Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Understanding Hard Disk: Connectors
Загружено:
hiro_nakamuraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Understanding Hard Disk: Connectors
Загружено:
hiro_nakamuraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UniCV/DECM – Departamento de Engenharia e Ciências do Mar
Understanding Hard Disk
Hard disk drives where introduced in 1956 as data storage for an IBM
accounting computer.
A hard disk (HD) drive is a digital data storage device that writes and reads
data via magnetization changes of a magnetic storage disk along concentric
tracks.
To maintain your HD healthy you have to deal with it with extreme care.
Contaminates on the heads or the disk surface can cause head-crash. Head
crashes can be caused by electronic failure, a sudden power failure, physical
shock, wear and tear, corrosion, or poorly manufactured platters and heads.
Hard drives are assembled in clean rooms (cleaner than surgery rooms) and
then sealed.
Connectors
Hard disk drives have basically two connectors, one for power and other for
exchanging data with the computer. This second connector is better known
as “interface”.
The master/slave jumper on ATA hard drives can be configured in three
different ways:
• Master: this means that this drive will be the only one attached to the
cable that connects the hard drive to the computer or will be the first
drive in a two-drive configuration.
• Slave: this means that this drive will be the second drive attached to
the cable that connects the hard drive to the computer.
• CS (Cable Select): this means that you will use a “special” cable
(called CS cable) that the configuration of whether a drive will be
master or slave will be made by the position of the hard drive on the
cable and not by a jumper configuration on the drive.
Hard disk interfaces
Hard disks also come in several flavors such as IDE (actually ATA), SCSI and
SATA, as do optical drives. ATA is the most common interface used today.
SCSI disks can usually be found on servers.
IDE - Integrated Drive Electronics, more commonly called by its acronym
IDE, is an interface for hard drives. IDE is a marketing term; the real
standard is called ATA.
EIDE - Enhanced IDE or ATA-2 was later developed and increased transfer
speed, added 32-bit transactions and DMA support.
ATA - Stands for Advanced Technology Attachment. The ATA -term is
commonly used interchangeably with IDE. The older and more common
parallel ATA (P-ATA) is currently being replaced by serial ATA (SATA).
SCSI - Small Computer System Interface. Pronounced "scuzzy". It's a
specification for a hardware interface for connecting devices such as hard
disks and scanners to a computer.
Balduino Melo Neves
Página 1 de 5
UniCV/DECM – Departamento de Engenharia e Ciências do Mar
Most PCs have an ATA (IDE) bus instead of SCSI for connecting internal hard
disks. SCSI is seen more often in servers, as it tends to be faster and more
reliable (though more expensive). Another advantage of SCSI controller is
that it requires only one IRQ and can handle usually at least 7 devices
whereas ATA can handle only 2.
Most PCs have two IDE controllers on the motherboard. One IDE controller
can support two devices, so four storage devices is usually the maximum.
Parallel ATA interface uses ribbon cables with 40 pin connectors to connect
the hard drives to the motherboard. The cable has usually three connectors.
Of these one is connected to the motherboard and the rest two are left for
hard drives. If two hard drives are connected to the same controller, one
must be defined as master and the other one as slave. This is done with
jumpers.
Serial ATA, also known as SATA or S-ATA, is a bus used to communicate
between the CPU and internal storage devices such as hard drives and
optical drives. It is designed to eventually replace the ATA (also known as
IDE) bus. Traditional ATA is beginning to be referred to as Parallel ATA, P-
ATA, or PATA to avoid confusion.
The main difference between SATA and PATA is in the cabling. PATA's
ungainly ribbon cables. Instead, SATA has much slimmer and easier to
manage cables. Truly native SATA drives will have different power
connectors also.
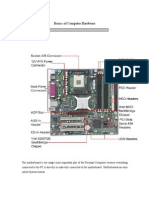
Logic Board
On the logic board you will find all circuitry in charge of controlling the hard
drive. In these days of highly integrated devices, you will find just three or
four big integrated circuits on the logic board.
The big circuit is the controller. It is in charge of everything: exchanging
data between the hard drive and the computer, controlling the motors on
the hard drive, commanding the heads to read or write data, etc.
Optionally there is a Flash-ROM circuit where the hard drive firmware is
located. Firmware is the name given to a program that is stored inside a
ROM (Read Only Memory). The hard drive firmware is the program its
controller executes.
The controller doesn’t drive enough current to turn on or move the hard
drive motors. So all hard drives use a motor driver chip. This chip is a
current amplifier. It takes the commands sent from the controller to the
motors and passes them to the motors, but with a higher current.
This motor driver chip is located between the controller chip and the motors.
