Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Untitled
Загружено:
rajaflyinfotech0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров1 страницаThe goal of digital signal processing is usually to measure, filter and / or compress continuous real-wo rld analog signals. The main applications of DSP are audio signal processing, audio compression, dig ital image processing, video compression, speech processing, speech recognition, digital communications, RADAR, SONAR, seismology, and biomedicine.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe goal of digital signal processing is usually to measure, filter and / or compress continuous real-wo rld analog signals. The main applications of DSP are audio signal processing, audio compression, dig ital image processing, video compression, speech processing, speech recognition, digital communications, RADAR, SONAR, seismology, and biomedicine.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров1 страницаUntitled
Загружено:
rajaflyinfotechThe goal of digital signal processing is usually to measure, filter and / or compress continuous real-wo rld analog signals. The main applications of DSP are audio signal processing, audio compression, dig ital image processing, video compression, speech processing, speech recognition, digital communications, RADAR, SONAR, seismology, and biomedicine.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
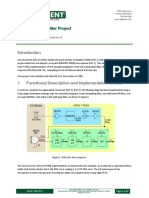
Digital signal processing (DSP) is concerned with the representation of signals
by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital
signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processi
ng. DSP includes subfields like: audioand speech signal processing, sonar and ra
dar signal processing, sensor array processing, spectral estimation, statistical
signal processing,digital image processing, signal processing for communication
s, control of systems, biomedical signal processing, seismic data processing, et
c.
The goal of DSP is usually to measure, filter and/or compress continuous real-wo
rld analog signals. The first step is usually to convert the signal from an anal
og to a digital form, by sampling it using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC),
which turns the analog signal into a stream of numbers. However, often, the req
uired output signal is another analog output signal, which requires a digital-to
-analog converter (DAC). Even if this process is more complex than analog proces
sing and has a discrete value range, the application of computational power to d
igital signal processing allows for many advantages over analog processing in ma
ny applications, such as error detection and correction in transmission as well
as data compression.[1]
DSP algorithms have long been run on standard computers, on specialized processo
rs called digital signal processors (DSPs), or on purpose-built hardware such as
application-specific integrated circuit (ASICs). Today there are additional tec
hnologies used for digital signal processing including more powerful general pur
pose microprocessors, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), digital signal con
trollers(mostly for industrial apps such as motor control), and stream processor
s, among others.[2]
Applications
The main applications of DSP are audio signal processing, audio compression, dig
ital image processing, video compression, speech processing, speech recognition,
digital communications, RADAR, SONAR, seismology, and biomedicine. Specific exa
mples are speech compression and transmission in digital mobile phones, room cor
rection of sound in hi-fi and sound reinforcement applications, weather forecast
ing, economic forecasting, seismic data processing, analysis and control of indu
strial processes, medical imaging such as CATscans and MRI, MP3 compression, com
puter graphics, image manipulation, hi-fi loudspeaker crossovers and equalizatio
n, and audio effectsfor use with electric guitar amplifiers.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Signal Processing FirstДокумент6 страницSignal Processing Firstnickswap100% (1)
- Blender & Z BrushДокумент20 страницBlender & Z BrushKurniawan SusiloОценок пока нет
- Sampling Theorem: - Presented By., - S.ShanmatheeДокумент16 страницSampling Theorem: - Presented By., - S.ShanmatheeSarah Kadhim MohsenОценок пока нет
- VHF FM Repeater: S-14425XZ-C1 Jun. 2008Документ44 страницыVHF FM Repeater: S-14425XZ-C1 Jun. 2008Jorge Enrique Anzola CarrilloОценок пока нет
- Handout For Diploma in Medical Image ProcessingДокумент4 страницыHandout For Diploma in Medical Image ProcessingkfaridrahmanОценок пока нет
- Finite Word Length Effects in FFT AlgorithmДокумент12 страницFinite Word Length Effects in FFT AlgorithmanuОценок пока нет
- 6th Semester - Time Table - 14.12.2009 (1) .XlsxaaaaaaaaaДокумент12 страниц6th Semester - Time Table - 14.12.2009 (1) .XlsxaaaaaaaaaBhawin PattnaikОценок пока нет
- An Image Fusion Using Wavelet and Curvelet TransformsДокумент5 страницAn Image Fusion Using Wavelet and Curvelet TransformsajayroyalОценок пока нет
- Easy Real-Time DSP Programming With Labview and Visual BasicДокумент10 страницEasy Real-Time DSP Programming With Labview and Visual BasicRakesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Nexys4 PDM RefProj2 V2Документ12 страницNexys4 PDM RefProj2 V2Vale Conde Cuatzo100% (2)
- Nyquist FrequencyДокумент2 страницыNyquist Frequencygurudev001Оценок пока нет
- Signals and Systems: EE-303 H. SaadatДокумент5 страницSignals and Systems: EE-303 H. SaadatscribsunilОценок пока нет
- EE-493 Digital Signal Processing - 2013Документ37 страницEE-493 Digital Signal Processing - 2013Sana MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Development of Digital Protective Relay Tester Under IEC61850Документ5 страницDevelopment of Digital Protective Relay Tester Under IEC61850violatorОценок пока нет
- SolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExДокумент51 страницаSolidWorks Education Detailed Drawing ExMarcos José da SilvaОценок пока нет
- ADC For NDETДокумент25 страницADC For NDETChaminda Abeysiri NarayanaОценок пока нет
- Histogram ToolДокумент3 страницыHistogram ToolAhmed El SayedОценок пока нет
- Video Compression - New Motion Estimation AlgorithmДокумент23 страницыVideo Compression - New Motion Estimation AlgorithmPriya GayathriОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Projects - DIP3EДокумент18 страницLaboratory Projects - DIP3Ecycliccrap0% (1)
- BMP TutorialДокумент7 страницBMP TutorialPhước Nguyên HoàngОценок пока нет
- DSP Exp 3Документ10 страницDSP Exp 3Hjalmark SanchezОценок пока нет
- DSP ToolsДокумент30 страницDSP ToolsSagar MahajanОценок пока нет
- Computer Vision Lab Manual 2023Документ63 страницыComputer Vision Lab Manual 2023VivekSinh RajputОценок пока нет
- Linear EqualizerДокумент39 страницLinear EqualizerVicky PatelОценок пока нет
- Bit-Plane Slicing - IMAGE PROCESSINGДокумент6 страницBit-Plane Slicing - IMAGE PROCESSINGdexpaulwОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ175 страницUnit 1Karthikeya SharmaОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Unit I Part A: Ae306-Digital Signal Processing AEIДокумент4 страницыQuestion Bank Unit I Part A: Ae306-Digital Signal Processing AEIGlanОценок пока нет
- Tesiraforté® Avb Ci Fixed I/O DSP: Data SheetДокумент2 страницыTesiraforté® Avb Ci Fixed I/O DSP: Data SheetMuhammad Naveed AshrafОценок пока нет
- EE392 ExamДокумент12 страницEE392 ExamAashutosh PratapОценок пока нет
- PhotoshopBook1 TextДокумент168 страницPhotoshopBook1 TextEbrahim AbdulqaderОценок пока нет