Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ans Bio 2010
Загружено:
jayquin93Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ans Bio 2010
Загружено:
jayquin93Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
267
Biology
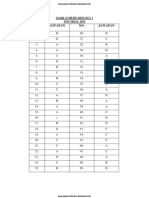
No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Answer B B C B D B A D D D No 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Jawapan
Biology Paper 1(4551/1)
Answer D B D C B B C C B C No 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Answer D A B D A B B A A D No 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Answer B A C C D B A B A B No 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Answer C A A D B D B A B C
[4551/1] [4551/2] [4551/3]
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Biology Paper 2(4551/2)
No. 1a) b)(i) (ii) Marking criteria Y : Carrier protein Z : Channel protein / pore protein It is composed of two layers of phospholipids Acts as a barrier between the internal and external environment of the cell // Allows only specific molecules to pass through it // provide the structural basis for all cell membrane. A semi-permeable plasma membrane is a membrane that allows only certain substances to move freely across it. Active transport is a movement of substances / molecules / ions against the concentration gradient / from low to high concentration across the plasma membrane with the help of carrier protein and energy / ATP. P1 there is no uptake of ions by root cells P2 metabolic poisons kill/ damaged the (root) cells P3 no energy/ ATP is produced P4 active transport does not occur 1 1 1 1 Marks 2 1 1
c) d)(i)
1 1
1 1
(ii)
(Any three)
1 1 1 1
268
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
e)
P1- The glucose with a high concentration acts as a hypertonic solution P2 - causing water in food to move out through plasma membrane P3 This causes food to dehydrate P4 condition not favourable to microorganisms
1 1 1 1 Total 1 1 1 1 1
(Any three)
3 12 2 2 1
2a)(i) W : chromatid X : spindle fibre (ii) b) c)(i)
or or or
Cell S : metaphase Cell T : metaphase I 4
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Total 1 1 1
(ii) (iii) d)
Testes//Ovary//Anther//Ovule 10 -Radiotherapy. -Radioactive rays will kill cancer cells -When all the cancer cells are destroyed, they cannot reproduce by mitosis Cloning -Problem: Costly // expensive//All clones have same resistant towards diseases / environmental factors Secretion : Bile Function : Lipids / fats emulsifier / breaking lipids into tiny droplets D Able to draw the following parts Blood capillary, epithelium, lacteal, finger-like projection L Able to label any two parts Blood capillary Epithelium Lacteal
1 1
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
e)
2 12 2
3a) b)
c)(i) (ii)
Absorption / Diffusion / Active transport / Facilitated Diffusion Thin wall / Single cell // long / folded// many microvilli// a network of blood capillaries
1 1
1 1
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
269
d)(i)
F1 : no / less secretion lipase E1 : no / incomplete lipid digestion F2 : no / less secretion amylase E2 : no / less starch digestion F3 : no / less secretion trypsin E3 : no / less protein digestion F4 : No insulin released E4 : the blood glucose level high F5 : No glucagon released E5 : the blood glucose level low (Any 4F and 4E)
Any 4
(ii)
1. Avoid / Reduce the intake of oily food 2. Avoid / Reduce the intake of carbohydrates /sugar 3. Reduce the intake of protein 4. Injections of insulin 5. Pancreas implantation Q : Mitochondria R : Golgi body/apparatus Function of Q: to generate energy / sites of cellular respiration -Has ribosomes embedded on its surface -synthesizes and transports protein made by ribosomes To get rid of stains on clothes: F1- biological detergents contain proteases, amylases and lipases P1- proteases acts on stains containing proteins / blood / saliva P2- amylases acts on stains containing starch / sauces / ice cream/gravy P3- lipases are effective in removing oil and grease (F1 & any P1/P2/P3) Helping to tenderize meat: F1 Protease acts on protein in meat P1 tenderize / softens meat - lock and key hypothesis. - The substrate is the key that fits into the enzyme lock - The substrate molecule fits into the active site of the enzyme molecule. - forms the enzyme-substrate complex. - the enzyme changes the substrate to its product. - The product leaves the active site. - The enzyme is not altered by the reaction and it can be reused.
