Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Notes - Plant Organ Systems
Загружено:
vaviОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Notes - Plant Organ Systems
Загружено:
vaviАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
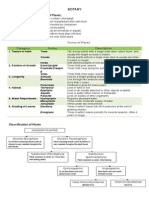
Plant Organ Systems
The Root System:
composed of typically underground structures that absorb water and minerals from
water or soil
Types of root systems:
• Tap root – one long very deep root with small
roots/ root hairs branching off. Example:
carrot, dandelion
• Fibrous root – many smaller roots with large
surface area, but not very deep Example:
grass
• Adventitious roots – roots that grow from
other parts of the plant rather than the base.
Example: Banyan tree, Ivy
The Shoot System:
The shoot system is composed of:
a) Leaves:
● The main photosynthetic structure of the plant – usually large surface area
● Photosynthesis word equation:
Chlorophyll
Light energy + Carbon Dioxide + Water Glucose + oxygen
● Consist of veins made of vascular tissues that transport substances
● Contain pores called stomata which allow for gas exchange
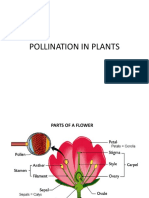
b) Flowers/Spores/Cones:
Flowers:
● are important for reproduction as they attract
pollinators to help with fertilization
● contain specialized structures important for
reproduction
o Male reproductive parts: stamen and anthers
which contain the pollen (sperm)
o Female reproductive parts: stigma and ovary
which contain the ovule/ova/egg
● some flowers will have both male and female parts allowing for self-pollination
Sexual reproduction in Plants:
● The pollen (male) lands on stigma and creates a pollen tube which carries the pollen to
the ovule where it fertilizes the egg.
● Pollen is transported to the stigma with the help of insects, wind, or animals
● Pollination results in the formation of seeds. Some seeds are enclosed in a fruit, which is
actually the ovary.
● The seeds are transported to other geographical locations through seed dispersal
mechanisms such as animals eating fruits and eliminating seeds as waste, carrying them
on their fur, blowing in the wind, falling off the parent plant.
● Seeds become new plants in favourable conditions.
Spores:
● Some plants such as mosses and ferns reproduce using spores
● Spores can grow in to mature plants if conditions are right
Cones:
● Coniferous plants (also called evergreens) produce
cones
● Cones can be male or female. Male cones produce
pollen. Female cones contain ovules and eggs.
c) Stems:
● Variety of stems
● Stems support the other structures of the plant
● Stems can be green and fleshy like grasses and flowers or dry and bark covered like in
trees
● Stems contain vascular tissue to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the
leaves, and sugars from the leaves to storage in the roots or other tissues
Вам также может понравиться
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОт EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОценок пока нет
- F Kingdom Plantae Part 1Документ11 страницF Kingdom Plantae Part 1JОценок пока нет
- Chapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203Документ76 страницChapter4 Primaryplantbodyrootstemleaves 171115154203chelseapujeda4Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Документ97 страниц2nd Quarter Lessons 2.0Jean Zyrelle AuronОценок пока нет
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsДокумент7 страницSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsrichie2885Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент37 страницLesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaОценок пока нет
- Botany 101Документ7 страницBotany 101Gladdin ChloeОценок пока нет
- Ch-12 NotesДокумент15 страницCh-12 NotesPta PОценок пока нет
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Документ101 страницаSexual Reproduction in Plants (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Gabrielle MorganОценок пока нет
- Parts of Plant and Their FunctionsДокумент23 страницыParts of Plant and Their Functionssarahbaharudin85Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Tissues and Primary Growth of StemsДокумент47 страницChapter 5 Tissues and Primary Growth of StemsJenilyn FarnacioОценок пока нет
- Chapter Four: Fasama Hilton KollieДокумент76 страницChapter Four: Fasama Hilton KollieASHFAQ AHMADОценок пока нет
- Plant ReproductionДокумент62 страницыPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaОценок пока нет
- Reproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceДокумент20 страницReproduction Flowering Plants Integrated ScienceSharina GeraldОценок пока нет
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterДокумент7 страницScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in Plants 7th GradeДокумент14 страницReproduction in Plants 7th Grade5545116.shreyastammeneniОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoДокумент70 страницPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in PlantsДокумент6 страницReproduction in PlantsjwonpediaОценок пока нет
