Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ielts: International English Language
Загружено:
Sai PrasadИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ielts: International English Language
Загружено:
Sai PrasadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
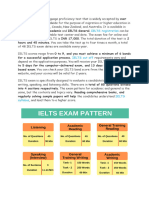
IELTS
OR 'INTERNATIONAL ENGLISH LANGUAGE TESTING SYSTEM',
Is an international standardised test of English language proficiency. It is jointly managed by University of Cambridge ESOL Examinations, the British Council and IDP Education Pty Ltd, and was established in 1989. There are two versions of the IELTS: the Academic Version and the General Training Version:
The
Academic Version is intended for those who want to enrol in universities and other institutions of higher education and for professionals such as medical doctors and nurses who want to study or practice in an English-speaking country. The General Training Version is intended for those planning to undertake nonacademic training or to gain work experience, or for immigration purposes. IELTS is accepted by most Australian, British, Canadian, Irish, New Zealand and South African academic institutions, over 3,000 academic institutions in the United States, and various professional organisations. It is also a requirement for immigration to Australia, New Zealand and Canada. No minimum score is required to pass the test. An IELTS result or Test Report Form is issued to all candidates with a score from 1 (no knowledge) to 9 (expert user) and each institution sets a different threshold. Institutions are advised not to consider valid a report older than two years, unless the user proves that he has worked to maintain his level.
IELTS characteristics The IELTS incorporates the following features:
variety of accents and writing styles have presented in text materials in order to minimise linguistic bias. IELTS tests the ability to listen, read, write and speak in English. Band scores used for each language subskill (Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking). The Band Scale ranges from 0 ("Did not attempt the test") to 9 ("Expert User"). The speaking module - a key component of IELTS. This is conducted in the form of a one-to-one interview with an examiner. The examiner assesses the candidate as he or she is speaking, but the speaking session is also recorded for monitoring as well as remarking in case of an appeal against the banding given. IELTS is developed with input from item writers from around the world. Teams are located in the USA, Great Britain, Australia, New Zealand, Canada and other Englishspeaking nations.
IELTS test structure
All candidates must complete four Modules Listening, Reading, and Writing and Speaking - to obtain a band score, which is shown on the IELTS Test Report Form (TRF). All candidates take the same Listening and Speaking Modules, while the Reading and Writing Modules differ depending on whether the candidate is taking the Academic or General Training Versions of the Test. LISTENING The listening module comprises four sections. Each section begins with a short introduction telling the candidates about the situation and the speakers. They then have some time to look through the questions. The first three sections
have a break in the middle allowing candidates to look at the remaining questions. Each section is heard only once. READING In the academic module the reading test comprises three sections, with 3 texts normally followed by 13 or 14 questions for a total of 40 questions overall. The General test also has 3 sections. However the texts are shorter, so there can be up to 5 texts to read. WRITING This consists of two sections. First section is where all candidates need to describe a diagram and with the second section taking the form of an essay. SPEAKING The speaking test contains three sections. The first section takes the form of an interview during which candidates may be asked about their hobbies, interests, reasons for taking IELTS exam as well as other general topics such as clothing, free time, computers and the internet or family. In the second section candidates are given a topic card and then have one minute to prepare after which they must speak about the given topic. The third section involves a discussion between the examiner and the candidate, generally on questions relating to the theme which they have already spoken about in part 2.
DURATION
The total test duration is around 2 hours and 45 minutes for Listening, Reading and Writing modules. Listening: 40 minutes, 30 minutes for which a recording is played centrally and additional 10 minutes for transferring answers onto the OMR (Optical Mark Recognition) answer sheet. Reading: 60 minutes. Writing: 60 minutes. Speaking: 1014 minutes.
(N.B.: No additional time is given for transfer of answers in Reading and Writing modules) The first three modules - Listening, Reading and Writing (always in that order) - are completed in one day, and in fact are taken with no break in between. The Speaking Module may be taken, at the discretion of the test centre, in the period seven days before or after the other Modules. The tests are designed to cover the full range of ability from non-user to expert user.
BAND SCALE
IELTS is scored on a nine-band scale, with each band corresponding to a specified competence in English. Overall Band Scores are reported to the nearest half band. The following rounding convention applies: if the average across the four skills ends in .25, it is rounded up to the next half band, and if it ends in .75, it is rounded up to the next whole band. The nine bands are described as follows: A 6.5 IELTS score lies roughly between B2 and C1 levels of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages and >8 scores are C2.
