Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-Spanish
Загружено:
Kayla Garcia0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров28 страницОригинальное название
Lesson 3
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров28 страницIntroduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-Spanish
Загружено:
Kayla GarciaАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 28
Introduction to Human Disease
HSC 2524
Humberto López Castillo, MD, PhD, CPH, CMI-Spanish
Cell Properties and Function
Textbook, Chap. 2
Learning Objectives
• Describe primary parts of the human cell and their function
• Differentiate between basic and specialized human cell
functions
• Describe the basic principles of cellular homeostatic control
• Identify an example of negative feedback loop in human
physiology
• Explain the role of cell biology across the health sciences
spectrum
Cells
• Basic unit of life
• Preform basic functions necessary to survival
• Building blocks
• Discovery
• Invention of microscope
• Mid-17th century
• Advances in cell physiology
Parts of the Cell
Cell Basics
Plasma (Cell) Membrane
• Selective barrier
• Fluid
• Intracellular fluid (ICF)
• Extracellular fluid (ECF)
• Control of movement into and out of cell
Cell Basics
Nucleus
• Largest single organized unit in cell
• Storage of genetic material
• Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
• Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
• Messenger RNA
• Ribosomal RNA
• Transfer RNA
Cell Basics
Cytoplasm
• Location
• Portion of cell not occupied by nucleus
• Composition
• Cytosol
• Organelles dispersed within
From your reading…
Which of the following is NOT a basic part of the human cell:
A. Cell Membrane
B. Cell Wall
C. Cytoplasm
D. Nucleus
Protein Synthesis
Key to life as we know it
Organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• Functions
• Protein synthesis
• Transportation of materials
• Structures
• Rough ER
• Ribosomes
• Smooth ER
Organelles
Golgi Complex and Lysosomes
• Golgi complex
• “Raw” proteins modified to final form
• Modified proteins sorted and distributed
Organelles
Lysosomes
• Lysosomes
• Digest and eliminate cellular waste
• Peroxisomes
• Contain powerful oxidative enzymes
Organelles
Vaults
• Shape
• Octagonal barrel-shaped structures
• Apparent function
• Transport messenger RNA or ribosomal units
• Transport vesicles
• Direct intracellular transportation
• Regulate cellular movements
• Play role in cell growth and division
Organelles
Mitochondria
• Role
• Derive energy from ingested nutrients
• Convert energy into usable form
• Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Organelles
Mitochondria
• Glycolysis
• Not very efficient
• Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle)
• Series of eight biochemical reactions
• ATP production
• Electron transport chain
• Essential for cellular respiration
Energy Production
Basic Cell Functions
• Necessary for survival of cell itself
• Include
• Obtaining nutrients and oxygen from the environment
• Converting nutrients and oxygen into energy
• Eliminating waste products of such conversions
• Synthesizing proteins for cell growth, structure, and function
• Controlling the exchange of materials in and out of the cell
• Moving materials around within the cell
• Monitoring the environment surrounding the cell
• Reproducing (except for nerve/muscle cell loss from disease/trauma)
Specialized Cell Functions
• Involve modification of basic cell function
• Contribute to survival of system or body
• Muscle cell contractions for movement
• Elimination of waste by kidney cells
• Secretion of digestive enzymes by specialized glands in the digestive
system
• Nerve cell messages to the brain in response to the surrounding
environment
From your reading…
Which of the following is NOT a level of cell organization:
A. Matrices
B. Organs
C. Systems
D. Tissues
Cell Organization
Tissues
• Muscle tissue • Epithelial
• Skeletal • Epithelial sheets
• Cardiac • Secretory glands
• Smooth • Exocrine or endocrine glands
• Nervous tissue • Connective
• Cells (neurons) • Loose connective tissue
• Cell body • Tendons
• Dendrites • Bones
• Axon • Blood
Cell Organization
Organs & Systems
• Two or more types of tissues
• Make up an organ
• Eleven major body systems
• Variety of intercoordinated systems
• Link together to form the whole body
Cell Exchanges
• External environment
• Extracellular fluid
• Plasma
• Interstitial fluid
• Systems that accomplish exchanges
• Digestive system
• Respiratory system
• Circulatory system
Homeostasis
• Maintenance of stable internal environment
• Factors
• Concentration of nutrients
• Concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide
• Concentration of waste products
• Concentration of water and electrolytes
• Temperature
• Volume and pressure
• Redox
Negative Feedback Loop
• Common regulatory mechanism
From your reading…
The HeLa cells in the Case Study in your textbook were sourced
from:
A. Heduvine Lagerfeld
B. Helen Lambert
C. Henrietta Lacks
D. Hens and Lambs
The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks
Questions?
