Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2
Загружено:
JESSA SUMAYANG0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров3 страницыОригинальное название
1MODULE 2_LESSON 2_ACTIVITY 2.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров3 страницы1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2
Загружено:
JESSA SUMAYANGАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
LEARNING DELIVERY MODALITIES 2 COURSE FOR TEACHERS
MODULE 2 MOST ESSENTIAL LEARNING COMPETENCIES
LESSON 2 UNPACKING AND COMBINING MELCS INTO LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Name of Teacher: Jessa Sumayang – Monicit
LAC Session ID: 002
School: Tabunan National High School
ACTIVITY 2:
1. Form a group of four members within your LAC, preferably with fellow teachers in
your respective learning area.
2. Using the curriculum guide and a list of the MELCs, choose MELCs in the first quarter
and unpack these into learning objectives.
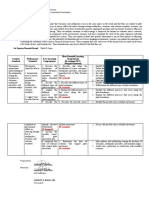
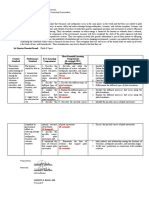
Subject: Earth and Life Science
Learning Competency Learning Objectives
Recognize the uniqueness of Earth, Recognize the difference in the physical and chemical
being the only planet in the solar properties between the Earth and its neighboring planes
system with properties necessary to Identify the factors that allow a planet to support life.
support life. Exhibit care and protection of the Mother Earth
Define the concept of a system
Explain that the Earth consists of Recognize the Earth as a system composed of
four subsystems, across whose subsystems
boundaries matter and energy flow. Appreciate the value of interconnections of the
subsystems in sustaining life
Identify some common rock-forming mineral
Demonstrate understanding about physical and
Identify common rock-forming
chemical properties of minerals and will be able to
minerals using their physical and
identify certain minerals using specific tests
chemical properties.
Learn to appreciate the importance of the presence of
rocks and minerals
Identify and describe the three basic rocks type
Establish relationships between rock types and their
Classify rocks into igneous, mode of origin and environment of deposition /
sedimentary, and metamorphic formation
Demonstrate understanding on the different geologic
process involved in rock formation
Know the sources and significance of the Earth's
internal heat
Describe where the Earth’s internal Describe what happens after the magma is formed
heat comes from. (plutonism and volcanism)
Understand and explain the requirements for magma
generation
Understand the different index minerals used for
Describe the changes in mineral metamorphic rocks.
components and texture of rocks due Understand what causes the metamorphic texture
to changes in pressure and Describe the changes in mineral components and
temperature (metamorphism) texture of rocks due to changes in pressure and
temperature
Describe how rocks behave under List different types of tresses that cause different type
different types of stress such as of deformation
compression, pulling apart, and Compare the different types of folds and the conditions
shearing under which they form
Compare fractures and faults and define how are they
related to earthquakes.
Explain the movement of plates that leads to the
Explain how the movement of plates
formation of fold and faults
leads to the formation of folds and
Describe the process of the formation of fold and faults
faults
Display cooperation in performing the activity
Describe how layers of rocks (stratified rocks) are
formed,
Describe how layers of rocks Describe the different methods (relative and absolute
(stratified rocks) are formed dating) to determine the age of stratified rocks
Explain how relative and absolute dating were used to
determine the subdivisions of geologic time.
Describe the different methods Follow the principles of different dating methods,
(relative and absolute dating) to Involve oneself in discovering Earth’s past
determine the age of stratified rocks Reflect the value of discovering Earth’s past
Describe how layers of rocks are formed and used to
explain the history of Earth.
Explain how relative and absolute
Differentiate relative and absolute dating as used
dating were used to determine the
tracing the history of the Earth.
subdivisions of geologic time scale
Relate the works of scientists to hardwork and
perseverance.
Describe how the Earth’s history can be interpreted
from the geologic time scale.
Describe how the Earth’s history can
Construct a diorama on how the Earth history can be
be interpreted from the geologic
interpreted (including the age of the Earth, major
time scale
geologic time subdivisions, and marker fossils).
