Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
RPH
Загружено:
jesmani0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
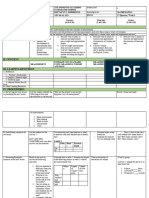
251 просмотров6 страницYEARLY PLAN - SCIENCE FORM 1 Week / Date Learning Area / Learning Objectives 1&2 4 / 1 - 15 / 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to science 1.1:: Understanding that science is part of everyday life Learning Outcomes List what he sees around him that is related to science Explain the importance of science in everyday life 160 min Name some careers in science such as: a. Science teacher b. Doctors c. Engineers d. Environment scientists 40 min State the steps
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
rph
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документYEARLY PLAN - SCIENCE FORM 1 Week / Date Learning Area / Learning Objectives 1&2 4 / 1 - 15 / 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to science 1.1:: Understanding that science is part of everyday life Learning Outcomes List what he sees around him that is related to science Explain the importance of science in everyday life 160 min Name some careers in science such as: a. Science teacher b. Doctors c. Engineers d. Environment scientists 40 min State the steps
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
251 просмотров6 страницRPH
Загружено:
jesmaniYEARLY PLAN - SCIENCE FORM 1 Week / Date Learning Area / Learning Objectives 1&2 4 / 1 - 15 / 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to science 1.1:: Understanding that science is part of everyday life Learning Outcomes List what he sees around him that is related to science Explain the importance of science in everyday life 160 min Name some careers in science such as: a. Science teacher b. Doctors c. Engineers d. Environment scientists 40 min State the steps
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
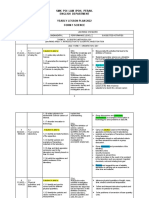
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
Learning Area/ Remarks
Week / Date Learning Outcomes
Learning Objectives 1A 1D 1G
List what he sees around him that is
related to science
Explain the importance of science in
Chapter 1: everyday life
Introduction to Science 160 min
1&2
1.1:: Name some careers in science such as:
4/1 – 15/1
Understanding that science a. Science teacher
is part of everyday life b. Doctors
c. Engineers
d. Environment scientists
40 min
State the steps in a scientific investigation
1.2::
3 / experiment
Understanding the steps in
18/1 – 22/1 Carry out a scientifi investigation
scientific investigation
200 min
State the physical quantities: length,
mass, time, temperature and electric
current
4 State the S.I. units and the corresponding
25/1 – 29/1 1.3:: symbols forthese physical quantities
- Knowing physical quantities State the symbols and values of prefixes
5 and their units for unitof length and mass: milli-, centi-
1/2 – 5/2 and kilo-
Identify and use appropriate prefixes in
the measurement of length and mass
160 min
Choose the right tool and measure length
in the context of an experiment
Estimate the area of regular and irregular
shapes using graph paper
80 min
Choose the right tool and measure the
6 1.4::
volume of liquid in the context of an
(8/2 – 12/2) Understanding the use of
experiment
measuring tools
Choose the right tool to measure body
temperature and the temperature of a
liquid
Determine the volume of solid using the
water displacement method
80 min
REVISION
7
TEST I
15//2 – 19/2
Determine the weight of an object
Explain the concept of weight
Explain the concept of mass
Determine the mass of an object
8 1.5::
40 min
(22/2 – 26/2) Understanding the concept
Explain the difference between mass and
of mass
weight
Apply the use of spring and beam/lever
balance in the context of an experiment
40 min
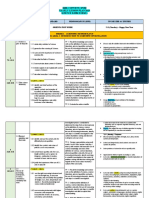
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
1.6:: Give examples of problems that may arise
Realising the importance of if standard units are not used
standard units in everyday
life 80 min
REVISION
9
(1/3 – 5/3)
- MID SEM EXAMINATION
10
(8/3 – 12/3)
15/3 – 19/3 MID SEM SCHOOL HOLIDAY
Identify that cells is the basic unit of living