Expert 9 User
Has full operational command of the language: appropriate, accurate and fluent with complete understanding.
Has full operational command of the language with only occasional unsystematic inaccuracies Very Good 8 and inappropriacies. Misunderstandings may User occur in unfamiliar situations. Handles complex detailed argumentation well. Has operational command of the language, though with occasional inaccuracies, inappropriateness and misunderstandings in 7Good User some situations. Generally handles complex language well and understands detailed reasoning. Has generally effective command of the language despite some inaccuracies, Competent 6 inappropriacies and misunderstandings. Can use User and understand fairly complex language, particularly in familiar situations. Has partial command of the language, coping with overall meaning in most situations, though is likely to make many mistakes. Should be able to handle basic communication in own field. Basic competence is limited to familiar situations. Has frequent problems in using complex language.
Modest user
Limited 4 User
Extremely Conveys and understands only general meaning 3 Limited in very familiar situations. User No real communication is possible except for the Intermitten most basic information using isolated words or 2 t User short formulae in familiar situations and to meet immediate needs.
Global test scores
Countries with highest averages
In 2007, the top five countries of residence with the highest average scores for the Academic Strand of the IELTS test were:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Germany Malaysia The Philippines Russia Hong Kong
Results by first language of candidate
The top 5 language-speaking (or nationality) groups that achieved the best results in 2007 for the Academic Strand of the IELTS test were:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Tagalog Spanish Malay Hindi Tamil
IELTS USE FOR IMMIGRATION PURPOSES
A number of Commonwealth countries use IELTS scores as a proof of prospective immigrants' competence in English.
Australia
Australia's immigration authorities have used IELTS to assess English proficiency of prospective migrants since May 1998, when this test replaced the access: test that had been previously used. Presently, to demonstrate the "proficient" level of English, applicants for Australias Independent Migrant visa (permanent residence) must either score at least 7 on each of
the modules of IELTS, or score at least "B" on Australia's Occupational English Test. One can receive a "partial credit" (fewer points on the point test that determines one's eligibility for the migrant's visa) for having merely a "competent" level of English, which requires scoring at least 6 on each of the modules of IELTS. Prospective migrants who are citizens of the majority-Englishspeaking countries (United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, the USA, or Republic of Ireland) may choose to automatically receive the credit for the "competent" level of English merely by virtue of their citizenship, without taking tests; however, if they desire to show the "proficient" level (e.g. in order to obtain a sufficiently high overall score on the migration point test) they still must take the IELTS or OET.
New Zealand
New Zealand has used the IELTS test since 1995. Initially, level 5 scores in each of the four modules were required of the prospective applicants; those who could not achieve required scores could pay a NZ$20,000 fee instead, which would be fully or partially refunded later if the migrant were able to successfully take the test within a certain period (3 to 12 months) after his or her arrival to the country. A few years later, the policy was changed: the fee was reduced, and, instead of being potentially refundable, it became treated as a "pre-purchase" of post-arrival ESL tuition. Presently, applicants desiring to achieve permanent residence in New Zealand via the "Entrepreneur Category" migration program must prove a "reasonable" level of competence in English. Unless the applicant has studied and/or work for a sufficiently long period in New Zealand or other English-speaking countries, this normally should be demonstrated by achieving the overall band of 6.5 on the IELTS.
Canada
Citizenship and Immigration Canada uses the results of IELTS and/or TEF as a conclusive evidence of one's ability to
communicate in English and/or French. For the purposes of the skill-based immigration points test, one receives separate points based on his or her performance on each of the four modules (reading, writing, speaking, and listening) or IELTS; the score of 6.5 on a particular IELTS module is sufficient to earn the maximum points for this particular capacity, except for the listening module, which requires the score of 7.5 to earn the maximum points.[19] The CELPIP (Canadian English Language Proficiency Index Program) test scores are mentioned by the Canadian immigration application forms as an alternative to IELTS.
United Kingdom
Under the UK's "Points Based System Tier 1" (General Migrant) programme, applicants can receive 10 points for their English language qualification if it is deemed "equivalent to the Council of Europe's Common European Framework for Language Learning level C1", which is said to approximately equivalent to IELTS level 6.5, or GCSE Grade C. Having had earned a university degree from an Englishmedium institution is an acceptable alternative proof of one's English level.