The fourth main chip you can find on a logic board is the RAM (Random
Access Memory) chip, also known as buffer. This chip has an ultimate role in
the hard drive performance. The higher its capacity, the fastest the data
transfer between the drive and the computer will be.
You may be wonder how we know the function of each chip on the logic
board. Actually it is fairly simple and you can learn the trick from us. Just
type in the numbers located on the first line of the chip package on Google
and it will return a lot of information about the chip!
Balduino Melo Neves
Página 2 de 5
UniCV/DECM – Departamento de Engenharia e Ciências do Mar
Inside the HD
I’ve said this before and i said it again: do not open your hard drive or you
will damage it.
Hard disks are aluminum platters coated on both sides with iron oxide or
thin-film metal. Most hard disk drives use disk packs which are several disk
platters stacked together.
The hard drive can have several discs. There is one read/write read for each
side of the disc – which is also called platter. The heads are stuck together
in an arm. So, all the heads move together. The distance between the head
and the platter is so small that you can’t see it without appropriate devices.
A motor (actually the correct term is “actuator”) called voice coil moves the
arm. It is called “voice coil” because it uses the same idea behind
loudspeakers: a coil inside a magnetic field provided by a magnet.
Depending on the current direction on the coil the arm moves to one side or
to the other side. And depending on the intensity of the current, the
actuator will move more or less.
The platters
The surfaces of the platters have a structure (invisible structure) composed
by tracks, cylinders, sectors and clusters.
Tracks are concentric circumferences. The number of tracks on a disk surface
therefore corresponds to the number of different radial positions of the head(s). The
collection of all tracks on all surfaces at a given radial position is known a cylinder
and each track is divided into sectors.
Sectors can be seen as pizza slice and the intersection between tracks and
sectors origin what we call cluster.
Cluster is an elementary unit of allocation of a disk.
The cluster size is a tradeoff between space efficiency, the bigger is the cluster, the
bigger is on the wasted space at the end of each file.
The capacity of an HD can be calculated with following equation:
Capacity = #cylinders * sectors * heads * 512
Hard Drive Manufacturers (a small list)
Fujitsu
Hitachi Global Storage
IBM
Maxtor
Seagate
Western Digital
Balduino Melo Neves
Página 3 de 5
UniCV/DECM – Departamento de Engenharia e Ciências do Mar
Images
Logic board
HD connectors Actuator
Inside the HD The head
Balduino Melo Neves
Página 4 de 5
UniCV/DECM – Departamento de Engenharia e Ciências do Mar
Balduino Melo Neves
Página 5 de 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Hard Disk DriveДокумент8 страницHard Disk DriveHelner TaghapОценок пока нет
- Hard DiskДокумент4 страницыHard Diskmrpatil186Оценок пока нет
- Hard DrivesДокумент69 страницHard Drivesprerana sheteОценок пока нет
- Peripheral Wires Used in ComputersДокумент7 страницPeripheral Wires Used in Computersayesha amjadОценок пока нет
- Cycle 1Документ106 страницCycle 1Srinivas KanakalaОценок пока нет
- Ide ScsiДокумент52 страницыIde ScsiPavel BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Computer and Their FunctionsДокумент33 страницыParts of A Computer and Their FunctionsMia Dess Angawa Ananayo100% (1)
- تقرير احترافيДокумент9 страницتقرير احترافيhayderjabbar686Оценок пока нет
- Motherboard and Other PartsДокумент32 страницыMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- HDDДокумент11 страницHDDTamil GuruОценок пока нет
- Computer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsДокумент70 страницComputer Hardware Servicing Safety and PrecautionsMary MillareОценок пока нет
- Unit - 4 PCДокумент7 страницUnit - 4 PCnanobala15Оценок пока нет
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Документ5 страницTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarДокумент23 страницыPresentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarSatyam JhawarОценок пока нет
- Module 05 Understanding Storage Media and File SystemДокумент29 страницModule 05 Understanding Storage Media and File Systemrohan0x80Оценок пока нет
- Computer PartsДокумент9 страницComputer PartsAlexis Dhave AlgireОценок пока нет
