Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Service Directions
Загружено:
frigoremont100%(10)100% нашли этот документ полезным (10 голосов)
2K просмотров33 страницыАвторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(10)100% нашли этот документ полезным (10 голосов)
2K просмотров33 страницыService Directions
Загружено:
frigoremontАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 33
etGram Refrigeration:
YORK INTERNATIONAL A/S
- Service Directions
Reciprocating Compressor
HC/HCL/HCH
6100/8100
® ‘Attn. 82 600 0049.00 Ordre nr 22 00%
Contents
1, In general
1.1, Introduction ..
Application.
‘Compressor type..
Avoid liquid slug-over..
Starting-up fie
Further information..
Identification
Ordering spare par
Instructions in general.
2. Operating and Maintenance
2.1, Maintenance Programme...
2.2. Service and repair ...
Dismanting the compressor.
Oil charge - during standstil.
1) Vacuum
1) Oil charging pump.
Checking the
Oi charge
1) Oil charging pump with non-return valv
Il) Throttling the suction valve.
Leak test...
Spare parts.
Trouble shootin
2.3. Compressor inspector
Coupling alignment...
V-belt
Inspection of V-beltflywheel...
Checking main- and axial bearing
Mounting the bearings in end covers.
Mounting the bearing cover, crank and checking clearance
‘Checking the crankshaft.
‘Checking connecting rods and bearings .
Checking piston pins,
Checking suction and discharge valves...
New suction and discharge valve plates
New suction and discharge valve springs
Checking valve seats and guides...
Pistons, cylinders and connecting rods
Mounting cylinders / noxious spack
~ eter retetes
BONAR ARa EEE
© OOOO OMOIVIIO00R
Checking cylinders
Checking pistons
Checking the shaft seal
Mounting the shaft seal and oil pressure valve.
Mounting and checking the carrier and oil pump.
‘Checking the oil system E
Mounting the oil fer.
‘Checking the capacity control.
Mounting the connecting tube between flang
Mounting tube for capacity control.
Mounting capacity control
Checking the bypass valves
Checking the oil control valve
Checking pressure switch function
Checking thermostat function.
Checking the oi return...
‘Checking the oil cooling ..
Mounting the oil cooler . :
‘Checking water-cooled top covers
2.4, Relief of trouble-shooting
2.5. HC/HCT Tolerance and adjusting measurements
Bearing clearance.
Piston / cylind.
Piston ring gap.
End clearance.
2.6. Survey of Torque Values
2.7. Placement of Cylinders and Discharge Valves ...
HC 6100/8100 R717 ~ Ammonia.
HC 6100/8100 HCFC, HFC.
HCL 6100/8100 R717 - Ammonié
HCL 6100/8100 HCFC, HFC.
HCH 6100/8100 R717 ~Ammoni
HCH 6100/8100 HCFC, HFC.
Reference List: .
[1] Operating and Maintenance Directions for HC/HCLHCH 6100/8100.
[2] Installation Directions for HC/HCL/HCH 6100/8 100.
Further documentation:
~ Technical Data.
~ Operating and Maintenance Directions for HC/HCL/HCH 6100/8100.
~ Installation Directions for HC/HCL/HCH 6100/8100.
~ Spare Parts List for HC/HCL/HCH 6100/8100.
~ Design Data.
2609201900
1.1.
Application
‘These service instructions apply to the mainte
nance of compressors.
If the operating range of the compressor is
changed or a’refrigerant is replaced by a new ty-
pe, the supplier must be contacted.
Compressor type
HC is designed for normal cold rooms.
HCH is designed for higher pressure and tempo-
rature, @.g. as in air conditioning plant.
HCL is for use as a low-pressure compressor in
two-stage plant,
To ensure economic and problem-free running,
it is important that the correct compressor be
used within the various operating ranges.
The primary difference between compressor ty-
pes lies in the suction and discharge valves, the
refore it is extremely important that these are of
the appropriate type, correctly assembled. See
details in the sections dealing with discharge and
suction valves.
Avoid liquid slug-over
To avoid slug-over itis important that the suction
gas be superheated at the compressor inlet. A
‘Superheat of at least 5°C is recommended.
It is also important that the heating element be
connected during the standstill period - and for
at least two hours before starting up.
zens 001000
Introduction
Starting-up filter
‘When supplied, the compressor is equipped with
a starting-up fiter (in the suction fiter). The star—
ting-up fiter must-be-removed “after about 50
hours'-running time. The starting-up fiter should
bbe used after major repair or modification, etc. of
the refrigeration plant.
Further information
if questions arise regarding installation, servi-
cing, operation, maintenance and ‘spare parts,
please contact your supplier.
