Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
Hanna La MadridИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Загружено:
Hanna La MadridАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
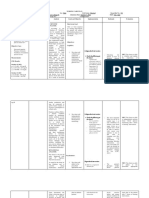
Subjective: Risk for Unstable After a day of - Administer basal and - Adherence to the After a day of
Blood Glucose as executing the prandial insulin. therapeutic regimen executing the
-- evidenced by necessary promotes tissue perfusion. necessary
Insulin deficiency interventions, the Keeping glucose in the interventions, the
or excess. patient will normal range slows the patient was able
Objective: achieve the progression of to achieve the ff.
following microvascular disease. outcomes:
CBG (before taking outcomes:
insulin): 273 mg/dl - Watch out for signs of - An elevated blood glucose - Patient has a
- Patient has a morning hyperglycemia. level arising in the morning blood glucose
CBG (after taking blood glucose due to insufficient level of reading of less
insulin): 51 mg/dl reading of less insulin (causes the dawn than 180 ml/dl;
than 180 ml/dl; phenomenon or BG levels fasting blood
- dizziness fasting blood begin to rise at 3 AM) glucose levels of
- slow to react glucose levels of less than <140
- confused less than <140 - Teach patient how to - Blood glucose is mg/dl;
- lethargic mg/dl; hemoglobin perform home glucose monitored before meals and hemoglobin A1C
- shakiness A1C level <7% monitoring. at bedtime. Glucose values level <7%
are used to adjust insulin
- Patient will doses. - Patient will
achieve and achieve and
maintain glucose - Report BP of more than - Hypertension is commonly maintain glucose
in satisfactory 160 mmHg. Administer associated with diabetes. in satisfactory
range of <140 hypertensive as Control of BP prevents range of <140
mg/dl prescribed. coronary artery disease, mg/dl
stroke, retinopathy, and
- Patient will nephropathy. - Patient will
acknowledge key acknowledge key
factors that may factors that may
contribute to - Instruct patient to take contribute to
unstable blood oral hypoglycemic unstable blood
glucose levels. medications as directed. glucose levels.
- Instruct patient to take
insulin as directed.
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
- Instruct patient on the - The absorption of insulin
proper injection of insulin. is more consistent when
insulin is always injected in
the same anatomical site.
- Stress the importance of - Control of blood glucose
achieving blood glucose levels within non-diabetic
control. range can significantly
reduce the development
and progression of
complications.
- Explain the importance - Recommendation is three
of having consistent meal meals of equal size, evenly
content or timing. spaced mealtimes (5-6
hours apart), with one or
two snacks. Pacing food
intake throughout the day
places more manageable
demands on the pancreas.
- Educate patient on - A consistent amount of
maintaining consistency food and time interval
in the amount of food and between meals helps
the approximate time prevent hypoglycemic
intervals between meals. reactions and maintain
overall blood glucose
control.
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
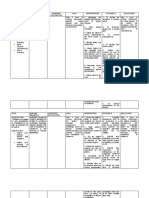
Subjective: Deficient After executing the - Explain that long-acting - Long-acting insulin does Before discharge,
knowledge necessary nursing insulin only needed to be not have a peak of action. patient was able to
“Ma’am, pwede po related to interventions, the injected once or twice daily. Insulin glargine is effective demonstrate
for over 24 hours.
bang unfamiliarity patient is expected knowledge of insulin
pakipaliwanag with information to achieve the - Explain that regular - Dosage may be adjusted
injection,
nang mabuti kung as evidenced by following outcome: prandial insulins (Humulin) based on the actual amount symptoms, and
ano po yung dapat requests of should be injected 30 of food ingested because treatment of
at hindi dapat na information. - Before discharge, minutes before meals. rapid-acting insulins can be hypoglycemia and
gawin sa patient will Rapid-acting insulins may given after a meal. diet.
kondisyon ko?” as demonstrate be injected before or after
verbalized by the knowledge of eating.
patient. insulin injection,
symptoms, and - Explain that insulin - Insulin dosage should be
dosage might need to be reduced when fasting for
Objective: treatment of
adjusted. surgery, when not eating, or
hypoglycemia and when hypoglycemia occurs.
- confused diet. Illness or infection may
- seek of increase insulin
information requirements.
