Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CVA. (Brain Attack) E.R
Загружено:
sonylynneИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CVA. (Brain Attack) E.R
Загружено:
sonylynneАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
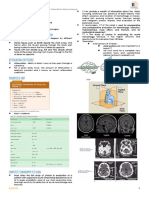
CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT (CVA)
EMERGENCY TREATMENT Stroke/BRAIN ATTACK
Emergency treatment of stroke from a blood clot is aimed at dissolving the clot. This
"thrombolytic
A stroke ortherapy"
brain attackis currently
occurs when performed mosttooften
blood flow with
an area of tissue plasminogen
the brain activator,
is interrupted or t-PA.or
by a blocked
This t-PA
broken must
blood be administered
vessel. When a within
stroke three
occurs, it
Fig - Subarachnoid Hemorrhage hours
kills of
brainthe stroke
cells in event.
the Therefore,
immediate area. patients
When who
the awaken
brain cells
withthey
die, stroke symptoms
release chemicalsarethat
ineligible
set off afor t-PA
chain therapy,
reaction that as the timebrain
endangers of onset
cells incannot be surrounding
a larger, accurately
determined.
area of brain The t-PA
tissue. therapyprompt
Without has been shown
medical to improve
treatment, thisrecovery
larger areaandofdecrease long-term
brain cells will alsodisability
die. in
selected patients. The t-PA therapy carries a 6.4% risk of inducing a cerebral hemorrhage, and is not
appropriate
When brain for
cellspatients
die, thewith bleeding
abilities disorders,
that area verycontrol
of the brain high blood
are lostpressure, known
or impaired. Someaneurysms, any
people recover
evidence of from
completely intracranial hemorrhage,
less serious or incidence
strokes, while others oflosestroke,
their head
lives trauma, or intracranial
to very severe ones. A surgery
stroke is
within the pasttreated
occasionally three months. Patients with
with thrombolysis clot-related
("clot (thrombotic
buster"), but usually or embolic) stroke who
with supportive careare ineligible
(speech and
for t-PA treatment
language may be treated
therapy, physiotherapy with
and heparin ortherapy)
occupational other bloodin a thinners, or with
"stroke unit" and aspirin or other
secondary anti-
prevention
clotting
with agents indrugs
antiplatelet casesArtery
some (aspirin Blood Flow
and often dipyridamole), blood pressure control, statins, and in selected
Fig - Hemorrhagic Stroke
patients with carotid endarterectomy and anticoagulation.
Emergency treatment of hemorrhagic stroke is aimed at controlling intracranial pressure.
Intravenous
TYPES OF STROKE urea or mannitol plus hyperventilation are the most common treatments. Corticosteroids
may also be used. Patients with reversible bleeding disorders such as those due to anticoagulant
treatment should have these bleeding disorders reversed, if possible.
Surgery for hemorrhage due to aneurysm may be performed if the aneurysm is close enough to
the cranial surface to allow access. Ruptured vessels are closed off to prevent rebleeding. For aneurysms
that are difficult to reach surgically, endovascular treatment may be used. In this procedure, a catheter
is guided from a larger artery up into the brain to reach the aneurysm. Small coils of wire are discharged
into the aneurysm, which plug it up and block off blood flow from the main artery.
“Stroke is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment. Prompt treatment improves the
chances of survival and increases the degree of recovery that may be expected. Fig - Ischemic
A person Stroke
who may have
suffered a stroke should be seen in a hospital emergency room without delay. Treatment to breakStroke
Ischemic up a
blood
In clot, the
ischemic major
stroke, cause
a clot of stroke,
blocks a bloodmust begin
vessel within
in the brain.three hours
A clot mayofform
the in
stroke to be
a blood effective.
vessel in the
Improved
brain medical
or leading treatment
to the of itallcan
brain, or types of stroke
be formed has resulted
elsewhere in theinbody,
a dramatic
usually decline in death
in the heart, and rates
travelinto
recent
the decade”
brain. Ischemic stroke can also happen as the result of the unhealthy blood vessels clogged with a
buildup of fatty deposits and cholesterol in the wall of an artery. Approximately 80 percent of all strokes
are ischemic.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Hemorrhagic Stroke
In hemorrhagic strokes, a blood vessel in the brain breaks or ruptures. Hemorrhagic stroke can be caused
by a number of disorders which affect the blood vessels, including long-standing high blood pressure and
cerebral aneurysms. An aneurysm is a weak or thin spot on a blood vessel wall. Hemorrhagic strokes
account for about 20 percent of all brain attacks.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Even among thoseFig
who- Electroencephalogram
recognize brain attack- EEG
as a medical emergency, many are unable to recognize
stroke symptoms. The most typical symptoms include:
To fullySudden
understand
numbness
yourorproblem
weaknessand of face,
plan arm
the orbest
leg,treatment
especiallyfor
on one
you,side
theofphysician
the body. may need
additional information
o An entire such
side
as:ofblood
the body,
tests,face,
special
armtests
and leg
or procedures
(hemiparesis).
to examine your brain, heart or
blood vessels.
o An arm or a leg (monoparesis).