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsДокумент29 страницMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemОценок пока нет
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Документ6 страницPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22Оценок пока нет
- Pollination in PlantsДокумент214 страницPollination in PlantsAbraham SekyiОценок пока нет
- PLANTAEДокумент25 страницPLANTAELyrra Jorramie Rull GragedaОценок пока нет
- SG-Life of Plants 2012Документ39 страницSG-Life of Plants 2012niku007Оценок пока нет
- Notes Ch-12 Reproduction in PlantsДокумент1 страницаNotes Ch-12 Reproduction in PlantsBobby NoharaОценок пока нет
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Документ83 страницыPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderОценок пока нет
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeДокумент9 страницPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosОценок пока нет
- Reproduction PLANTДокумент48 страницReproduction PLANTmonamoikoОценок пока нет
- Earth & Life Science: How Plants SurviveДокумент9 страницEarth & Life Science: How Plants Survivejames bonfОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsДокумент20 страницKingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsJunaedi Ahmad AlzОценок пока нет
- The Plant Kingdom: SOL 5.5: Kingdoms of Living ThingsДокумент80 страницThe Plant Kingdom: SOL 5.5: Kingdoms of Living ThingsDanny DonОценок пока нет
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSДокумент76 страницReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23Оценок пока нет
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomДокумент4 страницы1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Plantae 2023Документ28 страницKingdom Plantae 2023Shawn Xed De La VictoriaОценок пока нет
- Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Plant Structure, Growth, & DevelopmentДокумент74 страницыPlant Structure, Growth, & Development Plant Structure, Growth, & DevelopmentSophia AbatayОценок пока нет
- A Poison Tree by William BlakeДокумент6 страницA Poison Tree by William BlakeTiffany HorsfordОценок пока нет
- A1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Документ65 страницA1.2b Plant Reproduction - 2018Wayne DayataОценок пока нет
- 05 Plant Structure and FunctionДокумент87 страниц05 Plant Structure and Functionapi-263663768100% (1)
- Life Cycle of Plants: Unit 3 - Science FusionДокумент12 страницLife Cycle of Plants: Unit 3 - Science FusionFebrymaria LimbongОценок пока нет
- Examining Fruits and FlowersДокумент45 страницExamining Fruits and Flowerscarlos monteaОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Документ66 страницPlant Anatomy and Physiology: What Are The Parts of The Plant, and How Do They Work?Magy Tabisaura GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Science B. G8 3rdДокумент16 страницScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedОценок пока нет
- Presentation 2Документ21 страницаPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniОценок пока нет
- 8 Plant ReproductionДокумент8 страниц8 Plant Reproductionsrijansingha10Оценок пока нет
- Plant Organs RootsДокумент38 страницPlant Organs RootsMuammar KhadafiОценок пока нет
- Modern PlantsДокумент3 страницыModern PlantshomamunfatОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент38 страницPlant KingdomjuliankobieplaysОценок пока нет
- Kingdom PlantaeДокумент19 страницKingdom PlantaeDanny DonОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy & Physiology: Ayendago Emmanuel AtiahДокумент132 страницыPlant Anatomy & Physiology: Ayendago Emmanuel AtiahBelko Mark MubarakОценок пока нет
- 2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HДокумент57 страниц2 General Biology 2 - Parts of The Plants HBLESSIE MARIE ACADEMIAОценок пока нет
- PlantsДокумент22 страницыPlantsPotato ManОценок пока нет
- 3.2 The PlantsДокумент50 страниц3.2 The PlantsMohammed Faraaz MustafaОценок пока нет
- Palak SinghДокумент19 страницPalak SinghPalak Singh0% (1)
- Notes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsДокумент13 страницNotes - Chapter 12 Reproduction in PlantsAdnan SathikОценок пока нет
- Cluster Biology of PlantsДокумент48 страницCluster Biology of Plantsapi-452104023100% (1)
- Reproduction in PlantsДокумент8 страницReproduction in PlantsRenuОценок пока нет
- PlantsДокумент84 страницыPlantsYanyan PaydaОценок пока нет
- Reproduction Part 2Документ6 страницReproduction Part 2KELVIN CHIBINDAОценок пока нет
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Документ10 страницReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy FixДокумент48 страницPlant Anatomy FixAprilia ReniОценок пока нет
- 528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsДокумент58 страниц528211336-2-General-Biology-2-Part PlantsPeter MascarenhasОценок пока нет
- Best Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadДокумент1 страницаBest Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadArsh KrishОценок пока нет
- Ev Wireless Charging 5 PDFДокумент27 страницEv Wireless Charging 5 PDFJP GUPTAОценок пока нет