- Teach patient to rotate - Systematic rotation of
insulin injection sites. injection sites is
recommended to prevent
lipodystrophy.
- Explain the importance of - A 90-degree angle is the
inserting the needle best insertion angle because
perpendicular to the skin. this ensures deep
subcutaneous administration
of insulin. Injection that is
too deep or too shallow may
affect the rate of absorption
of the insulin.
- Use various tools to - In using variety of teaching
complement teaching and materials, make sure that
maintain flexibility with they match the patient’s
regard to teaching method. learning needs, language,
and reading level.
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
- Teach patient to follow a - A diet low fat and high in
diet that is low in simple fiber helps to control
sugars, low fat, and high in cholesterol and triglycerides.
fiber and whole grains. Three daily meals and an
evening snack is
recommended. Refined and
simple sugars should be
reduced and complex
carbohydrates, such as
cereals, rice should be
increased.
- Teach patient to recognize - Signs includes shakiness,
signs of hypoglycemia. sweating, nervousness,
weakness, hunger, changes
in LOC. Hypoglycemia occurs
when the blood glucose levels
drop to less than 60 mg/dl.
Explain that hypoglycemia
occurs when there is too
much insulin, too little food,
too much oral hypoglycemic
agents or excessive physical
activity.
- Teach patient to treat - Hypoglycemia should be
hypoglycemia with treated with a carbohydrate
crackers, a snack, or snack (15 mg from a fast
glucagon injection. acting source – soda, fruit
juices, candies)
- Provide written - Reinforces learning and
information about diabetes convey the maximum
management for the patient amount of information.
to refer to.
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
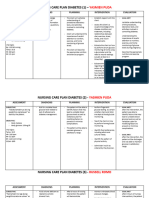
Subjective: After executing the - Teach and promote good - Hand hygiene is the single Before discharge,
Risk for infection necessary nursing hand hygiene. most effective way in patient was able to:
-- related to high interventions, the preventing the transmission
of diseases. Include the
glucose levels. patient is expected - Identify
patient’s SO in teaching.
to achieve the interventions to
Objective: following outcome - Maintain asepsis during - Increased glucose in the prevent/reduce risk
before his IV insertion, administration blood creates excellent of infection.
- flushed skin discharge: of medications, and medium for immune
- sweating providing wound care or dysfunction and for - Demonstrate
- chills - Identify site care. Rotate IV sites as pathogens to thrive. techniques, lifestyle
- warm to touch interventions to indicated. changes to prevent
prevent/reduce risk development of
Body Temp: of infection. - Provide catheter or - Urinary tract infections are infection.
perineal care. Teach female more prevalent in individuals
38°C/axilla
patients to clean from front with diabetes.
- Demonstrate to back after elimination.
WBC: 15.47 techniques, lifestyle
changes to prevent - Provide meticulous skin - An impairment or
development of care by gently massaging ineffective peripheral
infection. bony areas, keep skin dry. circulation can place the
Keep linens dry and patient at risk for increased
wrinkle-free. skin breakdown and
development of infection.
- Place in semi-Fowler’s - Facilitates lung expansion;
position. reduces risk of aspiration.
- Encourage coughing or - Helps in the ventilation of
deep breathing as the all lung areas and in
patient is alert and mobilizing secretions – stasis
cooperative. Frequent of secretions can increase the
repositioning is also risk of infection.
recommended.
- Provide tissues and trash - To help minimize the
bag in a convenient location spread of infection.
for sputum and other
secretions. Instruct patient
in proper handling of
secretions.
LA MADRID, Hanna Mae B.
- Encourage and assist with - Reduces risk of oral/ gum
oral hygiene. disease
- Encourage increase in - Increase fluid intake to
fluid intake unless approximately 3,000 mL per
contraindicated. day to increase urinary flow
and prevent stasis of urine
which may increase
susceptibility of infection.
