Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Modul Science Form 2
Загружено:
Nur Atiah DaudИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Modul Science Form 2
Загружено:
Nur Atiah DaudАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MODUL FORM 2
2.1 THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES
SKIN
1. Label each part of the skin with a suitable word from the following list.
Heat receptor Epidermis Cold receptor Hair Fat layer Dermis
Pain receptor Sweat gland Touch receptor Pressure receptor
f
g
h
i
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
NOSE
2. Label the part of the human nose with the following words.
1.Nostril 2.Nasal Cavity 3.Receptor Cell
3. (a) State the stimulatory reaction in the nose using the words given below :
Brain Analysis Dissolved in mucus Response
Smell 1 Smell receptor Impulse
4 Impulse 3 2
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
3(b) Match the different parts in the nose their function
i Smell A Smell is good/bad
Mucus B Analyses messages and gives the appropriate response
ii
iii Receptor C Chemicals in the air stimulate the nose
s
iv Brain
D Dissolve the chemicals in the air
v Detection
E Send messages to the brain about stimulus
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
TONGUE
4. Label each part P, Q, R and S using the following words.
Sweet Sour Bitter Salty
PP
(i) The tongue is covered with many tiny structures called the ____________
(ii) The taste buds are able to detect the taste of the food if the food can
dissolve in ______________
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
HUMAN EAR
5. The diagram below shows the cross section of a human ear. Label the t parts using the
word given in the box.
Pinna Ear canal Eardrum Ossicles
Oval windows Semicircular canal cochlea
Eustachian tube
A B C D
E
H G F
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
6. Match the different parts in the ear to their functions
Balance the air pressure on both sides
Eardrum P I of the eardrum
Ossicles Q It vibrates at the same frequency as
II
the sound waves and transfer
vibration to the ossicle
Auditory nerve R Detect the vibration and converts
III
them into nerve impulse
Collect and directs sound waves
Cochlea S IV (vibrating air) into the auditory canal
Oval window T Send the messages to the brain
V
ows
Transfers the vibration from the
Eustachian tube U VI ossicles to the cochlea
Pinna V VII Amplified the vibration and transfer
vibrations to the ossicles
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
7. State the functions of these structures in the ear
(a) Eardrum : ___________________________________________
___________________________________________
(b) Ossicles : ___________________________________________
___________________________________________
(c) Pinna : ___________________________________________
___________________________________________
(d) Cochlea : ___________________________________________
___________________________________________
(e) Eustachian tube : ________________________________
___________________________________________
(f) Auditory nerve : _____________________________________
__________________________________________
(g) Oval window : _____________________________________
__________________________________________
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
EYE
8. The diagram shows the human eye.
Label structures P, Q, R, S and T using the following words:
Cornea Iris Retina
Pupil Lens
S: T:
P:
R:
Q:
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
9. Draw lines to show the correct match between the structures
and their functions.
PART FUNCTION
P i. Controls amount of light entering the eye
Q ii. Helps to focus the light on the retina
R iii. Focuses the light to form an image on the retina
S iv. Controls the size of the pupil
T v. Receives light stimuli and changes the stimuli to
nerve impulses
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
10. State the function of the following stuctures:
Cornea ………………………………………………………………………………
Iris ………………………………………………………………………………
Pupil ………………………………………………………………………………
Retina ………………………………………………………………………………
Lens ………………………………………………………………………………
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
11. Fill in the blank using words given in the box.
Cornea Iris Retina
Pupil Lens
1 The ………………………… receives light stimuli and changes the stimuli
to nerve impulses
2 The …………………………. helps to focus the light on to the retina
3 The …………………………. focuses the light to form an image on the
retina.