Sudden confusion, troble speaking or understanding.
Tests to Define Expressing
o Stroke, or comprehending
Stroke Typing and where words (aphasia).
is the stroke:
o Slurring of words (dysarthria).
Sudden
Computedtrouble seeing in(CT
Tomography one scan)
or both eyes.
o Loss
Magnetic of visionImaging
Resonance in one eye.
(MRI)
o Loss of vision of one side.
o theDouble
Test to assess vision.
conditions of Blood Vessels in the Neck or Brain:
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination.
o Loss
Magnetic of balance
Resonance on standing(MRA)
Angiography or walking (truncal ataxia).
Carotido Of arm or
Duplex leg(CDS)
Scan (limb ataxia).
Transcranial Doppler (TCD)
Cerebral Angiogram
Вам также может понравиться
- Clinical Neurology: Key Structures and Stroke ClassificationДокумент19 страницClinical Neurology: Key Structures and Stroke Classificationalix dayОценок пока нет
- Stroke: Audrey LeeДокумент25 страницStroke: Audrey LeeLurbieleeОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Takotsubo SyndromeДокумент16 страницPathophysiology of Takotsubo Syndromegwyneth.green.512Оценок пока нет
- Linician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaДокумент6 страницLinician Pdate: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular TachycardiaSonia Rahma AОценок пока нет
- Treatment Concepts For Wake-Up Stroke and Stroke With Unknown Time of Symptom OnsetДокумент7 страницTreatment Concepts For Wake-Up Stroke and Stroke With Unknown Time of Symptom OnsetHùng Phạm Lý ChíОценок пока нет
- NEURO2 3.05 Neurosurgical Management of Stroke and CNS Infection - Dr. Domingo PDFДокумент3 страницыNEURO2 3.05 Neurosurgical Management of Stroke and CNS Infection - Dr. Domingo PDFPatricia Nicole AlcarazОценок пока нет
- Methodic Materials Ischemic StrokeДокумент22 страницыMethodic Materials Ischemic StrokeKapil PancholiОценок пока нет
- 7 Drug StudyДокумент17 страниц7 Drug StudyMa. Mechile MartinezОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutДокумент2 страницыIschemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutAlexandra OpreaОценок пока нет
- Your Health - 23 March 2021Документ5 страницYour Health - 23 March 2021Times MediaОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Arrhythmias and Sudden Death in Subarachnoid HemorrhageДокумент5 страницCardiac Arrhythmias and Sudden Death in Subarachnoid HemorrhageRaghul KrishnasamyОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Review On Craniectomy And.28Документ4 страницыContemporary Review On Craniectomy And.28ja.arenas904pfizerОценок пока нет
- NEURO2 1.02C Hemorrhagic Stroke - Dr. HiyadanДокумент2 страницыNEURO2 1.02C Hemorrhagic Stroke - Dr. HiyadanAra Diocos100% (1)
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Management Review For The HospitalistДокумент27 страницAcute Ischemic Stroke: Management Review For The HospitalistaddelinsОценок пока нет
- Stroke: Cerebro Vascular Accident" (CVA)Документ37 страницStroke: Cerebro Vascular Accident" (CVA)Elfrida HaznaОценок пока нет
- 01.CIR.11.6.963 - Jun1955Документ8 страниц01.CIR.11.6.963 - Jun1955kapmixalisОценок пока нет
- 01strok & AnatomyДокумент18 страниц01strok & AnatomyYudistira Wahyu Putra PradanaОценок пока нет
- Stroke 1985 Kassell 562 72Документ12 страницStroke 1985 Kassell 562 72aime_meldaОценок пока нет
- Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation 2nd Edition - (Chapter 3 Pathophysiology and Management of Acute Stroke)Документ13 страницStroke Recovery and Rehabilitation 2nd Edition - (Chapter 3 Pathophysiology and Management of Acute Stroke)Usamah HussainОценок пока нет
- Thrombolytic Therapy For StrokeДокумент13 страницThrombolytic Therapy For Strokereza ahda kadirОценок пока нет
- Brain Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The Role of Thrombin and IronДокумент4 страницыBrain Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The Role of Thrombin and Irongrandville cabildoОценок пока нет
- VascularДокумент3 страницыVascularalmira.s.mercadoОценок пока нет
- Plasticity After Brain DamageДокумент8 страницPlasticity After Brain DamageErika BОценок пока нет
- Plasticity After Brain DamageДокумент8 страницPlasticity After Brain DamageErika BОценок пока нет