TOEFL
The Test of English as a Foreign Language, or TOEFL (pronounced /tofl/ TOH-fl), evaluates the ability of an individual to use and understand English in an academic setting. It sometimes is an admission requirement for nonnative English speakers at many Englishspeaking colleges and universities. Additionally, institutions such as government agencies, licensing bodies, businesses, or scholarship programs may require this test. A TOEFL score is valid for two years and then will no longer be officially
reported since a candidate's language proficiency could have significantly changed since the date of the test. Colleges and universities usually consider only the most recent TOEFL score. The TOEFL test is a registered trademark of Educational Testing Service (ETS) and is administered worldwide. Policies governing the TOEFL program are formulated with advice from a 16-member board. Board members are affiliated with undergraduate and graduate schools, 2-year institutions and public or private agencies with an interest in international education. Other members are specialists in the field of English as a foreign or second language. The TOEFL Committee of Examiners is composed of 12 specialists in linguistics, language testing, teaching or research. Its main responsibility is to advice on TOEFL test content. The committee helps ensure the test is a valid measure of English language proficiency reflecting current trends and methodologies.
Formats and contents Internet-based Test
Since its introduction in late 2005, the Internet-based Test (IBT) has progressively replaced both the computerbased tests (CBT) and paper-based tests (PBT), although paperbased testing is still used in select areas. The IBT has been introduced in phases, with the United States, Canada, France, Germany, and Italy in 2005 and the rest of the world in 2006, with test centres added regularly. The CBT was discontinued in September 2006 and these scores are no longer valid. Although initially, the demand for test seats was higher than availability, and candidates had to wait for months, it is now possible to take the test within one to four weeks in most countries. The four-hour test consists of four sections, each measuring one of the basic language skills (while some tasks require integrating multiple skills) and all tasks focus on language used in an academic, higher-education environment.
Note-taking is allowed during the IBT. The test cannot be taken more than once a week. 1. READING The Reading section consists of 35 passages, each approximately 700 words in length and questions about the passages. The passages are on academic topics; they are the kind of material that might be found in an undergraduate university textbook. Passages require understanding of rhetorical functions such as cause-effect, compare-contrast and argumentation. Students answer questions about main ideas, details, inferences, essential information, sentence insertion, vocabulary, rhetorical purpose and overall ideas. New types of questions in the IBT require filling out tables or completing summaries. Prior knowledge of the subject under discussion is not necessary to come to the correct answer.
2. LISTENING The Listening section consists of six passages 35 minutes in length and questions about the passages. These passages include two student conversations and four academic lectures or discussions. A conversation involves two speakers, a student and either a professor or a campus service provider. A lecture is a self-contained portion of an academic lecture, which may involve student participation and does not assume specialized background knowledge in the subject area. Each conversation and lecture stimulus is heard only once. Test-takers may take notes while they listen and they may refer to their notes when they answer the questions. Each conversation is associated with five questions and each lecture with six. The questions are meant to measure the ability to understand main ideas, important details, implications, relationships between ideas, organization of information, speaker purpose and speaker attitude.
3.
SPEAKING
The Speaking section consists of six tasks: two independent tasks and four integrated tasks. In the two independent tasks, test-takers answer opinion questions on familiar topics. They are evaluated on their ability to speak spontaneously and convey their ideas clearly and coherently. In two of the integrated tasks, test-takers read a short passage, listen to an academic course lecture or a conversation about campus life and answer a question by combining appropriate information from the text and the talk. In the two remaining integrated tasks, test-takers listen to an academic course lecture or a conversation about campus life and then respond to a question about what they heard. In the integrated tasks, test-takers are evaluated on their ability to appropriately synthesize and effectively convey information from the reading and listening material. Test-takers may take notes as they read and listen and may use their notes to help prepare their responses. Test-takers are given a short preparation time before they have to begin speaking. The responses are digitally recorded, sent to ETSs Online Scoring Network (OSN) and evaluated by three to six raters. 4. WRITING The Writing section measures a test taker's ability to write in an academic setting and consists of two tasks: one integrated task and one independent task. In the integrated task, test-takers read a passage on an academic topic and then listen to a speaker discuss the same topic. The test-taker will then write a summary about the important points in the listening passage and explain how these relate to the key points of the reading passage. In the independent task, test-takers must write an essay that states, explains, and supports their opinion on an issue, supporting their opinions or choices, rather than simply listing personal preferences or choices. Responses are sent to the ETS OSN and evaluated by four raters.
