Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ubd Vs Trans Formative Education
Загружено:
zjeniferИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ubd Vs Trans Formative Education
Загружено:
zjeniferАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
THESIS TITLE:
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TRANSFORMATIVE EDUCATION (TE) AND UNDERSTANDING BY DESIGN (UBD) BY FACULTY MEMBERS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MANILA
Chapter 1 THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND The school is the institution that fulfills the social responsibility of preparing the future generations of any society. More than the family, it is what molds the youth as future, responsible citizens of society. Education can be an instrument for social transformation and become an over-all social movement for democracy and development. The challenge of education is how it can become an effective agent towards ending poverty. It, therefore, must not simply be relevant but be committed and responsive to actual problems of society. In transformative education, the educator recognizes his or her capacity not only to start changing the Philippine education system but also to mold his or her students into conscious, active citizens who constantly aspire for a democratic and modern Philippines. The vision of transformative education is to provide the students with the necessary skills, knowledge and values to become productive citizens, but also seeks to open the minds of the students and provide them with skills for critical thinking and social awareness. The school administration plays a key role in unifying the whole school for transformative education, and in inspiring everyone, not just the teachers, in participating in a process of personal and collective transformation and commitment. To do this effectively, the administration must practice an open, evocative, democratic leadership that seeks to draw all the staff to participate in solving the problems of the school and improving it further.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
This study is about a comparative study of Transformative Education and Understanding By Design by faculty members in the University of Manila. Specifically, the study seeks to answer the following questions: 1. How may the Understanding by Design (UBD) and Transformative Education (TE), as a tool in teaching, be described as to: objectives, content, strategies and evaluation? 2. In what areas do the two educational tools differ? 3. What problems are encountered in implementing UBD and TE? 4. What are possible solutions to eliminate these problems?
5.
How may the results be utilized in preparing an educational tool?
ASSUMPTION 1. The information obtained is reliable and valid.
2. The UBD and TE may be described differently as to objectives, content, strategies and evaluation. 3. Different problems are encountered in implementing UBD and TE. 4. There are valid solutions to eliminate problems in UBD and TE.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY This study may be deemed significant to the following: school administrators, curriculum planners, teachers and students. The School Administrators and Department Heads The result of this study will help them understand that they are one of the key components in realizing transformative education, by providing better and proper support to teachers and students to realize the goals of their school The Curriculum Planners The study poses a challenge for modern curriculum planners to be pro-active in creating avenues for students to develop critical thinking and social awareness. The Teachers and Parents This study will help them realize that progressive education goes beyond effectively providing skills, knowledge and values but covers the whole process of providing social conscience and social commitment, in order to develop the youth as responsible, committed citizens for social transformation. The Students This study will inspire them to become better citizens of the country who are prepared to meet the demands of modern living and the complexities of the fast changing world.
SCOPE AND DELIMITATION
The study deals with a comparative assessment of Transformative Education (TE) and Understanding by Design (UBD) by faculty members of the University of Manila in the Academic Year 2011 - 2012
DEFINITION OF TERMS
The following terms are defined contextually and operationally or as used in the study: Education Refers to the process of imparting knowledge or developing skills, understanding, attitudes, character or behavior; the process of acquiring knowledge; the field of study concerned with teaching and learning Curriculum - a complete course of study offered by a school; a syllabus is the outline of a single course Transformative Education - Transformative education is the continuing process of bringing out the best in students at all levels of schooling. Transformed learners are skilled in knowing, doing, being, and living together Understanding by Design - is a framework for designing curriculum, assessments, and instruction. It allows teachers to: Teach for understanding, unpack content standards to identify the important big ideas, know how students truly understand and can apply their understanding in a meaningful way, design courses and units to emphasize understanding rather than coverage engage instructional practices that are effective for developing student understanding
Chapter II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES
In the review of related literature and studies, there were no studies that dealt with A Comparative Study on Transformative Teaching and Understanding by Design as Assessed by the Faculty Members of the University of Manila but literature are available discussing the concept, principles and paradigm of both.
Chapter III METHODS OF RESEARCH
Research Design This study used the comparative and descriptive method of research. The study is concerned with a situation or condition existing at present. The researchers examined carefully the relationships-similarities and differences between UBD and TE. Comparative research depends on knowledge generated from descriptive research. The descriptive research method is concerned with the description of the present phenomena using qualitative data in interpreting the existing condition of the problem under investigation. In describing the existing conditions of the problem involved, it does not use only data that simply described the condition. It can be somewhat statistically measured to analyze the data because it is not entirely statistics-free, it may also apply simple statistics to present the profile of the respondents.
