Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
URINALYSIS
Загружено:
sheila_01Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
URINALYSIS
Загружено:
sheila_01Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
LABORATORY RESULTS
Name of Patient:
AGE:
SEX:
URINALYSIS
GROSS FINDINGS NORMAL RESULTS ANALYSIS
Color Straw to Amber dark brown or
smoky urine
Transparency Clear to slightly Slightly turbid Normal
turbid
pH 4.5-8 6.0 Normal
Sp.Gravity 1.005-1.030 1.010 Normal
Glucose Negative trace
Protien Negative +2
Squamous Epithelial Few Few
Cells
Red Blood Cells Few 2-7
Pus Cells Few 1-3
Mucus Few Few
Bacteria Few Few
HEMATOLOGY REPORT
NORMAL ACTUAL
PARAMETER ANALYSIS
VALUES VALUES
Increased; indicate high glucose level in the
Segmenters 0.55-0.65 0.86
blood
Lymphocytes 0.25-0.35 0.40 Increased; indicates infection
BLOOD CHEMISTRY REPORT
NORMAL ACTUAL
PARAMETER ANALYSIS
VALUES VALUES
Increased BUN levels suggest impaired kidney
BUN/ 1.7-8.3
10.10 function. This may be due to acute or chronic kidney
Urea Mmol/L
disease, damage, or failure.
GDMC/ Acute Glomerulonephritis 1
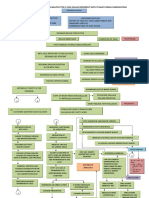
LAB RESULTS: Definition, Interpretation and Nursing Considerations
URINALYSIS
Definition: A urinalysis is an array of tests performed on urine and one of the most
common methods of medical diagnosis. A part of a urinalysis can be performed by
using urine dipsticks, in which the test results can be read as color changes.
Interpretation: the urinalysis results are normal. Normal urine may vary in color from
almost colorless to dark yellow. Usually, glucose, ketones, protein, and bilirubin are
not detectable in urine. The following are not normally found in urine Hemoglobin,
Nitrites, Red blood cells, White blood cells.
Nursing Consideration: Special diets can change test results. For example, a diet low
in carbohydrates and high in protein and fat can raise ketone levels in the blood
which can then enter the urine.
HEMATOLOGY
Definition: Hematology, is the branch of internal medicine, physiology, pathology,
clinical laboratory work, and pediatrics that is concerned with the study of blood, the
blood-forming organs, and blood diseases.
Interpretation: a low HGB indicates anemia, severe hemorrhage, hemolysis, cancer,
kidney disease, and splenomegaly. A low HCT indicates anemia, normal pregnancy,
hemorrhage and leukemia. A low RBC indicates anemia, which often leads to
fatigue. MCV decreases value may indicate iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia.
Decreased MCH occurs in microcytic anemia or hypochromic anemia. And the rest is
normal.
Nursing Consideration: should be aware of tests that do require special food
restrictions. Some tests require fasting prior to the test. Be sure you inform your
patient verbally and in writing. Be sure that the staff is informed of any food
restrictions. It is no secret that many tests and procedures had to be canceled at the
last minute because the patient ate some food. Be sure to mark the patient's chart,
diet list, and put signs in their room. Many hospitals have a specific procedure to
GDMC/ Acute Glomerulonephritis 2
follow for NPO. Be sure to follow this procedure and follow-up on keeping them
NPO, if required for testing or for the procedure. Also remember that some
tests/procedures might require that the patient consume a light meal, a liquid meal,
or other special diet.
X-RADIATION(X-RAYS)
Definition: X-radiation (composed of X-rays) is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 10 to 0.01 nanometers, corresponding to
frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3 × 1016 Hz to 3 × 1019 Hz) and
energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV
rays.
Interpretation: Mild perihilar pneumonia, Mild pulmonary congestion, Cardiomegaly
Bilateral moderate pleural effusion
Nursing Consideration: The effect of X-rays on the film depends upon three factors:
PPV, the intensity of X-rays and the contrast equivalent X-ray tube voltage.
