Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Text Analysis Prompts
Загружено:
jeanettelansИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Text Analysis Prompts
Загружено:
jeanettelansАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
text analysis prompts
REGISTER = purpose + audience + context
formal, informal, colloquial, slang, personal, expressive, transactional, poetic, etc …
Level of Language Explanation Examples
Formal This is language that is correct and proper. It does The care was dilapidated and needing
not contain contractions. It is carefully composed. repair.
This is how we speak in formal situations when we Mum was very upset because she was
are watching what we say. It is also the level we use extremely worried about us.
in essays. It is more elevated than colloquial
language. “Can you not come?”
Informal or This is everyday language. It is the level of language The car was an old bomb.
Colloquial we use with our friends and family. It may include
contractions and colloquialisms (every day Mum was having a fit because she was
expressions like, driving me crazy, over the moon…). worried sick about us.
It generally sounds far more chatty than formal “Can’t you come?”
language.
Slang This is language that belongs to a set group in In the 1960s and 1970s there was a lot
society. It is somewhat exclusive since, if you do not of slang that is no longer common eg
belong to the group, you are unlikely to understand fuzz for police, bread for money or cat
it. Slang tends to be words and phrases rather than for a hip young man. One word that
complete sentences. has moved into our colloquial
vocabulary is cool. Its use is so
Some slang is that of young people and some widespread that it is no longer
belongs to interest groups like surfers, skaters etc. exclusive.
Slang tends to date quickly. It can actually move
into everyday language if it becomes widespread More recently young people have used
and stays in our vocabulary. sick to mean ‘great’ and this is a form
of slang.
The language of the text is [FORMAL, INFORMAL, COLLOQUIAL, SLANG] that is ….
o understated o transactional o ambiguous
o impartial o sophisticated o persuasive
o assertive o simplistic o serious
o biased o superficial o condescending
o propagandistic o antagonistic o arrogant
o cynical o distorted o dignified
o ironic o euphemistic o indifferent
o polite o rational o angry
o sarcastic o emphatic o humorous
o enthusiastic o precise o scientific
o jovial o genial o considered
o hostile o vague o sincere
o affectionate o blunt o childish
o personal o passionate o poetic
o expressive
This language/visual feature/technique ….
o attracts/draws attention to … o emphasises … o tells the audience …
o shows that … o promotes … o discusses …
o suggests that … o illustrates … o highlights …
o contrasts with … o encourages … o features …
o implies … o creates empathy for … o creates a sense of …
o adds appeal by … o encourages … o suggests a sense of …
o reinforces … o enriches … o makes it more …
o enhances … o involves readers in … o maximizes …
o involves … o describes … o appeals to …
o describes … o enriches …
PURPOSE LANGUAGE FEATURE PURPOSE LANGUAGE FEATURE
o factual statements o slogans
o technical language o facts and figures
INFORM PERSUADE
o ‘who, what, when, where, and how’ o subjective comments
statements o emotive terms
o factual statements o action words beginning statements
o technical language o ‘how’ statements
EXPLAIN INSTRUCT
o ‘why and how’ statements o sequences / steps
o technical language
o poetic language
o adjectives
ENTERTAI
o subjective comments
N ….EDUCATE, CONVINCE, AMUSE, ADVERTISE ….