The Respondents The respondents of the study are the professors of the University of Manila. Sampling procedure and random sampling are the procedures applied in getting the member of the respondents needed in the study. There are 76 faculty members. The respondents for the study were selected
randomly from the list of faculty members where their names are listed, using the odd-even scheme. Out of 76 faculty members, 16 of them became the respondents which are 20% of the total population. Sampling Technique The researchers used random sampling. The respondents were selected on odd-even scheme based on the list of faculty members. Statistical Treatment of Data To solve the problems raised in the study, the following statistical techniques were used: Percent distribution was used to find the ratio of the frequency of responses to the total member of respondents in percent, applying this formula P = f/n x 100% Where P- percentrage f- frequency n- total number of respondents
To rate the difference of the two educational tools, the researchers used the criteria adopted by ABBAS which were evaluated to be as follows:
4.2 5 3.4 4.1
Excellent Very Good
2.6 3.3 1.8 2.5 1 1.7
Good Fair Poor
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- VTU-Viva - Time Table August - 2020 - B-Arch - Thesis and PT PDFДокумент1 страницаVTU-Viva - Time Table August - 2020 - B-Arch - Thesis and PT PDFCulinary InterestsОценок пока нет
- 31:03 Klassik Stiftung Weimar - International Summer SchoolДокумент2 страницы31:03 Klassik Stiftung Weimar - International Summer SchoolJulieta PestarinoОценок пока нет
- Silabus Speaking 1 Universitas Muhammadiyah MetroДокумент2 страницыSilabus Speaking 1 Universitas Muhammadiyah Metroapi-118157840100% (2)
- MBA 2010 BrochureДокумент66 страницMBA 2010 BrochureAjay KathuriaОценок пока нет
- ME010 805G01 Industrial Safety Electives at Mahatma Gandhi UniversityДокумент2 страницыME010 805G01 Industrial Safety Electives at Mahatma Gandhi Universityrajeesh4meОценок пока нет
- List of Most Visited Art Museums in The World PDFДокумент15 страницList of Most Visited Art Museums in The World PDFashu548836Оценок пока нет
- Tesco Training and DevelopmentДокумент3 страницыTesco Training and DevelopmentIustin EmanuelОценок пока нет
- Kinder New DLL Week 2Документ15 страницKinder New DLL Week 2Jainab Pula SaiyadiОценок пока нет
- Form 2 Personal Statement - Environmental Landscape ArchitectureДокумент2 страницыForm 2 Personal Statement - Environmental Landscape ArchitectureOniwinde OluwaseunОценок пока нет
- Lewin's Force Field AnalysisДокумент8 страницLewin's Force Field Analysischirag_dipsite100% (1)
- CAV JanuaryCOAДокумент58 страницCAV JanuaryCOAGina GarciaОценок пока нет
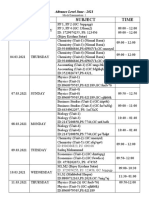
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewДокумент2 страницыMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibОценок пока нет
- 13.2.3a Practicing Good SpeakingДокумент9 страниц13.2.3a Practicing Good SpeakingNieyfa RisyaОценок пока нет
- CV Ankur Banerjee Accountant ResumeДокумент2 страницыCV Ankur Banerjee Accountant ResumesanchitОценок пока нет
- Republic Act No. 10029Документ12 страницRepublic Act No. 10029Mowna Tamayo100% (1)
- Field Study Course Helps StudentsДокумент81 страницаField Study Course Helps StudentsԱբրենիկա Ֆերլին100% (1)
- Mohini Jain v. State of KarnatakaДокумент12 страницMohini Jain v. State of KarnatakaNagendraKumar NeelОценок пока нет
- 08 Amber B11 Llgas Jeric B.Документ1 страница08 Amber B11 Llgas Jeric B.Loriene SorianoОценок пока нет
- Meaning and Needs of Value EducationДокумент21 страницаMeaning and Needs of Value EducationJM De Vera100% (1)
- Thesis Statements in EpistemologyДокумент2 страницыThesis Statements in EpistemologyBeatriz Sarah GaliОценок пока нет
- Divisoria High School PEH Class Teaches Cheer DanceДокумент2 страницыDivisoria High School PEH Class Teaches Cheer DanceMichelle Vinoray Pascual0% (1)
- The Teaching of Listening and ReadingДокумент2 страницыThe Teaching of Listening and ReadingRamil GofredoОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Design Considerations (1) M3Документ13 страницCurriculum Design Considerations (1) M3Hanil RaajОценок пока нет
- Time Sheet: Star Energy Wayang WinduДокумент3 страницыTime Sheet: Star Energy Wayang WindukusumamahardikaОценок пока нет
- (Univocal) Gilbert Simondon, Drew S. Burk-Two Lessons On Animal and Man-Univocal Publishing (2012)Документ89 страниц(Univocal) Gilbert Simondon, Drew S. Burk-Two Lessons On Animal and Man-Univocal Publishing (2012)Romero RameroОценок пока нет
- LLB Brochure 2022 23 VerSep28Документ11 страницLLB Brochure 2022 23 VerSep28Michelle MiaoОценок пока нет
- Sport Vs GameДокумент1 страницаSport Vs GameM.AhsanОценок пока нет
- FS2 Learning Episodes 1 4Документ38 страницFS2 Learning Episodes 1 4Ariane Vizconde Maranan0% (1)
- Edtpa Final Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыEdtpa Final Lesson Planapi-349551741Оценок пока нет
- Economics Matt Mcgee AnswersДокумент109 страницEconomics Matt Mcgee AnswersHetal GandhiОценок пока нет