4 The …………………………. controls the size of the pupil
5 The ………………………….controls amount of light entering the eye
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
2.2 NUTRITION
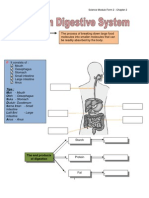
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
1. Label the parts of the human digestive system in the following words.
Liver Small intestine Gall bladder Pancreas Large intestine
Oesophagus Stomach Mouth Salivary glands
E
D
F
G
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
2. Draw lines to show the correct match between the structures and their
functions
Draw the lines as shown below
C i Produces bile
E ii Channels food to the stomach. This action is
called peristalsis
D iii Produces digestive enzymes such as
amylase, protease and lipase
G iv Digestion of fat, protein and starch and
absorption of food
I v Digestion of protein begins
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
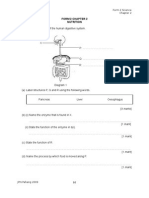
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
3. Fill in the blanks with suitable words in the box.
Fatty acids and glycerol, salivary amylase, liver, glucose,
protease, gall bladder, amino acids, dilute hydrochloric acid,
1. The enzyme in saliva, _____________________ breaks down the starch
molecules into maltose
2. The stomach secretes gastric juice which contains _______________ and
_________________ digestion of proteins
3. Bile is produced by __________________ and kept in the ___________
4. What are the end products of digestion of
a) Carbohydrates ? __________________
b) Proteins? ________________________
c) Fats? _______________________
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
2.3 INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS
IN THE ENVIRONMENT
CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS AND PLANTS
1. Fill in the blanks using the words given
Fish, Monocotyledons, Amphibians, Mosses, Non-flowering, Dicotyledons,
Fern, Algae, Mammals. Birds, Reptiles, Amphibians ,Birds, Reptiles, Mammals,
a)
Plants
Flowering i
ii iii
iv v vi
Fungi
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
b)
Vertebrates
i ii iii iv
Fish
c)
Vertebrates
Warm-blooded Cold-blooded
i ii
iii iv v
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
CLASSIFICATION
2. Based on your observation state one characteristic of each organism.
b
a
c
b
d
b
e f
g h
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
j
i
i j
i
k l
i i
m n
i
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
O P
i i
3. Classify the organisms into two groups based on their common characreristics
P Q R S
Common aa
characteristics a b
Letter of
The organisms i ii
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
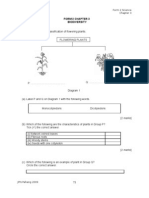
CLASSIFICATION OF PLANTS
4. The diagram shows the flowering plants.
Label structure P, Q, R, S, T, U, A, B, C, D and E using the following words
fibrous root, tap root, one cotyledon, two cotyledons, network of
veins, parallel veins, soft and non woody, hard and woody,
flower parts in threes, flower parts in fours or fives
DICOTYLEDONS
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
MONOCOTYLEDONS
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
5. Draw lines to show the correct match between the phrase and
explanation on Interdependence among living organism.
Draw the lines as shown below
PHRASE EXPLANATION
i A group of similar living organisms
Habitat A
Species B ii Made up of living and non-living components
iii Different communities interact with with one
Population C another and their environment in a habitat
iv The natural home of an organism where it
Community D lives and reproduces
v A group of individuals of the same species
Environment E that live and reproduce in a habitat at the
same time.
vii Made up of different populations of organisms
Ecosystem F living together and interacting with one
another in the same habitat
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
FOOD WEB
6. Fill in the blanks using the words from the following list
Food Chain, Producer, Consumer, Decomposer,
Food web, Pyramid of Number
1 ____________________ are living organisms that are able to make their
own food
2 ____________________ are living organisms that are not able to make
their own food
3 ____________________ are living organisms that feed on the remains of
dead organisms
4 ____________________ is a network of interconnected food chains
5 ____________________ shows the food relationship among living
organisms
6 _____________________ shows the different number of organisms in
a food chain.
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
TYPES OF INTERACTIONS BETWEEN LIVING ORGANISMS
7 Use letters to complete the phrase on types of interaction between
living organisms
C__ MM__NS__LISM
P__ RA__ITI_M
CO__P___TI __IO__
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use light to produce food.
carbon dioxide , oxygen
water , glucose ,
sunlight, chlorophyll
8. Write the word equation for photosynthesis.
a b e f
c
+ d +
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
2.4 WATER AND SOLUTION
Physical characteristics of water
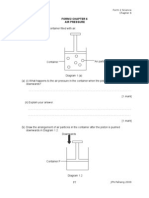
1. Diagram 1 shows the changes in the state of water.
P: Q:
R: S: T:
Diagram 1
On diagram 1, label P, Q, R, S and T using the following words.
