Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cadbury - PLC: Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1)
Загружено:
rebekah_beckyИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cadbury - PLC: Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1)
Загружено:
rebekah_beckyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CADBURY.
PLC
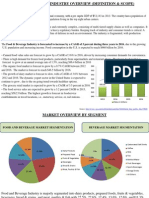
1.0 INTRODUCTION
Cadbury is a leading global confectionary company with an outstanding portfolio of
chocolate, gum and candy brands. Cadbury stands in a high position in people’s mind where is
creates brands people love – brands like Cadbury, Trident and Halls. Heritage of Cadbury starts
in 1824 when John Cadbury established a shop in Birmingham. He mainly sells cocoa and
chocolate. Since then Cadbury have lengthened its business throughout the world by a
programme of organic and acquisition led growth. Cadbury employs about 50,000 people and
have direct operations in over 60 countries, where it’s selling Cadbury products in almost every
country around the world. In 2006, the company had over $15 billion in overall sales. In March
2007, Cadbury announced that it intends to separate its confectionery and beverage businesses.
With almost 200 years in the business, Cadbury have intended to continue its duty to flourish in
the coming decades. Cadbury’s core purpose is “creating brands people love” captures the spirit
of what we are trying to achieve as a business. Cadbury collaborates and work as team to convert
products into brands. Simply put, Cadbury spread happiness.
This report will be explained about the success, problems by using PEST analysis, Porter’s five
forces and SWOT analysis. Ansoff growth strategy will be used to explain to analyze what type
of market it’s concentrating. Finally, recommendations will be given by using Porter’s Diamond
tool.
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 1
2.0 PEST ANALYSIS
A useful tool when scanning the general environment is PEST analysis. This refers to political,
economic, social, and technology factor. PEST analysis is simply another tool to help the
organization detect and monitor those weedy signals in the hope of recognizing the
discontinuities or fractures shaping the environment. It also can be used to help to detect trends
in the external environment that will ultimately find their way into the competitive environment.
Although the factors deal separately, it should be noted that it has interrelationship between the
factors exist. Cadbury has been listed under food industry. As a food industry it faces many
challenges in the wide market. These challenges can be identified and analyzed by using PEST.
2.1 Political Factors
The political factor of PEST deals with the effect of government policy. Moreover as
government policy is worked out through legislation, it encompasses all legal elements of this
analysis. This includes items such as government stability, taxation policy, and government
regulation. On the other hand they can place obligations and duties on organizations.
Political factors influence food and beverage industry in many ways. This can create situations
where the organization has to face obstacles in their business. Taxes, tariffs and subsidies are one
of the political factors which bring implication to the business. Government in many countries
are very carefully controls their own economy situations by various strategies, including
subsidizing some agriculture, taxing imports and not helping taxing and other agriculture. This
usually mirrors in food prices. In some situations, some countries taxes all imports and this will
bring the price of these imports increase. Particularly in democracies the government, and its
plan for agriculture changes regularly with ensuing variation in the prices of various foods.
Meanwhile the United States Food and Drug Administration (FBA) is a government agency
which is responsible for shielding and promoting the health of consumers. This agency provides
public service by observing the efficiency and the safety of food ingredients and packaging, food
security and many more. This proceed had become one of the major aggressive part of federal
legislation where it’s protecting the public. By establishing the FDA, it’s limiting the amount of
power and choices that the individual companies could make. This becomes an obstacle for the
food and beverage industry to create new products and it’s also make difficult way to new
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 2
entrance to enter in market. Moreover, the regulation affect most U.S and foreign entities that
manufacture, hold, process, grow or import food products for the U.S market.
2.2 Economic Factor
The second element of a PEST analysis absorbs a study of economic factors. All businesses are
affected by national and global economic factors. National and global interest rate and fiscal
policy will be set around economic conditions. The ambiance of the economy utters how
consumers, suppliers and other organizational stakeholders such as suppliers and creditors
behave within society. Key economic indicators include interest rates, disposable income,
unemployment rates, retail price index (inflation), gross domestic product (GDP), and exchange
rate.