Identification
‘When supplied, the compressor has a nameplate
giving year of manufacture, serial. number, type,
refrigerant, etc.
Ordering spare parts
When enquiring about or ordering spare parts,
please give model, serial nimber, refrigerant and
‘order number if applicable.
Instructions in general
Before carrying out repairs on the compressor,
please read both the Operating and Maintenance
Directions [1], and the Installation Directions [2]
for the type of compressor concerned.
2.1. Maintenance Programme
5 = 1. Normal maintenance, not calling for technical qualifications
‘Operating hours 5 | 50 | 500 | 4000 | 8000 [12000] 16000] 24000
- 1_| Check of V-belts for wear x [xxx [x fx [x lw
2 | Check of belt tension x [x [x [x [x Px Tx Tw
. 3 | Disassembling of start-up filter x
4 | Visual checking of coupling [x [x | x | x | x | x | x |
5 | Tightening up of bots x x 60)
6 | Oilchange x x |x [x Tx Tw
7 | Cleaning of crankcase x x | x [x [x Tw
8 | Oifiter change x x |x |x [x [| ®
9 | Cleaning of suction fiter x [x [xe [x [x [x fx Tw
10 | Check for leaks x |x |x |x |x fx fx |
11_| Check of oil return x |x [x fx |x. fx fx |
12 | Cleaning of fiterforoitretum [x [ x [| x | x | x | x | x | &
- The maintenance programme does not re- - Oil filers can be ordered from your agent. A
place the daily routines described under the set of spare parts consisting of gaskets, O-
Operating and Maintenance Directions [1] rings, aluminium rings etc. can be ordered
too.
= (8) indicates that the maintenance should be
done in co-operation with the refrigerating - An oil change can be replaced by a fine-fi-
firm in charge of the rest of the maintenance. tration 3 ym beta <75, and an analysis certi-
fying the continued use of the oil.
- The maintenance programme is repeated
‘every 24000 operating hours.
2. Compressor inspection, calling for technical qualifications
Operating hours 4000 [8000 [76000 [24000 | 32000 | 40000 [48000
1 [Alignment of coupling x [xx Tx [x [x Tx
2 [Change of V-belts x x
‘3 [Check of pulleys /fiywheels x [x [x |x fx Tx [x
4 | Check of main and thrust bearings x x
“| Check of connecting rods Tx x
and bearings
_| Check of piston pins x x
7_|Check*of suction and discharge valves | _x
'8_[ New suction and discharge valve plates: x [x [x [x fx [x
‘9 | New suction and discharge valve xlxlxtlxlxlsx
springs
10 [Check of valve seats and guides x |x |[x fx >xt[x lx
11 [Check of piston rings x x
12__| Check of cylinders x x
13_| Check of pistons x x
14 [Check of Crankshaft x x
15 | Check of shaft seal x [x [x Px [x Tx
16 [Check of oil pump x x
17_[Check of oil system x x
18 [Check of capacity control x x
19_ [Check of by-pass valves x x
[20 [Check of oil requiating valve x x
21 | Check of pressure control function x [x [x [x Px [x [x
'22_| Check of thermostat function x [x |x |x |x ][-x]-x
23 [Check of oil return x [x [x |x [x [x |x
24 [Check of oil cooling x |x [x [x |x {x fx
[25 [Check of water cooled top covers x [x [x [Tx ]x«fx [x
It is possible to order the following standard
Spare parts sets:
~ Sets of gaskets
~ Sets of spare parts, mini
= Sets of spare parts, maxi
For particulars, apply to your agent.
Further spare parts can be ordered according to
the spare parts lst.
In case of a total damage of the compressor
some hand-picked agents have a complete set
of spare parts for a total compressor renovation.
The intervals indicated only apply to normal
loaded compressors,
seeo0n000
At high speed and/ or high pressure conditions it
may be expedient to reduce the maintenance
intervals. The opposite applies to compressors
with a low speed,
Service during the guarantee period has to be
carried out by the refrigerating firm in charge of
the installation. Besides, some countries demand
statutory inspections by an authorized reftige-
rating firm,
The maintenance programme is repeated at the
same intervals as in the above table. Inspections
have to be carried out according to the
compressor service manual.
2.2.
Dismantling the compressor
‘When performing inspection or repairs, do not
loosen covers or dismantle parts before the
compressor has been sucked empty.
Close the suction’ stop valves and allow the
‘compressor to run until the suction pressure
‘gauge indicates maximum vacuum, then stop the
‘compressor and close the pressure stop valves
quickly.