- Popular Hard Disk Drive Manufacturers: Hardware Operating SystemДокумент10 страницPopular Hard Disk Drive Manufacturers: Hardware Operating SystemHimanshu GuptaОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Comp Uter and Their FunctionsДокумент14 страницParts of A Comp Uter and Their FunctionsDONITA DALUMPINESОценок пока нет
- Intro To It Hardware1Документ32 страницыIntro To It Hardware1tprastyanaОценок пока нет
- Cassy AssignmentДокумент8 страницCassy AssignmentrickОценок пока нет
- Unit 08 Storage DevicesДокумент28 страницUnit 08 Storage DevicesPrakash DangolОценок пока нет
- Types of Hard Disk-NotesДокумент2 страницыTypes of Hard Disk-NotesSudeep OnemОценок пока нет
- K13-03-04 Digital Tehniques / Electronics Intrument System - Nama: NDP: Le 2: Recognize The Basic Computer StructureДокумент12 страницK13-03-04 Digital Tehniques / Electronics Intrument System - Nama: NDP: Le 2: Recognize The Basic Computer StructureGanesh Ruban AnathanОценок пока нет
- ICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFДокумент5 страницICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFElleera RemorerasОценок пока нет
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardДокумент5 страницComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaОценок пока нет
- Identifying Expansion Module CardsДокумент44 страницыIdentifying Expansion Module CardsROSE TASIОценок пока нет
- Solid State Drive DocumentationДокумент11 страницSolid State Drive DocumentationVivek DasariОценок пока нет
- Identifying Expansion Module CardsДокумент44 страницыIdentifying Expansion Module CardsMaria Norberta MandacОценок пока нет
- A Computer Motherboard DiagramДокумент10 страницA Computer Motherboard Diagramlark77100% (1)
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsДокумент17 страницParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsREZA TAGLEОценок пока нет
- Hard Drive AcquisitionДокумент19 страницHard Drive AcquisitionJason KeysОценок пока нет
- Jhs !Документ25 страницJhs !Charles MensahОценок пока нет
- Sitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Документ15 страницSitti Analyn P. Omar Dcmt-1 Batch-2Maher ArakamaОценок пока нет
- PC Hardware Basics & Troubleshooting GuideДокумент43 страницыPC Hardware Basics & Troubleshooting GuideBhavin Joshi100% (39)
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsДокумент19 страницParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsJaried SumbaОценок пока нет
- Technical OverviewДокумент5 страницTechnical OverviewkarmaОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Diagram: Necessary If You Want To Replace Motherboard or TroubleshootДокумент3 страницыMotherboard Diagram: Necessary If You Want To Replace Motherboard or TroubleshootRye EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitДокумент35 страницBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalОценок пока нет
- Activity 1: Parts of The Hard Drive: Base CastingДокумент7 страницActivity 1: Parts of The Hard Drive: Base CastingKevinОценок пока нет
- Assignment CS by ABRARДокумент9 страницAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioОценок пока нет
- Measuring & Improving Drive PerformanceДокумент13 страницMeasuring & Improving Drive PerformanceMubashir Ch100% (2)
- Central Processing UnitДокумент4 страницыCentral Processing UnitChandan KumarОценок пока нет
- Hard Drive DiskДокумент17 страницHard Drive DiskMelbertОценок пока нет
- Hard Disk DriveДокумент20 страницHard Disk DriveBL A CKОценок пока нет
- Computer Unit 1Документ6 страницComputer Unit 1hindrixcatayas8Оценок пока нет
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardДокумент6 страницParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- The Motherboard: Basics of Computer HardwareДокумент34 страницыThe Motherboard: Basics of Computer Hardwareprashanth2222Оценок пока нет
- Artikel Bahasa Inggris Tentang Komputer The Definition of HarddiskДокумент3 страницыArtikel Bahasa Inggris Tentang Komputer The Definition of HarddiskaristaОценок пока нет
- Basic Comp 03 - Handout - 1Документ6 страницBasic Comp 03 - Handout - 1Rachelle GandaОценок пока нет
- Hard Disk DriveДокумент25 страницHard Disk DriveJasmine Dela Cruz- ParatonОценок пока нет
- It AssignmentДокумент6 страницIt AssignmentHanie joy TalhaОценок пока нет
- Workshop FileДокумент16 страницWorkshop FileTushar0% (1)
- HDD Types 1. Parallel Advances Technology Attachment-: 3. Small Computer System InterfaceДокумент2 страницыHDD Types 1. Parallel Advances Technology Attachment-: 3. Small Computer System InterfaceSanjay DeyОценок пока нет
- Construction and Operation of The Hard DiskДокумент7 страницConstruction and Operation of The Hard DiskSupreet NarangОценок пока нет