4a)
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Max 2 Total 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 12 2 1 2
b)(i) (ii) c)(i)
1 1 1 1 1
2 2
(ii)
d)
Any 1 Total
3 12
270
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
5(a)
Pain receptor
(b)
3 neurones 2 m 2 neurones - 1 m c) P1 - When an impulses arrives in the axon terminal P2- it stimulates (synaptic) vesicles to move towards and bind with the presynaptic membrane P3 -The vesicles fuse / release the neurotransmitter into the synapse P4 -The neurotransmitter molecules move across the synapse to the dendrite of another neurone P5 -Stimulated to trigger a new impulses which travels along the neurone M : Sensory receptor // finger tip N : Effector // muscles tissues 1. Accomodation of the eye 2. Production of saliva 1. The nerve impulse will not be sent from afferent neurone to the effector 2. The effector / muscles will not contract 3. The hand will not be removed immediately from the needle.
Max 4 1 1 1 1
4 2 2
d) e) f)
(Any one )
1 Total Total Marks
1 12 60
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
271
Section B
6(a) Pl- Tendons, ligaments, bones, muscles and joints are important features in a movement, P2- Tendons connect muscles to bones P3- Tendons are strong and non elastic P4- Force is transferred to bones through tendons. P5- Movement at the joint is possible with the aid of ligaments. P6- Ligaments connect two bones together P7- to give support and strength to the joint. P8- Ligaments are strong and elastic. P9- The quadriceps / extensor muscles contract while the biceps femoris muscles relax and the leg is straightened. P10- The biceps femoris muscles contract while the quadriceps / extensor muscles relax and the leg is bent. P11- Calf muscles contract to lift up the heels. P12- Feet push downward and backward P13- Repeated contraction and relaxation of muscles result in the running movement. Non-woody plants (herbaceous plants) Example: Balsam plant/ any suitable answer P1: (Support in herbaceous plants is) provided by the turgidity of the parenchyma / collenchyma cells P2: (When there is enough water in the ground). the cells take in water by osmosis and become turgid. P3: The turgor pressure of the fluids in the vacuoles pushes the cell contents / plasma membrane against the cell wall P4: creating support for it stem/ roots /leaves P5: The thin thickening die cell walls with cellulose / collenchyma cells gives support to herbaceous plants Woody plants : Example : Rambutan tree/ hibiscus/ any suitable example P6: Woody plants have specialised tissues/sclerenchyma tissues/xylem vessels/ tracheids to give them support; P7: These tissues have cellulose walls which have deposits of lignin for added strength. P8: Sclerenchyma cells have very thick walls (which do not allow water to pass through). P9: (These cells are dead cells and) their function is to provide support for the plant. P10: Xylem vessels have thick walls of lignin which are deposited during the plants secondary growth. P11: The lignified xylem vessels form the woody tissues of the stem. P12: This makes the plant stronger and also provides support for the plant. P13: Tracheids are also dead cells with thick walls and very small diameters. P14: They are found with the xylem vessels and together they support the plants.
MAX = 10 marks 1
10
b)
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Any 4 1
Any 4 MAX = 10 marks Total
10 20
272
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
7a)(i) F: Siamese twin P1: One sperm and one ovum are involve in fertilization P2: to produce one/single zygote P3: zygote undergoes mitosis repeatedly to form blastocyst P4: blastocyst does not divide completely P5: The two blastocyst implant/embedded into endometrium wall and develop to embryo) P6: they are joined at certain part of the body (F with any 5P) (ii) F: Downss Syndrome P1: due to the failure of the two homologous chromosome number 21 to separate normally P2: during anaphase 1/meiosis 1 P3: produce a gamete with a pair of homologous chromosome number 21 P4: when above gamete fuse/fertilized with the normal gametes it produces a zygote with a three chromosome number 21. (F with any 3P) Genetic factors F1: Crossing over during prophase 1/meiosis 1 P1:occur between chromatid from a pair of homologous chromosomes P2: the exchange of parts between chromatid results in new genetic combination. P3: produced a large number of gametes with different genetic composition. F2: independent assortment P4:homologous part of chromosome are arranged randomly on metaphase plate/ during metaphase 1 P5: during anaphase 1, each homologous pair of chromosomes separate. P6:resulting in an independent assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes into daughter cells F3: Random fertilization P7: sperms and ovum with a variety of combinations of chromosomes/genetically different are randomly fertilized. P8: Thus, variation exists between individuals from the same species//zygote produces will have a variety of diploid combination. P9:mutation causes permanent change in the genetic composition /genotype of an organism F4: Mutation Environmental factor F1: (can cause variation among individuals at same species) by interacting with genetic factor. P: examples of factors; at least 2 types - food/exercise/skill/ experience/education/ sunlight/climatic Any 9 from genetic factor And any 1 from environment factors