Retailers and manufacturers can culturally and organizationally grow and be equipped to execute
business strategies. But, economic factors eventually provide as the key restriction. Companies
that can’t invest cannot execute, without getting ready to access to capital market, many
companies cannot invest. In some point of view, as the cost of capital is too high, companies
have been forced deliberately. This brings to a situation where manufactures and retailers who
want to innovate, improve or capture market share are not able to do it without some kind of
financial underpinnings which are using debt or equity markets.
Meanwhile, currency is one of the key economic factors that influence the food and beverage
industry. Since the U.S is the leading trading partner and the currency swing has transpired
nearly overnight. Canadians are the most spoken about the effects of currency exchange. But
currency is a matter universally except for China, where Yuan is attached to the U.S dollar. The
U.S dollar has also recently crashed to a new all-time low versus the euro. So the downward
slide of the U.S has made it easier for the U.S to export to other countries and has also created
some unexpected barriers in the other way, especially for export-dependent producers.
According to The National Restaurant Association's Senior Vice President of Research and
Information Services Hudson Riehle, he said that, "the wholesale food price inflation we
currently see is the highest in 27 years. Last year, it jumped 7.6 percent, and on a 2008 year-to-
date basis through March, wholesale food prices continue to rise at 8.5 percent. Several
individual commodities critical to the majority of restaurant operations are also posting dramatic
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 3
gains this year, with flour (87%), eggs (73%), fats and oils (49%), cheese (27%), milled rice
(25%) and milk (20%) rising most sharply. Added, many of these increases are all coming on top
of double-digit growth rates in 2007. Several factors have contributed to the dramatic rise in food
prices in recent years, including higher oil and energy prices; the growing global demand from
rapidly developing economies such as China and India; a weak U.S. dollar; and a larger share of
the grain market being diverted to ethanol production”. Inflation is common statement about the
percent change in the overall price level between two periods as deliberate by a price index.
Chart 1.0 shows December to December changes over the past 53 years as measured by the
Consumer Price Index (CPI), a well-liked measurement of inflation in the U.S. Observed that the
rate of inflation different greatly during the 1970s and into the early 1980s but has been
relatively stable recently. Since the inflation rate is a national average of all prices, it may vary
greatly from the rate practiced by anybody particular household. Each household will have
different types and amount of items in their "market basket" and thus may experience the effects
of inflation in a different way. All these issues bring negative feedback to the food and beverage
industry.
2.3 Social Factors
Social factors include of culture changes within the environment and are frequently referred to as
socio-culture. Social forces affect our attitudes, interest s and opinions. These forces shape who
we are as people, the way we behave and ultimately what we purchase.
In our modern world with progressively more cheap, high calories food such as fast foods and
“junk food” are prepared food that are high in salt, sugar, or fat. These types of food which is
combined with many consumers’ lifestyles, growing urbanization and changing style of
transportation, consumers eating ethics all caused of obesity which has rapidly increased in the
last few decades, around the world. Although most food and beverage companies are firm in
their customer’s weight problem, they have also realized that ‘damage’ can be done to their
business if they do not respond to the obesity problem in society. They are therefore keen to play
a role in overcome the problem. A study was carried and in this study EIRIS has assessed the
selected companies’ policy statements, strategies and reporting mechanisms that specifically
address obesity. Table 2.0 shows the percentage of the production and sale of unhealthy products
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 4
produced by ‘High Exposure’ companies. According to the information collected by EIRIS, it’s
described that the management response to obesity by four of the six selected companies has
been assessed as transitional. Refer to Table 2.0, Unilever and McDonalds are assessed as
justifying the business risks related with obesity in a narrow way. Cadbury Schweppes is closest
to achieving a good estimation. Unilever is close to getting a transitional estimation. This brings
a cause where customers tend to choose products which not effecting the health. Continuously
this occur problems where the sales of some food and beverage industry will drop.
2.4 Technology Factor
Without doubt some of the major changes taking place in the general environment that are
impacting the competitive environment are technological. Technological advance have greatly
changed the manner in which business operates. Food and beverage industry uses technology in
many ways such as internet, telephone, multimedia of software, mobile phones, photocopies and
fax machine which transmit and record information.
Technology has created a society which expects instant results. This technological revolution has
increased the rate at which information is exchanged between stakeholders. A faster exchange of
information benefits the businesses as they are able to react quickly to changes within their
operating environment. However an ability to react quickly also creates extra pressure as
businesses are expected to deliver on their promises within ever decreasing timescales.