Perform accountability in accomplishing given task.
Describe and explain the hazards associated with
earthquakes
Describe the various hazards that Demonstrate their understanding of the scope of the
may happen in the event of effects and damage of earthquakes by determining the
earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and possibility of such effects occurring in their area and
landslides vicinity and where it will most likely happen
Manifest awareness by participating in earthquake-
related hazard prevention activities and drills.
Identify areas from the Philippine map where
Using hazard maps, identify areas earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and landslides are most
prone to hazards brought about by likely to happen.
earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and Manifest awareness by participating in earthquake,
landslides volcanic eruptions and landslides-related hazard
prevention, activities, and drills.
Identify and understand how certain human activities
can hasten the occurrence of landslides.
Find possible and practical solutions on how to lessen
Identify human activities that speed these identified human activities so as to lessen or
up or trigger landslides prevent the occurrence of landslides.
Design an information campaign to inform locals how
they contribute to the occurrence of landslides in their
area.
Using hazard maps, identify areas Identify and classify the different types of
prone to hazards brought about by hydrometeorological hazards
tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, Evaluate community for potential hazards induced by
or ipo-ipo extreme atmospheric and hydrologic conditions.
Recall that a hydrometeorological hazard is a condition
or an event that may cause harm to property and life as
a result of a hydrometeorological process such as
tropical cyclone, monsoon, flood, and tornado (or ipo-
ipo).
Describe how coastal processes result in coastal
erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion
Describe how coastal processes Recognize the coastal processes that influence the
result in coastal erosion, coastal landforms and associated hazards.
submersion, and saltwater intrusion Illustrate and describe how the coastal processes
determine the present coastal hazards whether coastal
erosion, submersion or saltwater intrusion
Вам также может понравиться
- 1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2Документ3 страницы1module 2 - Lesson 2 - Activity 2JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Origin and Structure of The EarthДокумент6 страницOrigin and Structure of The EarthAltea CalvoОценок пока нет
- Ahs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFДокумент6 страницAhs13 Filipino Sa Piling Larangan Akademik Week 2 PDFJoy RamosОценок пока нет
- Learning Guide: Earth and Life ScienceДокумент8 страницLearning Guide: Earth and Life Sciencelj BoniolОценок пока нет
- Year 4 Geography EOY Format and Content CoverageДокумент7 страницYear 4 Geography EOY Format and Content CoveragesijiazhaoОценок пока нет
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceДокумент6 страницSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth and LIfe ScienceBaby Yanyan100% (3)
- ELS and G10 ScienceДокумент8 страницELS and G10 ScienceJadeОценок пока нет
- BOL IN Earth & Life ScienceДокумент8 страницBOL IN Earth & Life ScienceJeyn T. Redoña IIОценок пока нет
- TOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Документ13 страницTOS sCIENCE 1ST Quarter 1st Sem 20 21Arjune PantallanoОценок пока нет
- First Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterДокумент11 страницFirst Semester Syllabus in Earth Science 11 First QuarterElvie CalinisanОценок пока нет
- DepED MELC Earth ScienceДокумент1 страницаDepED MELC Earth ScienceDodjie MaestrecampoОценок пока нет
- Flexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesДокумент5 страницFlexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesAisa EdzaОценок пока нет
- For F2FДокумент4 страницыFor F2FRjay NagilОценок пока нет
- CIE 0460 Theme 2 - OverviewДокумент30 страницCIE 0460 Theme 2 - OverviewBecka BondОценок пока нет