Any 5 1
Any 3
b)
Max = 9 1
Total
10 20
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
273
8a)(i) -Greenhouse effect. -Greenhouse effect happens as carbon dioxide is released to the atmosphere due to forest burning, emission from vehicles, factory and will form a layer of gas. - Deforestation also increases carbon dioxide - Glass building reflect heat -The layer of carbon dioxide which is denser than air, prevents heat that is reflected to the earth to be released. -The reflected heat will continue to increase the temperature of the Earth. (ii) Ways to minimise: 1. The use of technology to reduce pollution and destruction of nature, Eg; the smoke chimney is raised and there is a filter to decrease the release of pollutants to the atmosphere, catalytic filters, etc 2. Use alternative renewable sources of energy eg; wind, solar 3. Reforestation 4. Discourage open burning 5. Encourage planting of trees//Green the world campaign 6. Environmental education with emphasis on 4R concept: Reduce, Recycle, Reuse and Renew. Negative/bad effects 1. Expose soil to soil erosion// loss of nutrients//loss of water catchment area 2. Cause increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide 3. Deforestation causes the removal and thinning of the soil layer due to exposure to wind and air. 4. The bottom of river is silted by eroded soil. 5. Landslide occurs as the top layer of soil crumbles. 6. Loss of habitats. 7. Loss of thousand species of flora and fauna due to the loss of habitats. Positive/good effects 1. Increases job opportunities among villagers. 2. Improves the infrastructure such as new roads. 3. Increases the economic level of the villagers by selling logs. 4. For building of houses for villagers
1 1 1 1 1 1 6
Any 4
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
(b)
Any 10 Total
10 20
274
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
9a)
F: Production of gastric juice/pepsin/rennin decrease. P1: Digestion of protein become slow/decrease P2: Coagulation of milk protein by rennin decrease. P3: Unable to provide acidic medium for enzyme reaction//bacteria cannot be destroyed.
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(b)(i) F1: Chronic heart disease P1: Her diet contains large amounts of oil/cream/fat and it causes arteriosclerosis / heart problem / cardiovascular disease. F2: Constipation. P2: Lack of fruit/vegetables / fibers leads to constipation (ii) P1: Drink scheme milk/low fat milk and eat a boiled egg to reduce the cream and fat from her diet P2: Replace sausage with an orange to increase her fruit fibre intake Lunch: P3: Drink fresh fruit juice because it has lower sugar content/more vitamins P4: Eat steamed rice/steamed chicken to lower cholesterol intake P5: Eat vegetable/salad to increase the amount of roughage Dinner: P6: Drink clear soup to reduce the cholesterol P7: Use tomato sauce with her pasta because it contains less fat and more fibers. P8: Eat a slice of watermelon/any fruits to increase her intake of fiber to prevent constipation (c) Genetic engineering P1: Transfer the beneficial genes from one organism to another organism. P2: Obtain/produces genetic modified organism/transgenic organism P3: crop yield/animal contain gene that able to enhance growth/ nutritional properties/resistance against disease. Tissue Culture P4: tissue/cell of parent plant are grown in culture medium. P5: daughter plant is called clone. P6: Produce many clone in a short time/produce large fruit/maintain good characteristic of parent plant
Any 6 1 1 1
1 1 1 Total
6 20
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
275
Biology Paper 3(4551/3)
No. 1(a) Mark Scheme Able to record all 5 readings for the distance traveled by air bubble correctly Sample answers Fan speed 0 1 2 3 4 Distance traveled by air bubble (cm) 1.1 2.2 4.0 6.5 9.0 Score
Able to record all 4 readings for the distance traveled by air bubble correctly Able to record all 3 readings for the distance traveled by air bubble correctly No response or incorrect response No. 1 (b)(i)
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
2 1 0 Score
Mark Scheme Able to state two different observations correctly. Sample answers 1. At the fan speed of 0, the distance traveled by air bubble is 1.1 cm 2. At the fan speed of 4, the distance traveled by air bubble is 9.0 cm Able to state one observation correctly and one inaccurate observation Sample answers 1. At the fan speed of 0, the distance traveled by air bubble is short. 2. At the fan speed of 4, the distance traveled by air bubble is long. Able to state one observation correctly and one observation at idea level Sample answer 1. The distance traveled by air bubble changes / increases / decreases 2. As the fan speed increases, the distance traveled by air bubble increases No response or incorrect response
1 0 Score 3
No. 1 (b)(ii)