things
40 min
Prepare slides following the proper
procedures
Use a microscope properly
Identify the general structure of animal
Chapter 2: cells and plant cells
11
Cell as a unit of life 80 min
22/3 – 26/3
2.1:: Draw the general strcutures of an animal
Understanding cells cell and a plant cell
Label the general structure of an animal PEKA II
cell and a plant cell
40 min
State the function of each structure
State the similarities and differences
between the two cells
40 min
State the meaning of unicellular and
2.2:: multicellular organisms
Understanding unicellular Give examples of unicellular and
and multicellular organisms multicellular organisms
40 min
State correctly the organisation of cells
Arrange in sequence organisation of cells
12 from the simple to the complex using the
29/3 – 2/4 terms cells, tissue, organ, system and
2.3::
organism
Understanding that cells
80 min
form tissues, organs and
Relate the organs to the system suitable
systems in the human body
for them
80 min
:. Name the different types of human cells and
their functions
2.4:: Explain why human beings are complex
Realising that humans are organisms
complex organisms 40 min
State that things have mass and occupy
space
13 Chapter 3:
Explain the meaning of matter
5/4 – 9/4 Matter
Relate things with matter 40 min
3.1::
Carry out an experiment to show that air,
Understanding that matter
water, soil and living things have mass
has mass and occupies space
and occupy space
80 min
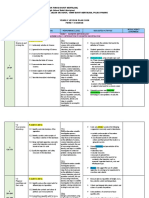
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
State that matter is made up of particles
State the different states of matter
40 min
3.2::
Understanding the three State the arrangement of particles in the
states of matter three states of matter
State the differences in the movement of
particles in the three states of matter
14 80 min
12/4 – 16/4 Define density
40 min
Explain why some objects and liquids float
3.3::
Solve simple problems related to density
Understanding the concept
80 min
of density
Carry out activities to explore the
densities of objects and liquids
80 min
Describe how man uses the different
states of matter
Describe how man applies the concept of
15
3.4:: density
19/4 – 23/4
Appreciating the use of the Carry out an activity to explore the
properties of matter in daily applications of the concept of floating and
life sinking related to density
120 min
:.Describe how man uses the concept of
buoyancy
Chapter 4: List the resources on earth needed to
The variety of resources on sustain life
earth List the resources on earth used in
4.1:: everyday life
Knowing the different
resources on earth 40 min
State what elements, compounds and
mixtures are
16
Give examples of elements, compounds
26/4 – 30/4
and mixtures
80 min
State the differences between elements,
compounds and mixtures
Carry out activities to compare the
properties of different metals and non-
4.2:: metals
Understanding elements, 80 min
compounds and mixtures Classify elements as metals and non-
metals based on their characteristics
Give examples of metals and non-metals
Carry out activities to separate the
17 components of a mixture
3/5 – 7/5 200 min
:. Carry out experiment to separate different
mixtures
:. Compare and contrast mixture and compound
4.3:: Explain the importance of variety of
18 Appreciating earth’s resources to man
10/5 – 14/5 the importance State the meaning of the preservation
of the variety and conservation of resources on earth
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
of earth’s State the importance of the preservation
resources to and conservation of resources on earth
man. Practise reducing the use, reusing and
recycling of materials
80 min
State what air is made up of
Explain why air is a mixture
State the average percentage of nitrogen,
Chapter 5:
oxygen and carbon dioxide in air
The air around us
Carry out ativities to show:
5.1::
i. The percentage of oxygen in air
Understanding the
ii. That air contains water vapour,
composition of air
microorganisms and dust
120 min
:. State the constituents of air
19
REVISION
17/5 – 21/5
20
24/5 – 28/5
- MID YEAR EXAMINATION
21
31/5 – 4/6
7/6 – 18/6 MID YEAR SCHOOL HOLIDAY
