Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SW 1spinjointdes
Загружено:
jjoejjoe0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыSpin welding is a technique for welding thermoplastic parts that utilizes a circular spinning motion, in conjunction with applied pressure to weld two parts together. Heat generated by the friction between the two parts causes the plastic interfaces to melt and fuse together producing a strong hermetic seal. This bulletin should be used as a guideline to aid the designer during the initial concept stage of designing a product for spin welding.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
SW-1Spinjointdes
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSpin welding is a technique for welding thermoplastic parts that utilizes a circular spinning motion, in conjunction with applied pressure to weld two parts together. Heat generated by the friction between the two parts causes the plastic interfaces to melt and fuse together producing a strong hermetic seal. This bulletin should be used as a guideline to aid the designer during the initial concept stage of designing a product for spin welding.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыSW 1spinjointdes
Загружено:
jjoejjoeSpin welding is a technique for welding thermoplastic parts that utilizes a circular spinning motion, in conjunction with applied pressure to weld two parts together. Heat generated by the friction between the two parts causes the plastic interfaces to melt and fuse together producing a strong hermetic seal. This bulletin should be used as a guideline to aid the designer during the initial concept stage of designing a product for spin welding.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Data Sheet
SW-1
Joint Design and Material
Compatibility for Spin Welding
General Description Primary Factors Influencing Joint
Spin welding is a technique for welding ther- Design
moplastic parts that utilizes a circular spinning All of the following questions should be
motion, in conjunction with applied pressure, answered prior to the design stage to gain a
to weld two parts together. The part-to-part total understanding of the weld joint require-
interface must be circular. One part is held sta- ments:
tionary in a holding fixture as another part is
rotated against it using applied pressure. Heat • What type of material(s) is to be welded?
generated by the friction between the two • What is the overall part size and configura-
parts causes the plastic interfaces to melt and tion?
fuse together producing a strong hermetic seal. • What are the final requirements of the
This bulletin should be used as a guideline to part?
aid the designer during the initial concept - Is a structural bond desired and, if so,
stage of designing a product for spin welding. what load forces does it need to resist?
Any dimensions given in the designs should be - Is a hermetic seal required? If so, to
used as guidelines only, since the specifics of what pressure?
your application may require a variation to the - Does the assembly require a visually
basic design. attractive appearance?
If you have questions or need assistance in - Is flash or particulate objectionable
designing your parts, contact your local inside and/or outside?
Branson representative, your regional techni- - Any other requirements?
cal center, Branson in Honeoye Falls, NY, or Driving (Spinning) Tool
the applications lab at Branson headquarters
Rib on Plastic Part
in Danbury, CT.
Key Design Considerations
There are several factors necessary for success-
ful spin welding, including a determination of Branson
Stationary Fixture Slot/Recess in Plastic
the speed for part rotation, and appropriate
Part
Worldwide
pressure of the driver as the parts are spun Figure 1. Drive Details Headquarters
together. Also, a good spin welding joint
should have a weld area greater than a typical 41 Eagle Road
wall section of the part and must also provide Danbury, CT
sufficient part-to-part alignment. Driving (Spinning) Tool 06813-1961
It is necessary that parts to be spin welded (203) 796-0349
have a circular axis (such as a sphere, cylinder, Fax (203) 796-9838
Email: info@bran-
disc, or ring) and a drive feature to enable sonultrasonics.com
spinning of the upper section (see Figures 1 Spinning (Upper) Part
and 2).
Figure 2. Self-Aligning Drive Details for
Automation
Note: Dimensions given Typical Spin Welding Joint Designs
in the designs should be
used as guidelines only,
since the specifics of your
application may require a
variation to the basic
design.
T = Wall thickness
B = 1.5 x T
C = Clearance ~0.005”
R = Radius ~ 0.050”
L = Lead-in 0.020 to 0.040”
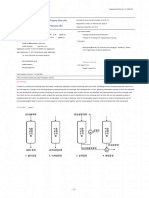
i = Interference 0.010 to 0.020”
Figure 4. Flanged Shear Joint Figure 5. Shear Joint Design for
Figure 3. Shear Joint Design Design Nylon
T = Wall thickness
F = 30o min.
A = Depth of weld
~ 0.5 x T to 0.8 x T
C + D = Weld surface,
~2.5 x T
E = A + 0.010”
Figure 6. Tongue and Groove Figure 7. Tongue and Groove Figure 8. Tongue and Groove
Joint with External Joint Joint with External
Skirt Flash Trap
Table 1. Material Weldability
The codes in this table indicate relative ease of welding for the more common thermoplastics. Note: The rat-
ings below do not relate to the strength of the weld obtainable. Use these tables as a guide only, since vari-
ations in resins, fillers, and part geometry may produce slightly different results.
Code: 1 = Easiest, 5 = Most difficult.
