Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Anterior Pituitary Disorders
Загружено:
Je Lyn0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
168 просмотров4 страницыAnterior pituitary disorders include hyperpituitarism and hypopituitarism. Hyperpituitarism is characterized by excessive secretion of pituitary hormones which can cause gigantism or acromegaly. Hypopituitarism is a deficiency of one or more anterior pituitary hormones and causes include infections, tumors, or surgery. Posterior pituitary disorders include diabetes insipidus, which is characterized by massive polyuria due to a lack of antidiuretic hormone or kidney insensitivity. Syndromes of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone cause persistent excretion of concentrated urine due to excessive antidiuretic hormone release.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
ANTERIOR PITUITARY DISORDERS
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документAnterior pituitary disorders include hyperpituitarism and hypopituitarism. Hyperpituitarism is characterized by excessive secretion of pituitary hormones which can cause gigantism or acromegaly. Hypopituitarism is a deficiency of one or more anterior pituitary hormones and causes include infections, tumors, or surgery. Posterior pituitary disorders include diabetes insipidus, which is characterized by massive polyuria due to a lack of antidiuretic hormone or kidney insensitivity. Syndromes of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone cause persistent excretion of concentrated urine due to excessive antidiuretic hormone release.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
168 просмотров4 страницыAnterior Pituitary Disorders
Загружено:
Je LynAnterior pituitary disorders include hyperpituitarism and hypopituitarism. Hyperpituitarism is characterized by excessive secretion of pituitary hormones which can cause gigantism or acromegaly. Hypopituitarism is a deficiency of one or more anterior pituitary hormones and causes include infections, tumors, or surgery. Posterior pituitary disorders include diabetes insipidus, which is characterized by massive polyuria due to a lack of antidiuretic hormone or kidney insensitivity. Syndromes of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone cause persistent excretion of concentrated urine due to excessive antidiuretic hormone release.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
ANTERIOR PITUITARY DISORDERS Medication: hormonal substitution
HYPERPITUITARISM post-surgery nursing care ( maybe for life)
• May be due to over activity of the gland semi to high fowler’s Corticosteroids
or the result of an adenoma position Levothyroxine
• Characterized by: protect from infection Androgen/estrogen
excessive serum concentration of and stressful situation Growth hormone
pituitary hormone ( GH, AGH, PRL) Hormone
morphologic and functional changes in replacement o Radiation: Indicated for larger
the anterior pituitary Constant neurologic tumors
checks o Surgery:
• GROWTH HORMONE
Monitor I&O to check trans-sphenoidal hypophysectomy
HYPERSECRETION
for diabetes Incipidus POSTERIOR PITUITARY DISORDERS
• Gigantism – prior to closure of
Encourage deep DIABETES INCIPIDUS
epiphyses; proportional growth
breathing but not coughing
• Acromegaly – after closure of the • Characterized by massive polyuria due to
Institute measures to
epiphyses; disproportional growth either lack of ADH or rnal insensitivity
prevent constipation
• CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS: • CENTRAL DI
Watch out for CSF
Arthritis - due to deficiency in ADH production
leak
Chest barreled shape • NEPHROGENIC DI
Rough facial features HYPOPITUITARISM - due to defect in the kidney
Odd sensations: hands and feet tubules that interferes with H2O
Muscle weakness & fatigue • Deficiency of one or more anterior
pituitary hormones absorption
Enlargement of organs - polyuria is unresponsive to
Growth of course hair • Causes:
Infections/inflammatory disorsers ADH, which is secreted normally
Amenorrhea; breast milk
production Autoimmune diseases • DIAGNOSTIC
Loss of vision; headaches Tumors Fluid deprivation test
Impotence; increased Surgery/radiation theraphy Administration of desmopressin
perspiration SIMMOND’S DISEASE 24-h urine collection for volume, glucose
Snoring - Panhypopituitarism and creatinine
- Complete absence of Serum for glucose, urea, nitrogen, calcium,
• Management:
pituitary hormones uric acid, potassium and sodium.