o humour
o emotive terms
This text’s purpose and intention:
o This language is designed to provoke … o The writer means to fuel the debate on …
o The clearest illustration of the writer’s purpose is … o The position we are asked to share is that …
o The writer has concentrated his/her effort on … o The article attempts to enlist the support of …
o This text pinpoints … o This text provides a view that contradicts …
o This text provides a map of … o The writer opts for …
o The writer probes … so that … o The writer stresses …
o The writer’s purpose emerges as … o The appealing imagery of the text is aimed at …
o The writer is attempting to sway the reader by … o This text describes interesting developments in …
o This text constructs a picture of … o The writer questions …
o The writer tends to … o This text clearly reveals the writer’s view on …
o Media attention is clearly focused on … o The writer enters the arena of discussion by …
o The argument advanced in the text is designed to.. o The writer’s attitude is exemplified by …
o The text gives prominence to … o The article endorses …
o The intensity of the focus on … o The text attempts to mobilize support for …
o The [feature] supports the purpose of the text to … o The meaning of this text is …
Analysis and impact of text:
o The composer has used [feature] to … o Perhaps the most surprising/interest aspect of the text is
o Using the feature of [ ] helps the composer to … …
o It reads rather like … o The general pattern of language evokes …
o This text is a significant contribution to discussion o A mood of … prevails in this text due to …
because … o A reader’s response may well be to …
o The [feature] draws the responder’s attention to … o Visual interest in the text is created by …
o The effect of this language feature is to … o The influence of this text lies in …
o We are made to … when the composer uses [feature] o The text generates …
because …. o The perceptions of the reader are sharpened by …
o The power of this text stems from … o This text increases the level of debate over … by …
o The coverage of the issue is extensive: …. o This text accentuates …
o The content of this article is dominated by … o The language features used attract …
o For the reader, this text produces … o This text sharply focuses attention on …
o The text magnifies
THESAURUS / WORD BANK to use when writing about texts:
THEMES/IDEA concerns, issues, messages, concepts, notions, principles, motivations
S
MAIN/ major, primary, central, pivotal, frontal, most intense, paramount, above all, key
IMPORTANT
LESS underlying, hinted at, implied, more subtle, underneath, secondary, minor
OBVIOUS
CERTAINLY clearly, definitely, absolutely, indeed, obviously, in fact, importantly, undoubtedly, without
doubt, surely, distinctly
SHOWS displays, emphasises, informs, presents, highlights, mirrors, acknowledges, reflects,
reinformces, delineates, expounds, elucidates, outlines, exposes, relates
THEREFORE consequently, hence, thus, since
BUT yet, however, although, alternatively, whereas, nevertheless, nonetheless, while,
admittedly,
EXPECIALLY in particular, moreover, more specifically
SIMILARLY likewise, again, once more, additionally
OTHER not surprisingly …, neither … nor, either … or, rather …, in summary …, not only … but also,
‘GOOD’ both …, in conclusion …, firstly …secondly … finally
EXPRESSIONS
THEMES
o family o identity o personal-growth o honesty
o love o change o loneliness o war
o hate o work o challenges o education
o relationships o betrayal o gender o despair
o trust o parents o good vs evil o race
o journeys o revenge o friendship o enemies
o childhood o peace o pressure o abuse
o adulthood o age o greed/desire o hope
o survival o birth o power o ????
MOOD (look up those you are not familiar with)
o sadness o sarcasm o arrogance o joy
o indifference o enthusiasm o tenderness o sincerity
o anger o geniality o excitement o hostility
o humour o friendliness o fun o affection
o politeness o frustration o emphatic o passion
o modesty o serious o precision o warmth
o simplicity o dignity
TONE (look up those you are not familiar with)
o friendly o sad o amiable o sarcastic
o frustrated o indifferent o jovial o cynical
o jubilant o angry o emphatic o joyful
o serious o humorous o precise o conversational
o adult o informal o excited o childish
o condescending o polite o pleasant o sincere
o meek o modest o genial o hostile
o arrogant o sarcastic o vague o blunt
o tender o formal o scientific o affectionate
o simple o considered o passionate
o enthusiastic
dignified
o warm
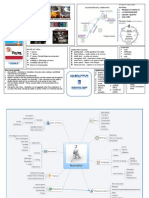
Language Features of Texts Effect of Text Features
Verbal Features Visual Features Text features can have many effects including:
• Figurative language eg. Dominant Image
similes, metaphors,
personification
Symbol Attracting attention
• Imagery
Composition Making the text more appealing and
• Alliteration/assonance/
Contrast/juxtaposition interesting
onomatopoeia Balance Highlighting one point or opinion in the text
• Verbs, nouns, adjectives, Graphics/pictures Making the text seem urgent
adverbs (word choice) Font style Creating a sense of sympathy or empathy
• Sentence structure (syntax) Font size
Getting the attention of a particular audience
• Emotive language Spacing
Starting something specific
• Punctuation White space
Persuading the audience about something.
• Use of pronouns Shape
• Repetition Frames & borders A single feature can also have more than one effect.
