Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Can
Загружено:
rix070 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
206 просмотров2 страницыActivity intolerance related to generalized weakness and fatigue. Nursing intervention and health teaching help patient verbalize increased activity. Long term objective: after 3 days the patient will be able to participate in prescribed physical activity and demonstrates increased activity tolerance.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
activitiy intolerance
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документActivity intolerance related to generalized weakness and fatigue. Nursing intervention and health teaching help patient verbalize increased activity. Long term objective: after 3 days the patient will be able to participate in prescribed physical activity and demonstrates increased activity tolerance.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
206 просмотров2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Can
Загружено:
rix07Activity intolerance related to generalized weakness and fatigue. Nursing intervention and health teaching help patient verbalize increased activity. Long term objective: after 3 days the patient will be able to participate in prescribed physical activity and demonstrates increased activity tolerance.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Jundale G.
Batbatan BSN-III Section: B
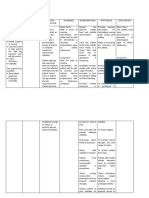
NURSING CARE PLAN
Problem: Activity intolerance
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance related to generalized weakness and fatigue.
Taxonomy: Exercise and Activity
Cause Analysis: Muscle activity, loss of energy results from reduction in the oxygen available in the muscle. Hemoglobin major component of RBC, binds easily with
oxygen necessary for the protection of body from fatigue and activity intolerance. (Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing 6th ed. By Black et.al, p454)
CUES OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Short term objective: Independent:
=Determine cause of activity -Determining the cause of a disease can
After 8 hours of giving intolerance and determine if its cause is help direct appropriate interventions.
The patient verbalizes…
nursing intervention and physical, psychological, or
“Abi nimo luya kaayo akong motivational.
lawas dili ko ganahan health teaching the patient
=Monitor and record client’s ability to -To determine the level of maximum
maglihok-lihok kay kapoy will be able to verbalize an
tolerate activity. performance of activity.
man gud. Diri lang siguro ko understanding of the need to =Teach client the need to pace activity -Rest periods decrease oxygen
sa katri maghigda lang ko gradually increase activity ad rest after meals. consumption.
diri. Unya rako maglakaw based on testing, tolerance, =Observe for pain before activity and, -Pain restricts the client from achieving
lakaw inig maayo na ako and symptoms. And expresses if possible, treat pain before activity. a maximum activity level and is often
paminaw.” an understanding of the need exacerbated by movement.
to balance rest and activity. =Perform passive range of motion -Inactivity rapidly contributes to muscle
exercises if client is unable to tolerate shortening and changes in periarticular
activity. and cartilaginous joint structure.
Objective:
The patient is Long term objective:
=Encourage client to change position -Immobilization and enforced bedrest in
always lying in bed and from supine to sitting several times the supine position have considerable
always sleeping. After 3 days of giving nursing
daily and to avoid prolonged bedrest. adverse effects on nearly every system
The patient intervention and health
in the body.
face appears to be teaching the patient will be
Dependent:
generally weak. able to participate in Collaboration with other health care
Administration of medication depends
prescribed physical activity on physicians order. workers will promote the healing
Appears to be
and demonstrates increased Refer to Physical therapies for further process of the patient.
exhausted
activity tolerance. activity.
The patient has
a sunken eyeballs.