Freezing Liquid Solid Boiling Gas
Fill in the blank using the word from the box given.
solid
( a ) Water can exist in …………………………… states.
( b ) An ice cube is water in the ………………… state. 7
( c ) Steam is water in the ……………………. state. liquid
( d ) We drink water in the ………………….. state. three
(e ) Liquid water …………………. to form ice. colourless
( f ) Water is …………………. tasteless and neutral. freezes
1
( g ) The pH value of pure water is ……………
gas
( h ) The density of water is ……………… g/cm3
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
The composition of water
2. Diagram 2 shows the electrolysis of water.
……………… On ………………..
gas is discharged gas is discharged
………………
+ dilute ………….
………………
The …………..
is the electrode The…………
that is is the electrode
connected to that is
the…………… connected
terminal of a to the…………
battery terminal of a
battery.
Diagram 2
On diagram 2, fill in the blanks using the following words.
Cathode Hydrogen Oxygen positive
Anode water Sulphuric acid negative
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
Solution and Solubility
3. Diagram 3 shows the process of making a solution.
z
y
Diagram 3
Solute Solvent Solution
On diagram 3 , label the substances using the following words.
4. Diagram 4 shows the making of a cup of hot coffee.
sugar
Black coffee
Hot coffee
Hot
water
Diagram 4
Based on diagram 4, determine the solute , solvent and solution in the hot coffee.
a. Solute : ……………………………
b. Solvent : ……………………………
c. Solution: ……………………………
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
5. Diagram 5 shows three beakers containing solutions and their types .
SATURATED SOLUTION
P
DILUTE SOLUTION
Q
CONCENTRATED
SOLUTION
Diagram 5 R
Draw lines to show the correct match between the solution in the beakers and their
types.
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
Methods of water purification
6. Diagram 6 shows methods of purification.
d
a
e
b
…………………………… ……………………………………
Diagram 6
On figure 6, name the method and label the apparatus used for each picture using the
following words.
Filter funnel Thermometer Measuring cylinder
Distillation Round bottom flask Conical flask
Filtration
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
2.5 SIMPLE MACHINE
1. Diagram 1 shows a first class lever.
Label J, K and L using the following words:
Effort Fulcrum Load
J:
K:
L:
Diagram 1
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
2. Diagram 2 shows a second class lever.
Label P, Q and R using the following words:
Effort Fulcrum Load
P:
Q:
R:
Wheelbarrow
Diagram 2
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
3. Diagram 3 shows a third class lever.
Label X, Y and Z using the following words:
Effort Fulcrum Load
Z:
Ice tongs
X:
Y:
Diagram 3
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
4. Draw lines to show the correct match between the classes of levers and the
simple machines.