Moreover, table 4.0 shows the global market for active, controlled and intelligent packaging for
food and beverages will increase from $15.5 billion in 2005 to $16.9 billion by the end of 2008.
It should reach $23.6 billion by 2013, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9%.
Controlled packaging has the largest share of the market; estimated to comprise 45.4% in 2008,
it will decrease slightly too approximately 40.5% in 2013. Active packaging will comprise
approximately 27% of the market in 2008 but will decrease slightly to 26.9% by 2013.
The pace of technological change is so fast that the average life of a computer chip is
approximately 6 months. Technology is utilized by all age groups, children are exposed to
technology from birth and new generations of technology sense pensioners known as “silver
surfers” have emerged. Technology will continue to develop and impact on consumer habits and
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 5
expectations, organizations that ignore this fact face extinction. Moreover, children also addicted
with the advertisement that published in internet. They easily adopted with the food which is not
healthy to eat.
3.0 SWOT ANALYSIS
SWOT summarizes the key issues from the business environment and the strategic capability of
an organization that are most likely to impact on strategy development. It refers to strength,
weakness, opportunity and threats. SWOT analysis will help the organization to prove useful in
both the general environment and the competitive environment.
Strength and weakness refer to the organization’s internal environment, over which the
organization has control. Strength is areas where the organization excels in comparison with its
competitors, while weakness is areas where the organization may be at a comparative
disadvantage. Meanwhile, opportunities and threats refer to the organization’s external
environment, over which the organization has much less control.
3.1 Strength
In this wide market Cadbury has a strong brand name. This strong brand adds the value and
consumers high in interest and is less likely to purchase competitors’ product. Moreover, it also
can force change and demand to be heard. Cadbury always characterized as family brand or
parent brand. A parent brand works as an ‘umbrella’ under which additional sub-brands can be
sold. Cadbury Dairy Milk, Cadbury Crunchie and Cadbury Wispa are those examples of a
mixture brand strategy. This approach allocates for the most favorable use of the corporate
(family) brand name. Meanwhile, it’s also allocating an individual brand to be recognized.
Cadbury Wispa is the well known product which can give as example for this statement. In
addition, research shows that 96% of Irish consumers identify the Cadbury brand. Meanwhile,
74% state that when it comes to chocolate, only Cadbury comes into people’s mind and only it
will do. The growth of strong brands has been input to the growth of Cadbury Ireland. The
benefits that Cadbury gets to gain are it will help to enhance company value by possessing of a
strong brand. Moreover, customers’ favorite and loyalty on this brand brings a positive view and
it will ideal to competitors. Cadbury successfully rule the market place by overcoming the barrier
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 6
to competition functions in market. This means competitors will find the path to enter the market
harder.
Between the year 2004 and 2007, Cadbury’s organic revenue growth averaged 6% a year, a
major increase on the previous four years. When Cadbury’s confectionery growth averaged less
than 3%, and the Adams business, which Cadbury brought in 2003, hardly grew. Cadbury have
drastically accelerated its growth since 2004 by unchaining the potential of the Adams business
and by largely growing its investment in innovation, marketing and sales. Graph 4.0 in Appendix
shows a significant growth of Cadbury. Cadbury successfully achieved its desire of achieving
between 4% and 6% annual organic growth for the 2008-2011. The reasons behind this success
are Cadbury has strength of its brands and market positioning. Moreover, Cadbury also increased
its investment in product innovation, marketing and sales. Cadbury also concentrates in its
greater exposure to faster growing categories such as, gum and emerging markets. Lastly, the
market has grown consistently at around 5% every year for the last four years because of the
strong demand for confectionery. Cadbury’s revenue aims allow for some good reasons of its
portfolio as Cadbury focus on its efforts on profitable growth.
3.2 Weakness
Cadbury has a fragile position in U.S market. Cadbury failed to run its business successfully in
U.S and they failed to make profit that they get to earn in other countries. Besides, Cadbury also
has lack of distribution channels and networks. Meanwhile, Cadbury’s total of market share
altogether also very small. According to market research firm Nielson, he said to the newspaper
reporter that Cadbury’s share market has dropped to lower than 30% for the first time year 2009.
