Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 5 Case Study
Загружено:
Alex ArmpИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 5 Case Study
Загружено:
Alex ArmpАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CCNA Exploration: LAN Switching and Wireless
Chapter 5 Case Study
Objectives:
• Consolidate the knowledge of the STP concept and configuration
• Enforce the difference between STP port roles and STP Port states
Intro:
Ajax had a failure in one of its secondary trunk links which kept a relevant portion of the network with no
connectivity. After this problem, they decided to implement redundancy between the switches in order to
avoid the problem from happening again.
The Scenario:
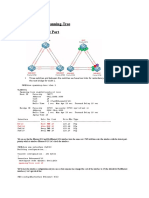
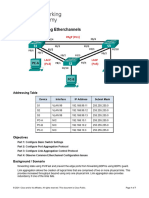
After a quick look at Ajax network, you decide to connect a few more cables between the switches in
order to achieve some redundancy. Ajax’s updated topology is shown below. Because Ajax now has
redundant links between its switches, the spanning tree protocol is necessary to avoid layer 2 loops.
Topology:
© 2009 Cisco Learning Institute
CCNA Exploration: LAN Switching and Wireless
Chapter 5 Case Study
Using crossed cables, you connect SW2’s ports fa0/20 and 21 to SW3’s port fa0/20 and 21 respectively
and SW3’s port fa0/22 and 23 to SW4’s port fa0/22 and 23. You also connect SW1’s port fa0/16 to SW2’s
port fa0/22, SW1’s port fa0/17 to SW3’s port fa0/19 and SW1’s port fa0/18 to SW4’s fa0/21. All of those
links will work as a backup path to reach the root bridge and you configure all of them as trunk links. The
table below has the port mapping you created:
From: To:
SW1 fa0/16 SW2 fa0/22
SW1 fa0/17 SW3 fa0/19
SW1 fa0/18 SW4 fa0/21
SW2 fa0/20 SW3 fa0/20
SW2 fa0/21 SW3 fa0/21
SW3 fa0/22 SW4 fa0/22
SW3 fa0/23 SW4 fa0/23
Because SW1 is a better switch when it comes to processing power and amount of memory, you decide
to make it the root bridge of the tree. To ensure no other switch but SW1 will be elected root bridge, you
change SW1 priority. Since a different instance of SPT is created for each VLAN and you want SW1
acting as root bridge for all 3 VLANs, in SW1, you issue the same command for each VLAN. The
command used changes the bridge priority of SW1 to make it the root bridge for the specified VLANs.
The commands are listed below:
SW1# configure terminal
SW1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 10 root primary
SW1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 20 root primary
SW1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 30 root primary
SW1(config)# end
© 2009 Cisco Learning Institute
CCNA Exploration: LAN Switching and Wireless
Chapter 5 Case Study
Question 1:
In a switched LAN environment, the switch elected as root bridge is the switch with highest-priority bridge
ID (lowest numeric bridge ID value). Based on the structure of the bridge ID, is it correct to state that a
switch with priority set to 0 will always become the root bridge? Explain.
Answer: No. Even if a switch has its priority set to 0, another switch, which also had its priority set to 0,
could be elected root bridge if its MAC address was lower than the first switch’s. Cisco created a feature
called Root Guard to ensure a switch will always be the root bridge. For more information on Cisco root
guard, see:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_tech_note09186a00800ae96b.shtml
To ensure SW1 will be the root bridge, you connect the console cable to SW2, SW3 and SW4 and check
their SPT priorities. Since SW2, SW3 and SW4 SPT bridge priorities are set to the default value, SW1 will
become the root bridge.
Question 2:
What is the default bridge priority?
Answer: 32768
Once you ensured SW1 will be elected the root bridge, you decide to do some adjustments in order to
optimize SPT operation and network overall performance.
Because the ports connected to end devices under SW2, SW3 and SW4 won’t have any switches, loops
will not be created through such ports. Since no loops will be created, there is no point to have such ports
going through all SPT states before they can forward traffic. You connect to SW2, SW3 and SW4 and
configure all ports connected only to end devices with the spanning-tree portfast command.