Decreased
hemoglobin count. !30-
1609 L Normal, Result is
1209 L
References: Nursing Diagnosis Handbook (A guide to planning care) Ackley & Ladwig 2nd edition. pp. 102-103
Вам также может понравиться
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент3 страницыActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanОценок пока нет
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceДокумент3 страницыNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleОценок пока нет
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaОценок пока нет
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyДокумент3 страницыNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreОценок пока нет
- NCP PTBДокумент2 страницыNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)Документ3 страницыNursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)kaimimiyaОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarОценок пока нет
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFДокумент3 страницыNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarОценок пока нет
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPДокумент2 страницыTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORОценок пока нет
- NCP of Endometrical CancerДокумент2 страницыNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethОценок пока нет
- SP CSДокумент4 страницыSP CSKhan HansОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For InjuryДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For Injurycristina_galang_2Оценок пока нет
- Risk For InjuryДокумент1 страницаRisk For Injuryandycamille7Оценок пока нет
- Student NurseДокумент2 страницыStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Оценок пока нет
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityДокумент1 страницаNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanОценок пока нет
- Cue Problem Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент5 страницCue Problem Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJanyn Abella ReyesОценок пока нет
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент1 страницаActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosОценок пока нет
- Cues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыCues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationhaniehaehaeОценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент4 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Planseeker009Оценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPShubhangi SarwanОценок пока нет
- NCP For Activity IntoleranceДокумент1 страницаNCP For Activity IntoleranceKristine LonyenОценок пока нет
- Cu 4Документ3 страницыCu 4Paul SahagunОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBДокумент2 страницыIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixОценок пока нет
- Medication ThalassemiaДокумент3 страницыMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoОценок пока нет
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Документ6 страницWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasОценок пока нет
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusДокумент3 страницыWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlanKatrene Lequigan100% (1)
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentДокумент2 страницыProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawОценок пока нет
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanДокумент3 страницыCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- A.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionДокумент4 страницыA.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionKate Aenyle AgsoyОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Acute PainAdelaine LorestoОценок пока нет
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroОценок пока нет
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыViii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationhehehe29Оценок пока нет
- NCP - Alteration in ComfortДокумент2 страницыNCP - Alteration in ComfortPatricia CastroОценок пока нет
- NCP PainДокумент1 страницаNCP Painsitz04Оценок пока нет
- Idoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPДокумент2 страницыIdoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.Оценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveДокумент4 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFaye Dianne Damian-BuenafeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing PatternДокумент7 страницIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisОценок пока нет
- Ortho NCPДокумент1 страницаOrtho NCPErjohn Vincent Lim100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaОценок пока нет
- NCP For Pain (Appendicitis)Документ2 страницыNCP For Pain (Appendicitis)Iris BalinoОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPJerome Vergel RubianesОценок пока нет
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageДокумент2 страницыNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPAnne De VeraОценок пока нет
- Parkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Документ2 страницыParkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Benjie DimayacyacОценок пока нет