In November, Cadbury had a 29.8% share, and a drop of 1.7% on the previous month. In
addition, Cadbury also lack in launching new brands in chocolate segment compare to its
competitor Nestle. But this scenario has changed where Cadbury’s value market share reached
over 70% which is the highest Cadbury brand share in the world. It also considered as “gold
standard” for chocolates in India.
In another hand, Cadbury is reliant on the confectionery and beverage market, while other
competitors such as Nestle have a more various product portfolio. It means Nestle profits can be
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 7
used to invest in other areas of the business and also for R&D. Rather than this, Cadbury’s
competitors have greater international experience but Cadbury traditionally has been strong in
Europe. Cadbury also new to U.S and its possible where Cadbury lack of understanding of the
new emerging markets compare to its competitors. All these have changed in Cadbury’s life.
Cadbury’s brand is well known internationally and consumers brand loyalty also still stands in
high position. Moreover, Cadbury also learned and now it merged with many companies. For an
example, Cadbury merged Jacob Schweppes and becomes Cadbury Schweppes in the early of
1969.
3.3 Opportunities
Cadbury merged with Jacob Schweppes and becomes Cadbury Schweppes in the early of 1969.
This brings many opportunities to Cadbury Schweppes. In 1879 Cadbury brothers begin build a
new factory outside of Birmingham. In 1881 the firm received its first export order from a agent
in Australia, and by the middle of the decade its overseas business had stretched to South Africa,
New Zealand, West India, India and both North and South America.
3.4 Threats
Innovation is key driver to success in a business market. To react to changes in consumer tastes
and favorites, healthier snacks with lower calories need to be developed. Due to its confectionary
products, it is very important for Cadbury to be aware of any present or upcoming threats. The
company should take note of the changes in the consumer’s buying trend. It is perceived that
consumers might shift from chocolates to “Healthy” snacks. If this were to happen, there might
be a poor product development which would smudge the Cadbury’s name. Needless to say price
wars would occur between its competitors like Mars, Hershey and Nestle. Due to the
abovementioned, there would be seasonal sales slumps all year round which will reflect to an
increase in cost of the raw materials needed. Cadbury would then have to be prepared for growth
of small local gourmet chocolates and regional candy manufacturers. R&D and new product
launches have led to sugar-free and centre filled chewing gum varieties and Cadbury premium
luxury treat. Low-fat, organic and natural confectionery order appears strong. Cadbury has
successfully overcome this threat to show that they make it possible. Cadbury functions in a
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 8
number of markets, including the efficient and health food and beverage sectors. Cadbury also
sells a broad range of other names such as, Green and Black chocolate, which is high in cocoa
content and it’s made by sustainable organic farming practices. This product is a leading
premium block chocolate at United Kingdom and it also available in other countries including
Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
4.0 ANSOFF GROWTH STRATEGY OF CADBURY
In order to grow organizations can pursue a number of different strategies depending on the level
of risk they are prepared to countenance, their resources and capabilities, and their management
expertise. The organization might choose to direct its energies to internal growth strategies or it
may seek to diversify in other businesses. Ansoff (1965) revised a matrix to analyze the different
strategic directions organizations can pursue. There are all together four strategies organizations
might follow which are, market penetration, product development, market development, and
diversification.
It is clear that if Cadburys was to use diversification and aim a new product at a new market. It helps
Cadbury to success where it covers the needs of customer. This generic strategy carried out through
extensive market research which helps Cadbury to identify an idea of people who would regularly
purchase Cadbury products. Moreover, product development also had been carried out by Cadbury. It has
carried some research using marketing mix 4P’s tools which are price, product, place and promotion. By
analyze the products, Cadbury gets find the negative and positive positions which will lead in future.
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 9
5.0 RECOMMENDATION
Short-term strategies help a business to focus mainly on the marketing mix which is four P’s,
product, price, place and promotion which are essential to all businesses. As these four elements
are the major things which help a business to achieve objectives if they are used correctly.
Meanwhile, in marketing there are long-term strategies which are used to plan the upcoming
events of a business, this can include fabricating tables such as Ansoff matrix which assists a
business to choose on many things such as, whether to launch a new product or to improve
previous products, overall making the right decisions on which type of strategy to use is
imperative, especially in the case of Cadburys as it helps to decide how to launch a new product,
to ensure that they reach maximum sales.