Task
Description
Approx. time
Readin 35 passages, each containing 12 60100 g 14 questions minutes Listeni 69 passages, each containing 56 6090 ng questions minutes Break Speaki 6 tasks and 6 questions ng Writin 2 tasks and 2 questions g 10 minutes
20 minutes
55 minutes
PAPER-BASED TEST
In areas where the internet-based test is not available, a paper-based test (PBT) is given. Test takers must register in advance either online or by using the registration form provided in the Supplemental Paper TOEFL Bulletin. They should register in advance of the given deadlines to ensure a place because the test centres have limited seating and may fill up early. Tests are administered on fixed dates 6 times each year. The test is 3 hours long and all test sections can be taken on the same day. Students can take the test as many times as they wish. However, colleges and universities usually consider only the most recent score.
1.
LISTENING (30 40 minutes)
The Listening section consists of 3 parts. The first one contains 30 questions about short conversations. The second part has 8 questions about longer conversations. The last part asks 12 questions about lectures or talks. 2. STRUCTURE AND WRITTEN EXPRESSION (25 minutes) The Structure and Written Expression section has 15 exercises of completing sentences correctly and 25 exercises of identifying errors. 3. READING COMPREHENSION (55 minutes) The Reading Comprehension section has 50 questions about reading passages. 4. WRITING (30 minutes) The Writing section is one essay with 250300 words in average.
TEST SCORES
Internet-based Test The IBT version of the TOEFL test is scored on a scale of 0 to 120 points. Each of the four sections (Reading, Listening, Speaking, and Writing) receives a scaled score from 0 to 30. The scaled scores from the four sections are added together to determine the total score. Each speaking question is initially given a score of 0 to 4, and each writing question is initially given a score of 0 to 5. These scores are converted to scaled scores of 0 to 30.
Paper-based Test The final PBT score ranges between 310 and 677 and is based on three sub scores: Listening (3168), Structure (31 68), and Reading (3167). Unlike the CBT, the score of the Writing section (referred to as the Test of Written English, TWE) is not part of the final score; instead, it is reported separately on a scale of 06.
The score test takers receive on the Listening, Structure and Reading parts of the TOEFL test is not the percentage of correct answers. The score is converted to take into account the fact that some tests are more difficult than others. The converted scores correct these differences. Therefore, the converted score is a more accurate reflection of the ability than the correct answer score is.
Accepted TOEFL Scores Most colleges use TOEFL scores as only one factor in their admission process. Each college or program within a college often has a minimum TOEFL score required. The minimum TOEFL IBT scores range from 61 (Bowling Green State University) to 109 (MIT, Columbia, Harvard). A sampling of required TOEFL admissions scores shows that a total TOEFL IBT score of 74.2 for undergraduate admissions and 82.6 for graduate admissions may be required. It is recommended that students check with their prospective institutions directly to understand TOEFL admissions requirements.
NOTE: Both IELTS & TOEFL scores are valid only for 2 years and it should not be expired before submitting application. Otherwise the test should be re-taken.
Вам также может понравиться
- System, Is An International Standardised Test of English LanguageДокумент12 страницSystem, Is An International Standardised Test of English Languagebanking51Оценок пока нет
- IELTS WikipediaДокумент6 страницIELTS Wikipedianicholas pritchardОценок пока нет
- IeltsДокумент10 страницIeltsDian HerianiОценок пока нет
- IeltsДокумент2 страницыIeltsmxiixmОценок пока нет
- IELTS Tips and Strategies Your Blueprint to Success a Complete Study GuideОт EverandIELTS Tips and Strategies Your Blueprint to Success a Complete Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Ielts Info April 2024Документ4 страницыIelts Info April 2024Lucy PondОценок пока нет
- Academic or General Training: Test Samples Official IELTS Practice MaterialsДокумент6 страницAcademic or General Training: Test Samples Official IELTS Practice Materialsmarck_cahiganОценок пока нет
