Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
HRM CH 11
Загружено:
Eiimae Villanueva0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров21 страницаОригинальное название
HRM Ch 11
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
6 просмотров21 страницаHRM CH 11
Загружено:
Eiimae VillanuevaАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 21
Human Resources Management in
Canada
Fourteenth Canadian Edition
Chapter 11
Strategic Pay Plans
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 1
Learning Objectives (1 of 2)
11.1 Explain the strategic importance of total
rewards.
11.2 Describe four core considerations an
organization needs to make when determining
compensation decisions.
11.3 Define pay equity and explain its importance
today.
11.4 Explain equity theory of motivation and how an
organization can address feelings of inequity.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 2
Learning Objectives (2 of 2)
11.5 Explain in detail each of the three stages in
establishing pay rates.
11.6 Describe the elements of compensation for
special positions: executives, managers, and
professionals.
11.7 Discuss competency-based pay.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 3
Total Employment Rewards (1 of 5)
Employee Compensation:
• All forms of pay going to employees and arising from their
employment.
• Two main components:
– Direct financial payments (wages, salaries, incentives,
commissions, and bonuses).
– Indirect financial payments (financial benefits like employer-
paid insurance and vacations).
• Pay plans must adhere to legal requirements, union
issues, rewards alignment and equity.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 4
Total Employment Rewards (2 of 5)
Aligning Total Rewards with Strategy:
• Aligned reward strategy is directly related to employee
behaviours the firm needs to achieve its competitive
strategy.
• Total rewards include also more challenging jobs, career
development, and recognition programs.
• Considerations in setting compensation policy:
– Does the firm want to be a leader or follower regarding
pay.
– Business strategy.
– Cost of different types of compensation.
Important policies: basis for salary increases, promotion
and demotion policies, overtime pay policy, policies on
probationary pay and military service leave, jury duty, and
holidays.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 5
Total Employment Rewards (3 of 5)
Legal Considerations in Compensation:
Legislation affecting compensation are:
• Employment/Labour Standards Acts (Canada Labour
Code).
– Sets minimums for pay, wages, hours of work, vacations,
statutory holidays, termination pay, and record keeping of
pay information.
• Workers’ compensation laws:
– Each jurisdiction has own laws to provide reasonable
income to victims of work-related accidents/illnesses.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 6
Total Employment Rewards (4 of 5)
Legal Considerations in Compensation:
• Human rights acts:
– Protect workers from discrimination.( such as in
compensation)
• Canada/Quebec Pension Plans:
– Mandatory contributions by employees and employers.
• Pay Equity Act:
– Equal pay for jobs of equal value to all classes of
employees.
– Regardless of requirement, wage gaps still persist.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 7
Total Employment Rewards (5 of 5)
Union Considerations on Compensation Decisions:
• Unions and labour relations laws influence pay plans.
• The Canadian Industrial Relations Board ensures
employees are treated in accordance with their legal
rights.
• Union attitudes toward compensation:
– Concerns about managerial malpractice.
– Workers are the only ones who can judge the relative value
of each job.
– Management’s method in job evaluation can be manipulative
in order to restrict or lower pay.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 8
Equity Theory and Its Impact on Pay
Rates (1 of 2)
Equity Theory of Motivation:
• Proposes that people are motivated to maintain a balance
between what they perceive as their contributions and
their rewards.
• External equity – how does a job’s pay rate in one
company compare to a pay rate in other companies.
• Internal equity – compare pay rates with co-workers doing
the same or similar jobs.
• Individual equity – fairness of pay compared to
performance.
• Procedural equity – fairness in pay decisions.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 9
Equity Theory and Its Impact on Pay
Rates (2 of 2)
Addressing Equity Issues:
• Managers can use various means to address equity
issues:
– Salary surveys to monitor and maintain external equity.
– Job analysis and comparisons to maintain internal equity.
– Performance appraisals and incentive pay to maintain
individual equity.
– Communication, grievance mechanisms, and employee
participation to maintain procedural equity.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 10
Establishing Pay Rates (1 of 6)
• Stage 1: Preparing for Job Evaluation- determines which
factors to be compensated.