Wait until pressure in the compressor is equali-
zed, i.e. suction and manometers show the same
pressure. The pressure must be as close as
possible to atmospheric pressure, preferably with
‘no more than 0.2-0.3 bar deviation,
Oil charge - during standstill
1) Vacuum.
Connect a hose to the oil charging valve and le-
ad the hose down into a vessel containing refti-
geration machine oil. Then connect the vacuum
Pump to atmospheric pressure. Carefully open
the oil charging valve. Oil will flow into the com-
pressor.
Avoid sucking air into the system.
The normal oil level is the middle og the sight
glass, maximum level is the top, minimum level
the bottom.
Il) Oil charging pump
Connect the hose from the oil charging pump to
the oil charging valve. Lower the pump suction
pipe into a vessel containing refrigeration
‘machine oil and pump oil into the compressor.
The normal oil level is the middle of the sight
glass, maximum level is the top, minimum level
the bottom.
Service and repairs
Checking the oil level
After the compressor has been charged with oil
and started, check the oil level regularly. Ifthe oil
level falls below the bottom of the sight glass, it
must be replenished. Oil replenishment is
possible while the compressor is running.
Oil charge ~ while running
1) Oil charging pump with non-return valve
Connect the pump to the oil charging valve.
Lower the suction hose into a vessel containing
refrigeration machine oil. Open the oil charging
valve and pump oil into the compressor.
The normal oil level is the middle of the sight
glass, maximum level is the top, minimum level
the bottom.
I) Throttling the suction valve
Connect a hose to the oil charging valve, fill the
hose with refrigeration machine oil and lower into
vessel containing refrigeration machine oil
Throttle the suction stop valve on the
‘compressor so that pressure in the crankcase
falls to slightly below atmospheric pressure.
Now carefully open the oil charging valve. Oil will
then flow into the compressor. Avoid sucking air
into the compressor.
The normal cil level is the middle of the sight
glass, maximum level is the top, minimum level
the bottom.
Leak test
After repair or inspection, check all joints for
leaks before starting the compressor.
R 717 (ammonia) units can be checked by
brushing a concentrated soap solution on joints
and welds.
Another possibility is the use of sulphur sticks or
litmus paper. When in contact with R717, a
burning sulphur stick emits white smoke; red
moist litmus Paper becomes blue. Electronic leak
detection equipment must be used where HCFC
and HFC are involved. .
s2eo000000
Spare parts
The spare parts list contains parts that can be
ordered by stating spare part numbers, item No.,
and compressor size,
When ordering spare parts, remember to give
the compressor machine number.
Trouble shooting
The following pages describe the remedies for
faults.that might occur.
cH
2.3.
Coupling alignment
‘See Installation Directions, 2.2, [2].
V-belt
For belt tension, alignment and number of belts,
see Installation Directions, 2.3, [2].
Inspection of V-beltflywheel
Operating wear will occur on belts, motor pulley
and flywheel. At some point, wear on the motor
pulley and/or flywheel will become such that belt
replacement alone will not be the most economic
remedy. A worn pulley and flywheel subject the
belts to extraordinary wear and then the most
appropriate step is to replace the whole
transmission.
Wear canbe checked using a DIN 2211 gauge
for the SPB profile. Note that there is a difference
in profile between pulleys < 190 mm or > 190
mm. If wear has occurred, the pulley profile wil
appear concave, as in fig. 1.
Compressor inspection
‘The gauge can be ordered.
For belt tensions, see Installation Directions, 2.8
and 2.9, (2)
Fig. 1
20000000
Checking main- and axial bearings
‘After pressing in new main bearings, check that
the bearing clearance is as stated in the
appropriate table. Also check whether the
the
Mounting the bearings in end covers
‘Main bearing pressed in as shown
14 mm from rear edge
The end clearance can be adjusted by the
number of gaskets used on the rear bearing
cover.
Insert thrust bearing
I Lubricate bearings with
ite refrigeration machine oil al
ZZ
Press the main bearing
SaaS 4
flush with the edge of the
8 bearing hole
3 The opening pressure of
d
q
Z
Eber ZTTEDEEEETEEEEEE
Mounting the bearing cover, crank and checking clearance
the pressure control valve
is checked
Opening pressure:
4 Bar
Before insertion, lubricate the
crank, main and thrust
bearings with refrigeration
machine oil
HH
Checking the crankshaft
‘See table of clearances for wear measurement.
776006907,
0.6-1.0 MM
Clearance between crank-
shaft and pressure bearing
Checking connecting rods and bearings
See table of clearances for wear measurement.
Checking piston pins
‘See table of clearances for wear measurement.
Checking suction and discharge valves
Check suction and discharge valves for wear.