List the properties of oxygen and carbon
dioxide
5.2:: 40 min
22
Understanding the Identify oxygen and carbon dioxide based
21/6 – 25/6
properties of oxygen and on their properties
carbon dioxide Choose a suitable test for oxygen and
carbon dioxide
160 min
State that energy, carbon dioxide and
water vapour are the products of
respiration
Relate that living things use oxygen and
give out carbon dioxide during respiration
80 min
Compare and contrast the content of
5.3::
oxygen in inhaled and exhaled air in
Understanding that oxygen
humans
is needed in respiration
23 80 min
28/6 – 2/7 State that oxygen is needed for
- respiration
24 Carry out an experiment to show that
5/7 – 9/7 living things use oxygen and give out
carbon dioxide during respiration
80 min
State what combustion is
State that oxxygen is needed for
5.4:: combustion
Understanding that oxygen List the products of combustion
is needed in combustion Carry out experiments to investigate
combustion
160 min
25 5.5:: Explain what air pollution is
12/7 – 16/7 Analysing the effects of the List examples of air pollution
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
pollution List the sources of air pollution
Describe the effects of air pollution
Explain the steps needed to prevent and
control air pollution
160 min
REVISION
26
TEST II
19/7 – 23/7
Describe how life would be without clean
5.6:: air
Realising the importance of Suggest ways to keep the air clean
keeping the air clean Practise habits that keep the air clean
40 min
List the various forms of energy
27 List the various sources of energy
26/7 – 30/7 Chapter 6: Identify energy changes
Souces of energy Identify the sun as the primary source of
6.1:: energy
Understanding various forms Carry out activities to investigate energy
and sources of energy change from potential to kinetic energy
and vice versa
160 min
Define renewable and non-renewable
sources of energy
6.2:: Group the various sources of energy into
28
Understanding renewable renewable and non-renewable energy
2/8 – 6/8
and non-renewable energy Explain why we need to conserve energy
Suggest ways to use energy efficiently
240 min
Describe the importance of conserving
6.3:: energy sources
29
Realising the importance of Explain the use and management of
9/8 – 13/8
conserving energy sources energy sources
160 min
State that the sun gives out heat
State other sources of heat
Chapter 7: State that heat is a form of energy
Heat Give examples of the uses of heat
7.1:: 200 min
Understanding heat as a State the meaning of temperature
form of energy State the differences between heat and
temperature
160 min
30
State that heat causes solids, liquids and
16/8 – 20/8
gases to expand and contract
-
40 min
32
State that heat flows in three different
30/8 – 3/9
ways (conduction, convection and
7.2:: radiation)
Understanding heat flow 80 min
and its effect State that heat flow from hot to cold
Give examples of heat flow in natural
phenomena
State what a heat conductor is
State what a heat insulator is
120 min
33 SCHOOL HOLIDAY
YEARLY PLAN – SCIENCE FORM 1
6/9 – 10/9
List the uses of heat conductors and heat
7.2:: insulators in daily life
34
Understanding heat flow Carry out an experiment to investigate
13/9 – 17/9
and its effect different materials as heat insulators
200 min
State the change in state of matter in
physical processes
Explain that change in state of matter
7.3::
35 involves the absorption and release of
Analysing the effect of heat
20/9 – 24/9 heat
on matter
Give examples of daily observations
which show a change in state of matter
200 min
Explain with examples the use of
expansion and contraction of matter in
7.4::
daily life
Applying the principle of
160 min
expansion and contraction
Apply the principle of expansion and
of
contraction of matter in solving simple
matter
36 problems
27/9 – 1/10 160 min
- State that dark, dull objects absorb heat
38 better than white, shiny objects
7.5::
11/10 – 15/10 State that dark, dull objects give out heat
Understanding that dark,
better than white, shiny objects
dull
120 min
objects absorb and give out
Carry out experiments to investigate heat
heat better
absorption and heat release
80 min