• Idioms • Depth – background & foreground It is important that you can explain how features help
• Hyperbole Proportion create the meaning in a text. To do this, you need
• Imperative Camera shots/angles to:
• Pun Colour
• Quotation Light & shadows 1. Identify the feature
• Statement Lines 2. Identify the purpose (or effect required)
• Rhetorical Question Vectors 3. Explain how the feature helps achieve the
• Rhyme Allusion purpose
• Rhythm Sequence
• Motif/Symbols Structure
Helpful phrases:
• Allusion/association Shot
The meaning of this text is …
• Dialogue Camera movement The composer has used [verbal/visual
• Script Texture
feature] to …
• Headings Mood
Using the feature of [verbal/visual feature]
• Voice-over Scenery
helps the composer to …
• Sound effects Logos & graphics
The features support the purpose of the text
• Tone of voice Facial expressions
by …
• Music Body language The [verbal/visual feature] draws the
• Silence Caption responder’s attention to …
• Captions Layout The effect of this language feature is to …
• Point of View Logos/icons We are made to … when the composer uses
• Connotation Symbols [verbal/visual feature] because …
Вам также может понравиться
- StoryTelling PlanДокумент4 страницыStoryTelling PlanangycarrillogОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ39 страницLecture 2Reynaldo LugtuОценок пока нет
- How To Write A Dialogue RECAP 1Документ1 страницаHow To Write A Dialogue RECAP 1leonora.viudes22Оценок пока нет
- TARLAC STATE UNIVERSITY VICE PRESIDENT FOR ACADEMICS AFFAIRSДокумент2 страницыTARLAC STATE UNIVERSITY VICE PRESIDENT FOR ACADEMICS AFFAIRSHyunjin MinotozakiОценок пока нет
- Oral Presentation Rubric: Superior Adequate Minimal InadequateДокумент2 страницыOral Presentation Rubric: Superior Adequate Minimal InadequateClarabel LanuevoОценок пока нет
- Oral Presentation RubricДокумент1 страницаOral Presentation RubricMaris daveneОценок пока нет
- Midterm Module 5Документ86 страницMidterm Module 5jannet lansanganОценок пока нет
- 1semantics IntroДокумент21 страница1semantics IntroRoberto HrvatinОценок пока нет
- G-Oal R-Ole A-Udience S-Ituation: A. Y. 2018-2019 Performance Task in English 7 First QuarterДокумент9 страницG-Oal R-Ole A-Udience S-Ituation: A. Y. 2018-2019 Performance Task in English 7 First QuarterGenesis AguilarОценок пока нет
- Analyzing DICTIONДокумент7 страницAnalyzing DICTIONZeynepОценок пока нет
- Level 8-English PDFДокумент59 страницLevel 8-English PDFAimee RoswellОценок пока нет
- CL C7 (1) (1) (Autosaved)Документ15 страницCL C7 (1) (1) (Autosaved)Shalani KarnanОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 3 - Purposive CommunicationДокумент12 страницCHAPTER 3 - Purposive CommunicationiamysaaahhhОценок пока нет
- Creative Writing - Q1 - M4Документ10 страницCreative Writing - Q1 - M4Aldous AngcayОценок пока нет
- Syntax Powerpoint 2016 NovemberДокумент31 страницаSyntax Powerpoint 2016 NovemberHenry ChaoОценок пока нет
- Level I Narrative HandoutДокумент10 страницLevel I Narrative HandoutameliaОценок пока нет
- Voice Lessons Full Text PDFДокумент156 страницVoice Lessons Full Text PDFRobertMaldini0% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Partido State University College of Education Goa, Camarines Sur A/Y: 2016-2017Документ10 страницRepublic of The Philippines Partido State University College of Education Goa, Camarines Sur A/Y: 2016-2017Jeric nojor nuleanОценок пока нет
- For INHS Classroom Use Only) : Iloilo National High School Luna Street, La Paz, Iloilo City English 10Документ3 страницыFor INHS Classroom Use Only) : Iloilo National High School Luna Street, La Paz, Iloilo City English 10Mikaela Julianne EradaОценок пока нет
- Oral Language KindergartenДокумент1 страницаOral Language KindergartenKendra WongОценок пока нет
- Oral Presentation Rubric in Geo 3Документ4 страницыOral Presentation Rubric in Geo 3Ron Patrick CervantesОценок пока нет
- S4 Theatre Studies M4 - PraxisДокумент4 страницыS4 Theatre Studies M4 - PraxisambutvlmОценок пока нет
- Gold First Unit 2Документ10 страницGold First Unit 2SamОценок пока нет
- Listening LP1Документ6 страницListening LP1Zee KimОценок пока нет
- Stories and Storytelling: An SEO-Optimized TitleДокумент28 страницStories and Storytelling: An SEO-Optimized TitleEHdz D. JameraОценок пока нет