- NCP PpwardДокумент15 страницNCP PpwardKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentДокумент6 страницCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical MobilityДокумент2 страницыImpaired Physical MobilityJayson OlileОценок пока нет
- NCP BronchopneumoniaДокумент8 страницNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliОценок пока нет
- Seizure NCPДокумент2 страницыSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Acute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessДокумент3 страницыAcute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessrlinaoОценок пока нет
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance DeliveryДокумент3 страницыActivity Intolerance Deliveryjunex123100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance NCPДокумент2 страницыActivity Intolerance NCPAdriano Odysseus Jon O.Оценок пока нет
- Cva NCP 1Документ3 страницыCva NCP 1MarcieОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Breast MilkДокумент6 страницPhysiology of Breast Milkrix07Оценок пока нет
- Doctor's Order SheetДокумент1 страницаDoctor's Order Sheetrix07Оценок пока нет
- Rooster ListДокумент1 страницаRooster Listrix07Оценок пока нет
- Lab ResultsДокумент2 страницыLab Resultsrix07Оценок пока нет
- Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент3 страницыDecreased Cardiac OutputCristina L. JaysonОценок пока нет
- V. Pathophysiology Precipitating Factor: Predisposing FactorsДокумент1 страницаV. Pathophysiology Precipitating Factor: Predisposing Factorsrix07Оценок пока нет
- Abruptio PlacentaeДокумент5 страницAbruptio Placentaerix07Оценок пока нет
- NCP ApДокумент2 страницыNCP Aprix07Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Myasthenia Gravis DateДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Myasthenia Gravis DateSheryl Ann Barit Pedines100% (1)
- A Route of Drug Administration Is The Path by Which A Drug or Other Substance Is Brought Into Contact With The BodyДокумент9 страницA Route of Drug Administration Is The Path by Which A Drug or Other Substance Is Brought Into Contact With The BodyZyrine JhenОценок пока нет
- Activity IntoleranceДокумент3 страницыActivity Intolerancelouie roderos0% (1)
- Facioscapulohumeral Muscular DystrophyДокумент7 страницFacioscapulohumeral Muscular DystrophynellieauthorОценок пока нет
- Intra Bba - LL.B - 2017-2022 Batch Moot Court Competition - 2019 Icfai Law School, The Icfai University, DehradunДокумент12 страницIntra Bba - LL.B - 2017-2022 Batch Moot Court Competition - 2019 Icfai Law School, The Icfai University, DehradunAman jainОценок пока нет
- Dr-Breath by Carl Stough PDFДокумент128 страницDr-Breath by Carl Stough PDFkrishna2205100% (12)
- Approach To Floppy InfantДокумент44 страницыApproach To Floppy InfantShauki AliОценок пока нет
- An Approach To A Floppy InfantДокумент33 страницыAn Approach To A Floppy InfantayunisallehОценок пока нет
- Blood Biomarkers All Athletes Should KnowДокумент10 страницBlood Biomarkers All Athletes Should KnowkadarzoltanОценок пока нет
- Mu 089Документ4 страницыMu 089Rahul RaiОценок пока нет
- Myasthenia GravisДокумент6 страницMyasthenia GravisNader Smadi100% (2)
- Localisation in NeurologyДокумент19 страницLocalisation in NeurologyArnav GuptaОценок пока нет
- 3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsДокумент18 страниц3 Brain Spinal Cord and Nerve Disorders of DogsKoleen Lopez ÜОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент28 страницNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Kołtuniuk Et Al., 2017 PDFДокумент11 страницKołtuniuk Et Al., 2017 PDFDiba Eka DiputriОценок пока нет
- Cciv Civil Law Internal Moot Court Problems 5 Years B.A.,LL.B - A Semester XДокумент8 страницCciv Civil Law Internal Moot Court Problems 5 Years B.A.,LL.B - A Semester X165Y064 OM KISHORE KUMAR NОценок пока нет
- Neuro 4 - AnswersДокумент107 страницNeuro 4 - AnswerskimОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus NCP MandoДокумент7 страницDiabetes Mellitus NCP MandoJan Mar BueraОценок пока нет
- PBL 2Документ46 страницPBL 2maisara aisyahОценок пока нет
- Origen HipotoniaДокумент7 страницOrigen HipotoniaPablo Hernández MaripillánОценок пока нет
- DMD PosterДокумент2 страницыDMD PosterPanduRespatiОценок пока нет
- Application of The Betty Neuman Systems Model in The Nursing Care of Patients/clients With Multiple SclerosisДокумент8 страницApplication of The Betty Neuman Systems Model in The Nursing Care of Patients/clients With Multiple Sclerosisputu noviyantiОценок пока нет
- Cell Salt Reference ChartДокумент3 страницыCell Salt Reference ChartRidalyn Adrenalyn100% (7)
- C - The Microwave Syndrome - 13 CategoriesДокумент4 страницыC - The Microwave Syndrome - 13 CategoriesEmf RefugeeОценок пока нет
- Peter Holmes - Jade Remedies - A Chinese Herbal Reference For West Life Vol 2Документ504 страницыPeter Holmes - Jade Remedies - A Chinese Herbal Reference For West Life Vol 2jeanroОценок пока нет
- Nclex ChartsДокумент39 страницNclex ChartsDuvu99100% (6)
- Approach To QuadriplegiaДокумент4 страницыApproach To QuadriplegiaPraveen BabuОценок пока нет
- Altar Rle Case StudyДокумент6 страницAltar Rle Case StudySi Kio'Оценок пока нет
- Neuromuscular Junction DisorderДокумент10 страницNeuromuscular Junction DisorderZosmita Shane GalgaoОценок пока нет
- OKMGF Miastenia y ReishiДокумент8 страницOKMGF Miastenia y ReishirubsrubsОценок пока нет