SW2(config)# int ra fa0/1 – 15
SW2(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
%Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host.
Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to this interface when
portfast is enabled, can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with CAUTION.
%Portfast has been configured on FastEthernet0/1 - 15 but will only
have effect when the interface is in a non-trunking mode.
SW2(config-if)# end
SW3(config)# int ra fa0/1 – 15
SW3(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
%Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host.
Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to this interface when
portfast is enabled, can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with CAUTION.
%Portfast has been configured on FastEthernet0/1 - 15 but will only
have effect when the interface is in a non-trunking mode.
SW3(config-if)# end
© 2009 Cisco Learning Institute
CCNA Exploration: LAN Switching and Wireless
Chapter 5 Case Study
SW4(config)# int ra fa0/1 – 15
SW4(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
%Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host.
Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to this interface when
portfast is enabled, can cause temporary spanning tree loops. Use with CAUTION.
%Portfast has been configured on FastEthernet0/1 - 15 but will only
have effect when the interface is in a non-trunking mode.
SW4(config-if)# end
Note: As shown on the output above, be careful when configuring ports as SPT portfast.
Verifying
You connect to SW1 and issue the sh spanning-tree vlan command to ensure it became the root
bridge for VLAN 10, 20 and 30. Notice that the priority value has changed from the default of 32768 to a
smaller value and SW1 is actually the root bridge.
SW1#show spanning vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24596
Address 000f.90e2.1300
This bridge is the root
SW1#show spanning vlan 20
VLAN0020
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24606
Address 000f.90e2.1300
This bridge is the root
SW1#show spanning vlan 30
VLAN0030
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24606
Address 000f.90e2.1300
This bridge is the root
© 2009 Cisco Learning Institute
CCNA Exploration: LAN Switching and Wireless
Chapter 5 Case Study
You watch the switches and notice while SPT assign correct port roles to the switch ports. As expected,
since SW1 is the root bridge, all SW1 ports are playing the role of designated ports and are in the SPT
forwarding state.
SW4 has one port playing the role of root port (fa0/21) and one port playing the role of designate port
(fa0/22). The other SW4 ports took the Non-Designated port role and are in SPT blocking state.
SW3 has one root port (fa0/19) and 2 designated ports (fa0/20 and fa0/22). All other ports are non-
designated ports and are in blocking state.
As SW4, SW2 also has one root port (fa0/22) and one designated port (fa0/20) and all other port are non-
designated ports in blocking state.
Note: In some implementations of SPT, non-designated ports are called alternate port.
You watch port roles being assigned and ports going through SPT states while the switched LAN
converges.
© 2009 Cisco Learning Institute
Вам также может понравиться
- Ccie Enterprise Infrastructure Practice Lab3 Ver - 1Документ39 страницCcie Enterprise Infrastructure Practice Lab3 Ver - 1Aye KyawОценок пока нет
- Ccna Rs Workbook PDFДокумент151 страницаCcna Rs Workbook PDFJesse Oliveira100% (1)
- Java PuzzlersДокумент55 страницJava Puzzlersme100% (21)
- Senior Mainframe Software Developer in Dallas FT Worth TX Resume Stephen RookДокумент3 страницыSenior Mainframe Software Developer in Dallas FT Worth TX Resume Stephen RookStephenRookОценок пока нет