o Medication: Bromocriptine
CACHEXIA • MANAGEMENT:
cabergoline
- most prominent feature CENTRAL DI
-dopamine agonist
follows destruction of the Desmopressin, lypressin
GH
pituitary by surgery, infection, (intranasal)
hypersecretion and
injury or tumor Vassopresine tannate in oil (IM)
prolactinoma
SHEEHAN’S SYNDROME NEPHROGENIC DI
Ocreotide
-post partum pituitary necrosis Indomethacin
sematostatin
- a complication of delivery -hydrochlorothiazide
-GH
results from severe blood loss and -desmopressin
hypersecretion
hypovolemia -amiloride
• CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS: Clofibrate chlorpropamide
o Radiation: Indicated for larger
tumors HYPO-thermia, glycemia, tension
o Surgery: Loss of vision, strength, libido &
secondary sexual characteristics
trans-sphenoidal
hypophysectomy • MANAGEMENT
• Increased basal metabolic rate o Use for pregnant women and patients
who have refused surgery or RA1
SYNDROME OF INNAPROPRIATE ADH • CAUSES: treatment
• Disorder due to excessive ADH o Grave’s disease o During pregnancy, PTU is DOC.
release o Initial manifestation of o 1% of infants born to mothers on
• CLINICAL MANIFESTATION thyroiditis antithyroid theraphy will be hypothyroid
Persistent excretion of concentrated o TSH-screening pituitary o WOF agranulocytosis
urine tumor RAI (131I), K or Na iodide, SSKl (Lugol’s)
Signs of fluid overload o Toxic adenoma Adjuct to other anti-thyroid drugs in preparation
Hyponatremia for thyroidectomy
o Factitious thyrotoxicosis
LOC changes- increased ICP Treatment for thyroroxic crisis
o Amiodarone theraphy
• DIAGNOSTIC Inhibits release and synthesis of TH
Low serum sodium CLINICAL MSNIFESTATION
o GI Hypermotility MEDICATIONS:
Low serum osmolality
o Rapid weight loss Digitalis,proprandol (inderal)Phenobarbital
High urine osmolality
Well balance, high calorie diet with vitamin and
High urine sodium excretion o Apphrehension
Normal renal function mineral supplement
o Volume deficit;voracious appetite
• MANAGEMENT Subtotal or total thyroidectomy
o Exopthalmos; erratic menses NURSING IMPLICATION
Maintain fluid balance
o Systolic BP elevated;sweating o NPO post midnight
MIOW
Fluid restriction o TSH decreased in primary o Initial dose:
Loop diuretic disease o Urine and saliva slightly radioactive
Lithium or democlocycline o Increased in secondary disease o 24h vomitus highly radioactive x 6-8h
Maintain Na balance TYROID STORM/ THYROTOXIC CRISIS
Increased Na intake o Institute full radiation precations
o Marked delirium
Emergency treatment of 3% NaCl o Instruct the patient to use appropriate
o Severe tachycardia
followed by furosimide disposal methods when coughing and
Excessive rapid correction of o Vomiting expectorating
hyponatremia: central pontine myelinolysis o Diarrhea o Dilute oral doses in water or fruit juices
THROID DISORDERS o Dehydration and give witm meals to prevent gastric
• Function test o High fever irritation
Fine needle aspiration biopsy -occurs in patient with exsisting but o LUGOL’s Solution
-Sampling of thyroid tissue to detect unrecognized thyrotoxicosis, stressful o Decreased vascularity of thyroid
malignancy. Initial test for evaluation of illness, thyroid surgery,RAI gland
thyroid masses o Discoloration of the teeth provide
NURSING INTERVENTION Increased systemic adrenergic activity straw for the patient when drinking
o Determine whether the patient has severe hypermetabolism o Encourage for increased H2O
taken medications or argents that MANAGEMENT
intake
contains iodine because they may o Anti-thyroid drugs
o May caused tyrotoxic crisis
alter the test results o Prophylthiouracil (PTU);
HYPOTHYROIDISM
o Assess allergy to iodine or shellfish methimazole o State of low serum thyroid hormone in the