- 1-Gaikindo Category Data Jandec2020Документ2 страницы1-Gaikindo Category Data Jandec2020Tanjung YanugrohoОценок пока нет
- Lifelong Learning: Undergraduate Programs YouДокумент8 страницLifelong Learning: Undergraduate Programs YouJavier Pereira StraubeОценок пока нет
- Approach To A Case of ScoliosisДокумент54 страницыApproach To A Case of ScoliosisJocuri KosoОценок пока нет
- Oral Oncology: Jingyi Liu, Yixiang DuanДокумент9 страницOral Oncology: Jingyi Liu, Yixiang DuanSabiran GibranОценок пока нет
- Journal Entry EnrepДокумент37 страницJournal Entry Enreptherese lamelaОценок пока нет
- Emma The Easter BunnyДокумент9 страницEmma The Easter BunnymagdaОценок пока нет
- The Permission Wheel Hawkes L PDFДокумент8 страницThe Permission Wheel Hawkes L PDFNandita Asthana SankerОценок пока нет
- Consortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 3rd List - CLAT 2020 - PGДокумент3 страницыConsortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 3rd List - CLAT 2020 - PGSom Dutt VyasОценок пока нет
- 401 Lourdes School Quezon City Inc. v. GarciaДокумент2 страницы401 Lourdes School Quezon City Inc. v. GarciaIldefonso HernaezОценок пока нет
- TrematodesДокумент95 страницTrematodesFarlogy100% (3)
- Kampfgruppe KerscherДокумент6 страницKampfgruppe KerscherarkhoshОценок пока нет
- PS4 ListДокумент67 страницPS4 ListAnonymous yNw1VyHОценок пока нет
- Novedades Jaltest CV en 887Документ14 страницNovedades Jaltest CV en 887Bruce LyndeОценок пока нет
- Sabbir 47MДокумент25 страницSabbir 47MMd.sabbir Hossen875Оценок пока нет
- (IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesДокумент51 страница(IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesFilipe Galiza79% (14)
- Company Profile ESB Update May 2021 Ver 1Документ9 страницCompany Profile ESB Update May 2021 Ver 1Nakaturi CoffeeОценок пока нет
- Management of Graves Disease 2015 JAMA AДокумент11 страницManagement of Graves Disease 2015 JAMA AMade ChandraОценок пока нет
- Eradication, Control and Monitoring Programmes To Contain Animal DiseasesДокумент52 страницыEradication, Control and Monitoring Programmes To Contain Animal DiseasesMegersaОценок пока нет
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamДокумент6 страницDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamSuvedhya ReddyОценок пока нет
- Fort - Fts - The Teacher and ¿Mommy Zarry AdaptaciónДокумент90 страницFort - Fts - The Teacher and ¿Mommy Zarry AdaptaciónEvelin PalenciaОценок пока нет
- Mendoza - Kyle Andre - BSEE-1A (STS ACTIVITY 5)Документ1 страницаMendoza - Kyle Andre - BSEE-1A (STS ACTIVITY 5)Kyle Andre MendozaОценок пока нет
- KV3000 Programming TutorialДокумент42 страницыKV3000 Programming TutorialanthonyОценок пока нет
- Science Technology and SocietyДокумент46 страницScience Technology and SocietyCharles Elquime GalaponОценок пока нет
- Research PaperДокумент9 страницResearch PaperMegha BoranaОценок пока нет
- Taxation: Presented By: Gaurav Yadav Rishabh Sharma Sandeep SinghДокумент32 страницыTaxation: Presented By: Gaurav Yadav Rishabh Sharma Sandeep SinghjurdaОценок пока нет
- OPSS 415 Feb90Документ7 страницOPSS 415 Feb90Muhammad UmarОценок пока нет
- Landslide Hazard Manual: Trainer S HandbookДокумент32 страницыLandslide Hazard Manual: Trainer S HandbookMouhammed AbdallahОценок пока нет
- Foucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)Документ11 страницFoucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)YashinОценок пока нет
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceОт EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerОт EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesОт EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (397)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceОт EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)От EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (411)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessОт Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОт EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОценок пока нет
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainОт EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (65)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainОт EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomОт EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (216)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperОт EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (16)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveОт EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (66)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueОт EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (38)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedОт EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemОт EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (115)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouОт EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (62)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindОт EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (93)