- Assessment, Controversy, and Confounding Factors: Brain DeathДокумент23 страницыAssessment, Controversy, and Confounding Factors: Brain DeathdewiОценок пока нет
- ANT Aug 2016 CE 630Документ6 страницANT Aug 2016 CE 630Maged SaadОценок пока нет
- Surgical Treatment of ArrhythmiaДокумент8 страницSurgical Treatment of ArrhythmiaVirgilio AbellanaОценок пока нет
- Stroke InfographДокумент1 страницаStroke Infographapi-512543832Оценок пока нет
- Critical care in the emergency department: shock and circulatory supportДокумент6 страницCritical care in the emergency department: shock and circulatory supportPaulHerreraОценок пока нет
- Stroke NotecardsДокумент7 страницStroke NotecardsmissjasminerwilsonОценок пока нет
- Management Wake Up StrokeДокумент6 страницManagement Wake Up StrokeHùng Phạm Lý ChíОценок пока нет
- Life-Threatening Headaches in Children: Clinical Approach and Therapeutic OptionsДокумент7 страницLife-Threatening Headaches in Children: Clinical Approach and Therapeutic OptionsdelilamhrnОценок пока нет
- Actilyse AIS 2Документ30 страницActilyse AIS 2UunsariОценок пока нет
- Bradycardia MGTДокумент7 страницBradycardia MGTTHARUN kumarОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseДокумент4 страницыCerebrovascular DiseaseAJ TeohОценок пока нет
- Insignis Surgery NeurosurgeryДокумент15 страницInsignis Surgery NeurosurgeryAla'a Emerald AguamОценок пока нет
- Management of Cerebral Edema: Pediatrics in Review January 1983Документ11 страницManagement of Cerebral Edema: Pediatrics in Review January 1983odi pjОценок пока нет
- Anaphysio 9b Cva Bleed Vs InfarctДокумент5 страницAnaphysio 9b Cva Bleed Vs InfarctAngayan, Merry GraceОценок пока нет
- Stroke PDF SlidesДокумент10 страницStroke PDF SlidesIbsaa UsmanОценок пока нет
- (Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyДокумент3 страницы(Clonidine) : Drug Class: Ates Alpha-Adrenoceptors in The Brain Stem. Blood Pressure and Pulse Rate Frequent LyKrizha Angela NicolasОценок пока нет
- Anastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockageДокумент5 страницAnastomosis Left Anterior Cerebral Artery BlockagemcwnotesОценок пока нет
- AHA Guideline Best TenДокумент12 страницAHA Guideline Best Tenviva dialysisОценок пока нет
- 01 Cir 41 6 899Документ14 страниц01 Cir 41 6 899אני זאקОценок пока нет
- Wise Et Al 1972 The Treatment of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor DrugsДокумент6 страницWise Et Al 1972 The Treatment of Brain Ischemia With Vasopressor DrugsvinhanОценок пока нет
- Stroke NCPДокумент5 страницStroke NCPChantal Caragan100% (1)
- Jurnal 12Документ10 страницJurnal 12Zella ZakyaОценок пока нет
- What You Should Know About Retinal Transient Ischemic Attacks (Amaurosis Fugax)Документ2 страницыWhat You Should Know About Retinal Transient Ischemic Attacks (Amaurosis Fugax)Zakiyul FuadОценок пока нет
- Symmetry: Symmetry of The Brain Is The Key To RadiologicДокумент7 страницSymmetry: Symmetry of The Brain Is The Key To RadiologicVon HippoОценок пока нет
- Intracraneanal PressureДокумент8 страницIntracraneanal PressurearturoОценок пока нет
- Chen Et Al 2018 Angioedema and Hemorrhage After 4 5 Hour Tpa (Tissue Type Plasminogen Activator) ThrombolysisДокумент9 страницChen Et Al 2018 Angioedema and Hemorrhage After 4 5 Hour Tpa (Tissue Type Plasminogen Activator) Thrombolysisdiajeng gayatriОценок пока нет
- Advances in Acute Ischemic Stroke TherapyДокумент22 страницыAdvances in Acute Ischemic Stroke TherapylorenaОценок пока нет
- 01 Cir 27 1 5Документ7 страниц01 Cir 27 1 5YabesОценок пока нет
- Activase for Acute Ischemic Stroke and Heart ConditionsДокумент3 страницыActivase for Acute Ischemic Stroke and Heart Conditionsmharjoe pulmanoОценок пока нет
- A Case of Complete Heart Block With Diagnostic ChaДокумент4 страницыA Case of Complete Heart Block With Diagnostic ChaZulkarnain MuinОценок пока нет
- Management of Brainstem HaemorrhagesДокумент9 страницManagement of Brainstem HaemorrhagesadsfdhОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Practical GuideДокумент12 страницCerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Practical Guidedanby danbyОценок пока нет