Typically, wear manifests itself by concentric
rings inthe valve plates. If such wear has
‘occurred, replace the valve plates.
Wear can also occur on the springs. This
appears in the form of notching (see fig. 2)
typically from compressor liquid slug-over.
Replace the spring and take steps to prevent
liquid slug-over. When valves become
damaged, ‘the repair of valve springs and plates
isnot advised.
When springs have been taken out for checking,
they must be refitted so that an open gap is
created inside the ring, see fig. 3. The correct
assembly of these springs is of the utmost
importance to compressor running and output.
I 8
al :
i i
Fig. 2.
‘The open crack should
be in the ring
Open crack
Fig. 3.
New suction and discharge valve plates
When fitting new valve plates, make sure that
they havethe correct number, see spare parts
list. To ensure optimum compressor output and
operation it is essential that the correct plates be
fitted,
New suction and discharge valve springs
When fitting new springs, make sure that they
have the correct number, see parts list. It is
important that the springs be fitted correctly, Le.
that an open gap is created inside the ring. See
fig. 3 above under "Checking suction and
discharge valves". To ensure optimum
‘compressor output and operation it is essenti
that springs be fitted correctly.
Checking valve seats and guides
Check valve seats and guides for wear. Impact
marks or similar must not appear on the
surfaces. If there are marks, replace the parts.
Also check that the seat has not become too
wide. Slightly damaged valve seats can be
lapped using compound and a lapping block.
tons, cylinders and connecting rods
When fitting new pistons and cylinders, check to
ensure that the clearance is as given in the table,
The easiest way to fit pistons and cylinders is to
assemble and fit them and the connecting rod at
the same time.
Because of the small tolerances, it can
sometimes be necessary to heat pistons when
inserting piston pins.
When replacing piston rings, check that they
move easily in the piston grooves and that the
gap between the ends when the rings are fitted _
are as stated in the table.
Insert standard piston rings and then a scraper
ring. Fit an oil check ring in the bottom groove.
A bearing is inserted in the connecting rod eye; a
split bearing bush in the connecting rod end.
When inserting new bearings, check that the
clearance in the piston pin bearing and the
clearance between crank pin and bearing are as
given in the table,
Mounting cylinders / noxious space
Check to ensure that the numbers marked on top
and bottom parts of the connecting rod are the
same and that they face in the same direction
Lubricate crankshaft and connecting rod bearing
with refrigeration machine oil.
‘Cylinder installed with piston, piston rings,
scraper ring and connecting rod is passed
through the valve lifting ring and fastened to the
frame.
Assemble bearings with connecting rod bolts and
nuts.
Tightening torque: 50 Nm
Pour 5 cm? refrigeration machine oil into each
oylinder. Fit discharge valves and liquid slug-
‘over springs to the cylinders.
Now mount top covers with gaskets.
Tightening torque: 190 Nm
776006909
Checking cylinders
Each cylinder must be checked for visible and
perceptible rim where the piston is at top or
bottom.in this case the cylinder is replaced. Also
ensure that there are no fractures or cracks in
the cylinder
Checking pistons
When assembling, check that the clearance
between the piston in its top position and
thedischarge valve seat is 1.1-1.5 mm,
corresponding to a distance between discharge
valve seat and bottom of piston top of 16.7-17.1
mm,
See table of clearances for wear measurement.
Check the noxious space
i
10
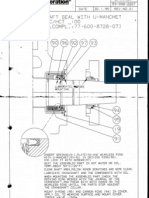
Checking the shaft seal
The shaft seal consists of a special cast iron,
spring-loaded, lapped ring that rotates against a
stationary, lapped carbon ring.
(O-rings provide the seal between cast iron ring
and crankshaft, and between carbon ring and
cover. Before fing, inspect the O-rings, clean
all parts thoroughly and lubricate them with the
oil used in the compressor.
‘Check the shaft sebl to ensure that all surfaces
are clean and plane. It is possible to remove
small scratches and eliminate minor leakage by
lapping the wearing surfaces.
If there ate tarry deposits around the shaft seal,
remove them and check the oil system.
Cap
Guide
Cone
Mounting the shaft seal and oil pressure
valve
Lubricate all components. Insert spring holder,
stop end against the crankshaft collar.
Check that the holder meshes with the crank—
case shatt pin,
~ Insert the wearless ring with inside o-ring and
spring and rotate so the ring's locking track
meshes with the crankshaft pin.
‘When the ring is released, check the dimensions
specified,
Lubricate o-ring and mount in cover. Mount
‘carbon ring in cover. Apply oil to wearing surface
and mount the cover using four M16x30 cyl.
screws.