Mark Scheme Able to make two inferences correctly. (Sample answers) 1. At the fan speed of 0, the air movement is slow, thus the plant loses loses less water. 2. At the fan speed of 4, the air movement is high/fast, thus the plant loses a lot of water. Able to make one inferences correctly and one two inaccurate inferences (Sample answers) 1. The short distance traveled by air bubble shows a low air movement. 2. The long distance traveled by air bubble shows a high . Able to state one inferences correctly and one two inferences at idea level (Sample answer) 1. Transpiration occurs at the shoot 1. Light intensity increases as distance from light source decreases. No response or incorrect response
276
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
No. (c)
Mark Scheme Able to state all 3 variables and the 3 methods to handle the variable Sample answers Variable Manipulated variable Fan speed//air movement Responding variable Distance traveled by air bubble// Rate of transpiration Constant variable Light intensity// temperature// humidity of the surrounding // Type of plant Method to handle the variable Carry out the experiment at different fan speed Measure and record the distance traveled by air bubble by using a ruler // Calculate the rate of transpiration by using the formula : Distance traveled by air bubble Time Fix the light intensity of the surrounding/ Fix the temperature at room temperature/ Fix the air humidity to be the same throughout the experiment // Use the same type of plant
Score 3
Able to state 4-5 variables and methods to handle the variable correctly Able to state 2-3 variables and methods to handle the variable correctly No response or incorrect response No. 1 (d)
2 1 0
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Mark Scheme Score Able to make a hypothesis relating the manipulated variable and the responding variable correctly. 3 Sample answer The higher the air movement, the longer the distance traveled by the air bubble// The higher the air movement, the higher the rate of transpiration// inversely Able to make a hypothesis relating the manipulated variable and the responding variable incorrectly. Sample answer The rate of transpiration is affected by air movement. Able to make a hypothesis relating the manipulated variable and the responding variable at idea level. Sample answer Air movement causes transpiration. No response or incorrect response 2
0 Score 3
No. Mark Scheme 1 (e)(i) Able to construct a table correctly according with following aspect. 1. Able to state the 3 titles with units 1 mark 2. Able to record all the data correctly 1 mark 3. Able to calculate and record fan speed and rate of transpiration correctly 1 mark
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
277
No.
Mark Scheme Sample answer Fan speed Distance traveled by air bubble (cm) 0 1.1 1 2.2 2 4.0 3 6.5 4 9.0 Any two correct. Any one correct No response or incorrect response Transpiration rate (cm min-1) 0.22 0.44 0.80 1.30 1.80
Score
2 1 0 Score 3
No. 1 (e)(ii)
Mark Scheme Able to draw graph correctly according with following aspect. P : Correct title with unit on both horizontal and vertical axis 1 mark T : All points plotted correctly 1 mark B : Able to join all points to form a smooth graph 1 mark Any two correct. Any one correct No response or incorrect response
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
2 1 0
No. 1 (f)
Mark Scheme Score Able to interpret data and explain with the following aspect : 3 1. Able to state the relationship between rate of transpiration and air movement 2. Able to relate fan speed to air movement 3. Able to relate to rate of evaporation. Sample answer The higher the air movement, the higher the rate of transpiration. A higher fan speed means higher air movement. At a higher air movement, the rate of evaporation is high. Hence the loss of water from the plant is high. Able to interpret data and with 2 aspects. Able to interpret data and with 1 aspect. No response or incorrect response 2 1 0 Score 3
No. 1 (g)
Mark Scheme Able to define operationally rate of transpiration based on the result of the experiment. 1. Distance traveled by air bubble 2. At different fan speed 3. Factor affecting it. Sample answer The rate of transpiration is the distance traveled by an air bubble and is affected by different fan speed which means different air movement. Able to interpret data and with 2 aspects. Able to interpret data and with 1 aspect. No response or incorrect response
2 1 0
278
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
No. 1(h)
Mark Scheme Able to predict the outcome of the experiment correctly. 1. Correct prediction 2. Reason 3. Effect Sample answer The rate of transpiration increases, that is the distance traveled by the air bubble is more than 1.1 cm and the rate of transpiration is more than 0.22 cm min-1 because there is an increase in light intensity. A higher light intensity increases the rate of evaporation of water vapour that accumulates at the stomata of the leaves. Hence more water is lost at a faster rate from the leaves. Able to interpret data and with 2 aspects. Able to interpret data and with 1 aspect. No response or incorrect response
Score 3
2 1 0 Score 3
No.