- Caso de Estudio STPДокумент5 страницCaso de Estudio STPgattoboxОценок пока нет
- IEWB-RS Volume 2 Lab 1: Difficulty Rating (10 Highest) : 5 Lab OverviewДокумент18 страницIEWB-RS Volume 2 Lab 1: Difficulty Rating (10 Highest) : 5 Lab OverviewAlejandro PerezОценок пока нет
- CAP 9Документ51 страницаCAP 9jhonathan.f.t.1996Оценок пока нет
- CCNA3 FINAL (91,8%) : WWW - Ccna4u.tk WWW - Ccna4u.infoДокумент30 страницCCNA3 FINAL (91,8%) : WWW - Ccna4u.tk WWW - Ccna4u.infoBaies CosminОценок пока нет
- A5 byCCIEMAN2016 - NonvrfДокумент60 страницA5 byCCIEMAN2016 - Nonvrfperico100% (1)
- CCNP LAB SwitchingДокумент138 страницCCNP LAB SwitchingAbdelhaiОценок пока нет
- 3e 06.4.1 Inter Vlan RoutingДокумент14 страниц3e 06.4.1 Inter Vlan RoutingEnrique Daniel Sanchez CordovaОценок пока нет
- Networking Technology NET 272 Lab Exercise Advanced STP - RSTP+, RSTP, MST ObjectivesДокумент5 страницNetworking Technology NET 272 Lab Exercise Advanced STP - RSTP+, RSTP, MST ObjectiveschrisncissОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Lab 2 Assignment-1Документ10 страницWeek 3 Lab 2 Assignment-1Wenyang WuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices Using Network Time Protocol (NTP)Документ15 страницChapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices Using Network Time Protocol (NTP)alexis pedrozaОценок пока нет
- Incorrect Root Port: Troubleshooting Spanning-TreeДокумент9 страницIncorrect Root Port: Troubleshooting Spanning-Treetjr120Оценок пока нет
- HSRP, VRRP, STPДокумент12 страницHSRP, VRRP, STPAshutosh SaxenaОценок пока нет
- ESwitching Lab 3 5 1Документ7 страницESwitching Lab 3 5 1Ninja NuggetОценок пока нет
- 16-Troubleshooting EtherChannel IДокумент11 страниц16-Troubleshooting EtherChannel Imansoorali_afОценок пока нет
- Inter-VLAN Routing ConfigurationДокумент10 страницInter-VLAN Routing ConfigurationGoodsonОценок пока нет
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab7-1 NTP InstructorДокумент20 страницCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab7-1 NTP InstructorCarlos CaicedoОценок пока нет
- Lab - Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology (Use F0/1 Anywhere It Says G0/1) (Most Answers Appear, You Complete Last Two Questions On pp6-7)Документ17 страницLab - Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology (Use F0/1 Anywhere It Says G0/1) (Most Answers Appear, You Complete Last Two Questions On pp6-7)Muhd SyarafuddinОценок пока нет
- CCNP BCMSN - Module - 3 - Exam-CCNPSpanning-TreeДокумент6 страницCCNP BCMSN - Module - 3 - Exam-CCNPSpanning-TreetootootoОценок пока нет
- Ccnpv7.1 Switch Lab7-1 NTP StudentДокумент11 страницCcnpv7.1 Switch Lab7-1 NTP Studentutoso utosoОценок пока нет
- 01.more LAN SwitchingДокумент45 страниц01.more LAN SwitchingasegunloluОценок пока нет
- 3.4.6 Lab - Configure VLANs and TrunkingДокумент8 страниц3.4.6 Lab - Configure VLANs and TrunkingFrizzy ArtsОценок пока нет
- Activity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration NOTE TO USER: This Activity Is A Variation of Lab 3.5.1. Packet Tracer May NotДокумент6 страницActivity 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration NOTE TO USER: This Activity Is A Variation of Lab 3.5.1. Packet Tracer May NotmedrekОценок пока нет
- Ccna Rs WorkbookДокумент149 страницCcna Rs Workbookwjjjxs0% (1)
- Lab 1Документ10 страницLab 1Tomas Rodriguez RamirezОценок пока нет
- Module 4Документ11 страницModule 4هبة عمار كاظمОценок пока нет
- Q in Q TunnelingДокумент17 страницQ in Q TunnelingNabeel SalmanОценок пока нет
- ESwitching Lab 5 5 2Документ20 страницESwitching Lab 5 5 2Ninja NuggetОценок пока нет
