 Sample A Solutionsayana damtewОценок пока нет
- Worked SolutionsДокумент17 страницWorked SolutionsanuОценок пока нет
- JEE Advanced Application of Integrals Important QuestionsДокумент19 страницJEE Advanced Application of Integrals Important QuestionsAkshat KolawatОценок пока нет
- Alg End Term Exam ReviewerДокумент4 страницыAlg End Term Exam ReviewerFranco Luis C. MapuaОценок пока нет
- UNIT 23 Algebraic Manipulation Introduction To SIM: Learning ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыUNIT 23 Algebraic Manipulation Introduction To SIM: Learning ObjectivesCharlotte BОценок пока нет
- Calculus 1 exam questions and solutionsДокумент3 страницыCalculus 1 exam questions and solutionsAnh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОт EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОценок пока нет
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)От EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Оценок пока нет
- General journal entries for medical clinicДокумент3 страницыGeneral journal entries for medical clinicAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Description PR Debit Credit Date General Journal Pg.1Документ3 страницыDescription PR Debit Credit Date General Journal Pg.1Andrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2.2 Economic SupplyДокумент2 страницыLesson 2.2 Economic SupplyAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- KWL ChartДокумент2 страницыKWL ChartAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- "All Other Things Being Equal": Price Lowers Quantity Demanded IncreasesДокумент4 страницы"All Other Things Being Equal": Price Lowers Quantity Demanded IncreasesAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Math IV Solution SetДокумент3 страницыMath IV Solution SetkupaloidОценок пока нет
- Area PDFДокумент2 страницыArea PDFAndrea SalesОценок пока нет
- Abstract Reasoning Test PDFДокумент9 страницAbstract Reasoning Test PDFAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Chapter IiiДокумент3 страницыChapter IiiAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Chapter IIIДокумент3 страницыChapter IIIAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Terminologies in VolleyballДокумент6 страницTerminologies in VolleyballAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Title: SubtitleДокумент1 страницаTitle: SubtitleAndrea Nicole SalesОценок пока нет
- Digital Systems and Binary NumbersДокумент55 страницDigital Systems and Binary NumbersHarshaОценок пока нет
- MMW Module 9Документ2 страницыMMW Module 9Gin MananganОценок пока нет
- Section PlaneДокумент38 страницSection PlaneDeepakDeepОценок пока нет
- Torrent Downloads - Download Free Torrents!Документ1 страницаTorrent Downloads - Download Free Torrents!André Brandão50% (2)
- Dual Priority Switch MonitorДокумент2 страницыDual Priority Switch MonitorAshiq Salman100% (1)
- Application Engineer Job DescДокумент2 страницыApplication Engineer Job DescifteeeОценок пока нет
- Clearpath User Manual PDFДокумент127 страницClearpath User Manual PDFWaleed El-BadryОценок пока нет
- Making a Python list of namesДокумент14 страницMaking a Python list of namesSoniaОценок пока нет
- Math 10 Problem SetДокумент2 страницыMath 10 Problem SetMonka GigaОценок пока нет
- Files - MC-WP-012 5 Key Factors To Consider When Selecting An Embedded Testing Tool - 5Документ22 страницыFiles - MC-WP-012 5 Key Factors To Consider When Selecting An Embedded Testing Tool - 5Rafael R QueirozОценок пока нет
- Directorate of Estates: Subject: How To Use Automated System of Allotment For GPRA ObjectiveДокумент5 страницDirectorate of Estates: Subject: How To Use Automated System of Allotment For GPRA Objectivesofia guptaОценок пока нет
- Pinsex Response BriefДокумент22 страницыPinsex Response BriefMarcJohnRandazzaОценок пока нет
- 98-366 MTA Networking Fundamental - SlidesДокумент232 страницы98-366 MTA Networking Fundamental - Slidesharyanto100% (3)
- SM Mastertigmls 3003 Acdc en v1 2 PDFДокумент32 страницыSM Mastertigmls 3003 Acdc en v1 2 PDFkazambo78Оценок пока нет
- LCMДокумент100 страницLCMANSHUMAN MISHRAОценок пока нет
- Master Transition Plan DocumentДокумент16 страницMaster Transition Plan Documentrlfisch100% (1)
- Cricut Learn DesignSpace ShortcutsДокумент1 страницаCricut Learn DesignSpace ShortcutsMr. pianistОценок пока нет
- Easy-to-use digital scale manualДокумент18 страницEasy-to-use digital scale manualsrboghe651665Оценок пока нет
- DigiKeyboard 6keysДокумент7 страницDigiKeyboard 6keysHarald DasselОценок пока нет
- XL2576 DatasheetДокумент14 страницXL2576 DatasheetMo Hit MksОценок пока нет
- Nant-D Ab Uds 3fe61555abaatqzza04Документ16 страницNant-D Ab Uds 3fe61555abaatqzza04Akm AnisuzzamanОценок пока нет
- Mcquay Modbus User Manual: (Thermostat Ac2981C) V2.2Документ14 страницMcquay Modbus User Manual: (Thermostat Ac2981C) V2.2RaymondОценок пока нет
- CFD LectureДокумент19 страницCFD LectureRobi Afrizal100% (1)
- Ethereum White Paper Made SimpleДокумент29 страницEthereum White Paper Made SimpleSamir BennaniОценок пока нет
- Program Objectives and Its Relationship To College GoalsДокумент8 страницProgram Objectives and Its Relationship To College GoalsRaymond RamirezОценок пока нет
- Hasan Zaman Mohd. Reza-E-RabbiДокумент3 страницыHasan Zaman Mohd. Reza-E-RabbiHasan ZamanОценок пока нет
- Cny 17Документ9 страницCny 17Krista TranОценок пока нет
- Assessor's Package For HNS - L4Документ9 страницAssessor's Package For HNS - L4bayushОценок пока нет
- Hacking Module 11Документ53 страницыHacking Module 11Chye HengОценок пока нет
- 10gen-MongoDB Operations Best PracticesДокумент26 страниц10gen-MongoDB Operations Best PracticesRohit WaliОценок пока нет