- STROKEДокумент11 страницSTROKEluvvemulleОценок пока нет
- Intracranial HemorrhageДокумент5 страницIntracranial HemorrhageMa. Cathlea SarmientoОценок пока нет
- A New Lease on Life: Defying the Odds of Survival Following a Brain AneurysmОт EverandA New Lease on Life: Defying the Odds of Survival Following a Brain AneurysmОценок пока нет
- Neonatal SepsisДокумент87 страницNeonatal Sepsisyhanne100% (129)
- OSTEOSARCOMA Final Case PressДокумент33 страницыOSTEOSARCOMA Final Case Presssonylynne100% (6)
- NCP NewbornДокумент2 страницыNCP Newbornsonylynne94% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan for Activity IntoleranceДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan for Activity IntolerancesonylynneОценок пока нет
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Gynecology Department Case PresentationДокумент27 страницGestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Gynecology Department Case PresentationsonylynneОценок пока нет
- Safety Aspects of Probiotic ProductsДокумент4 страницыSafety Aspects of Probiotic ProductsSrinivas PingaliОценок пока нет
- Alpers' DiseaseДокумент5 страницAlpers' DiseaseDANY PAUL BABYОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент12 страницUntitledjhony192Оценок пока нет
- DIABETIC FOOT ULCER CASEДокумент28 страницDIABETIC FOOT ULCER CASEBima Sena Arya YudhaОценок пока нет
- Applying Neuromuscular Techniques in The Orthodontic SettingДокумент13 страницApplying Neuromuscular Techniques in The Orthodontic SettingMahdi ChahrourОценок пока нет
- Journal InternasionalДокумент6 страницJournal InternasionalRizka ZahroОценок пока нет
- National Leprosy Eradication ProgrammeДокумент9 страницNational Leprosy Eradication ProgrammeRekha ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Nursing Practice IIДокумент18 страницNursing Practice IIstuffednurseОценок пока нет
- Metastatic Bone DiseaseДокумент14 страницMetastatic Bone DiseaseNanda GemaОценок пока нет
- Nail PsoriasisДокумент13 страницNail PsoriasisAira KellyОценок пока нет
- Amlodipine Side EffectsДокумент6 страницAmlodipine Side Effects1976gt500Оценок пока нет
- Aspartame's DangersДокумент67 страницAspartame's DangersCrazy LukeОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource Was: Spinal Cord Injury Case StudyДокумент3 страницыThis Study Resource Was: Spinal Cord Injury Case StudyMiss GОценок пока нет
- End Stage Renal DiseaseДокумент9 страницEnd Stage Renal DiseaseShantanu DixitОценок пока нет
- Ethics Quiz 1Документ4 страницыEthics Quiz 1Estelle LegrosОценок пока нет
- Types of AnemiaДокумент11 страницTypes of AnemiaCHRISTIE MONTANO50% (2)
- ProjectДокумент64 страницыProjectPradip DindaОценок пока нет
- Understanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentДокумент16 страницUnderstanding Leukaemia: Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentArnab Ghosh100% (1)
- Endophthalmitis 1Документ42 страницыEndophthalmitis 1Nasrin sultana rmcОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Managing and Coordinating Nursing Care Fifth EditionДокумент7 страницTest Bank For Managing and Coordinating Nursing Care Fifth Editionkelliejenkinsxzqnyeajkt100% (23)
- Scientific evidence for clinical use of horsetailДокумент23 страницыScientific evidence for clinical use of horsetailDanilo Maciel Carneiro100% (1)
- Presentation CISPДокумент46 страницPresentation CISPPradeep87% (15)
- Clinical Trial Gadavala SarahДокумент60 страницClinical Trial Gadavala SarahSejal khuman100% (1)
- Hot Sitz Bath ReliefДокумент10 страницHot Sitz Bath ReliefJohn Aladin ArcetaОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal MotilityДокумент20 страницGastrointestinal Motilitymuh nuerОценок пока нет
- Carotid Sinus Massage Procedure DetailsДокумент3 страницыCarotid Sinus Massage Procedure DetailsSandeep m rОценок пока нет
- Final EPHA & JOSI IPCДокумент44 страницыFinal EPHA & JOSI IPCephrembz33Оценок пока нет
- Cases in Nephrology by Muhammad Rafiqul AlamДокумент9 страницCases in Nephrology by Muhammad Rafiqul AlamSELLULARОценок пока нет
- Delfinm QsenДокумент57 страницDelfinm Qsenapi-346220114Оценок пока нет
- Allopurinol & ColchicineДокумент1 страницаAllopurinol & ColchicineSibel ErtuğrulОценок пока нет