- Core4B Earth Science 2021 22Документ3 страницыCore4B Earth Science 2021 22f l o u n d e rОценок пока нет
- 8science Earth and Space Science (Earthquakes) PDFДокумент3 страницы8science Earth and Space Science (Earthquakes) PDFQueen RojoОценок пока нет
- Table 1 SpirallingДокумент17 страницTable 1 Spirallingmichael sto domingoОценок пока нет
- UNIT E: Planet Earth: Grade 7 Science - Mr. BexsonДокумент55 страницUNIT E: Planet Earth: Grade 7 Science - Mr. Bexsonapi-265758110Оценок пока нет
- Geology Midterm CoverageДокумент1 страницаGeology Midterm CoverageShara ZeynОценок пока нет
- K-12 Science Curriculum Grade 10 Earth and Space: Edited By: Jevy Dacunes-CarbonquilloДокумент65 страницK-12 Science Curriculum Grade 10 Earth and Space: Edited By: Jevy Dacunes-CarbonquilloMark Jesson DatarioОценок пока нет
- Teacher GuideДокумент7 страницTeacher Guideapi-322046670Оценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science 11Документ4 страницыEarth and Life Science 11deborah dumapeОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science 11Документ4 страницыEarth and Life Science 11DEBORAH DUMAPEОценок пока нет
- Melc Earth and Life ScienceДокумент3 страницыMelc Earth and Life ScienceLyreyann Collado Abella-Cordero0% (1)
- Geologia Zonei - Puncte CheieДокумент2 страницыGeologia Zonei - Puncte CheieAlexandra IonescuОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 3Документ9 страницEarth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 3aiahОценок пока нет
- Report STEMДокумент1 страницаReport STEMJobelle Cassandra CortezОценок пока нет
- DLP in ScienceДокумент4 страницыDLP in ScienceTabada Nicky67% (3)
- Programa Académico de Estudio: Rev. 1 Ref: PR-DA-01 Código: FO-DA-01Документ4 страницыPrograma Académico de Estudio: Rev. 1 Ref: PR-DA-01 Código: FO-DA-01doctorsimulacroОценок пока нет
- Activity ELS11 Week2 LiaДокумент4 страницыActivity ELS11 Week2 LiaKim FloresОценок пока нет
- Budget of Lesson Earth and Life ScienceДокумент7 страницBudget of Lesson Earth and Life Sciencejeseca cincoОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life - Grade 11Документ2 страницыEarth and Life - Grade 11Jarven SaguinОценок пока нет
- MELCS Unpacking2Документ2 страницыMELCS Unpacking2Tawagin Mo Akong MertsОценок пока нет
- MELCS UnpackingДокумент2 страницыMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (5)
- MELCS UnpackingДокумент2 страницыMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong MertsОценок пока нет
- Ees Pacing Guide Fall 2016Документ13 страницEes Pacing Guide Fall 2016api-323312952Оценок пока нет
- Test: 1: Physical GeographyДокумент3 страницыTest: 1: Physical GeographyJohnОценок пока нет
- DLL Els Quarter 1 Week 4Документ4 страницыDLL Els Quarter 1 Week 4Ryan Christopher ReynadoОценок пока нет
- 3Q Week 5Документ5 страниц3Q Week 5Glorylyn CruzОценок пока нет
- Module ELSДокумент40 страницModule ELSnotzi6942018890420Оценок пока нет
- 4 Earthquake HazardsДокумент69 страниц4 Earthquake HazardsJonathan Pinto100% (2)
- Els Final ExamДокумент5 страницEls Final ExamNi ValОценок пока нет
- Assignment Part 1 PDFДокумент54 страницыAssignment Part 1 PDFMuh adis alfandi100% (1)
- Quaternary Coral Reef Systems: History, development processes and controlling factorsОт EverandQuaternary Coral Reef Systems: History, development processes and controlling factorsОценок пока нет
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceДокумент5 страницBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- SHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceДокумент6 страницSHS Core Subjects MELC Earth CienceBaby Yanyan67% (3)
- Historical Geology 8Th Edition Wicander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент28 страницHistorical Geology 8Th Edition Wicander Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFAimeeMcdonalddjax100% (12)
- Learning Matrix TemplateДокумент2 страницыLearning Matrix TemplateGlenn ClementeОценок пока нет
- MELCs in Earth and Life ScienceДокумент5 страницMELCs in Earth and Life ScienceAdonis Besa100% (14)
- Science Grade 4Документ22 страницыScience Grade 4Jocel MalonesОценок пока нет