Moreover, Cadbury have to understand and keep ahead of competitors. This can be done through
market research to help a business stay above competitors. Cadbury can come out with strategies
using secondary research to help to know their biggest rivalry within the market. This will help
the organization to stay above them.
In addition, Cadbury also should aware of constraints. In this case Cadbury should also have to
be aware of the constraints they face on the marketing activities, to make sure that Cadbury
willing to work the way around it. To identify the constraints from many various factors,
Cadbury can come out with both SWOT and PEST analysis to identify it.
Understanding customer needs also one of the strategies that Cadbury should consider about.
This can be found through extensive market research to help the business determine the
customer’s outlook
on Cadbury’s products and also the new tendency within the market. Through doing market
research can find a correct segment for business and ensure success with the new product as
Cadbury have covered the needs of its chosen segment.
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 10
6.0 CONCLUSION
In this wide market organizations should follow some cultures where it will keep the company in
safe position. Cadbury becomes a leading confectionery company although it’s facing problems
in its business. By using marketing tools like above or other tools such as Porter’s Diamond,
Ansoff Matrix, International research and do on. Meanwhile, food industry is a high demand and
it’s surrounded by many other competitors. Effective steps should be taken and make sure it’s in
the right track.
-The End-
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 11
REFERRENCE
1. www.cadbury.com
2. Anthony Henry, “Understanding Strategic Management”, 2008, Oxford.
3. Jennifer G, “Food and Drug Administration (FDA)”, 2010.
Source: www.wikinvest.com
4. EIRIS, “Obesity Concerns in the Food and Beverage Industry”, 2006.
Source: www.eiris.org
5. Jeffrey P, Koplan; Kelly D. Brownell, “Response of the food and beverage industry to the
obesity threat”, 2010.
Source: www.jama.com
6. Mike Donohue, Washington D.C., “Media Statement: How Spiking Food Prices Impact
Restaurants”, 2008, National Restaurant Association.
7. US Bureau of Labor Statistics, :Frequently Asked Questions”,
Source: www.bls.gov
8. Miller, R.L.; Benjamin, D.K; “The Economies of Macro Issue”, Boston, MA, Pearson-
Addison Wesley, 2004.
9. UBM International Media BV, 2010.
Source: www.ingredientsnetwork.com
10. Philip Kotler; Kevin Lane Keller; Swee Hoon Ang, Siew Meng Leong; Chin Tiong Tan;
“Marketing Management” 5th edition, Pearson.
11. Geoff Riley, “Cadbury’s Share of UK confectionery market melts away”, 2009.
Source: tutor2u.net
12. www.cadburyindia.com
13. David, L “Strategic Marketing in a new market”, 2004, Harvard Business Review.
14. Laura. H, “Cadbury India New York Times’, 2008.
15. The Gale Group Inc, 2009.
Source: www.allbusiness.com
16. Subir Majumdar, “Marketing Segmentation strategies used by Cadbury’s and Titan”,
2009.
Source: www.indiastudychannel.com
17. “Food and Beverage”, 2008
Source: www.bccresearch.com
18. Ireland, Hoskisson, Hitt, “Understanding Business Strategy” South Wester, 2008.
19. Henry Mintzberg, Joseph Lampel, James Brian Quinn, Sumantra Choshal, “The Strategy
Process Concept”, 4th edition, Prentice Hall, 2003.
20. Philip Sadler, James C. Craig, “Strategic Management” Great Britain, 2nd edition, 2005.
21. Anthony Henry, “Understanding Strategic Management,” Oxford University Press, 1 st
edition, 2008.
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 12
22. Micheal A. Hitt, R. Duanne Ireland, Robert. E, “Strategic Management Text and
Cases” South Western, 3rd edition, 2007.
23. Professor Raphael Amit , “Strategic Management”, Faculty of Commerce and Business
Administration, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, 2003.
24. William, “Management”, International Student 4th edition, Thomson 2007.
25. Robbins, Bergman, Stagg and Coulter, “Management 5”, Pearson Education 2009.
26. Tony Morde, “Principles of Strategic Management,” Ashgate publishing limited, 3rd
edition, 2007.
27. Kesho Prasad, “Strategic Management Text and Cases,” Eastern Economy Edition,
2009.