ULTRASOUND
Definition: Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the
upper limit of human hearing. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is
approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy, young adults and thus, 20 kHz
serves as a useful lower limit in describing ultrasound.
Interpretation: Kidneys – mild diffuse parenchymal disease consistent with AGN
Urinary bladder – unremarkable
Nursing Consideration: Patient education is an important part of preparation.
Discussion and consensus of the exact treatment goals with patients and their
families must be done prior to treatment.
GDMC/ Acute Glomerulonephritis 3
CREATININE BLOOD TEST
Definition: Creatinine blood test is used along with a BUN (blood urea nitrogen) test
to assess kidney function. Both are frequently ordered as part of a basic or
comprehensive metabolic panel (BMP or CMP), groups of tests that are performed to
evaluate the function of the body’s major organs.
Interpretation: Urine that is foamy, bloody, or coffee-colored , decrease in the
amount of urine, Problems urinating, such as a burning feeling or abnormal
discharge during urination, or a change in the frequency of urination, especially at
night , Mid-back pain (flank), below the ribs, near where the kidneys are located,High
blood pressure .
Nursing Consideration: Avoid Drugs that can interfere with creatinine clearance
measurements include: cimetidine, trimethoprim, and nephrotoxic drugs, such as
cephalosporins (e.g., cefoxitin). Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to
another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from
some people may be more difficult than from others.
GDMC/ Acute Glomerulonephritis 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison ChartДокумент9 страницAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison ChartBonnieОценок пока нет
- Anemia Table283Документ2 страницыAnemia Table283Bridget ParkerОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIEricka Genove100% (1)
- CaseДокумент4 страницыCaseCamille Ann Robante CastilloОценок пока нет
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Diltiazem Cardizem Antianginals, AntiarrhythmicsДокумент1 страницаGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Diltiazem Cardizem Antianginals, AntiarrhythmicsChristopher LeeОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeMikhael Briones ApasОценок пока нет
- Bot Med Final CHARTДокумент33 страницыBot Med Final CHARTapi-26938624100% (3)
- Medication Calculation Study GuideДокумент4 страницыMedication Calculation Study GuidekateОценок пока нет
- RevalidaДокумент5 страницRevalidaHawkins FletcherОценок пока нет
- Protein Case SummaryДокумент2 страницыProtein Case SummaryGlydenne Glaire Poncardas Gayam100% (2)
- Renal Concept MapДокумент1 страницаRenal Concept MapShaira Ann CalambaОценок пока нет
- Ulcerative ColitisДокумент18 страницUlcerative ColitisHoussein EL HajjОценок пока нет
- CholestyramineДокумент1 страницаCholestyramineKatie McPeekОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics Lecture on Malnutrition Criteria and InterventionsДокумент8 страницPediatrics Lecture on Malnutrition Criteria and InterventionskrishОценок пока нет
- Case 5Документ16 страницCase 5Angel MayОценок пока нет
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart GuideДокумент9 страницAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart Guideconcoz100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFДокумент14 страницDRUG STUDY FINAL (Onco) PDFFrancis Anthony LoslosoОценок пока нет
- 1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraДокумент13 страниц1.05 General Pathology - Diseases of The Immune System (Part 2) - Dr. AleraCherry RahimaОценок пока нет
- Medicine OB History and PE TemplateДокумент9 страницMedicine OB History and PE TemplateJanella SuerteОценок пока нет
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTДокумент1 страницаCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasОценок пока нет
- CVD HypertensionДокумент15 страницCVD HypertensionAbigail BascoОценок пока нет
- UrinalysisДокумент9 страницUrinalysisSukma EffendyОценок пока нет
- MSU Buug College Nursing Assessment for Abdominal PainДокумент30 страницMSU Buug College Nursing Assessment for Abdominal Painllanelli.graciaОценок пока нет
- Bronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsДокумент9 страницBronchial Asthma: West Visayas State University Medical Center - Department of PediatricsPGI Miayo, StephenОценок пока нет
- Signs and symptoms of heart failureДокумент9 страницSigns and symptoms of heart failureMelanie GaledoОценок пока нет
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Normal Laboratory Study Values: DefinitionДокумент6 страницComplete Blood Count (CBC) Normal Laboratory Study Values: DefinitionGlare RhayneОценок пока нет
- ConceptMap AMLДокумент1 страницаConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDrug StudyDanian AntonioОценок пока нет
- Top Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesДокумент25 страницTop Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesericОценок пока нет
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYДокумент23 страницыAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenОценок пока нет
- Common Antidotes Used in Clinical PracticeДокумент42 страницыCommon Antidotes Used in Clinical PracticeAUASSIRIОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Документ25 страницNeonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Dennis MiritiОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab FindingsДокумент4 страницыElectrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab Findingsworleyb83Оценок пока нет
- Morphine (Astramorph)Документ1 страницаMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoОценок пока нет
- Urinalysis PDFДокумент34 страницыUrinalysis PDFAzeli SiquianОценок пока нет
- Anemia Flow ChartДокумент1 страницаAnemia Flow ChartCynthiaОценок пока нет
- Infective Endocarditis CaseДокумент3 страницыInfective Endocarditis CaseMershen GaniaОценок пока нет
- Complete Stool ExaminationДокумент4 страницыComplete Stool Examinationnaxo128Оценок пока нет
- AnemiaДокумент41 страницаAnemiaBang FadОценок пока нет
- Anemia-Careplan For AdultДокумент29 страницAnemia-Careplan For AdultdjbhetaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacotherapy of AsthmaДокумент53 страницыPharmacotherapy of AsthmaStella Aprilia NurОценок пока нет
- Finals Trans (Hema)Документ16 страницFinals Trans (Hema)Ayesha CaragОценок пока нет
- Biomedical Case StudyДокумент5 страницBiomedical Case StudyHannan AtharОценок пока нет
- RabiesДокумент10 страницRabiesWinda LiraОценок пока нет
- ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS GUIDEДокумент54 страницыACUTE GASTROENTERITIS GUIDEVincent LaranjoОценок пока нет
- Anaemia Diagnosis & Treatment in PregnancyДокумент97 страницAnaemia Diagnosis & Treatment in PregnancyHema MaliniОценок пока нет
- ScabicidesДокумент17 страницScabicidesEmman AguilarОценок пока нет
- Concept Map Meningitis TheoryДокумент3 страницыConcept Map Meningitis TheoryMia AuliaОценок пока нет
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyДокумент27 страницMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- Physical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityДокумент1 страницаPhysical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityKEn PilapilОценок пока нет
- Protein Metab 2 Dra. SantosДокумент7 страницProtein Metab 2 Dra. SantosMelissa SalayogОценок пока нет
- Alzheimer's DiseaseДокумент19 страницAlzheimer's DiseaseMission JupiterОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis of AnemiaДокумент14 страницDiagnosis of AnemiaAnggie AnggriyanaОценок пока нет
- C191W003 Control Bleeding and Hypovolemic ShockДокумент51 страницаC191W003 Control Bleeding and Hypovolemic ShockEmad Hussien Haj-AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Ropinirole (Requip)Документ1 страницаRopinirole (Requip)EОценок пока нет
- 2-Sickle Cell Anemia PDFДокумент21 страница2-Sickle Cell Anemia PDFJennyu YuОценок пока нет
- MSU-IIT student drug study on Tekturna (AliskirenДокумент2 страницыMSU-IIT student drug study on Tekturna (AliskirenLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOОценок пока нет
- Retention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesДокумент2 страницыRetention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesQueenie Rose ArsenalОценок пока нет