Material Weldability Material Weldability
Amorphous Polymers Semi-Crystalline Polymers
ABS 1-2 Acetal 2-3
Branson ABS/polycarbonate alloy 2 Cellulosics 2
41 Eagle Road Acrylic 2 Fluoropolymers 3-4
Acrylic multipolymer 2 Liquid crystal polymers 2-3
Danbury, CT
Butadiene-styrene 1-2 Nylon 1-2
06813-1961 Phenylene-oxide based resins 2 Polyester, thermoplastic
Polyamide-imide 2-3 Polyethylene terephthalate/PET 2-3
475 Quaker Meeting Polyarylate 2 Polybutylene terephthalate/PBT 2
House Road Polycarbonate 1-2 Polyetheretherketone - PEEK 3
Honeoye Falls, NY Polyetherimide 2 Polyethylene 3
Polyethersulfone 1-2 Polyphenylene sulfide 2
14472 Polystyrene (general purpose) 1-2 Polypropylene 2
(585) 624-8000 Polystyrene (rubber modified) 2
Fax (585) 624-1262 Polysulfone 2
PVC (rigid) 1-2
© Branson Ultrasonics SAN-NAS-ASA 1-2
Corporation, 2002 PBT/polycarbonate alloy 2
Revised and Printed in
U.S.A.1/06
www.Branson-PlasticsJoin.com
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFДокумент49 страницDual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFabhishekОценок пока нет
- Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient and Pipe Length CalculationДокумент2 страницыOverall Heat Transfer Coefficient and Pipe Length CalculationCaleb FalcoteloОценок пока нет
- Element of PowerДокумент334 страницыElement of Powermwu08Оценок пока нет
- Silo Protection PDFДокумент4 страницыSilo Protection PDFjovanivanОценок пока нет
- Fat Digestion and Metabolism in RuminantsДокумент23 страницыFat Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminantsshahbaz zafarОценок пока нет
- Streeter-Phelps equation for predicting dissolved oxygen levelsДокумент7 страницStreeter-Phelps equation for predicting dissolved oxygen levelsAditya SheoranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17Документ97 страницChapter 17Marco KrugerОценок пока нет
- Methods For Waste Waters Treatment in Textile IndustryДокумент5 страницMethods For Waste Waters Treatment in Textile Industryjpsingh75Оценок пока нет
- Assignment Open and Closed Thermodynamic SystemДокумент1 страницаAssignment Open and Closed Thermodynamic SystemJenellie BahintingОценок пока нет
- Dehydration of Ethanol To EthyleneДокумент10 страницDehydration of Ethanol To EthylenewiboonwiОценок пока нет
- 02 Filtros de Ingreso A CompresorДокумент6 страниц02 Filtros de Ingreso A CompresorLuis Alonso Dipaz ZeaОценок пока нет
- Zahid Husain M.Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Faculty of Pharmacy, IU, LucknowДокумент24 страницыZahid Husain M.Pharm (Pharmaceutics) Faculty of Pharmacy, IU, LucknowQA Dhq OkaraОценок пока нет
- I-V Characterization of Tunnel Diodes and Multojunction Solar CellsДокумент7 страницI-V Characterization of Tunnel Diodes and Multojunction Solar CellsMaura MusioОценок пока нет
- Cutting Tools TypeДокумент3 страницыCutting Tools TypeneurraОценок пока нет
- FAME - Automated Fatty Acid Derivatization & GC - MS AnalysisДокумент3 страницыFAME - Automated Fatty Acid Derivatization & GC - MS AnalysisHushla ShudriОценок пока нет
- Information Booklet Elements Compounds and MixturesДокумент40 страницInformation Booklet Elements Compounds and MixturesnowhinesonchemistryОценок пока нет
- 04 - Spektroskopi UV-Vis - 3Документ16 страниц04 - Spektroskopi UV-Vis - 3muktadi-amri-8721Оценок пока нет
- Nickel CobaltДокумент8 страницNickel CobaltSunnyОценок пока нет
- Cracking and Repair of Closing Welds in 2.25 Cr1 Mo Steel Vessels Operating in High Temperature Synthesis GasДокумент9 страницCracking and Repair of Closing Welds in 2.25 Cr1 Mo Steel Vessels Operating in High Temperature Synthesis Gasvaratharajan g rОценок пока нет
- Computational LaboratoryДокумент31 страницаComputational LaboratoryFrendick LegaspiОценок пока нет
- United States: Patent OfficeДокумент4 страницыUnited States: Patent OfficesherlybonitaОценок пока нет
- Completing The Puzzle:: 100% Plant-Derived PETДокумент4 страницыCompleting The Puzzle:: 100% Plant-Derived PETAtif AzamОценок пока нет
- (Chapter 1) Fluid Mechanics For Mechanical EngineeringДокумент38 страниц(Chapter 1) Fluid Mechanics For Mechanical EngineeringAnn Razon0% (1)
- IJREI_Thermal modelling of three stage vapour compression cascade refrigeration system using entropy generation principle for reducing global warming and ozone depletion using ecofriendly refrigerants for semen preservationДокумент7 страницIJREI_Thermal modelling of three stage vapour compression cascade refrigeration system using entropy generation principle for reducing global warming and ozone depletion using ecofriendly refrigerants for semen preservationIjrei JournalОценок пока нет
- Welding: Dr. Sunil JhaДокумент21 страницаWelding: Dr. Sunil JharassdriverОценок пока нет
- SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNДокумент60 страницSHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNniaaparamita100% (1)
- Build Up MaterialsДокумент5 страницBuild Up MaterialsMishell CarolinaОценок пока нет
- Spectrex UV IR 20 20LBДокумент2 страницыSpectrex UV IR 20 20LBGustavo Alejandro Flores GarriОценок пока нет
- Tooth Colour Restorative Materials in Ped DentДокумент27 страницTooth Colour Restorative Materials in Ped DentNilay ShahОценок пока нет