Tightening torque: 190 Nm
Spring holder
Spring
O-ring
Wearless ring
Carbon ring
O-ring
Cover for shaft seal
Gasket
77600631 1001004
Mounting and checking the carrier and oll pump
Make sure that the pump is correctly assembled,
in accordance with the direction of rotation.
‘Check for wear on gearwheel and housing.
Check bearings for wear and replace with new
ones if necessary.
776006918
Press the carrier into the bu:
‘mount in crankshaft as shown,
Pump housing
—
Reference surfacg
c
Gear whe@ |
‘Space between cover and rotor:
B>A B-A=0.08- 0.13 mm
‘Space between cover and gear wheel:
C>A C-A=0.03 - 0.08 mm
Spacer 072/59 x 0.05 42-17-0455
72156 x 0.10 42-17-0458
Measures are checked by means of a dial.
‘Gauge. Spacers has to be mounted here.
"
O-ring
776006919
‘Mount the o-ring in the track of the bearing cover.
Insert the oil pump pin into the bearing covers
bearing boring.
‘Check that the pump rotor canter pin meshes with
the cranks carrier.
Attach the oil pump by using the two inlaid M10x80
‘screws, which can be tightened through holes in
the outside cover of the pump. M10x120 screws
are to be mounted and tightened.
Tightening torque: 40 Nm
‘Check that the pin in the outer cover of the pump
shows the correct direction of the crankshaft
rotation.
776006912
Pin in this hole.
(Crank turning
anticlockwise
seen from the
pump side,
Fin in this hole.
Crank turning
clockwise seen
from the pump
side,
12
Checking the oll system
Check the oil system for circulation and leakage.
For oil change after a given number of hours,
Mounting the oil filter
see the Operating and Maintenance Directions,
22, [1].
Checking the capacity control
‘The compressor unloading device consists of a
spring assembly in which two rods press a valve
lifting ring with pins against the suction valve
plate. The suction valve is thus forced open and
the cylinder put out of action. A hydraulic piston
‘compress the spring assembly to release the
suction valve plate and bring the cylinder back
into normal operation.
il from the pump is supplied to the unloading
cylinders via the solenoid valves.
{tthe control fails, check the oil pressure, O-ring,
sealing ring and the contact face of the pins on
the lifing ring.
Check the capacity control devices to ensure that
they are able to raise the lifting pins and thus
unload the valves. Check also whether the pins
retract so that they do not ‘striket the valve
plates. If this is the case, adjust the capacity
control,
Mounting the connecting tube between flanges
3/8" RC elbow for G15 mm tube
776006916
Mounting tube for capacity control
1/8" RC elbow for 98 mm tube
776006915
Mounting capacity control
14
‘Screw in cylinder for capacity
regulation from crankcase until
the control figures shown are
reached. Tighten cylinder using
nut M24,
151
MAX .
Insert the crossbar and lifting
arm into the suction chamber
and assemble using a locking
nut and disc spring. Check to
ensure that the spring is facing
the right way.
oN @
a
After tightening, it should be
possible to move the crossbar
and lifting arm in relation to each
other with noticeable friction,
Insert the cylinder into the mounting guide.
Place the spacers on the mounting guide.
‘Compress the spring, keeping itin position
using mounting clamps.
Place the compressed spring on the bottom
of the suction chamber around nut M24,
Place the spring guide on the mounting guide.
Place the crossbar with lifting arm on the
mounting guide,
az
Nut
Litting arm,
Locking nut
Dis spring
Crossbar
Spring control
Spacer
Mounting clamp.
‘Spring
Mounting guide
e2eos001000
15
Press the mounting guide outwards
from above, using the piston rod with ra
fitted o-ring. Zi
Mount the piston plate with fitted ened
u-sleave on the piston rod and tighten,
using the locking nut.
. !
O-ring
, Zz Piston plate
U-sleeve
Locking nut
Position the valve ling ring
between the lifing arms
Insert the valve lifting ring H 1
nearest to the pressure t 1
outlet end first. t i 1
L
t
Lifting ring
H
Release the spring by removing
the mounting clamps. Zi
f
g
16
Checking the bypass valves
The compressor is fitted with differential.
pressure-independent bypass valves. These
‘open at 25 bar and allow gas to flow from the
compressor discharge side to the suction side.
‘Check the bypass valves to ensure that they
‘open at the pressure for which they are set. The
check ‘must be performed on a suitable test
stand ory alternatively, the valves can be
returned to the manufacturer for checking.
Checking the oil control valve
‘The oil pressure of the compressor is set at 3-
4.0 bar for normal operation. The oil pump is
fitted with an internal bypass that opens at 5 bar
to prevent-pump overload when starting with cold
oil.