REVISION
39
18/10 – 22/10
- FINAL EXAMINATION
40
25/10 – 29/10
41
DISCUSSION
1/11 – 5/11
7.6:: Put into practice the principle of heat
42
Appreciating the benefits of flow to provide comfortable living
8/11 – 12/11
heat flow
43
SCIENCE ACTIVITIES
15/11 – 19/11
Вам также может понравиться
- DLL-G7 Q2 Week 1Документ7 страницDLL-G7 Q2 Week 1Gen-GenAlcantaraBaldado100% (1)
- Scheme of Work For Form 1 ScienceДокумент22 страницыScheme of Work For Form 1 ScienceJila NfmОценок пока нет
- Word Search Form 1Документ1 страницаWord Search Form 1jesmaniОценок пока нет
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and QuestionsДокумент133 страницыCSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questionslram70100% (20)
- Mechanical Performance and Analysis of Banana Fiber Reinforced Epoxy CompositesДокумент10 страницMechanical Performance and Analysis of Banana Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Compositesdawuud09Оценок пока нет
- Science Lab Report Reactivity of Metalsthis One2Документ6 страницScience Lab Report Reactivity of Metalsthis One2api-237517118100% (2)
- FT-NIR For PIRДокумент13 страницFT-NIR For PIRDovganОценок пока нет
- Nano DeBeeДокумент2 страницыNano DeBeeCarmen RaveОценок пока нет
- This Difference Between Living and NonДокумент1 страницаThis Difference Between Living and Noncuongtran_siegenОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Stripe CoatingДокумент164 страницыFundamentals of Stripe Coatinganangwahjudi100% (1)
- RPT Science FRM 1Документ9 страницRPT Science FRM 1yunianisОценок пока нет
- RPT Science F1 2018Документ22 страницыRPT Science F1 2018zulhariszan abd mananОценок пока нет
- R PT Science FRM 12013Документ9 страницR PT Science FRM 12013bartОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Harian Science T1 - 2021Документ14 страницRancangan Harian Science T1 - 2021g-90227065Оценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f1Документ14 страницYearly Lesson Plan SC f1noor mazitaОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f1Документ16 страницYearly Lesson Plan SC f1Mary IdrusОценок пока нет
- Sow For Combined Science Year 9 (2+2 Programme) v2 - 2 YearsДокумент80 страницSow For Combined Science Year 9 (2+2 Programme) v2 - 2 YearsYenny TigaОценок пока нет
- Sow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsДокумент56 страницSow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsYenny Tiga100% (2)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Документ7 страницYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1Nurul AzuwinОценок пока нет
- SOW Physics F3-F5 (2020-2022)Документ51 страницаSOW Physics F3-F5 (2020-2022)Nurul FadhilahОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Science Form 1 2019 (Dlp-English)Документ14 страницRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Science Form 1 2019 (Dlp-English)Nur IzzyОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan Phy f4 2018Документ16 страницYearly Lesson Plan Phy f4 2018TS ShongОценок пока нет
- Physics - SyllabusДокумент29 страницPhysics - SyllabusJhun Lerry TayanОценок пока нет
- RPT Science Form 1 2020Документ29 страницRPT Science Form 1 2020Norshamsiah SamsudinОценок пока нет
- Math 7 - 2Q - 1ST WeekДокумент5 страницMath 7 - 2Q - 1ST WeekReynalyn RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Sow Combined Science Year 9 - 2+3 Programme - v2Документ37 страницSow Combined Science Year 9 - 2+3 Programme - v2Airul YantiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation: Theme 1: Scientific Methodology (12 Hours)Документ14 страницChapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation: Theme 1: Scientific Methodology (12 Hours)Anonymous ESQwNOtfe6Оценок пока нет
- SMK Seri Kembangan Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Science KSSM Form 1Документ16 страницSMK Seri Kembangan Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Science KSSM Form 1ryeОценок пока нет
- SMK Datuk Onn Butterworth Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2019 Mata Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Документ17 страницSMK Datuk Onn Butterworth Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2019 Mata Pelajaran Fizik Tingkatan 4Izzat FuatОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan f1 SC DLP 2022Документ29 страницYearly Plan f1 SC DLP 2022NURULKAMILAH KHAIRIRОценок пока нет