28. Jessica Bosari, “What is Strategic Management Process” 2003-2010 Conjecture
Corporation.
29. S.E. Jackson & J.E. Dutton, “Discerning Threats and Opportunities,” Administrative
Science Quarterly 33 (1988).
30. Gerry Johnson; Kevan Scholes; Richard Whittington, “Exploring Corporate Strategy”, 8th
edition, 2008 Prentice Hall.
Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1) Page 13
Вам также может понравиться
- Cadbury - PLC: Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1)Документ11 страницCadbury - PLC: Gayathiri Thiagaraj (089044856/1)rebekah_beckyОценок пока нет
- Environmental AnalysisДокумент4 страницыEnvironmental AnalysisShara Mae GarciaОценок пока нет
- Sysco CorporationДокумент12 страницSysco CorporationNazish SohailОценок пока нет
- Iii. External Analysis: 3.1 General EnvironmentДокумент19 страницIii. External Analysis: 3.1 General EnvironmentBlanche PenesaОценок пока нет
- Penesa-Chptr 3Документ19 страницPenesa-Chptr 3Blanche PenesaОценок пока нет
- MacroДокумент8 страницMacroRaindel Carl OlofernesОценок пока нет
- Pestel AnalysisДокумент3 страницыPestel Analysisapi-254405516100% (1)
- Edited Presentation FINAL COPY - Whole FoodsДокумент46 страницEdited Presentation FINAL COPY - Whole FoodsShahriar AlamОценок пока нет
- The PESTLE AnalysisДокумент6 страницThe PESTLE AnalysisAgumas KinduОценок пока нет
- COCA-COLA Group - 1Документ22 страницыCOCA-COLA Group - 1Pravin ShimpiОценок пока нет
- Nutrition AssignmentДокумент10 страницNutrition Assignmentwudineh debebeОценок пока нет
- Iccr Draft Resolution Food Commodities 2-1Документ3 страницыIccr Draft Resolution Food Commodities 2-1rakeshОценок пока нет
- Business EnvironmentДокумент15 страницBusiness Environmentgift lunguОценок пока нет
- CVP Analysis ProjectДокумент63 страницыCVP Analysis ProjectMBA Sec AОценок пока нет
- Propose An Innovative Food Product Using The Traditional Technique. Present It Through Video Presentation or Through A Paper by Writing The ProposalДокумент2 страницыPropose An Innovative Food Product Using The Traditional Technique. Present It Through Video Presentation or Through A Paper by Writing The ProposalIan AmuraoОценок пока нет
- Typhon Food Inc Business Plan - EditedДокумент14 страницTyphon Food Inc Business Plan - EditedMeshack MateОценок пока нет
- Yahia Business DevelopmentДокумент16 страницYahia Business DevelopmentTauhid Uddin MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Essay MarketingДокумент5 страницEssay MarketingMaximiliano GoRoОценок пока нет
- Case Report - Group 4 Yum! BrandsДокумент28 страницCase Report - Group 4 Yum! Brandseagleputt1984Оценок пока нет
- Explain Why Environmental Analysis Is So Important?Документ1 страницаExplain Why Environmental Analysis Is So Important?s4ndishОценок пока нет
- Marketing PlanIncompleteДокумент28 страницMarketing PlanIncompleteArfieboy TekenemenetsuОценок пока нет
- Is The Us Responsible For ObesityДокумент4 страницыIs The Us Responsible For ObesityManileima SinghaОценок пока нет
- FOOD AND BEVERAGES Porters Pestel & Industry TrendsДокумент8 страницFOOD AND BEVERAGES Porters Pestel & Industry TrendsGreeshma SharathОценок пока нет
- SWOT and PESTLE Analysis Case Study: Yum: IndexДокумент10 страницSWOT and PESTLE Analysis Case Study: Yum: IndexAntonio Annicchiarico RenoОценок пока нет
- Economic Insight Food PricesДокумент8 страницEconomic Insight Food PricesVivek AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Pestel Pepsi ExampleДокумент2 страницыPestel Pepsi ExampleSalman Shah0% (1)
- PESTLE Analysis of The Food IndustryДокумент6 страницPESTLE Analysis of The Food IndustryShahzad Saif100% (2)
- UK CB Food and Beverage 2020Документ28 страницUK CB Food and Beverage 2020HisExcellencyОценок пока нет