Mark Scheme Able to classify all the factors that can affect the rate of transpiration into environment factors and structural factors correctly. Sample answer Environment factors Light intensity Air humidity Temperature Able to classify 4 factors in the inaccurately. Able to classify 3 factors at the idea level. No response or incorrect response
2 1 0
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Structural factors Number of stomata on the leaf Distribution of stomata on the leaf Size of leaf
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
279
Aspect Identifying Problem Statement
Criteria Able to write a problem statement correctly base on 3 criteria: Manipulated variables- (Volume of water intake) Responding variables- (Volume of urine released) Relationship. Sample Answer 1. How does the volume of water intake affect the volume of urine released? 2. What is the effect of volume of water intake on the volume of urine released? Able to write a problem statement but less correctly base on 2 criteria. Able to give an idea about the problem statement base on 1 criterion. Wrong or no response
Score 3
2 1 0 Score
Aspect Objective /Aim
Criteria Able to state the objective of the experiment correctly Sample Answer To determine the effect of drinking different volume of water on the volume of urine released. Criteria Able to identify all the three variables correctly Sample Answer Manipulated variable : volume of water intake Responding variable : volume of urine released Fixed variable : same student/same environment/ time Criteria Able to write a suitable hypothesis correctly base on the 3 criteria: Manipulated variable Responding variable Relationship Sample Answer 1. The higher the volume of water intake, the higher the volume of urine released. 2. As the volume of water intake increases, the volume of urine released increases. Able to write a hypothesis but less correctly base on the 2 criteria. Able to give an idea about the problem statement base on 1 criterion. No response
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Aspect Variables
Score
Aspect Making hypothesis
Score 3
2 1 0
280
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
Aspect
Criteria Able to list all materials and apparatus needed to carry out the experiment successfully.
Score 4A + 2M 3
Materials Sample Answer and Materials : Boy/girl/student, water Apparatus (M) Apparatus : Beakers, glass/cup/mug, measuring cylinder (A) stop watch Able to list some materials and apparatus needed to carry out the experiment successfully Able to list some materials and apparatus needed to carry out the experiment successfully Incomplete list or wrong or no response Aspect Technique Criteria Able to state the technique used in carrying out the experiment correctly Sample Answer Measure and record the volume of urine released (after a fixed hour of consuming water) by using a measuring cylinder. Criteria Able to write all the steps in carrying out the experiment successfully. K1 : Steps to set up the apparatus K2 : Steps to handle the fixed variable K3 : Steps to handle the manipulated variable K4 : Steps to handle the responding variable K5 : Precautionary steps / steps taken to get accurate results / readings Scoring Rubric All K1-K5 present Any 3 4K present Any 2K present 1K or wrong response [] is given for any 1K present.