- RPH Week 4Документ16 страницRPH Week 4mexfloziaОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Scheme 2019 Term 1 1Документ10 страницForm 1 Scheme 2019 Term 1 1Tapiwa Trust Kanyai100% (2)
- Lesson Plan For Form Four Physics: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsДокумент22 страницыLesson Plan For Form Four Physics: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To Physicsahchin5Оценок пока нет
- Physics Course OutlineДокумент11 страницPhysics Course OutlineMertcanОценок пока нет
- RPT Science Form 1 2019Документ17 страницRPT Science Form 1 2019Anne Marian Anak JOSEPHОценок пока нет
- SMK Tinggi Bukit Mertajam, 77, Jalan Sri Bukit, 14000 Bukit Mertajam, Pulau PinangДокумент21 страницаSMK Tinggi Bukit Mertajam, 77, Jalan Sri Bukit, 14000 Bukit Mertajam, Pulau PinangPei TingОценок пока нет
- Ylp Remove 2018Документ5 страницYlp Remove 2018mexfloziaОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент63 страницыChemistryTheophilus Asante-TannorОценок пока нет
- Week 1Документ13 страницWeek 1angelicaamormanzanoОценок пока нет
- RPT Science f1 2022Документ25 страницRPT Science f1 2022NURULKAMILAH KHAIRIRОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 CH 1 Lesson 1measuring UnitsДокумент2 страницыUnit 1 CH 1 Lesson 1measuring UnitsAhmed HassanОценок пока нет
- RPT SN F1 2021 (DLP)Документ18 страницRPT SN F1 2021 (DLP)zuraihan mat ludinОценок пока нет
- College SyllabusДокумент14 страницCollege SyllabusJosephine SarvidaОценок пока нет
- RPT 2024 Biology KSSM t4 EnglishДокумент30 страницRPT 2024 Biology KSSM t4 EnglishFatin NazihaОценок пока нет
- Jul. 25/2010 Ph0101 Lecture Scheme/Plan Physics For TechnologistsДокумент8 страницJul. 25/2010 Ph0101 Lecture Scheme/Plan Physics For TechnologistsSURESH SURAGANIОценок пока нет
- RPT Science Form 1 2023Документ16 страницRPT Science Form 1 2023fiezah halimОценок пока нет
- RPT SC Year 3 (DLP) 2023-2024Документ25 страницRPT SC Year 3 (DLP) 2023-2024Nur FathirahОценок пока нет
- Tle-Dll Grade 7 (Week 3) January 27-31,2020Документ2 страницыTle-Dll Grade 7 (Week 3) January 27-31,2020Josephine Rivera100% (1)
- Ylp Science f1 2024 Fara Asrab GoayДокумент17 страницYlp Science f1 2024 Fara Asrab Goayg-90227065Оценок пока нет
- General Physics Practical IДокумент3 страницыGeneral Physics Practical IEnoch YaoОценок пока нет
- Technology Lesson Plan Term 1 Week 4 of 2024Документ2 страницыTechnology Lesson Plan Term 1 Week 4 of 2024Maphothego MogodiОценок пока нет
- Measurements: by CHED On May 28, 2020Документ5 страницMeasurements: by CHED On May 28, 2020Raze De La CroixОценок пока нет
- Science Physics 5124Документ24 страницыScience Physics 5124Susan MweembaОценок пока нет
- Sow f1 Igcse Phy 2021Документ21 страницаSow f1 Igcse Phy 2021Immy MaysmeekaОценок пока нет
- RPT Science Form 1 2017 SemesraДокумент15 страницRPT Science Form 1 2017 Semesracikgu ayu100% (3)
- General Chemistry 1Документ83 страницыGeneral Chemistry 1ibano626Оценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter Examination Grade 7 Household Services TOSДокумент3 страницы3rd Quarter Examination Grade 7 Household Services TOSAngellie Arsaga AlaparОценок пока нет
- Integrated ScienceДокумент26 страницIntegrated ScienceAris TotleОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated CurriculumДокумент12 страницGrade 8 - Integrated Science Consolidated Curriculumshonaishot hottieОценок пока нет
- Yearly Plan F1 SC 2022Документ29 страницYearly Plan F1 SC 2022DAYANG AZWA NADIA BINTI AWG AHMAD ISHAK MoeОценок пока нет
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021Документ19 страницRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Form 1 Science DLP 2021SITI SHAHARZAD BINTI WAHAB MoeОценок пока нет
- Yearly Lesson Plan: Science Form 1 2019 KSSMДокумент18 страницYearly Lesson Plan: Science Form 1 2019 KSSMSITI NURSYIFA BINTI ROZALI MoeОценок пока нет