- Performance Check 1 - Earth ScienceДокумент2 страницыPerformance Check 1 - Earth Scienceyuuna yuunaОценок пока нет
- Earth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Документ38 страницEarth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Hilary Grace Sumbi GargarОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesДокумент7 страницDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolОценок пока нет
- Science10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics v1Документ14 страницScience10 q1 slk1 Plate-Tectonics v1Ervis BahintingОценок пока нет
- Objectives No. of DaysДокумент2 страницыObjectives No. of DaysMa Cristina D. MagadiaОценок пока нет
- Review Dynamic Earth CoreScienceДокумент3 страницыReview Dynamic Earth CoreScienceVikram BologaneshОценок пока нет
- GHT-102 MMR Lecture-1Документ23 страницыGHT-102 MMR Lecture-1Md. Mostafizur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Module in Earth and Life ScienceДокумент20 страницModule in Earth and Life ScienceKenjie SobrevegaОценок пока нет
- The Way the Wind Blows: Climate Change, History, and Human ActionОт EverandThe Way the Wind Blows: Climate Change, History, and Human ActionОценок пока нет
- Q4 - Las 8Документ2 страницыQ4 - Las 8JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Faculty and Staff Meeting - June 20, 2022Документ2 страницыFaculty and Staff Meeting - June 20, 2022JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Q4 - Las 11Документ4 страницыQ4 - Las 11JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Q4 - Las 10Документ2 страницыQ4 - Las 10JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Enrichment Class ScheduleДокумент1 страницаEnrichment Class ScheduleJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Graduation 2022 Meeting of TeachersДокумент3 страницыGraduation 2022 Meeting of TeachersJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Q4 - Las 13Документ2 страницыQ4 - Las 13JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- 101 Amazing Earth FactsДокумент9 страниц101 Amazing Earth FactsJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент1 страницаUntitledJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- CIM in ELS - Q2Документ1 страницаCIM in ELS - Q2JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Election Accomplishment ReportДокумент1 страницаElection Accomplishment ReportJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- BongdoNhs Multifactoranalysis 2ndQДокумент2 страницыBongdoNhs Multifactoranalysis 2ndQJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Competency ChecklistДокумент3 страницыCompetency ChecklistJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Day 3 Inset AccomplishmentДокумент1 страницаDay 3 Inset AccomplishmentJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Application LettersДокумент2 страницыApplication LettersJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 3 - September 27-October 1 2021Документ3 страницыPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 3 - September 27-October 1 2021JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: Tabunan National High School Tabunan, Borbon, CebuДокумент1 страницаRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: Tabunan National High School Tabunan, Borbon, CebuJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- 2022 - 2023 DocumentationДокумент4 страницы2022 - 2023 DocumentationJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- 2022 - 2023 Teachers' LoadingДокумент2 страницы2022 - 2023 Teachers' LoadingJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: Tabunan National High School Tabunan, Borbon, CebuДокумент1 страницаRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: Tabunan National High School Tabunan, Borbon, CebuJESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 3 - September 27-October 1 2021Документ3 страницыPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 3 - September 27-October 1 2021JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 6 - October 18 - 22, 2021Документ2 страницыPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 6 - October 18 - 22, 2021JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 5 - October 11 - 15, 2021Документ2 страницыPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 5 - October 11 - 15, 2021JESSA SUMAYANG100% (1)