CLASS OF LEVER SIMPLE MACHINE
First class
stapler
Second class
scissors
Third class
nutcracker
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
5. Fill in the blanks using words given in the box.
first second third
1 A stapler is an example of the ………………………………class lever.
2 A scissors is an example of the …………………………….class lever.
3 A nutcracker is an example of the ………………………….class lever.
4 A wheelbarrow is an example of the ……………………….class lever.
5 An ice tongs is an example of the …………………………class lever.
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
MODUL 2 FORM 2 STF 2007
Вам также может понравиться
- Nexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 131 (Questions)Документ3 страницыNexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 131 (Questions)Ms_SyazanaОценок пока нет
- Exercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Документ2 страницыExercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Nor Adila100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionДокумент7 страницForm 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Modul F2 Science Chapter 1Документ21 страницаModul F2 Science Chapter 1NorelyanaAli95% (21)
- Modul F2 Science C2Документ14 страницModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- Form 2 Chapter 3Документ7 страницForm 2 Chapter 3naza977588% (8)
- Form 3 Chapter 9Документ3 страницыForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Form 3 Chapter 8Документ8 страницForm 3 Chapter 8naza9775100% (6)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceДокумент10 страницChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Chapter 3 MatterДокумент8 страницChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Science Form 1 Objective TestДокумент7 страницScience Form 1 Objective TestSITI ZAIDAH AHMAD50% (6)
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Документ11 страницLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeДокумент5 страницForm 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeJames WongОценок пока нет
- Form 3 Chapter 2Документ9 страницForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- See-saw balance distance calculationДокумент9 страницSee-saw balance distance calculationchaiseng yong100% (1)
- The reactivity series of metalsДокумент11 страницThe reactivity series of metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 1Документ6 страницForm 2 Chapter 1naza977562% (13)
- MOdul Science Form 3Документ27 страницMOdul Science Form 3Nur Atiah Daud95% (19)
- Form 2 Chapter 5Документ10 страницForm 2 Chapter 5naza977587% (15)
- Science Form 2 Paper 1 Exam QuestionДокумент10 страницScience Form 2 Paper 1 Exam Questionchaiseng yongОценок пока нет
- Science Form 1Документ11 страницScience Form 1uminoriah67% (6)
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Документ7 страницSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinОценок пока нет
- STF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Документ12 страницSTF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Syahrul67% (3)
- Chap 4 Science Form 2Документ9 страницChap 4 Science Form 2Yobal Yeu80% (5)
- Form 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Документ6 страницForm 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Sce Form 2Документ22 страницыSce Form 2williamkong123Оценок пока нет
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Документ46 страницForm 2 Science Chapter 1qq23589% (66)
- Form 3 Chapter 7Документ15 страницForm 3 Chapter 7naza9775100% (5)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Документ7 страницForm 2 Chapter 2naza977579% (19)
- Form 1 Chapter 2Документ7 страницForm 1 Chapter 2ajakazОценок пока нет
- Exercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Документ3 страницыExercise On Chapter 8 Science Form 3Sasi RekaОценок пока нет
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Документ62 страницыForm 2 Science Chapter 5qq23585% (41)
- Softcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)Документ144 страницыSoftcopy Science Form 2 (Book A)VANAJA A/P NALLAPPAN MoeОценок пока нет
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Документ31 страницаScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Science Notes Form 1Документ20 страницScience Notes Form 1Farah Asnida0% (2)
- Form 3 Science Chapter 2Документ9 страницForm 3 Science Chapter 2Mohamad Harith100% (5)
- Form 2 Chapter 9Документ10 страницForm 2 Chapter 9naza9775100% (3)
- Form 2 Chapter 6Документ9 страницForm 2 Chapter 6naza9775100% (7)
- Worksheet Science Form 2 Chapter 1Документ5 страницWorksheet Science Form 2 Chapter 1KhadijahMadhadzirОценок пока нет