Checking pressure switch function
On compressors with pressure control, check
whether the pressure switches cut in/out at the
required pressure and whether they are correctly
set
‘Checking thermostat function
Check whether the thermostats cut in/out at the
required temperatures and whether they are
correctly set.
Checking the oil return
Remove and clean the filter. Inspect the solenoid
valve.
Checking the oil cooling
Check that the oil temperature is satisfactory.
If not, look for possible calcium deposits.
Check the solenoid valve.
Mounting the oil cooler
Nut Sealing ring ~
g
k13 Cf
rA\
eck rv
Tube coil
‘Checking water-cooled top covers
Check that the discharge temperature is
satisfactory.
If not, look for calcium deposits in the hoses.
Check the solenoid valve.
s2e00000000
2.4.
7
Relief of trouble-shooting
‘Symptom or difficulty
Possible reason
Remedy
High condenser pressure
Insufficient water passage
through condenser, condenser
pipes clogged up.
Spaces between fins of air-
cooled condenser have been
fouled up,
Incorrect setting of high-
pressure cut-out.
Check whether water supply to
‘condenser has been turned off.
Set cooling water control valves,
Check and if necessary, clean
condenser pipes and filter in
water line,
Clean spaces between fins and
check fan.
Check whether high-pressure
‘cut-out is switching off at cor
rect pressure.
‘Compressor short cycling Evaporator coils frosted up. | Defrost evaporators.
{at connection and
disconnection of low pressure | Filters of liquid valves, suction | Clean filters.
control). valves, or regulation valves
clogged up.
Phial of regulating valve has lost] Remove phial from suction line.
its charge, or insufficient liquid | Hold itn one hand and feel on
charge in plant. suction line with the other. If the
suction line does not get colder,
add more refrigerant.
‘The compressor starts and The system is overfilled with
stops too often (at the high refrigeant,
pressure switch).
‘The high pressure switch
switches in and out bedause the|
condenser is overfilled and
partly inactive as a large number
of the condenser pipes are
‘submerged in the refrigerant,
Drain off refrigerant
s2ec0004800
18
‘Symptom or difficulty Possible reason Remedy
Compressor running Lack of refrigerant Check charge. If insuificient, add
continuously the necessary quantity. Check
for leaks,
Compressor discharge and /or | Check valves, if damaged or
De suction valves damaged or worn] worn away, repair or replace.
= away.
High condenser pressure Air or non-condensable gases | Purge at condenser and/ or
in system. receiver.
Install air purger.
s Too warm cooling water or | Check and clean water valve
insufficient passage through | and water filer. Check whether
condenser. water valve has been suficientiy
3 open,
Pipes in water condenser fouled] Clean condenser pipes.
‘ or furred up.
: ‘Spaces between fins of ai Clean spaces between fins, and
cooled condenser fouled up. | check fan.
Too much liquid in receiver and | Drain refrigerant and fil itinto
condenser. empty drum,
Low condenser pressure Condenser receiving too much | Regulate water supply.
cooling water.
Leaky discharge and/or suction
valves
Unloading system has put some|
of the cylinders out of operation,
Remove top covers, check valve}
plates and valve springs,
replace if required.
‘See service instructions.
200004800
19
‘Symptom or difficulty Possible reason Remedy
High suction pressure Leaky suction valves. Remove top cover, check valve
plates and valve springs,
replace if required.
Unloading system has put some| -See service instructions.
of the cylinders out of operation.
Low suction pressure ‘Clogging of liquid line, regulating] “Evacuate, check, and clean
Y valve, or suction filters, filters.
Insufficient refrigerant charge. | Add reftigerant.
‘Too much oil circulating in ‘Check whether excessive oil is
system (HCFC/HCF). found in system, drain
superfluous oil.
Incorrect setting of regulating — | .Set regulating valves for correct
valves. flow.
Regulating valve frozen Unfreeze regulating valve by
(HCFCIHCR). means of warm, soaked rags,
and let freon from receiver pass
through the drying filter. Never
add antifreeze to freon.
Noisy compressor Excessive oil circulation ‘Check oil level.
resulting in liquid slug-over.
Liquid slug-over as a result of | Regulating valves opening to
not evaporated refrigerant being] much - close a litle.
drawn back to compressor.
Phial placed incorrectly or loose.) Move or fasten the phial of
regulating valve.
ES
20
Possi
le reason.
Remedy
‘Symptom or difficulty
il disappearing from crankcase
Liquid refrigerant returning to
compressor.