2A + 2M 2 1A + 2M 1 0 Score B1 = 1
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Aspect Procedure
Score
3 2 1 0
SOALAN ULANGKAJI SPM 2010
281
K1 K3 K1 K1 K2 K5 K2 K1 K1/ K5 K5 K5 K4
1. 2. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 12 13 14
Procedure A student (Sample A) is chosen and instructed to empty his bladder before the start of the experiment Measure 200ml of water and put it into the mug/cup/glass A student (Sample A) is given 200ml of water to drink. A stop watch is started immediately after consuming the water. During the experiment, he is kept in (any fixed suitable room) within 2 hours (any suitable time range). He is instructed not to eat or perform any vigorous physical activities (within the given time). After 2 hour, the stop watch is stopped and he is asked to empty his bladder. The volume of urine collected is measured and recorded. Steps 2 8 is repeated for different amount of water drank (400 ml, 600ml, 800ml, 1000ml) The whole experiment is repeated using 2 different students to get a more accurate result. Dispose the measured urine properly Measure and record data collected into a table. Graph of urine output against the water intake is plotted. Criteria Able to draw a complete table to record the relevant data base on the 3 criteria: Volume of water intake Volume of urine released The units in ml or cm3 Sample Answer Volume of water intake (ml) 200 400 600 800 1000 Student A Volume of urine released (ml) Student B Student C Average
Score
5K = 3 m 3-4K = 2 m 1-2K = 1 m Score B2 =1
JAWAPAN BIOLOGY
Aspect Communicating data
Aspect Criteria Conclusion Able to write a suitable conclusion for the experiment: Sample Answer The higher the volume of water intake, the higher the volume of urine released. Hypothesis is accepted. Planning 7-9 ticks = 3m experiment 4-6 ticks = 2m 1-3 ticks = 1m
Score
Вам также может понравиться
- The Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyОт EverandThe Biochemistry of Development: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyОценок пока нет
- Skema Trial 2014 Batu PahatДокумент25 страницSkema Trial 2014 Batu PahatKavinesh GanesanОценок пока нет
- Osmotic and Ionic Regulation in Animals: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyОт EverandOsmotic and Ionic Regulation in Animals: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied BiologyОценок пока нет
- 4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018Документ15 страниц4551 Biologi Skema Pemarkahan 2018danialОценок пока нет
- Answers Biologi Kertas 1 Mid Year 2007Документ21 страницаAnswers Biologi Kertas 1 Mid Year 2007BtgPeiiYiingОценок пока нет
- 2008 Kedah SPM Biology AnsДокумент24 страницы2008 Kedah SPM Biology Ansjee2kkОценок пока нет
- Calcium Movement in Excitable Cells: Pergamon Studies in The Life SciencesОт EverandCalcium Movement in Excitable Cells: Pergamon Studies in The Life SciencesОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme P1 and P2 KedahДокумент20 страницMark Scheme P1 and P2 KedahRozaini OthmanОценок пока нет
- Answer Bio F4 Mid 2021Документ14 страницAnswer Bio F4 Mid 2021DHAARSHANAH A/P DHANABALAN MoeОценок пока нет
- Principles of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth SciencesОт EverandPrinciples of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth SciencesJohn W. NealeОценок пока нет
- Section A No. of Answer Mark Remark: EpidermisДокумент11 страницSection A No. of Answer Mark Remark: EpidermisFerguson TehОценок пока нет
- Principles of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth Sciences, Vol. 2От EverandPrinciples of Zoological Micropalaeontology: International Series of Monographs on Earth Sciences, Vol. 2Оценок пока нет
- IBO1998 PapersДокумент98 страницIBO1998 PapersNelson NelОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchemeДокумент29 страницTrial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchememarwaniОценок пока нет
- The Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyОт EverandThe Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyОценок пока нет
- Retest Answer Scheme BiologyДокумент7 страницRetest Answer Scheme Biologyg-16355677Оценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: The Biochemistry of PlantsОт EverandPhotosynthesis: The Biochemistry of PlantsM. D. HatchОценок пока нет
- SPM Trial 2010 Bio Ans (Pahang)Документ32 страницыSPM Trial 2010 Bio Ans (Pahang)SimPorОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchemeДокумент24 страницыTrial SPM SBP 2010 Biology Marking SchemeMr.D-SIM100% (6)
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERДокумент11 страницMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Perak 2007 BIOLOGY SPM PAPERhasimahazitОценок пока нет