- HR Report (LEON)Документ12 страницHR Report (LEON)ZeeОценок пока нет
- Finance ResearchДокумент11 страницFinance ResearchMadiha RasheedОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2: Student Number 1710D3613374Документ9 страницAssignment 2: Student Number 1710D3613374Aaron Iron Tsaka100% (1)
- Mid Term Online Paper: Reg.#: 9655 Name: Shahkar ZebДокумент6 страницMid Term Online Paper: Reg.#: 9655 Name: Shahkar ZebShah KhanОценок пока нет
- Rising Food Prices: Are There Right Policy Choices?Документ4 страницыRising Food Prices: Are There Right Policy Choices?dbf12345Оценок пока нет
- 768 MZA TheEdge 11april11Документ2 страницы768 MZA TheEdge 11april11Kenji CtlОценок пока нет
- Assessment Global MarketingДокумент12 страницAssessment Global Marketingramanpreet kaurОценок пока нет
- Top 10 Trends For 2015Документ98 страницTop 10 Trends For 2015PublicaОценок пока нет
- Noor's Discussion PostДокумент2 страницыNoor's Discussion PostravneetОценок пока нет
- Executive Office of The President: Council of Economic AdvisersДокумент14 страницExecutive Office of The President: Council of Economic AdviserslosangelesОценок пока нет
- Examples of PESTLE AnalysisДокумент4 страницыExamples of PESTLE AnalysisShahinОценок пока нет
- Project Report On F&BДокумент45 страницProject Report On F&BManisha Gupta80% (5)
- The Continuing Food Crisis: Global Policy Reforms LagДокумент6 страницThe Continuing Food Crisis: Global Policy Reforms LagAditya MohantyОценок пока нет
- US Food & Beverage Industry Analysis - Sakshi GuptaДокумент8 страницUS Food & Beverage Industry Analysis - Sakshi GuptaSakshi GuptaОценок пока нет
- Gea Pre-Analysis.: Japan & VenezuelaДокумент8 страницGea Pre-Analysis.: Japan & Venezuelaapi-555578456Оценок пока нет
- Obesity PresentationДокумент3 страницыObesity Presentationwappy01Оценок пока нет
- Tran Yen Trang - 23853854 - AS2 - MKT3040Документ17 страницTran Yen Trang - 23853854 - AS2 - MKT3040Yến TrangОценок пока нет
- Pest PepsicoДокумент4 страницыPest PepsicoRohit RamachandranОценок пока нет
- Tran Yen Trang - 23853854 - AS2 - MKT3040-2Документ17 страницTran Yen Trang - 23853854 - AS2 - MKT3040-2Yến TrangОценок пока нет
- Matter For EnvironmentДокумент9 страницMatter For EnvironmentMohammad Yusuf NabeelОценок пока нет
- MKT - Final TestДокумент28 страницMKT - Final TesthoangkieuthanhthaoОценок пока нет
- Pestle Analysis by PepsicoДокумент2 страницыPestle Analysis by PepsicoWycliffe Aluang'aОценок пока нет
- SapsДокумент5 страницSapsromkhanОценок пока нет
- The Effects of The Environment On Mcdonald'S: The External, Internal and Competitive Environment: External EnvironmentДокумент28 страницThe Effects of The Environment On Mcdonald'S: The External, Internal and Competitive Environment: External EnvironmentJamilah MuminОценок пока нет
- Business Plan: Papa Boudreaux's KitchenДокумент30 страницBusiness Plan: Papa Boudreaux's Kitchenapi-310636313Оценок пока нет
- Global Business Strategy of Coca-ColaДокумент35 страницGlobal Business Strategy of Coca-ColaVasile TotalBiscuit MihaiОценок пока нет
- Food & Beverage SectorДокумент13 страницFood & Beverage SectorKartheek UdayОценок пока нет
- Assignment 22Документ11 страницAssignment 22thandiОценок пока нет
- Obesity and AgДокумент2 страницыObesity and Aghoneyjam89100% (1)
- Tem1002020 Business PlanДокумент7 страницTem1002020 Business PlanCLARISSA VICTORIA LUMAINОценок пока нет
- External Audit WPS OfficeДокумент3 страницыExternal Audit WPS OfficeKristina SisonОценок пока нет
- Advanced Cost AccountingДокумент5 страницAdvanced Cost AccountingPrathamesh ChawanОценок пока нет