- VLAN workshop (2024)Документ6 страницVLAN workshop (2024)Theshika NavodОценок пока нет
- Dis3 Ch3.4.3.5B LabДокумент6 страницDis3 Ch3.4.3.5B Labdoomer2k51452Оценок пока нет
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IGДокумент5 страниц2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IGJose Affleck100% (1)
- Configure additional commands needed for remote switch accessДокумент28 страницConfigure additional commands needed for remote switch accessHassoun Ben AissaОценок пока нет
- AOS-CX Simulator - VRF Part 1 Lab GuideДокумент17 страницAOS-CX Simulator - VRF Part 1 Lab Guiderashmi mОценок пока нет
- 17-Troubleshooting EtherChannel IIДокумент12 страниц17-Troubleshooting EtherChannel IImansoorali_afОценок пока нет
- STP spanning tree protocol overviewДокумент28 страницSTP spanning tree protocol overviewjohnОценок пока нет
- CCNA3 Chap 3 Study QuestionsДокумент5 страницCCNA3 Chap 3 Study QuestionsGuillermo RemacheОценок пока нет
- Cisco Lab AnswersДокумент20 страницCisco Lab AnswersNada Nader El-ibiary100% (1)
- INFT-WEEK03 - Lab02 - Implement VLANs and Trunking - Fall2023Документ6 страницINFT-WEEK03 - Lab02 - Implement VLANs and Trunking - Fall2023mookshoОценок пока нет
- Final 3 Modelo 2Документ5 страницFinal 3 Modelo 2ROD333Оценок пока нет
- Ccna 3 Final Exam NotesДокумент67 страницCcna 3 Final Exam NotesaoryaОценок пока нет
- Lab5test - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMДокумент12 страницLab5test - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMaizatfikriОценок пока нет
- HCIE-R&S Lab Mock Exam 1 With SolutionsДокумент34 страницыHCIE-R&S Lab Mock Exam 1 With SolutionsAnonymous 4Db63nJ4G100% (1)
- Configure Port Security, VLANs, Trunking, STP and CDPДокумент4 страницыConfigure Port Security, VLANs, Trunking, STP and CDPشيماء عياشيОценок пока нет
- Task 1: Prepare The Network: System and Network Admin Lab 2Документ8 страницTask 1: Prepare The Network: System and Network Admin Lab 2Bethelhem YetwaleОценок пока нет
- Cisco Basic CCNA Lab Setup InstructionsДокумент6 страницCisco Basic CCNA Lab Setup InstructionstouzogОценок пока нет
- Ccna3 Final - Eswitching Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)Документ29 страницCcna3 Final - Eswitching Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)m1chhОценок пока нет
- Assist 2.2 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU GuardДокумент18 страницAssist 2.2 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast, and BPDU GuardrewdasОценок пока нет
- Lab To Do - Configuring VTP Clients and Servers On Catalyst SwitchesДокумент6 страницLab To Do - Configuring VTP Clients and Servers On Catalyst SwitchesToufik AblaouiОценок пока нет
- Native VLAN and Default VLANДокумент6 страницNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyОценок пока нет
- 14-Troubleshooting Spanning TreeДокумент13 страниц14-Troubleshooting Spanning Treemansoorali_afОценок пока нет
- LAN Switching and Wireless Final Exam AnswersДокумент16 страницLAN Switching and Wireless Final Exam AnswersMoacir MoraesОценок пока нет
- Spanning Tree-At-A-Glance: Courtesy of Cisco Enterprise MarketingДокумент1 страницаSpanning Tree-At-A-Glance: Courtesy of Cisco Enterprise MarketingKishore LakkamrajuОценок пока нет
- Lab 3.1Документ7 страницLab 3.1Riia PangilinanОценок пока нет
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IG MarioДокумент18 страниц2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring PVST+ Instructions IG MarioARОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент4 страницыCase StudyRuthsiñaRuizZuletaОценок пока нет
- Performance Analysis of A Spanning Tree Protocol: Harsha Natarajan, Karthik Ram,, Abhishek ChallaДокумент4 страницыPerformance Analysis of A Spanning Tree Protocol: Harsha Natarajan, Karthik Ram,, Abhishek ChallaGiang ĐỗОценок пока нет