o For scans, tell patient that radiation o Blocks thyroid hormones
blood resistance to TH
is only minimal synthesis Autoimmune
HYPERTHYROIDISM Developmental
Dietary o Decreased all body function o Phenitoin or laxative abuse
Iodine o Decreased v/s CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
Oncologic o Precipitating Factors: o Constipation
Drugs induce Acute illness o Apathy
Iatrogenic Rapid withdrawal to medication o Lordosis
Nonthyroidal anesthesia o Cardiac dysthemia
Endocrine Thyroidectomy o Upset GI tract
o COMMON CAUSES: Opiod use o Low energy level Increased BP
o Autoimmune hypothyroiditis aka MANAGEMENT SYMPTOMS
hashimoto disease Prevention o Increased calcium
o Failure of the hypothalamus Prophylaxis o Increased parathyroid hormone
o Failure of the pituitary gland Hormonal replacement
MANAGEMENT
o Inborn errors of EH synthesis Levothyroxine (syncroid)
o Decreased calcium intake
o History of thyroidectomy Liothyronine (cytomel)
o Increased phosphorus intake
o Expose to radiation Liothrix (thyrolar)
Doses increased every 2-3 weeks o Calcitonin
o Antithyroid theraphy o Surgery to remove adenoma
o COMMON CAUSE: iron Watch out for:
o Chest pain o Furosemides
Deficiency o Biphosponates
CLASSIFICATIONS o Palpitation
o Profuse sweating HYPOPARATHYROIDISM
o CRETINISM – in infants and Auto immune
young children o Nervousness
o Drink meds at exact time each Injury to the parathyroid theraphy
o LYMPHOCYTIC Ischemic thyroid surgery
THYROIDITIS – self limiting day
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
and appears after 6 yrs of o May develop insomia if taken at
Dypsnea, dysrrhytmia
age and peak during night
Extremities tingling
adolescent o Monitor bp and apical pulse
Fhotophobia
o HYPOTHYROIDISM W/O o If pulse morethan 100 bpm-stop Increased bone density
MYXEDEMA- mild thyroid NURSING IMPLICATION Cramps; chvostek sign
failure common in older o Low calorie Trousseau sign; tetany
children and adult o Warm environment MANAGEMENT
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION o Stool softener o IV calcium gluconate-drug of choice
Dry brittle hair, dry course skin o Maintain patent airway o Oral calcium salts
Edema in periorbital HYPERPARATHYROIDISM o Vit d supplementation
Reduce BMR Primary o Elevated serum phosphate
Apathy, anorexia, anemia o Single adenoma o Low calcium
Increased weight, intolerance to food o Genetic disorders
Lethargy, loss of libido o Trousseau & chvostek sign
o Multiple endocrine neoplasias o Elevated serum phosphate
Enlarged tongue Secondary
Drooling saliva o Low calcium
o Rickets
TSH increased in primary o Akalosis/arrhythmias
o Vit. D deficiency
Decreased in secondary o Narrowing of airways
o Chronic renal failure
MYXEDEMA COMA o Irritability
o Cramps o Monitor Weight and glucose
o Parathormone injection o 24h urine specimen collection
o High calcium diet-spinach o Bronze skin discoloration
o Low phosphate o Avoid stress
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA o Avoid contacts
Adrenal tumor CUSHING SYNDROME
Increased epinephrine and norepinephrine Enlargement of adrenal gland
Tumor in the adrenal corex which is Increased stimulation
responsible for the regulation of BP CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
Buffalo hump
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION Unusual behavior
Headache Facial features; moon facesfat; trunkal
Anxiety obesity
Nausea ACTH is elevated
Eye disturbances Loss of muscle mass
Sever hypertension Over extended skin
Dilate blood vessels by nitroprussside Hypertension, hypernatrimia
Monitor bp Urinary cortisol elevated
Monitor I & o Menstrual irregularity
Fluid replacement Pourosity of the bone
Decreased environment stimulation MANAGEMENT