Piston rings or cylinder liner
worn,
Possible oil return line from oil
separator to crankcase clogged
up.
Set regulating valves correctly
‘so that the compressor will work|
ata suitable superheating,
Replace piston rings, and
replace pistons, and cylinder
liners, if necessary.
Clean oil filter in return fine,
joes not return to crankcase
(HCFC/HCF)
Regulating valve admitting
insufficient liquid to evaporator.
Filler for solenoid valve in oil
return pipe clogged up.
‘Solenoid valve coil in oil return
line burned,
Set expansion valve to admit
more liquid.
Clean filter,
Replace coil
Compressor will not start
Oil pressure cut out interrupted
current, safety fuses have fused |
Main switch not switched on.
Adjust oil pressure cut out, fit
new fuses, and locate cause of
trouble.
‘Switch on current.
‘Compressor starts, but stops
again at once
Insufficient compressor
(il differential pressure contro)
Oil differential pressure control
defective.
Oil slug-over.
‘Add oi
Repair or replace pressure
control. Check whether liquid
refrigerant is drawn into
crankcase,
Check oil level, and correct.
2000001009
24
. ‘Symptom or difficulty Possible reason Remedy
V-belts are turning in groves | Pulleys not inline. Check alignment of pulleys.
‘Wrong belt/ pulley profile. ‘Check whether pulley and belt
match.
. Defective keyways. } Replace V-belt pulleys.
Insufficient V-belt tension. Tighten up.
7
Abnormal wear on V-belt slopes| Incorrect groove angle. Replace or machine pulleys.
Defective keyways. Replace pulleys.
@ Pulleys out ofline. Check alignment.
Insufficient V-belt tension. Tighten up.
Bolts run agains¥/hit belt guard. | Align belt drive to prevent
dragging.
‘Abnormal noise level Pulleys out of line. ~] Check alignment.
Insufficient V-belt tension. Tighten up.
Irregular V-belt elongation Defective pulley grooves. Replace pulleys.
New and old V-belts in same | Replace all V-belts.
belt drive.
Different belt makes in same | Replace all belts by belts of
belt drive. ‘same make,
Cam
2000000 -
Pat
22
[Symptom or difficulty
Possible reason
Remedy
V-belts breaking after few hours|
of operation
Incorrect installation of V-belts,
Belt drive has been blocked.
When fiting V-belts on pulleys,
comply strictly with instructions
for installation of V-belts.
Find reason for blocking,
Fractures in bottom part of
V-belts
Abnormal belt slip,
Excessive heating stress,
Excessive cold stress.
Check belt tension,
Protect V-belt drive against
heating stress.
Have V-belts warmed before
fiting.
Excessive vibrations in V-belts
Insufficient V-belt tension.
Pulleys not dynamically
balanced.
Tighten up.
Balance pulleys at correct
speed
Further tensioning of V-belts not
possible
Incorrect length of V-belts in
belt drive,
Replace by shorter V-belts.
23
2.5. HC/HCT Tolerance and adjusting measurements
Bearing clearance
[.~«Y TG2075-HCBO7S .| HOBTOOHCETOO HCBI25
HCT4075/HCT8075 | HCT6100/HCT8100 | HCT8125
Main bearing aes 0,14 0,20 ar a
Connecting rod bearing eames ogeaet Seer Ses
ee 1s a
Replace bearing and /or shaff, if max. is exceeded.
Piston / cylinder
At right angle to piston pin
Piston, top (Manufactured
HIC2075-HC8075
HCT4075/HCT8075
HC8100/HCB100
HCT6100/HCT8100
C8125
HCTB125
Imax.
[Manufactured
Piston, bottom fae
Replace cylinder, pistons and rings, if max. is exceeded.
Piston ring gap
HC2075-H807S
HCT4075/HCT8075
THCB1OOHCBT00
HCT6100/HCT8100
ICBI25
HCT8125
‘The gap is measured, while the ring is placed in the cylinder.
End clearance
HG2075-HO807S
HCT4075/HCT8075
04-08
TICBTOOC8TO0
HCT6100/HCT8100
06-1,0
C8125
HCTB125
08-15.
(Manufactured
Imax.