- Appendicitis Case Pres 1 PDFДокумент52 страницыAppendicitis Case Pres 1 PDFCharmaine Anne Olalde JulianoОценок пока нет
- MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF DEHYDRATIONДокумент14 страницMEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF DEHYDRATIONJosh BlasОценок пока нет
- MCN JournalДокумент5 страницMCN JournalElleОценок пока нет
- Dds Logbook 2012Документ81 страницаDds Logbook 2012তৌহিদ তপুОценок пока нет
- Child Health FormДокумент4 страницыChild Health FormAaron Jay MondayaОценок пока нет
- Question Preparation Exam2023-1Документ350 страницQuestion Preparation Exam2023-1alicОценок пока нет
- Bronchial AsthmaДокумент10 страницBronchial AsthmaHlaSoe WinОценок пока нет
- The Potential Use of Biomarkers in Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney InjuryДокумент17 страницThe Potential Use of Biomarkers in Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injuryumie khoirunОценок пока нет
- Abdominal Injuries: Dr. Aftab Ahmed MustafaДокумент26 страницAbdominal Injuries: Dr. Aftab Ahmed MustafaRakhshanda khanОценок пока нет
- Dermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizДокумент3 страницыDermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizheshamОценок пока нет
- Requisites in Dearmatology - Dermatopathology (PDF) (Tahir99) VRG (Dragged) 12 PDFДокумент1 страницаRequisites in Dearmatology - Dermatopathology (PDF) (Tahir99) VRG (Dragged) 12 PDFJUSASBОценок пока нет
- TheTruth About Food Grade Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 by James Paul RoguskiДокумент86 страницTheTruth About Food Grade Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 by James Paul RoguskiTheRazorsEdge80% (5)
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitДокумент4 страницыNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoОценок пока нет
- Principles of Casting and SplintingДокумент8 страницPrinciples of Casting and Splintingbobtaguba100% (1)
- Angela R. Torriero: Torrieroa@sacredheart - EduДокумент2 страницыAngela R. Torriero: Torrieroa@sacredheart - Eduapi-455430839Оценок пока нет
- Guideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsДокумент7 страницGuideline On Use of Local Anesthesia For Pediatric Dental PatientsLisna K. RezkyОценок пока нет
- Panic Disorder With AgoraphobiaДокумент17 страницPanic Disorder With AgoraphobiaVanessa100% (6)
- Neuro-Ophthalmology ICD-10 Quick Reference GuideДокумент4 страницыNeuro-Ophthalmology ICD-10 Quick Reference GuideFaisal ApendixОценок пока нет
- Proyecto Final Ángela P. FierroДокумент39 страницProyecto Final Ángela P. Fierro9bh4spchgsОценок пока нет
- CHARM X Brochure PDFДокумент64 страницыCHARM X Brochure PDFSwathi GovindarajanОценок пока нет
- Circ Res-1979-Laine-317-23Документ8 страницCirc Res-1979-Laine-317-23SurgaveryОценок пока нет
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Mental IllnessesДокумент4 страницыNeurodevelopmental Disorders and Mental IllnessesRain Simonette GuanОценок пока нет
- Examples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepДокумент24 страницыExamples of Jumps: Strong vs. Weak Fast vs. Slow Floating vs. DeepJatro100% (1)
- Essential Blood Test Reference SheetДокумент1 страницаEssential Blood Test Reference Sheetd3nny89Оценок пока нет
- Cholesterol TestДокумент2 страницыCholesterol TestMarcio AurélioОценок пока нет
- WHO Top 10 Causes of DeathДокумент4 страницыWHO Top 10 Causes of DeathMas IyoОценок пока нет
- Admitting Conference: Bantasan, Anna Lee Clinical ClerkДокумент63 страницыAdmitting Conference: Bantasan, Anna Lee Clinical ClerkAnna Lee BantasanОценок пока нет
- L Hi Appt Results 06252021Документ7 страницL Hi Appt Results 06252021C RealОценок пока нет
- GINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFДокумент22 страницыGINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFPhuong HuynhОценок пока нет
- Advanced Training in Neurology in AustraliaДокумент45 страницAdvanced Training in Neurology in AustraliaMario AndersonОценок пока нет
- Notification Janakpuri Super Speciality Hospital Nursing Officer Other PostsДокумент27 страницNotification Janakpuri Super Speciality Hospital Nursing Officer Other PostsMonikaОценок пока нет
- (Vanbanphapluat - Co) 19 2016 TT BytДокумент32 страницы(Vanbanphapluat - Co) 19 2016 TT BytNTKОценок пока нет