- Inside Hard DisksДокумент23 страницыInside Hard DisksAnonymous OCDJg17ZОценок пока нет
- ICT 1101 - PC Hardware Assembly 02Документ30 страницICT 1101 - PC Hardware Assembly 02honorableekouoОценок пока нет
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsДокумент78 страницFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsVencent BuellОценок пока нет
- ICT 10 FIRST QUARTER Topic-8-Hardware-fundamentals-Storage-DevicesДокумент53 страницыICT 10 FIRST QUARTER Topic-8-Hardware-fundamentals-Storage-DevicesDonna Joy AmahitОценок пока нет
- Tle 8 g4 ReportДокумент28 страницTle 8 g4 ReportJoshua RaipОценок пока нет
- Administrator & Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОт EverandAdministrator & Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОценок пока нет
- Ms Dos Manual PDF DownloadДокумент4 страницыMs Dos Manual PDF DownloadtempОценок пока нет
- Replacement Guidelines: Logix 5000 Controllers: Reference ManualДокумент170 страницReplacement Guidelines: Logix 5000 Controllers: Reference ManualRoger MantillaОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor (PRACTICAL FILE)Документ11 страницMicroprocessor (PRACTICAL FILE)बृज भूषण सिंह86% (7)
- On No SQLДокумент7 страницOn No SQLp998uy9034Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ40 страницChapter 1josemoses100% (1)
- Marble Point BIOS Update GuideДокумент6 страницMarble Point BIOS Update Guidecodigorojo2000Оценок пока нет
- Activity 1Документ7 страницActivity 1Ruy AniversarioОценок пока нет
- CADWorx DraftPro Questions and AnswersДокумент8 страницCADWorx DraftPro Questions and AnswersprasathbalaОценок пока нет
- 1K/2K/4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package TypesДокумент20 страниц1K/2K/4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package TypesJoão PauloОценок пока нет
- List TT Devices sort3-NavcoreGeneration DeviceNameДокумент6 страницList TT Devices sort3-NavcoreGeneration DeviceNameAhmetović SabahudinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Preventive Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Instructor MaterialsДокумент33 страницыChapter 4: Preventive Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Instructor MaterialsJose De PinaОценок пока нет
- Devicenet and Can-Bus ExtendersДокумент2 страницыDevicenet and Can-Bus ExtendersAnonymous 8RFzObvОценок пока нет
- Preview Hacking With Raspberry Pi 4 PDFДокумент27 страницPreview Hacking With Raspberry Pi 4 PDFspada1975Оценок пока нет
- B Voc Cyber Security and Forensics SyllabusДокумент116 страницB Voc Cyber Security and Forensics SyllabusreemalimbadОценок пока нет
- HP Elitebook 8460pДокумент62 страницыHP Elitebook 8460pFerreira da Cunha0% (1)
- Activity Sheets in Ict (Computer Systems Servicing) Grade 7 Quarter 1, Week 1Документ7 страницActivity Sheets in Ict (Computer Systems Servicing) Grade 7 Quarter 1, Week 1Kesha Callanta100% (2)
- Python Crash Course 0.07 PDFДокумент68 страницPython Crash Course 0.07 PDFMatheus Rodrigues BorbaОценок пока нет
- Hive ManagerДокумент2 страницыHive ManagerMichele BrunelliОценок пока нет
- Manual de Servicio MB460 - 470 - 480 - MM - Rev2 PDFДокумент247 страницManual de Servicio MB460 - 470 - 480 - MM - Rev2 PDFErick MarzОценок пока нет
- A785GM-A Manual2Документ92 страницыA785GM-A Manual2Evert Romero GarridoОценок пока нет
- Concepts of Cloud Computing by Eng. Mubiru Abubakari - Note 2Документ62 страницыConcepts of Cloud Computing by Eng. Mubiru Abubakari - Note 2Yasira MugangaОценок пока нет
- DW1601 DW1702 DW1703 DW1705 DW1707 and DW1901 Release Notes CS WIN7 Combo 01 10 2014Документ12 страницDW1601 DW1702 DW1703 DW1705 DW1707 and DW1901 Release Notes CS WIN7 Combo 01 10 2014Abir BaidyaОценок пока нет
- Session16385 WAS TimeoutsДокумент75 страницSession16385 WAS Timeoutsshashank_w85m_312965Оценок пока нет
- 9.2.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine TCP and UDP CapturesДокумент14 страниц9.2.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine TCP and UDP CapturesaliefОценок пока нет
- Preps 6.1 PrinergyGuide enДокумент18 страницPreps 6.1 PrinergyGuide enWilliam MendozaОценок пока нет
- CIVENG 186 - Design of IoTДокумент3 страницыCIVENG 186 - Design of IoTMatthew McGoffinОценок пока нет
- TMS Advanced TreeViewДокумент63 страницыTMS Advanced TreeViewGilmar CesarОценок пока нет
- Common Criteria Evaluated Configuration Guide For Netscaler 10 Platinum EditionДокумент80 страницCommon Criteria Evaluated Configuration Guide For Netscaler 10 Platinum EditionNguyen AnhОценок пока нет
- High Performance ComputingДокумент18 страницHigh Performance ComputingschaphieyqaОценок пока нет