• Stage 2: Conduct a Wage Salary Survey
• Stage 3: Combine the Job Evaluation and Salary
survey- determines pay rate for each job.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 11
Establishing Pay Rates (1 of 6)
Stage 1: Preparing for Job Evaluation:
• Job evaluation is a formal and systemic comparison of
jobs to determine the relative worth of a job.
• Establish a benchmark job against which other jobs are
compared.
• Compensable factors:
– Fundamental elements of a job such as skill, effort,
responsibility, and working conditions.
– May include know-how, problem solving, accountability.
– All comparable jobs are evaluated using the same factors.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 12
Establishing Pay Rates (2 of 6)
Stage 1: Preparing for Job Evaluation:
• Job evaluation committee:
– May include employees, HR staff, managers, and union
representatives.
– Committee identifies key benchmark job which will be
evaluated first.
– Relative value and importance of all other jobs will be
compared to the benchmark jobs.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 13
Establishing Pay Rates (3 of 6)
Stage 1: Preparing for Job Evaluation:
• Job evaluation methods:
– Classification/grading method: categorizing jobs into groups.
▪ Classes are groups of similar jobs.
▪ Grades are groups of jobs similar in difficulty but otherwise
different.
▪ Pay grade comprises jobs of approximately equal value or
importance.
– Point method identifies number of compensable factors in
a job.
▪ Most common factors: skill, effort, responsibility, and working
conditions.
▪ The extent to which each factor present in the job is evaluated
and points assigned for each factor.
▪ Points for each factor summed up to get overall value of job.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 14
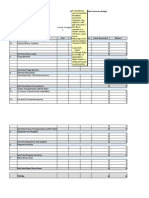
Establishing Pay Rates (4 of 6)
Stage 1: Preparing for Job Evaluation:
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 15
Establishing Pay Rates (5 of 6)
Stage 2: Conduct a Wage/Salary Survey:
• Use survey to:
– Determine pay rates for benchmark jobs.
– Determine pay based on marketplace rates.
– Collect data on benefits, pay-for-performance, etc.
• Formal/informal surveys by the employer.
• Commercial, professional, and government salary
surveys.
• Any survey data must be carefully assessed for accuracy.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 16
Establishing Pay Rates (6 of 6)
Stage 3: Combine Job Evaluation and Salary
Surveys to Determine Pay for Jobs:
• Determine pay for pay grades and develop rate ranges.
• Benefits of using pay ranges:
– Allows employers to provide for performance differences.
– More flexibility for employees with greater experience of
seniority.
• Broadbanding reduces the number of salary grades and
ranges; allows flexibility in compensation.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 17
Special Considerations in
Compensation (1 of 4)
Correcting Out-of-Line Rates:
• Underpaid employees should have wages raised to the
minimum of the rate range for their pay grade.
• Overpaid employees are often called red circle pay
rates.
– Freeze the rate paid.
– Transfer or promote to jobs that match the rate.
– Freeze rate for a period to time; if promotion is not
possible, the cut the rate to the maximum in the pay range
for their grade.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 18
Special Considerations in
Compensation (2 of 4)
Pay for Knowledge: Competency-Based Pay Plans:
• Pay for range, depth and types of knowledge employees
are capable of using, rather than for the job they hold.
– Core competencies – knowledge and behaviours.
– Functional competencies – organizational function.
– Behavioural competencies – expected behaviours.
– Pay-for-knowledge program should include:
▪ Measurable competencies/skills directly important for job
performance.
▪ New and different competencies.
▪ On-the-job training.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 19
Special Considerations in
Compensation (3 of 4)
Pay for Executive, Managerial and Professional
Jobs:
• Executives and managers Compensation package:
– Salary, benefits, short term incentives, long-term incentives,
and perquisites.
– Salary depends on the value of the person’s work to the
organization and how well responsibilities are carried out.
– Compensation tends to emphasize performance incentives.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 20
Special Considerations in
Compensation (4 of 4)
Pay for Executive, Managerial and Professional
Jobs:
• Compensating professional employees:
– Compensable factors not easily measured for analytical
jobs.
– Focus is on problem solving, creativity, job scope and
technical knowledge and expertise.
– Job evaluation does not show value of professional work.
Knowledge is extremely difficult to quantify and measure.