- ST 3Документ2 страницыST 3JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- ST 1Документ2 страницыST 1JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- PR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 7 - October 25 - 29, 2021Документ4 страницыPR2 LAS - Quarter 1 - Week 7 - October 25 - 29, 2021JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- ST 2Документ2 страницыST 2JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- ST 4Документ2 страницыST 4JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- ST 2Документ2 страницыST 2JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- ST 3Документ2 страницыST 3JESSA SUMAYANGОценок пока нет
- Botswana Ref Ranges PaperДокумент7 страницBotswana Ref Ranges PaperMunyaradzi MangwendezaОценок пока нет
- Review by Dr. Jim B. TuckerДокумент5 страницReview by Dr. Jim B. TuckerGumnamОценок пока нет
- Yamaha TW 125 Service Manual - 1999Документ275 страницYamaha TW 125 Service Manual - 1999slawkomax100% (11)
- Your Song.Документ10 страницYour Song.Nelson MataОценок пока нет
- Minneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Документ4 страницыMinneapolis Police Department Lawsuit Settlements, 2009-2013Minnesota Public Radio100% (1)
- A Manual For A Laboratory Information Management System (Lims) For Light Stable IsotopesДокумент131 страницаA Manual For A Laboratory Information Management System (Lims) For Light Stable IsotopesAlvaro Felipe Rebolledo ToroОценок пока нет
- Essential Nutrition The BookДокумент115 страницEssential Nutrition The BookTron2009Оценок пока нет
- Catibog Approval Sheet EditedДокумент10 страницCatibog Approval Sheet EditedCarla ZanteОценок пока нет
- Learning TheoryДокумент7 страницLearning TheoryIMS AcadОценок пока нет
- Corporate Plan 2018 2021Документ94 страницыCorporate Plan 2018 2021Nkugwa Mark WilliamОценок пока нет
- UBFHA V S BF HomesДокумент11 страницUBFHA V S BF HomesMonique LhuillierОценок пока нет
- VVP Engg. CollegeДокумент32 страницыVVP Engg. Collegechotaimanav17Оценок пока нет
- Part - 1 LAW - 27088005 PDFДокумент3 страницыPart - 1 LAW - 27088005 PDFMaharajan GomuОценок пока нет
- Martin Vs MalcolmДокумент17 страницMartin Vs Malcolmronnda100% (2)
- Case Study - Lucky Cement and OthersДокумент16 страницCase Study - Lucky Cement and OthersKabeer QureshiОценок пока нет
- Astm A709-04Документ8 страницAstm A709-04Артем ТитовОценок пока нет
- A Detailed Lesson Plan - The Fundamental Law of ProportionДокумент10 страницA Detailed Lesson Plan - The Fundamental Law of ProportionPrincess De LeonОценок пока нет
- Pam ApplicationДокумент3 страницыPam Applicationapi-534834656Оценок пока нет
- Do or Does1.1.2Документ4 страницыDo or Does1.1.2dzanardipintoОценок пока нет
- AgrippaДокумент4 страницыAgrippaFloorkitОценок пока нет
- An/Trc - 170 TrainingДокумент264 страницыAn/Trc - 170 Trainingkapenrem2003Оценок пока нет
- The Organization of PericentroДокумент33 страницыThe Organization of PericentroTunggul AmetungОценок пока нет
- Connecting Microsoft Teams Direct Routing Using AudioCodes Mediant Virtual Edition (VE) and Avaya Aura v8.0Документ173 страницыConnecting Microsoft Teams Direct Routing Using AudioCodes Mediant Virtual Edition (VE) and Avaya Aura v8.0erikaОценок пока нет
- Review - ChE ThermoДокумент35 страницReview - ChE ThermoJerome JavierОценок пока нет
- 2 - (Accounting For Foreign Currency Transaction)Документ25 страниц2 - (Accounting For Foreign Currency Transaction)Stephiel SumpОценок пока нет
- Activity 1Документ18 страницActivity 1Kevin T. OnaroОценок пока нет
- SMTP/POP3/IMAP Email Engine Library For C/C++ Programmer's ManualДокумент40 страницSMTP/POP3/IMAP Email Engine Library For C/C++ Programmer's Manualadem ademОценок пока нет
- MCSE Sample QuestionsДокумент19 страницMCSE Sample QuestionsSuchitKОценок пока нет
- CEO - CaninesДокумент17 страницCEO - CaninesAlina EsanuОценок пока нет
- VC++ Splitter Windows & DLLДокумент41 страницаVC++ Splitter Windows & DLLsbalajisathyaОценок пока нет