Stress o Remove steroids
Maintain dosage of steroids o Irradiation
Follow up check up o Hypophesectomy
ADDISON’S DISEASE o Adrenalectomy
Hyposecretion of adenocortical hormones o DRUGS
Idiophatic atrophy o Cyproheptadine
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
(perjactine)
o Weakness
o Nysodrine
o Excess stress
o Aminoglutethamine
o Anorexia, vomiting, nausea
( cytadrin)
o Low sodium o Monitor V/S
o Decreased potassium o Monitor I & O
o Decreased bp o Stress reduction
MANAGEMENT
o Replacement of
hormones:hydrocortisone
o Increased carbohydrate and protein
o Potassium
o Sodium
o Monitor v/s 4x a day
o Monitor I & O
Вам также может понравиться
- Hypertensive Renal DiseaseДокумент2 страницыHypertensive Renal DiseaseHenry KaweesaОценок пока нет
- Patients With Hypertensive Nephropathy and Chronic Kidney Disease Might Not Benefit From Strict Blood Pressure Control PDFДокумент10 страницPatients With Hypertensive Nephropathy and Chronic Kidney Disease Might Not Benefit From Strict Blood Pressure Control PDFSayf QisthiОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology 2Документ92 страницыPathophysiology 2Princess AgarwalОценок пока нет
- CRFДокумент50 страницCRFKevin MontoyaОценок пока нет
- Med Surg 2 - 8 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic DisordersДокумент8 страницMed Surg 2 - 8 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic DisordersMaxinne RoseñoОценок пока нет
- Concept Map 5Документ2 страницыConcept Map 5api-354331689Оценок пока нет
- Journal - Alzheimer DiseaseДокумент1 страницаJournal - Alzheimer DiseaseTriLightОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel BakyДокумент8 страницSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel Bakyahmed gabrОценок пока нет
- NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVEr DISEASE (NAFLD) - NASHДокумент4 страницыNON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVEr DISEASE (NAFLD) - NASHJason FooОценок пока нет
- Nootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionДокумент12 страницNootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionMuhammad TalhaОценок пока нет
- Rhabdomyolysis Case Study WeeblyДокумент18 страницRhabdomyolysis Case Study Weeblyapi-241865788Оценок пока нет
- AtaxiaДокумент8 страницAtaxiaDivya Gupta0% (1)
- Nursing Ethics and Jurisprudence 1Документ17 страницNursing Ethics and Jurisprudence 1Lovely PlazaОценок пока нет
- Esrd FinalДокумент26 страницEsrd FinalCreighton A. BayonganОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Gastroparesis: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and ManagementДокумент10 страницDiabetic Gastroparesis: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and ManagementboomОценок пока нет
- Burns Pathophysiology 2Документ1 страницаBurns Pathophysiology 2Monique Ann DanoyОценок пока нет
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsДокумент5 страницPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonОценок пока нет
- Aneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)Документ55 страницAneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)tejuteju067100% (1)
- Renal 2 MTC PDFДокумент55 страницRenal 2 MTC PDFDrbee10Оценок пока нет
- Pepti C Ul Cer Dis Ea SeДокумент36 страницPepti C Ul Cer Dis Ea Segerald_ichigoОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho PhysiologyДокумент11 страницPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaОценок пока нет
- X. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Goal MetДокумент10 страницX. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Goal MetAnonymous TpI3Lk50Оценок пока нет
- Portal Vein Thrombus ChildrenДокумент11 страницPortal Vein Thrombus ChildrenViswas ChhapolaОценок пока нет