- Administer antibiotics as - Early treatment may help
indicated. prevent sepsis as patients
with diabetes are more prone
to serious infectious
diseases.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- NCP DM and HCVDДокумент3 страницыNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: IndependentДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Independent: Independentzebzeb STEMAОценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- Subjective: Elevated Blood Glucose STO: After 4 Hours of Independent: STO: After 4 Hours ofДокумент9 страницSubjective: Elevated Blood Glucose STO: After 4 Hours of Independent: STO: After 4 Hours ofDacillo GailleОценок пока нет
- ACTIVITY 1: Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыACTIVITY 1: Nursing Care PlanChelsea JardelezaОценок пока нет
- NCP 1Документ3 страницыNCP 1AGUSTIN PRECIOUS JOY CОценок пока нет
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPДокумент4 страницыUncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPRawan KhateebОценок пока нет
- BSN 2 7C - NCPДокумент4 страницыBSN 2 7C - NCPIsaackurt AdaОценок пока нет
- Presentation TomorrowДокумент8 страницPresentation TomorrowRafik LakhdarОценок пока нет
- CUESДокумент3 страницыCUESJannarie EstebanОценок пока нет
- Oral RevalidaДокумент39 страницOral Revalidajunathancortez123Оценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseNathalie kate petallar75% (8)
- CHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaДокумент6 страницCHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaenesОценок пока нет
- Gestational Diabetes NCP SelДокумент3 страницыGestational Diabetes NCP Selcherrymae mata100% (3)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент9 страницAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJordz PlaciОценок пока нет
- NCP DMДокумент4 страницыNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- Less Hypoglycemia With Insulin Glargine in Intensive Insulin Therapy For Type 1 DiabetesДокумент5 страницLess Hypoglycemia With Insulin Glargine in Intensive Insulin Therapy For Type 1 DiabetesUduman IsmailОценок пока нет
- Continuous Insulin InfusionДокумент6 страницContinuous Insulin Infusionbobobo22Оценок пока нет
- DM TreatmentДокумент9 страницDM TreatmentAshraf AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Clinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1Документ11 страницClinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1JezraleFame AntoyОценок пока нет
- NCP Roldan OncoДокумент6 страницNCP Roldan OncoCeegi Arville RoldanОценок пока нет
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionДокумент12 страницPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanОценок пока нет
- Novolin and HumulinДокумент3 страницыNovolin and HumulinChynnaОценок пока нет
- NCP 1Документ7 страницNCP 1Mark PabalanОценок пока нет
- NCP - Gestational DiabetesДокумент2 страницыNCP - Gestational DiabetesKailah Rose CabantoyОценок пока нет
- CommmmmДокумент3 страницыCommmmmAriane Gay DuranОценок пока нет
- Effective Use of Insulin: PreviewДокумент6 страницEffective Use of Insulin: Previewprad1973Оценок пока нет
- Compilation P2 MS2 PDFДокумент31 страницаCompilation P2 MS2 PDFGwenn SalazarОценок пока нет
- NCP - Diabetes MellitusДокумент5 страницNCP - Diabetes MellitusYasmien MarieОценок пока нет
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Документ4 страницыRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Ace Khiel Peralta50% (2)
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Lack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementДокумент2 страницыLack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementDanica Kate GalleonОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: No Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Level R/T Deficient Knowledge of Diabetes Management Inference: Short Term: Short TermДокумент1 страницаAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: No Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Level R/T Deficient Knowledge of Diabetes Management Inference: Short Term: Short TermMark PabalanОценок пока нет
- Type 1 Diabetes MellitusДокумент55 страницType 1 Diabetes MellitusAidos BolatovОценок пока нет
- Analogos de Insulina en DM 1 2017Документ15 страницAnalogos de Insulina en DM 1 2017LaurenArperОценок пока нет
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseДокумент4 страницыRisk For Unstable Blood GlucosehallegendОценок пока нет
- NicesugarДокумент15 страницNicesugarMedicina94Оценок пока нет
- ENCPДокумент12 страницENCPShin PenielОценок пока нет