- MCD502 Script Writing Complete Handouts Downloaded FromДокумент195 страницMCD502 Script Writing Complete Handouts Downloaded FromShahid SaeedОценок пока нет
- Asean Lit ReviewerДокумент4 страницыAsean Lit ReviewerCarlos Miguel MendozaОценок пока нет
- Oral Presentation RubricДокумент3 страницыOral Presentation RubricEvaine EspedillonОценок пока нет
- CW M8Документ3 страницыCW M8Judith JanerОценок пока нет
- UNIT 2 - Seeing A New OpportunityДокумент10 страницUNIT 2 - Seeing A New Opportunityrahmatamrullah08Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Demonstration RubricsДокумент4 страницыTeaching Demonstration RubricsErnst Lorenz CimatuОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 RubricДокумент4 страницыUnit 6 Rubricapi-338768649Оценок пока нет
- Oral Communication Remedial ExamДокумент1 страницаOral Communication Remedial Examanon_787709098100% (8)
- Vocabulary and Phrases For Language AnalysisДокумент6 страницVocabulary and Phrases For Language AnalysisShivamОценок пока нет
- DIDLS Packet SabolcikДокумент12 страницDIDLS Packet Sabolciklittle.goldens96Оценок пока нет
- R1 Writing TechniquesДокумент4 страницыR1 Writing TechniquesSagnik KarОценок пока нет
- Level B2: Communicative ObjectivesДокумент1 страницаLevel B2: Communicative ObjectivesEmmaОценок пока нет
- Literary Appreciation SkillsДокумент69 страницLiterary Appreciation SkillsAlmarez BastyОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5CNFДокумент6 страницLesson 5CNFGenshiner FsОценок пока нет
- Pope's 1970 Speech to Filipino StudentsДокумент22 страницыPope's 1970 Speech to Filipino Studentsdez umeranОценок пока нет
- CNF Module 3Документ30 страницCNF Module 3Jean RamosОценок пока нет
- Checklist: Elements of Literary StyleДокумент2 страницыChecklist: Elements of Literary StyleARVEREN SYLVEREОценок пока нет
- English Rare Daniya d12071 XGДокумент5 страницEnglish Rare Daniya d12071 XGDANIYA ALIОценок пока нет
- English Rare Daniya D12071 XGДокумент5 страницEnglish Rare Daniya D12071 XGDANIYA ALIОценок пока нет
- PoesmallgrouprubricДокумент1 страницаPoesmallgrouprubricapi-404033802Оценок пока нет
- 001 2015 4 BДокумент210 страниц001 2015 4 BLethukuthula Ponokgeti RadebeОценок пока нет
- Teaching LiteratureДокумент61 страницаTeaching LiteratureTeacher Education100% (1)
- PovДокумент17 страницPovcarmelladelossantos487Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3 4Документ7 страницUnit 3 4rosendophil7Оценок пока нет
- Theater Scenewriting RubricДокумент1 страницаTheater Scenewriting Rubricapi-709173349Оценок пока нет
- Elements of Literary Style PDFДокумент1 страницаElements of Literary Style PDFTufail AhmadОценок пока нет
- Tone Power PointДокумент26 страницTone Power PointconnorОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary: Civil Service ReviewДокумент53 страницыVocabulary: Civil Service ReviewCherry-Ann C. Olajay0% (1)
- Activity 1: True or False. Write T If The Statement Is Correct and F If It Is NotДокумент3 страницыActivity 1: True or False. Write T If The Statement Is Correct and F If It Is Notjoseph5689Оценок пока нет
- Module 1 ActivityДокумент3 страницыModule 1 Activityjoseph5689Оценок пока нет
- Spoken TextДокумент57 страницSpoken TextMia Ruth BarrogaОценок пока нет
- Beginning The Knowledge QuestДокумент27 страницBeginning The Knowledge QuestChantal CatimbangОценок пока нет
- Valuing Others Through Communicative StylesДокумент6 страницValuing Others Through Communicative Stylesian razoОценок пока нет
- French In Your Face!: 1,001 Smiles, Frowns, Laughs, and Gestures to get your point across in FrenchОт EverandFrench In Your Face!: 1,001 Smiles, Frowns, Laughs, and Gestures to get your point across in FrenchОценок пока нет
- How to Craft Killer Dialogue for Fiction & Creative Non-Fiction: Writer Productivity Series, #3От EverandHow to Craft Killer Dialogue for Fiction & Creative Non-Fiction: Writer Productivity Series, #3Оценок пока нет
- Narrative OverviewДокумент2 страницыNarrative OverviewjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Blue Sky MineДокумент7 страницBlue Sky Minejeanettelans50% (2)