- The Investment Function.2Документ12 страницThe Investment Function.2Angelica T. GenovaОценок пока нет
- Triburg ReportДокумент38 страницTriburg Reportluvlinamorya100% (4)
- 21 02 08 DP More Margin More Upside Buy TP 38 From 32Документ24 страницы21 02 08 DP More Margin More Upside Buy TP 38 From 32tarun606Оценок пока нет
- MPS 01 Block 05 PDFДокумент64 страницыMPS 01 Block 05 PDFSarvesh KysОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Specific Factors ModelДокумент4 страницыChapter 3 - Specific Factors ModelFrancisca QueirozОценок пока нет
- Rosen SummaryДокумент35 страницRosen SummaryNurun Nabi MahmudОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics, History Of: Paola Tubaro, University of Greenwich, Greenwich, UKДокумент7 страницMicroeconomics, History Of: Paola Tubaro, University of Greenwich, Greenwich, UKRanjan Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Lee SpringsДокумент152 страницыLee Springsjbjb2000Оценок пока нет
- ITP Assignment1,2Документ6 страницITP Assignment1,2gohibОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three: The Location Decisions of Firms and Development of CitiesДокумент46 страницChapter Three: The Location Decisions of Firms and Development of CitiesAbdirizak Ali AbdillahiОценок пока нет
- Ecological ApproachДокумент7 страницEcological ApproachVanshika KunduОценок пока нет
- Research Proposal On BiogasДокумент18 страницResearch Proposal On BiogasKibrom GmichaelОценок пока нет
- Marketing Management: Quiz: PricingДокумент2 страницыMarketing Management: Quiz: PricingLamia AbdelhameedОценок пока нет
- ACCT 611 CHP 22Документ25 страницACCT 611 CHP 22kwame100% (1)
- Demand and Supply - Group DiscussionДокумент3 страницыDemand and Supply - Group DiscussionNhat Linh HuynhОценок пока нет
- Clique Pens Case AnalysisДокумент2 страницыClique Pens Case Analysischunnu RaiОценок пока нет
- 03 9609 32 MS Prov Rma 26022024072913Документ15 страниц03 9609 32 MS Prov Rma 26022024072913raekiki82100% (1)
- Titan Earnings Call Transcript Q3 FY'22Документ17 страницTitan Earnings Call Transcript Q3 FY'22alim shaikhОценок пока нет
- Final Report 2022Документ6 страницFinal Report 2022AstridОценок пока нет
- Sales Law ReviewerДокумент4 страницыSales Law ReviewerWillard Apeng100% (2)
- Accounting Multiple Choice Questions & Answers: Answer: CДокумент2 страницыAccounting Multiple Choice Questions & Answers: Answer: Cshafqat aliОценок пока нет
- 21.10 M - D T - F T T: Mrunal's Economy Pillar#2A: Budget Revenue Part Tax-Receipts Page 123Документ3 страницы21.10 M - D T - F T T: Mrunal's Economy Pillar#2A: Budget Revenue Part Tax-Receipts Page 123Washim Alam50CОценок пока нет
- Economics 121: Introduction To Industrial Organization and Public Policy Professor Aaron EdlinДокумент15 страницEconomics 121: Introduction To Industrial Organization and Public Policy Professor Aaron EdlinMatthew RyanОценок пока нет
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP - FinalsДокумент8 страницENTREPRENEURSHIP - FinalsPolОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Principles and Applications 5th Edition Hall Test Bank 1Документ14 страницMacroeconomics Principles and Applications 5th Edition Hall Test Bank 1tylerphillipsfxwqamkpei100% (24)
- Final FileДокумент11 страницFinal FileMd Tahidur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Online Trading Operating GuidelinesДокумент5 страницOnline Trading Operating GuidelinesKenneth BatchelorОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Business 9609/21Документ35 страницCambridge International AS & A Level: Business 9609/21Maitaishe GoraОценок пока нет
- Ultimate Guide To Trading Binary OptionsДокумент20 страницUltimate Guide To Trading Binary OptionsBigOption100% (3)