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Документ8 страницForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Kelvin0% (1)
- How Our Senses WorkДокумент36 страницHow Our Senses WorkAJ MukunОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesДокумент12 страницChapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesNor Faizahbaizura Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- Modul Science Form 1Документ30 страницModul Science Form 1Nur Atiah Daud76% (38)
- LEC M3.3 BlockAДокумент8 страницLEC M3.3 BlockASieg100% (1)
- Stimuli and Responses FOCUS PT3Документ24 страницыStimuli and Responses FOCUS PT3julia ahmadОценок пока нет
- Module c1 Form 3Документ4 страницыModule c1 Form 3Yan YanОценок пока нет
- Igcse AccommodationДокумент3 страницыIgcse AccommodationChr1zFX4Оценок пока нет
- Modul 1 - Form 1 STFДокумент31 страницаModul 1 - Form 1 STFmadrosli100% (3)
- SECTION A: Each Question Is Followed by Four Possible Answer A, B, C and D. Choose TheДокумент8 страницSECTION A: Each Question Is Followed by Four Possible Answer A, B, C and D. Choose TheCik Farrah KhairОценок пока нет
- USS 2019: Stimulus and ResponseДокумент13 страницUSS 2019: Stimulus and ResponsedevinahОценок пока нет
- Physics Experiment 1Документ2 страницыPhysics Experiment 1Debraj SarkarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 QuestionsДокумент10 страницChapter 1 QuestionshmОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test BankДокумент10 страницIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Solomon Test Bankmenaionemperilgtod26100% (25)
- Ujian Sains Tingkatan 2Документ10 страницUjian Sains Tingkatan 2SITI ZAIDAH AHMAD50% (6)
- Chapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesДокумент21 страницаChapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesMona MohtarОценок пока нет
- Nms wb2B10 eДокумент32 страницыNms wb2B10 eShafiquemohammad AsimОценок пока нет
- Write The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer SheetДокумент5 страницWrite The Name of Each Numbered Part On The Corresponding Line of The Answer Sheetsilva, april joy c.Оценок пока нет
- PowerpointДокумент44 страницыPowerpointmina bacayОценок пока нет
- CCC - A Ñ C!$ %$C!$ %Документ18 страницCCC - A Ñ C!$ %$C!$ %zeamay1315qorayОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Stimuli & Responses in HumanДокумент5 страниц1.2 Stimuli & Responses in Humanding dongОценок пока нет
- Idioms and Phrasal Verbs PracticeДокумент3 страницыIdioms and Phrasal Verbs PracticeNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Poems - I Wonder (Form 1)Документ1 страницаPoems - I Wonder (Form 1)Nor AishahОценок пока нет
- ENGLISH LANGUAGE PBS Listening and Speaking Revised BAND 1-6Документ15 страницENGLISH LANGUAGE PBS Listening and Speaking Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Computer Hardware Devices/peripheralsДокумент1 страницаComputer Hardware Devices/peripheralsNur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Novel Asked in Form1 & 2 - Journey To The Centre of The EarthДокумент4 страницыNovel Asked in Form1 & 2 - Journey To The Centre of The EarthNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Phrasal VerbsДокумент4 страницыPhrasal VerbsNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- English Language PBS Writing Revised BAND 1-6Документ10 страницEnglish Language PBS Writing Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (2)
- A Fighter's LineДокумент3 страницыA Fighter's LineNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- ENGLISH LANGUAGE Reading Revised BAND 1-6Документ12 страницENGLISH LANGUAGE Reading Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Making It WorksДокумент25 страницMaking It WorksNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1-10Документ16 страницScience Form 3 Chapter 1-10Nur Atiah Daud57% (7)
- B Y C P: Ooting OUR Omputer and OSTДокумент4 страницыB Y C P: Ooting OUR Omputer and OSTNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1 - 7Документ12 страницScience Form 1 Chapter 1 - 7Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Документ14 страницScience Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Nur Atiah Daud88% (8)
- Module 1-Intro To SoftwareДокумент2 страницыModule 1-Intro To SoftwareNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Operating SystemДокумент2 страницыModule 2 - Operating SystemNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Input, Output, Storage DevicesДокумент4 страницыInput, Output, Storage DevicesNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- System Unit WorksheetДокумент4 страницыSystem Unit WorksheetNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Computer Evolution WorksheetДокумент1 страницаComputer Evolution WorksheetNur Atiah Daud50% (2)