- Discussion Essay ExemplarДокумент1 страницаDiscussion Essay ExemplarjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Blooms ActivitiesДокумент1 страницаBlooms ActivitiesjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- CartoonsДокумент1 страницаCartoonsjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- 103 Things To Do When ReadingДокумент5 страниц103 Things To Do When ReadingjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Year 7 Semester 1 ReportДокумент1 страницаYear 7 Semester 1 ReportjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Universal Declaration - PlainДокумент2 страницыUniversal Declaration - PlainjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Stage 4 & 5 Visual TextsДокумент2 страницыStage 4 & 5 Visual TextsjeanettelansОценок пока нет
- Types of Nouns Worksheet For Grade 5 EnglishДокумент2 страницыTypes of Nouns Worksheet For Grade 5 EnglishSuvashreePradhanОценок пока нет
- Close-Up On Subtitling and DubbingДокумент5 страницClose-Up On Subtitling and DubbingPat Ricia100% (1)
- Social Media Management & Marketing PlanДокумент11 страницSocial Media Management & Marketing PlanMonique EscoverОценок пока нет
- That-Complement ClausesДокумент14 страницThat-Complement Clausesapi-27419886250% (2)
- Hellenic American Ecpe Teachers Guide-Winter-2009Документ40 страницHellenic American Ecpe Teachers Guide-Winter-2009Nerak0% (2)
- 100 Errors Sbi Clerk 2018 (Ibt)Документ9 страниц100 Errors Sbi Clerk 2018 (Ibt)Sai Swaroop AttadaОценок пока нет
- Prosodic Means That Affects The Realization of Simple Speech PatternsДокумент10 страницProsodic Means That Affects The Realization of Simple Speech PatternsAcademic JournalОценок пока нет
- Use of The SuffixesДокумент160 страницUse of The Suffixes2PlusОценок пока нет
- Miriam Sheen Cuba - Passive VoiceДокумент18 страницMiriam Sheen Cuba - Passive VoiceMiriamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 SummaryДокумент5 страницChapter 2 SummaryCollins DC100% (1)
- Nonverbal Sentences in Tagalog - ManueliДокумент14 страницNonverbal Sentences in Tagalog - Manueliapi-3732946Оценок пока нет
- EGRA EDA Final Report JulyДокумент49 страницEGRA EDA Final Report JulyedaethiopiaОценок пока нет
- Types of Speech Act Locution Illocution PerlocutionДокумент18 страницTypes of Speech Act Locution Illocution PerlocutionJennifer DumandanОценок пока нет
- HL Essay RubricДокумент5 страницHL Essay Rubricapi-495087389Оценок пока нет
- Dosuna - 2012 - Ancient Macedonian As A Greek Dialect - A Critical Survey On Recent WorkДокумент13 страницDosuna - 2012 - Ancient Macedonian As A Greek Dialect - A Critical Survey On Recent WorkMakedonas AkritasОценок пока нет
- Eng1l Ci SheetДокумент2 страницыEng1l Ci Sheetapi-275834887Оценок пока нет
- Caning Dictionary Jun 16Документ36 страницCaning Dictionary Jun 16Hakki YazganОценок пока нет
- Q1: What Is Difference Between Dialects and Accent ? What Role Do Dialects of A Language Play in The Existence of That LanguageДокумент24 страницыQ1: What Is Difference Between Dialects and Accent ? What Role Do Dialects of A Language Play in The Existence of That Languagemuhammad zahirОценок пока нет
- Poem in Praise of MenstruationДокумент9 страницPoem in Praise of MenstruationkaleylaneОценок пока нет
- Rubric - Philo Performance TaskДокумент2 страницыRubric - Philo Performance TaskRizalyn GarciaОценок пока нет
- Kushabhau Thakre Patrakarita Avam Jansanchar Vishwavidyalaya, Raipur (C.G.)Документ31 страницаKushabhau Thakre Patrakarita Avam Jansanchar Vishwavidyalaya, Raipur (C.G.)irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Spelling Reform: Midterm Week 4Документ10 страницSpelling Reform: Midterm Week 4Jake BatallerОценок пока нет
- Indra Rosniyati Ohorella ThesisДокумент116 страницIndra Rosniyati Ohorella ThesisNimat SabanОценок пока нет
- Singapore Health Promotion Board Facebook Ad Case StudyДокумент2 страницыSingapore Health Promotion Board Facebook Ad Case StudySocial Fresh ConferenceОценок пока нет
- 1123 Example Candidate Responses Paper 1Документ28 страниц1123 Example Candidate Responses Paper 1Anonymous 52xcAR988% (16)
- Old English VerbsДокумент5 страницOld English VerbsHye WonОценок пока нет
- DLL Week 17Документ13 страницDLL Week 17Junrel flores100% (1)
- Everyday Vocabulary Words PDFДокумент2 страницыEveryday Vocabulary Words PDFHeather34% (35)
- How To DebateДокумент31 страницаHow To DebateNur FarhinОценок пока нет
- Methodo Pedago MCQДокумент7 страницMethodo Pedago MCQdivya mathew100% (4)