- SMK Seri Hartamas Scheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2016 Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsДокумент19 страницSMK Seri Hartamas Scheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2016 Learning Area: 1. Introduction To Physicssyam123456789Оценок пока нет
- General Physics 1 Lesson PlanДокумент22 страницыGeneral Physics 1 Lesson PlanKazuya Sensei100% (1)
- PhysicsДокумент111 страницPhysicsAashish Dubey0% (1)
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Документ22 страницыSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Sean71% (7)
- Bahan Guru ReliefДокумент1 страницаBahan Guru ReliefjesmaniОценок пока нет
- Jadual Pra SPM 2012Документ1 страницаJadual Pra SPM 2012jesmaniОценок пока нет
- Word Search Lower Form (F2 & F3)Документ1 страницаWord Search Lower Form (F2 & F3)jesmaniОценок пока нет
- Teka Silang Kata Sains t5Документ1 страницаTeka Silang Kata Sains t5jesmaniОценок пока нет
- 2 Effect of Heat On SolidДокумент8 страниц2 Effect of Heat On SolidjesmaniОценок пока нет
- 3 Effect of Heat On GasesДокумент10 страниц3 Effect of Heat On GasesjesmaniОценок пока нет
- Arun Sir JoCP PaperДокумент50 страницArun Sir JoCP PaperAmrit KumarОценок пока нет
- Design and Installation of Chemical-Resistant Protection Systems For Concrete Surfaces (BASED ON EN 14879-PARTS 1, 3, 5 AND 6)Документ22 страницыDesign and Installation of Chemical-Resistant Protection Systems For Concrete Surfaces (BASED ON EN 14879-PARTS 1, 3, 5 AND 6)sudeep9666Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Designing Elastomeric Vibration IsolatorsДокумент26 страницIntroduction To Designing Elastomeric Vibration IsolatorsDurukan Burak DilekОценок пока нет
- Construciton SupervisorДокумент16 страницConstruciton SupervisorkinleyОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions Test Yourself 3Документ2 страницыChemical Reactions Test Yourself 3Nizar MTechОценок пока нет
- Confining Pressure 10 Mpa Von Mises StressДокумент2 страницыConfining Pressure 10 Mpa Von Mises StressMoj TabaОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet-CF.S10Документ1 страницаData Sheet-CF.S10nicolasОценок пока нет
- Box Culvert - ISДокумент14 страницBox Culvert - ISShyamontika Choudhury ChakrabartiОценок пока нет
- 2 Taefdxtoht 4 Oo 8 AДокумент16 страниц2 Taefdxtoht 4 Oo 8 AmelsabaeОценок пока нет
- 3 - MeroxДокумент22 страницы3 - MeroxAn Lê TrườngОценок пока нет
- Hysys PrintДокумент1 страницаHysys Printlebiatan89Оценок пока нет
- Hempel Paint Manual 2019Документ98 страницHempel Paint Manual 2019copperratt7228Оценок пока нет
- Crystallographic Imperfections PDFДокумент17 страницCrystallographic Imperfections PDFAmitОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationДокумент6 страницSafety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationJessie O.BechaydaОценок пока нет
- Dulux 1.1.2 Mild Steel - Surface PreparationДокумент2 страницыDulux 1.1.2 Mild Steel - Surface PreparationHIPAPОценок пока нет
- Simulation of A Triple Effect EvaporatorДокумент19 страницSimulation of A Triple Effect EvaporatorAnonymous LSPoghJ5n100% (1)
- Mixed Flowing Gas (MFG) Tests For Electrical ContactsДокумент11 страницMixed Flowing Gas (MFG) Tests For Electrical ContactsEugene OgosiОценок пока нет
- Pipe Rolers and SupportДокумент16 страницPipe Rolers and SupportAhmed YousriОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of Sodium Polyacrylate (Superabsorbent Polymer) As A Growing Medium of Hydroponically Grown Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)Документ18 страницEffectiveness of Sodium Polyacrylate (Superabsorbent Polymer) As A Growing Medium of Hydroponically Grown Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)Research ParkОценок пока нет
- 1.5 Atomic Structure and PeriodicityДокумент13 страниц1.5 Atomic Structure and PeriodicitychwalidОценок пока нет
- VMS WetarДокумент24 страницыVMS WetarErwin AnshariОценок пока нет
- Saudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Review Procedure - Post Test Reinstatement & Checklist SAIC-A-2006 30-Apr-13 PipingДокумент15 страницSaudi Aramco Inspection Checklist: Review Procedure - Post Test Reinstatement & Checklist SAIC-A-2006 30-Apr-13 Pipingpookkoya thangalОценок пока нет
- Intensifying Screen 1Документ39 страницIntensifying Screen 1Faris Afif100% (1)