- Course 4 2019 Hypoglicemia HyperuricemiaДокумент57 страницCourse 4 2019 Hypoglicemia HyperuricemiaAmelia PricopОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Storage Disease, Type II (Pompe Disease) : BackgroundДокумент7 страницGlycogen Storage Disease, Type II (Pompe Disease) : Background201111000Оценок пока нет
- Anemia in CKD Patient On HeamodialysisДокумент32 страницыAnemia in CKD Patient On HeamodialysisEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- Rhabdomyolysis: Sheeba Hakak AmnchДокумент28 страницRhabdomyolysis: Sheeba Hakak AmnchMona MorrisОценок пока нет
- Hyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismДокумент12 страницHyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismCésar Augusto Sánchez SolisОценок пока нет
- RabiesДокумент10 страницRabiesWinda LiraОценок пока нет
- DELIRIUMДокумент68 страницDELIRIUMVarada PanikkathОценок пока нет
- Protein Metab 2 Dra. SantosДокумент7 страницProtein Metab 2 Dra. SantosMelissa SalayogОценок пока нет
- Heart BNHAДокумент13 страницHeart BNHAX OloGyОценок пока нет
- Glomerulonephritis PresentationДокумент23 страницыGlomerulonephritis Presentationjacksonyu1234Оценок пока нет
- Agis Mira Dewi, S.kedДокумент35 страницAgis Mira Dewi, S.kedAgiish EMdeОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Storage Disorders PDFДокумент4 страницыGlycogen Storage Disorders PDFAHMEDОценок пока нет
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisДокумент69 страницAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganОценок пока нет
- Acid Base BalanceДокумент9 страницAcid Base BalanceNawarajendra MunakarmiОценок пока нет
- PancreatitisДокумент12 страницPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
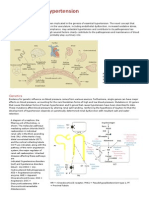
- Mechanism of HypertensionДокумент4 страницыMechanism of HypertensionAlya Putri KhairaniОценок пока нет
- Physiology Finals ReviewerДокумент22 страницыPhysiology Finals ReviewerDeomicah SolanoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology MaiaДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology Maiajia88Оценок пока нет
- Lymphocytosis 2017Документ3 страницыLymphocytosis 2017HafsahMalik100% (1)
- Glomerular FiltrationДокумент3 страницыGlomerular FiltrationyolandadwiooОценок пока нет
- High Acuity and Emergency SituationДокумент9 страницHigh Acuity and Emergency SituationRENEROSE TORRESОценок пока нет
- GERDДокумент2 страницыGERDRee AhmedОценок пока нет
- Final GIT Case PresentationДокумент53 страницыFinal GIT Case PresentationRovan100% (1)
- Neurological Manifestations of HIVДокумент34 страницыNeurological Manifestations of HIVashuОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionДокумент19 страницHeart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fractioncosmin balanОценок пока нет
- ConceptMap AMLДокумент1 страницаConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsОценок пока нет
- Management of OliguriaДокумент14 страницManagement of OliguriaAhmed El-MalkyОценок пока нет
- Hepatic EncephalopathyДокумент22 страницыHepatic EncephalopathyHussain RazaОценок пока нет
- Presentasi CKDДокумент21 страницаPresentasi CKDNubli LohОценок пока нет
- 4 Circulation Disorders PDFДокумент69 страниц4 Circulation Disorders PDFSetiawan SukmadjaОценок пока нет
- Renal PathologyДокумент28 страницRenal PathologyApril Deveras JudillaОценок пока нет
- Acute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanДокумент30 страницAcute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanHandre Putra100% (1)
- CPC Acute AppendicitisДокумент57 страницCPC Acute AppendicitisYS Nate100% (1)
- An Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriДокумент22 страницыAn Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDz PutraОценок пока нет