- ICTL Mic. Word-Toolbar Icons ExercisesДокумент2 страницыICTL Mic. Word-Toolbar Icons ExercisesNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Puter Lab Management - Mrs AtiahДокумент4 страницыPuter Lab Management - Mrs AtiahNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Ictl Form1-Module 6) Basic MaintenanceДокумент20 страницIctl Form1-Module 6) Basic MaintenanceNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- Modul Science Form 1Документ30 страницModul Science Form 1Nur Atiah Daud76% (38)
- Ictl Form 1 - Module 7) Computer SettingДокумент21 страницаIctl Form 1 - Module 7) Computer SettingNur Atiah DaudОценок пока нет
- MOdul Science Form 3Документ27 страницMOdul Science Form 3Nur Atiah Daud95% (19)
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia UniversityДокумент38 страницChapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia UniversitycatherineОценок пока нет
- LKPD Narrattive TextДокумент5 страницLKPD Narrattive TextFakhri MukaromahОценок пока нет
- Bio Enzyme Prep Uses BenefitsДокумент6 страницBio Enzyme Prep Uses BenefitsPravin ZendeОценок пока нет
- The Fall of Fredie The LeafДокумент4 страницыThe Fall of Fredie The LeafRenz FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Importance of Forest and Trees in Sustaining Water Supply and RainfallДокумент11 страницImportance of Forest and Trees in Sustaining Water Supply and Rainfallshafique ahmedОценок пока нет
- Factory Machine Quote CompilationДокумент6 страницFactory Machine Quote CompilationAshish SavantОценок пока нет
- San Pedro Cactus Extraction of Mescaline at DuckDuckGoДокумент3 страницыSan Pedro Cactus Extraction of Mescaline at DuckDuckGojavasoloОценок пока нет
- Effects of Wind On Plant Production Lecture NotesДокумент7 страницEffects of Wind On Plant Production Lecture NotesvyllegnitlandasyangОценок пока нет
- Moyaney (Molasses, Yakult and Honey) : An Alternative Natural Fertilizer and Pesticide For Allium CepaДокумент5 страницMoyaney (Molasses, Yakult and Honey) : An Alternative Natural Fertilizer and Pesticide For Allium CepaTitusОценок пока нет
- Spellbound by KatrinaДокумент55 страницSpellbound by KatrinaAzaan Kamau100% (3)
- Knolkhol CultivationДокумент47 страницKnolkhol CultivationDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyОценок пока нет
- Resume Selva RathinamДокумент9 страницResume Selva RathinamSelvaОценок пока нет
- 2405 - Complete Instruction Manualbook 00Документ532 страницы2405 - Complete Instruction Manualbook 00Valerian Gheorghe100% (1)
- Vydehi School of Excellence (2019-20) Worksheets Grade-Xi A Subject-EnglishДокумент12 страницVydehi School of Excellence (2019-20) Worksheets Grade-Xi A Subject-Englishi am meОценок пока нет
- D.111.14.0059 15 File Komplit 20190308095807Документ84 страницыD.111.14.0059 15 File Komplit 20190308095807Dimahya chanelОценок пока нет
- Snurfle Meiosis WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSnurfle Meiosis WorksheetTaylon OsorioОценок пока нет
- A Vine On A House by Ambrose BierceДокумент6 страницA Vine On A House by Ambrose BierceEnviando TareasОценок пока нет
- Cover CropsДокумент248 страницCover CropsmradojcinОценок пока нет
- Color in LandscapeДокумент4 страницыColor in LandscapeLynnaFadilahОценок пока нет
- Section A: Mathsclinic - Official Mathsclinickata ThemathsclinicДокумент10 страницSection A: Mathsclinic - Official Mathsclinickata ThemathsclinicIrna ChanОценок пока нет
- Veratrum VirideДокумент11 страницVeratrum VirideNanda S RОценок пока нет
- Cells - Structure and Function NotesДокумент26 страницCells - Structure and Function NotesPrabal SinghОценок пока нет
- Theories of Evolution: LamarckismДокумент18 страницTheories of Evolution: LamarckismsangeegptОценок пока нет
- Andersen 2001Документ8 страницAndersen 2001Trúc NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Geopraphy NotesДокумент86 страницGeopraphy NotesIrfan GondalОценок пока нет
- 2012 National Greening Program CatanduanesДокумент59 страниц2012 National Greening Program Catanduanesapi-202017354Оценок пока нет
- Ams College Landscape Design CLDP: Planting PlanДокумент1 страницаAms College Landscape Design CLDP: Planting PlanAbisha TeslinОценок пока нет
- #4009 Taurinafanto V2.3Документ32 страницы#4009 Taurinafanto V2.3Romuald ARTILLAC100% (1)
- Electricity Tariff Schedule for Delhi 2019-20Документ8 страницElectricity Tariff Schedule for Delhi 2019-20Sharma ShiviОценок пока нет