- ENCPДокумент12 страницENCPShin PenielОценок пока нет
- Slide Clinical Use of Insulin Therapy (ADA)Документ36 страницSlide Clinical Use of Insulin Therapy (ADA)Dian SobaОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraДокумент12 страницPancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraKiarra Angelu Martinez EstreraОценок пока нет
- VALDEZ - Nursing Process of Diabetes Mellitus PDFДокумент4 страницыVALDEZ - Nursing Process of Diabetes Mellitus PDFDexel Lorren ValdezОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент9 страницAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAce Khiel PeraltaОценок пока нет
- How Should We Manage Insulin Therapy Before SurgeryДокумент3 страницыHow Should We Manage Insulin Therapy Before Surgerytsiko111Оценок пока нет
- Insulin Therapy in Type 1 DiabetesДокумент11 страницInsulin Therapy in Type 1 DiabetesrendraОценок пока нет
- Insulin in DiabetesДокумент9 страницInsulin in DiabetesAbdul SamadОценок пока нет
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.Документ8 страницRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.eleinsamОценок пока нет
- NCP 1Документ3 страницыNCP 1Andrea Marie SevillaОценок пока нет
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thДокумент2 страницыNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaОценок пока нет
- NUR 327 Women & Newborn Health CareДокумент2 страницыNUR 327 Women & Newborn Health CareAsmaa ahmedОценок пока нет
- Cdho Assignment 2 Type 1 DiabetesДокумент10 страницCdho Assignment 2 Type 1 Diabetesapi-596913754Оценок пока нет
- Pearson 2001Документ4 страницыPearson 2001314084914Оценок пока нет
- Name University Course Professor DateДокумент13 страницName University Course Professor DateKaliunga CleophasОценок пока нет
- Insulin Treatment in DiabetesДокумент86 страницInsulin Treatment in DiabetesAhsan Rauf100% (1)
- Manejo de La DMGДокумент5 страницManejo de La DMGsandymejiaОценок пока нет
- Quizzes NCM116Документ10 страницQuizzes NCM116mendozajanice0601Оценок пока нет
- Diabetic CorrectionДокумент8 страницDiabetic CorrectionBlaise PascalОценок пока нет
- Preoperative Checklist: Ilocos Sur Provincial Hospital-Gabriela SilangДокумент1 страницаPreoperative Checklist: Ilocos Sur Provincial Hospital-Gabriela SilangHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- University of Northern Philippines: WWW - Unp.edu - PH CP# 09177148749, 09175785986Документ3 страницыUniversity of Northern Philippines: WWW - Unp.edu - PH CP# 09177148749, 09175785986Hanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- 12 Lead Electrocardiogram (Ecg) Placement: Module DescriptionДокумент11 страниц12 Lead Electrocardiogram (Ecg) Placement: Module DescriptionHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- WHO Surgical Safety Checklist: Before Induction On Anesthesia Before Skin Incision Before Patient Leaves Operating RoomДокумент1 страницаWHO Surgical Safety Checklist: Before Induction On Anesthesia Before Skin Incision Before Patient Leaves Operating RoomHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Group 7: Nervou SystemДокумент3 страницыGroup 7: Nervou SystemHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- International Journal of Pharmacotherapy: Case Study On Dengue Fever With ThrombocytopeniaДокумент3 страницыInternational Journal of Pharmacotherapy: Case Study On Dengue Fever With ThrombocytopeniaHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент11 страницDrug StudyHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumДокумент5 страницPathophysiology: Etiology: Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Campylobacter Jejuni, ClostridiumHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- University of Northern Philippines: WWW - Unp.edu - PH CP# 09177148749, 09175785986Документ23 страницыUniversity of Northern Philippines: WWW - Unp.edu - PH CP# 09177148749, 09175785986Hanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Bibliography PDFДокумент1 страницаBibliography PDFHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- The Use of Reason. Deliberately Performed Means That It Is Done Freely and KnowinglyДокумент7 страницThe Use of Reason. Deliberately Performed Means That It Is Done Freely and KnowinglyHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- 1 Rotation NVH WARD: CI: Kimberly PalacpacДокумент5 страниц1 Rotation NVH WARD: CI: Kimberly PalacpacHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Results and Interpretations of AGEДокумент3 страницыLaboratory Results and Interpretations of AGEHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Managing