– Employers use market-pricing approach.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Canada Inc. 11 - 21
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Vanisha Patika Sari - c1c020055 - Tugas Minggu Ke 14 BingДокумент7 страницVanisha Patika Sari - c1c020055 - Tugas Minggu Ke 14 BingVanisha PatikaОценок пока нет
- Organizational BehaviourДокумент3 страницыOrganizational BehaviourMuzna KhalidОценок пока нет
- Research Proposal On Cash TransfersДокумент28 страницResearch Proposal On Cash TransfersMartin0% (1)
- CARE GBV - Concept Note Summary Budget TДокумент10 страницCARE GBV - Concept Note Summary Budget TtawandaeltonОценок пока нет
- Week 2 National Income-2Документ41 страницаWeek 2 National Income-2elijah thonОценок пока нет
- Hw1a - G6Документ3 страницыHw1a - G6CHUA JO ENОценок пока нет
- Static Labor SupplyДокумент34 страницыStatic Labor SupplyPAWAN SAROJОценок пока нет
- Ampa Fairley Rationalisation Project Onshore Compression Plant EPICOM (Contract #980085/EAF)Документ25 страницAmpa Fairley Rationalisation Project Onshore Compression Plant EPICOM (Contract #980085/EAF)Alireza entОценок пока нет
- Chapter-13 Evaluation of Countries For Operations: Presented By: Raju ShresthaДокумент35 страницChapter-13 Evaluation of Countries For Operations: Presented By: Raju Shresthaajambar khatriОценок пока нет
- Residency StatusДокумент13 страницResidency StatusPhương NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Employee Provident Fund Scheme: Boon or BaneДокумент8 страницEmployee Provident Fund Scheme: Boon or BaneAkash PanigrahiОценок пока нет
- The Role of Labor Unions.....Документ2 страницыThe Role of Labor Unions.....Glorrya TambotoОценок пока нет
- Dessler - CH - 03Документ28 страницDessler - CH - 03Tashriful AlamОценок пока нет
- Globalization and International Linkages: Assignment OnДокумент6 страницGlobalization and International Linkages: Assignment OnShuvorehmanОценок пока нет
- S Tudents' Activity Sheet in Applied Economics SAS #2 Week 2 Controlled Activity 2.1Документ5 страницS Tudents' Activity Sheet in Applied Economics SAS #2 Week 2 Controlled Activity 2.1Mark DomingoОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Mathematics For Business and Consumers, Third EditionДокумент4 страницыContemporary Mathematics For Business and Consumers, Third Editionবিষাক্ত মানবОценок пока нет
- Economics Project Final DraftДокумент28 страницEconomics Project Final Draft' Devansh Rathi 'Оценок пока нет
- HR 92777 Brochure Nieuw in Nederland Niet+EU Engels v4Документ26 страницHR 92777 Brochure Nieuw in Nederland Niet+EU Engels v4ccОценок пока нет
- 2017 Amendment in Maternity ActДокумент7 страниц2017 Amendment in Maternity ActBhola PrasadОценок пока нет
- DPS Assignment Individual MitikuДокумент14 страницDPS Assignment Individual MitikuChaka YohannesОценок пока нет
- Unit 10 PacketДокумент5 страницUnit 10 Packetprissy the mf libraОценок пока нет
- Econ Oct - Nov 2023 Paer 23Документ5 страницEcon Oct - Nov 2023 Paer 23Ibrahim AbidОценок пока нет
- EAB-1Документ6 страницEAB-1Vipin VipsОценок пока нет
- Unemployment Benefit Programs: Start Here!Документ1 страницаUnemployment Benefit Programs: Start Here!Moyosade Ridwan OlayemiОценок пока нет
- EconomicsДокумент22 страницыEconomicsShonit kediaОценок пока нет
- MMW Culminating ActivityДокумент2 страницыMMW Culminating ActivityJarlyn AcedilloОценок пока нет
- AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key FormulasДокумент6 страницAP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key FormulasThanh Phu TranОценок пока нет
- Construction Contract TemplateДокумент5 страницConstruction Contract TemplatesithumОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 13 Answers 2nd EdДокумент3 страницыIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 13 Answers 2nd EdDesre50% (2)
- Introduction To Social SecurityДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Social SecurityDevanshu JulkaОценок пока нет