Replace bearing, check shaft and adjust, if exceeded
10
13
19
24
2.6. Survey of Torque Values
‘Steel bpits
Grade 8.8 M M M M M M
4 6 8 10 12 14
Fe ASSES oS Nm 25 8 18 40 70 120
= eS ny 8) 6) ww
Thin = Tepe Tip = TON
‘Steel bolts
M M M M M
16 18 20 22 24
EE oS Nm 199 250 350 480 600
= & (ety (137 (18) 53) AT) (484)
Connecting rod ‘Central screw
bolts :
Cylinder bore 7 100 125 152 75/100 125 152
‘Steel bolt M M M M M M M
ext 10x1,25 | 12x1,25 | 14x1,5 | 12x1,75 14x1,5 16x1,5,
Grade Nm 2 50 90 140 100 140 190
10.9 (tot) (18) (38) (65) (100) (72) (100) (137)
‘Where two nuts are used, both should be tightened to the torque given.
seeoo0ne8 co
25
2.7. Placement of Cylinders and Discharge Valves
Hc 6100/8100
Notice the difference between HC-HCL-HCH and refrigerants.
6100 '
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6630
CYLINDER, 77-600-6620
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER. 77-800-6625
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER: 77-60-6620
8100
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6630
CYLINDER, 77-60-6620
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER: 77-800-6620
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6630
CYLINDER, 77-600-6625
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER 77-60-6620
cé cS
C3
cl
C8: C7
cé
R717 - Ammonia
6100
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER: 77-60-6620
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER: 77-60-6625
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6630
CYLINDER: 77-60-6620
8100
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER, 77-600-6620
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER. 77-60-6620
DISCHARG, VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER: 77-60-6625
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6630
CYLINDER. 77-60-6620
26
He 6100/8100 HCFC, HFC
Notice the difference between HC-HCL-HCH and refrigerants.
6100 6100
:DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631 C6 (C5 DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6631
CYLINDER 77-800-6621 CYLINDER 77-00-6621
1g DISCHARG, VALVE 77-60-6631 cs
S:CYLINDER = 77-600-6626
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631
CYLINDER 77600-6626
*DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631 C1 viscHare. vaALvE 77-60-6631
*CYLINDER - 77-60-6621 CYLINDER, 77-60-6621
8100 7 8100
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6631 cé c DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6631
CMUNDER — 77-800-0621 See YLINDER rrceno-oe2t
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631 ©5 oscuana. vaLvE 77-600-6601
CYLINDER 77-800-6621 CYLINDER, 77-600-6621
cs
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631 DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631
CYLINDER 717-600-6828 (5 Cy CYLINDER 77-60-6626
DISCHARG. VALVE 77-60-6631 = + DISCHARG. VALVE 77-600-6631
CYLINDER 77-60-6621 CYLINDER ‘77-600-6621
seo 004800
Вам также может понравиться
- XRV Compressor Package - Maintenance Schedule: RemarksДокумент1 страницаXRV Compressor Package - Maintenance Schedule: RemarksfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Technical Information: C S ™ D S R CДокумент17 страницTechnical Information: C S ™ D S R Cfrigoremont100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- ITT характеристики BITZER BOCK Frascold Copeland DORINДокумент7 страницITT характеристики BITZER BOCK Frascold Copeland DORINfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Seal - Eagle BurgmanДокумент149 страницMechanical Seal - Eagle BurgmanAmol Patki71% (7)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Service Manual: WRV & Wrvi Compressor RangeДокумент51 страницаService Manual: WRV & Wrvi Compressor Rangefrigoremont75% (4)
- XRV 127 Service Manual - Sept - 2013Документ86 страницXRV 127 Service Manual - Sept - 2013frigoremont50% (6)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- XRV 163 & 204 Service ManualДокумент65 страницXRV 163 & 204 Service Manualfrigoremont63% (8)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- COMMISSIONNINGДокумент1 страницаCOMMISSIONNINGfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- R 201007Документ1 страницаR 201007frigoremontОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Compressor SpecificationsДокумент1 страницаCompressor SpecificationsfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- DORIN H Range - K Range Cross ChartДокумент4 страницыDORIN H Range - K Range Cross Chartfrigoremont100% (5)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- WRV-WRVi Service Manual - September 2012Документ64 страницыWRV-WRVi Service Manual - September 2012frigoremont79% (24)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Sabroe PDFДокумент3 страницыSabroe PDFfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- Dorin K4PДокумент6 страницDorin K4Pfrigoremont100% (1)
- Dorin H32Документ6 страницDorin H32frigoremontОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- SEMIERMETICДокумент2 страницыSEMIERMETICfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- Shaft SealДокумент2 страницыShaft Sealfrigoremont100% (2)
- Stal Service ManualДокумент184 страницыStal Service Manualfrigoremont100% (5)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Dorin H1Документ6 страницDorin H1frigoremontОценок пока нет
- Dorin H2Документ6 страницDorin H2frigoremontОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Four Stage Remote Bulb ThermostatsДокумент1 страницаFour Stage Remote Bulb ThermostatsfrigoremontОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)