- SPM Chemistry Trial 2009 MS SBPДокумент20 страницSPM Chemistry Trial 2009 MS SBPhttp://spmchem.blogspot.com/Оценок пока нет
- Jawapan Biolog I Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan An Tahun 2010Документ6 страницJawapan Biolog I Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan An Tahun 2010Nur Liyana ShafawiОценок пока нет
- Biology Ans (1) - MinДокумент2 страницыBiology Ans (1) - MinJoseph LeeОценок пока нет
- 2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W AnsДокумент93 страницы2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- SPM Bio Ans (Kedah)Документ24 страницыSPM Bio Ans (Kedah)SimPor100% (1)
- Skema Kertas 1&2 N9 2020Документ25 страницSkema Kertas 1&2 N9 2020Azween SabtuОценок пока нет
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Документ21 страницаMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarОценок пока нет
- Ans P2 Johor 2010Документ15 страницAns P2 Johor 2010Rozaini OthmanОценок пока нет
- JAM 2018 Biotechnology - BTДокумент15 страницJAM 2018 Biotechnology - BTSuman duttaОценок пока нет
- Biology Xii PB 1 MS Set AДокумент6 страницBiology Xii PB 1 MS Set Aanushree04361s.no5ishiftОценок пока нет
- Ans Chem 2010Документ9 страницAns Chem 2010benzz993Оценок пока нет
- Revisi Cepat PT3 Science KSSM Form 1, 2 & 3 (Answers)Документ14 страницRevisi Cepat PT3 Science KSSM Form 1, 2 & 3 (Answers)lea louisОценок пока нет
- Perfect Score Module 2018 Form 4 Answer SchemeДокумент32 страницыPerfect Score Module 2018 Form 4 Answer SchemevisvanithaОценок пока нет
- Skema f4Документ11 страницSkema f4HAMIRAH ABD HAMIDОценок пока нет
- Set 5 Q&aДокумент8 страницSet 5 Q&ayijieeОценок пока нет
- Bio PPT T4 2021 SkemaДокумент4 страницыBio PPT T4 2021 SkemaHaslinda SheikhОценок пока нет
- Melaka Marking Scheme Biology Paper 2 & 3Документ29 страницMelaka Marking Scheme Biology Paper 2 & 3smtsp0% (1)
- Skema Science PMR Kertas 1 Dan 2 2006Документ7 страницSkema Science PMR Kertas 1 Dan 2 2006Azim SufieОценок пока нет
- CSSC Ms Science 10 CSSC Set1Документ8 страницCSSC Ms Science 10 CSSC Set11770Оценок пока нет
- Ujian Mac 2020, Sains Tingkatan 5: Animal ProteinДокумент3 страницыUjian Mac 2020, Sains Tingkatan 5: Animal Proteinhuda186Оценок пока нет
- Radioactivity AnswersДокумент13 страницRadioactivity AnswersPavit SuphawirojlertОценок пока нет
- Biology-Set-3-Ms-3-Pb - 2023-24Документ4 страницыBiology-Set-3-Ms-3-Pb - 2023-24loxif49565Оценок пока нет
- Kunci Igcse Uas Bio: Answer Marks 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1Документ4 страницыKunci Igcse Uas Bio: Answer Marks 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1imeОценок пока нет
- Science Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09Документ6 страницScience Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09azmijaaffarОценок пока нет
- SPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta SkemaДокумент96 страницSPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta Skemahilmi72100% (1)
- GATE XL 2013 Exam Microbiology Solved Question Paper PDFДокумент5 страницGATE XL 2013 Exam Microbiology Solved Question Paper PDFMichael JeevaganОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY Question PaperДокумент2 страницыBIOLOGY Question PaperofficialsumankarmakarОценок пока нет
- New Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - eДокумент45 страницNew Senior Secondary MASTERING BIOLOGY OXFORD Mock - Bio - Set6 - eChun Kit LauОценок пока нет
- Barki Lahore Cantt 03085192560: Circle The Correct OneДокумент3 страницыBarki Lahore Cantt 03085192560: Circle The Correct OneAtique Ahmed RanaОценок пока нет
- G11 - Third Term Examination (2019) Answers - Department of Education, Western ProvinceДокумент8 страницG11 - Third Term Examination (2019) Answers - Department of Education, Western ProvinceXiao ShadowlordОценок пока нет
- Skema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Biologi PPT 2016, PPD Hulu SelangorДокумент15 страницSkema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Biologi PPT 2016, PPD Hulu SelangorFerguson TehОценок пока нет
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeДокумент18 страницTrial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeFain Sudais100% (1)
- Che SP 10Документ6 страницChe SP 10saapldesign1 1Оценок пока нет
- STPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: SulitДокумент14 страницSTPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: Sulitrevathy varatharajahОценок пока нет
- Bio-1 1ST QTR PDFДокумент2 страницыBio-1 1ST QTR PDFJunaid Ahmed MuazzamОценок пока нет