Вам также может понравиться
- Exam 2Документ64 страницыExam 2Kayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-SpanishДокумент23 страницыIntroduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-SpanishKayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- Origin of Species: Chapter 18.2 and 18.3Документ18 страницOrigin of Species: Chapter 18.2 and 18.3Kayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 24 - Genes and Chromosomes - Slides (Autosaved)Документ293 страницыChapter 24 - Genes and Chromosomes - Slides (Autosaved)Kayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19.1Документ17 страницChapter 19.1Kayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-SpanishДокумент26 страницIntroduction To Human Disease: Humberto López Castillo, MD, PHD, CPH, Cmi-SpanishKayla GarciaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Assignment of PhysiologyДокумент13 страницAssignment of PhysiologySalman aliОценок пока нет
- F4 CHP 2 PYQДокумент10 страницF4 CHP 2 PYQmuraliMuОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles - Structure and Functions of Cell OrganellesДокумент18 страницCell Organelles - Structure and Functions of Cell OrganellesUnza WaqarОценок пока нет
- BIO101 Difference Between Cytosol and CytoplasmДокумент2 страницыBIO101 Difference Between Cytosol and CytoplasmmelihmorgulОценок пока нет
- MCQ Cell & Tissue by Gunjan RawalДокумент13 страницMCQ Cell & Tissue by Gunjan RawalgunjanОценок пока нет
- INSPIRE 2020 SyllabusДокумент10 страницINSPIRE 2020 SyllabusKevin ContrerasОценок пока нет
- CellsДокумент45 страницCellsapi-233187566Оценок пока нет
- Exercises On Cell and TissuesДокумент14 страницExercises On Cell and TissueskamilОценок пока нет
- Activity 8 - Blood and HematopoiesisДокумент8 страницActivity 8 - Blood and HematopoiesisMarissa CordovaОценок пока нет
- General Biology Teaching GuideДокумент85 страницGeneral Biology Teaching GuideJaja BualОценок пока нет
- SecretstoUltimateMuscleGrowth RДокумент23 страницыSecretstoUltimateMuscleGrowth RMarcelo LautaroОценок пока нет
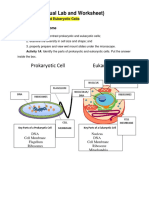
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Lab 3 (Virtual Lab and Worksheet)Документ2 страницыProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Lab 3 (Virtual Lab and Worksheet)Enzo MendozaОценок пока нет
- DAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 2: Cells and OrganellesДокумент48 страницDAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 2: Cells and OrganellesEmilyОценок пока нет
- Module 1.1 Cell and Molecular Physiology 2020 Handout PDFДокумент8 страницModule 1.1 Cell and Molecular Physiology 2020 Handout PDFJohn Stephen Clavel IIIОценок пока нет
- Cell-PreparedДокумент33 страницыCell-PreparedFarhanОценок пока нет
- Animal TissuesДокумент15 страницAnimal TissuesLitaMeilinaОценок пока нет
- Cell The Unit of LifeДокумент5 страницCell The Unit of LifeeloelОценок пока нет
- The Mitosis Song Paired Activities Sheet PDFДокумент2 страницыThe Mitosis Song Paired Activities Sheet PDFArshe OmaguingОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedДокумент7 страницWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanОценок пока нет
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsДокумент7 страницAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Review SheetДокумент2 страницыFinal Exam Review Sheetapi-264668182Оценок пока нет
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىДокумент7 страницتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgОценок пока нет
- K.14 Histology of Nasopharynx & PleuraДокумент26 страницK.14 Histology of Nasopharynx & Pleuraenri0% (1)
- Microbenotes Com Gram Stain Principle Reagents Procedure and Result InterpretationДокумент5 страницMicrobenotes Com Gram Stain Principle Reagents Procedure and Result Interpretationzoology qauОценок пока нет
- Test 1 Biology F4Документ12 страницTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinОценок пока нет
- XOXOXДокумент7 страницXOXOXVazima QtОценок пока нет
- Jurnal PendidikanДокумент8 страницJurnal PendidikanQothrun Nada FYОценок пока нет
- Smooth e RДокумент6 страницSmooth e Rapi-286681880Оценок пока нет
- Blood TransfusionДокумент22 страницыBlood TransfusionDinda KusumaОценок пока нет
- Tissues and MembranesДокумент2 страницыTissues and MembranesRav Evan VigillaОценок пока нет