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksОт EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksОценок пока нет
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsОт EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor Lab Manual - FinalДокумент157 страницMicroprocessor Lab Manual - FinalDr. N.Shanmugasundaram100% (6)
- W M U G NL: Automation How To Make My IT Life EasierДокумент34 страницыW M U G NL: Automation How To Make My IT Life EasierHamelОценок пока нет
- UNYOUG Exadata NiemiecДокумент178 страницUNYOUG Exadata NiemiecasifanwОценок пока нет
- Java Fundamentals 4-4: Strings Practice Activities: Lesson ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыJava Fundamentals 4-4: Strings Practice Activities: Lesson Objectivesvoceho3066Оценок пока нет
- RAID LevelsДокумент2 страницыRAID LevelsVamsi BonamОценок пока нет
- Assignment No 2: My SQL Server Data Types and Their PurposesДокумент2 страницыAssignment No 2: My SQL Server Data Types and Their PurposeszaianbОценок пока нет
- Ec2 Ug PDFДокумент1 001 страницаEc2 Ug PDFGisha RoyОценок пока нет
- The Work Life of Developers: Activities, Switches and Perceived ProductivityДокумент17 страницThe Work Life of Developers: Activities, Switches and Perceived ProductivityDante Callo FuentesОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoДокумент77 страницIntroduction To Computers and Java: Walter Savitch Frank M. CarranoBrandon KozakОценок пока нет
- Resolve "Failed to set (contentViewController) user defined inspected property on (NSWindowДокумент2 страницыResolve "Failed to set (contentViewController) user defined inspected property on (NSWindowlazkrissОценок пока нет
- Samsung YP-S5 ManualДокумент121 страницаSamsung YP-S5 ManualRossDoughtyОценок пока нет
- An 97076Документ60 страницAn 97076Bedreddin KarakuşОценок пока нет
- LOGO Soft Comfort V6.0Документ1 страницаLOGO Soft Comfort V6.0Felix Sanchez0% (1)
- F5 Solutions Playbook September 2016 PDFДокумент92 страницыF5 Solutions Playbook September 2016 PDFlinwintkОценок пока нет
- Computer-Networks Lecture 2 SlideДокумент26 страницComputer-Networks Lecture 2 SlidekdkdkdОценок пока нет
- DH XVR7x16-X MultiLang V4.001.0000000.15.R.211013 Release-Notes PDFДокумент6 страницDH XVR7x16-X MultiLang V4.001.0000000.15.R.211013 Release-Notes PDFMinou NmiОценок пока нет
- TC-P42X3X: 42 Inch Class 720p Plasma HDTVДокумент7 страницTC-P42X3X: 42 Inch Class 720p Plasma HDTVEstuardoОценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting VMMДокумент119 страницTroubleshooting VMMCash Sly0% (1)
- McAfee SIEM Collector Installation and Configuration v1 2Документ19 страницMcAfee SIEM Collector Installation and Configuration v1 2hemant shekhawatОценок пока нет
- DevSecOps A CASE STUDY ON A SAMPLE IMPLEMENTATIONДокумент4 страницыDevSecOps A CASE STUDY ON A SAMPLE IMPLEMENTATIONQuân - VCCloud Đinh CôngОценок пока нет
- Products3329CM284 S12Документ2 страницыProducts3329CM284 S12Imran ShaukatОценок пока нет
- ELX025 QuickStartGuideДокумент4 страницыELX025 QuickStartGuidesohaibsindhuОценок пока нет
- Java LanguageДокумент17 страницJava LanguageAna RamonaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ12 страницChapter 3Thoviti Lava KumarОценок пока нет
- Display Translator Users Guide EP-DSX816Документ68 страницDisplay Translator Users Guide EP-DSX816BouazzaОценок пока нет
- LogДокумент69 страницLogBryan Grimaldo MababaoОценок пока нет
- Tutorial NUnitДокумент6 страницTutorial NUnitHasam HassanОценок пока нет
- Method Overloading vs Overriding PresentationДокумент17 страницMethod Overloading vs Overriding Presentationbit0203Оценок пока нет