The Client With Problems On Cellular Aberration: Brain CancerДокумент18 страницManaging The Client With Problems On Cellular Aberration: Brain CancerHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Quiz LeukemiaДокумент4 страницыQuiz LeukemiaHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Activity in CHN SkillsДокумент1 страницаActivity in CHN SkillsHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Discussion No. 2 Sentiments, Reason, and Impartiality: Approbation and Vice The ContraryДокумент10 страницDiscussion No. 2 Sentiments, Reason, and Impartiality: Approbation and Vice The ContraryHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Standards of Public Health Nursing PracticeДокумент1 страницаStandards of Public Health Nursing PracticeHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- Isla de Bigan PDFДокумент24 страницыIsla de Bigan PDFHanna La MadridОценок пока нет
- DKA ProtocolДокумент3 страницыDKA Protocolpinky222255554100% (1)
- Glucocorticoid-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: An Important But Overlooked ProblemДокумент10 страницGlucocorticoid-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: An Important But Overlooked ProblemRengganis PutriОценок пока нет
- Stepwise Approach To Continuous Glucose Monitoring Interpretation For Internists and Family PhysiciansДокумент10 страницStepwise Approach To Continuous Glucose Monitoring Interpretation For Internists and Family PhysiciansRafael Baybay100% (1)
- Endo Main Base LvivtechДокумент103 страницыEndo Main Base LvivtechGiridhar SolasaОценок пока нет
- Eco 2Документ11 страницEco 2Walaa KhasawnehОценок пока нет
- Bell KJ Thesis 2 PDFДокумент84 страницыBell KJ Thesis 2 PDFlifeinhimОценок пока нет
- Switching Between InsulinДокумент2 страницыSwitching Between InsulinThoufiОценок пока нет
- Pregestational Diabetes Mellitus: Group 2Документ24 страницыPregestational Diabetes Mellitus: Group 2Jellie An TalattagОценок пока нет
- Ref - Guide For People With DiabetesДокумент70 страницRef - Guide For People With DiabetesJamie SmithОценок пока нет
- Vol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New BiologyДокумент716 страницVol 4 - Autocoids Diagnostics - and Drugs From New Biologyjoshigauta50% (2)
- Dosage Calculations PacketДокумент39 страницDosage Calculations PacketJack KeurigОценок пока нет
- Hyperglycemia Algorithm 2Документ1 страницаHyperglycemia Algorithm 2damondouglasОценок пока нет
- Med-Surg 1Документ42 страницыMed-Surg 1Stephen Gabriel Tito100% (1)
- Insulin Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыInsulin Drug StudyRai Hanah92% (13)
- KNH 413 - Case Study - Type 1 DMДокумент14 страницKNH 413 - Case Study - Type 1 DMapi-301118772Оценок пока нет
- Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin InfusionДокумент6 страницContinuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusiondonny elhamdouniОценок пока нет
- Rapid-Acting Insulin (Onset: 15-30 MinsДокумент5 страницRapid-Acting Insulin (Onset: 15-30 MinsBea TanОценок пока нет
- KNH 413 Case Study 2Документ7 страницKNH 413 Case Study 2api-272540385Оценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementДокумент10 страницCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: Health Promotion, Restoration, and Preservation Through Patient EducationДокумент9 страницThis Study Resource Was: Health Promotion, Restoration, and Preservation Through Patient EducationAnn A.Оценок пока нет
- Paper 2 Unit 1 Humulin IntroductionДокумент2 страницыPaper 2 Unit 1 Humulin IntroductionSandeep GupteОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateДокумент36 страницDiabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateHiKa SaGoОценок пока нет
- Kankee Briefs (2021-2022) - LD - Right To StrikeДокумент72 страницыKankee Briefs (2021-2022) - LD - Right To StrikeGet VectoredОценок пока нет
- Early Insulin TherapyДокумент6 страницEarly Insulin TherapyEKОценок пока нет
- Carb Counting Type1Документ22 страницыCarb Counting Type1Dhanalakshmi ThiyagarajanОценок пока нет
- Novolin R SQ (Regular Insulin)Документ3 страницыNovolin R SQ (Regular Insulin)EОценок пока нет
- Insulin - Types of InsulinДокумент11 страницInsulin - Types of InsulinAddison Enernest JonesОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Case StudiesДокумент20 страницDiabetes Case StudiesManish KanojiyaОценок пока нет
- Simplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-FormulationДокумент31 страницаSimplify Insulin Therapy With IDegAsp Co-FormulationRiamintan SihotangОценок пока нет
- Case PresentationДокумент24 страницыCase PresentationSumit Yadav0% (1)