- Arthur Jones - Arthur Jones - Strength Curve AnalysisДокумент15 страницArthur Jones - Arthur Jones - Strength Curve AnalysisRafael Tavares LacerdaОценок пока нет
- Penjelasan Consort Utk Artikel KlinisДокумент28 страницPenjelasan Consort Utk Artikel KlinisWitri Septia NingrumОценок пока нет
- Khan, Chap 11Документ63 страницыKhan, Chap 11E. Saeedzadeh100% (1)
- Case ReportДокумент50 страницCase ReportTajul AnshorОценок пока нет
- Theoretical Models - Module 1 With ExercisesДокумент9 страницTheoretical Models - Module 1 With ExercisesCedrick Mesa Sali-otОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Positive Psychology PDFДокумент5 страницChapter 1 - Introduction To Positive Psychology PDFRhalfОценок пока нет
- Autism Insurance WorkshopДокумент1 страницаAutism Insurance Workshopsbockmann7148Оценок пока нет
- Eating Disorders PaperДокумент7 страницEating Disorders Paperapi-237474804Оценок пока нет
- Philippine Nursing Seminars and Training March 2011Документ3 страницыPhilippine Nursing Seminars and Training March 2011PhilippineNursingDirectory.comОценок пока нет
- Ovarian TumoursДокумент24 страницыOvarian TumoursBinta BaptisteОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент8 страницNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP Acute PainAngel HernandezОценок пока нет
- Firefly Product BrochureДокумент20 страницFirefly Product BrochureKidz to Adultz ExhibitionsОценок пока нет
- Autonomic HyperreflexiaДокумент3 страницыAutonomic HyperreflexiaGibe BebitaОценок пока нет
- Nclex 70 Question: Week 7Документ26 страницNclex 70 Question: Week 7RJ MarthewОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartДокумент3 страницыDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- NHS Highland Wound Management Guidelines and FormularyДокумент91 страницаNHS Highland Wound Management Guidelines and FormularyAnton NopiarОценок пока нет
- Trigger Point Manual PDFДокумент15 страницTrigger Point Manual PDFAngela Pagliuso67% (3)
- Pulpotomy Procedures in Primary Dentition PedoДокумент32 страницыPulpotomy Procedures in Primary Dentition PedoFourthMolar.comОценок пока нет
- Behavior Modification: Child Physical Exercise As A Reinforcer To Promote Calmness of An ADHDДокумент8 страницBehavior Modification: Child Physical Exercise As A Reinforcer To Promote Calmness of An ADHDrobfoxОценок пока нет
- Ameloblastoma of The Jaw and Maxillary Bone: Clinical Study and Report of Our ExperienceДокумент7 страницAmeloblastoma of The Jaw and Maxillary Bone: Clinical Study and Report of Our ExperienceKharismaNisaОценок пока нет
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesДокумент31 страницаMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesAzmi FarhadiОценок пока нет
- 8D-LRIS New ManualДокумент135 страниц8D-LRIS New Manualabap281471% (7)
- The Aetiology of Gingival RecessionДокумент4 страницыThe Aetiology of Gingival RecessionshahidibrarОценок пока нет
- Gracewell Product Faq's & Competetor KnockoutsДокумент25 страницGracewell Product Faq's & Competetor KnockoutskurutalaОценок пока нет
- What Is SkincareДокумент9 страницWhat Is SkincareSYEDA UROOJ BSSEОценок пока нет
- Proposal ThesisДокумент6 страницProposal ThesisJemarse GumpalОценок пока нет
- Board Exam Compilation Book 1Документ141 страницаBoard Exam Compilation Book 1Aaron Cy Untalan75% (8)
- Clinical Skills: Explaining Malaria To A Patient: WWW - Osce-Aid - Co.ukДокумент2 страницыClinical Skills: Explaining Malaria To A Patient: WWW - Osce-Aid - Co.ukRisfandi Ahmad TaskuraОценок пока нет
- Controlled Release Oral Drug Delivery SystemsДокумент37 страницControlled Release Oral Drug Delivery Systemsamitchauhan09Оценок пока нет