- Ielts HandbookДокумент18 страницIelts HandbookRobertMcCaulОценок пока нет
- IELTS Handbook 2007Документ22 страницыIELTS Handbook 2007rampotayahОценок пока нет
- 19.05 IELTS HanbookДокумент28 страниц19.05 IELTS Hanbookrendyaryaduta04Оценок пока нет
- Ielts2003 HandbookДокумент17 страницIelts2003 HandbookHaider AliОценок пока нет
- What Is TOEFL?Документ6 страницWhat Is TOEFL?yuvarajsahОценок пока нет
- EPrepz IELTS GuideДокумент54 страницыEPrepz IELTS GuidePaulo CarneiroОценок пока нет
- Preparation For Ielts TestДокумент55 страницPreparation For Ielts TestOrdinary Human BeanОценок пока нет
- THE COMPLETE ACADEMIC IELTS GUIDE – ALL FOUR SKILLS / SELF STUDY©От EverandTHE COMPLETE ACADEMIC IELTS GUIDE – ALL FOUR SKILLS / SELF STUDY©Оценок пока нет
- Helping You Get Ready For Test DayДокумент22 страницыHelping You Get Ready For Test DayJavi SierraОценок пока нет
- Ielts Support Tools 0915.originalДокумент22 страницыIelts Support Tools 0915.originalmahabubОценок пока нет
- Score Pattern For IeltsДокумент3 страницыScore Pattern For IeltstzastrianaОценок пока нет
- Ielts: International English Language Testing SystemДокумент8 страницIelts: International English Language Testing Systemyesh_tiwariОценок пока нет
- IELTS Coaching in MohaliДокумент5 страницIELTS Coaching in MohaliDolphinHeadHunterОценок пока нет
- International English Language Testing System: IELTS - Test Takers - Academic or General Training?Документ9 страницInternational English Language Testing System: IELTS - Test Takers - Academic or General Training?Loga NathanОценок пока нет
- IELTS (Pronounced / Aɪ - Ɛlts/), or 'International English LanguageДокумент28 страницIELTS (Pronounced / Aɪ - Ɛlts/), or 'International English LanguagesunmiskinОценок пока нет
- Information For CandidatesДокумент8 страницInformation For CandidatesNatsukiОценок пока нет
- How To Improve Your English Proficiency - CD - 161023Документ10 страницHow To Improve Your English Proficiency - CD - 161023Maher AlyОценок пока нет
- Ielts Course OutlineДокумент4 страницыIelts Course OutlineFatima RazzaqОценок пока нет
- IELTS - Complete GuideДокумент11 страницIELTS - Complete GuideAkash Acky Arya100% (1)
- IELTS Handbook PDFДокумент22 страницыIELTS Handbook PDFLimaRomskaОценок пока нет
- IELTS Speaking Made Easy: Techniques for Univeristy Graduates, Professionals, and ESL StudentsОт EverandIELTS Speaking Made Easy: Techniques for Univeristy Graduates, Professionals, and ESL StudentsОценок пока нет
- IELTS VersionДокумент2 страницыIELTS VersionJohanesTangdiОценок пока нет
- Resume IELTSДокумент2 страницыResume IELTSMelvina Larissa JanuarОценок пока нет
- Ielts IntroductionДокумент22 страницыIelts IntroductionBilbo BagginsОценок пока нет
- IELTS HandbookДокумент21 страницаIELTS HandbookAugustОценок пока нет
- Acting Well The IELTS ExamДокумент4 страницыActing Well The IELTS ExamMasoudОценок пока нет
- IELTS Handbook 2007Документ22 страницыIELTS Handbook 2007dulche21763Оценок пока нет
- IELTS High Score System: Learn How To Identify & Answer Every Question With A High Score!От EverandIELTS High Score System: Learn How To Identify & Answer Every Question With A High Score!Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Ielts 2013Документ8 страницIelts 2013SuperSubbu2010Оценок пока нет
- Information For Candidates Booklet 2010Документ8 страницInformation For Candidates Booklet 2010Boom EnriquezОценок пока нет
- What Is TOEICДокумент3 страницыWhat Is TOEICInsaf.mgassebОценок пока нет
- Ielts Exam: What Is IELTS and Who Conducts IELTS?Документ4 страницыIelts Exam: What Is IELTS and Who Conducts IELTS?shubham tiwariОценок пока нет
- IELTS Speaking Section - Quick Guide To IELTS Speaking Success! (Written By An Experienced IELTS Teacher)От EverandIELTS Speaking Section - Quick Guide To IELTS Speaking Success! (Written By An Experienced IELTS Teacher)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (9)
- IeltsДокумент2 страницыIeltschickribersОценок пока нет
- Teaching IELTS For Positive ResultsДокумент15 страницTeaching IELTS For Positive Resultsmichaelfoy1Оценок пока нет
- Ielts Exam: 1-What Is IELTS Exam?, Purpose and Scope. What Are The Benefits?Документ7 страницIelts Exam: 1-What Is IELTS Exam?, Purpose and Scope. What Are The Benefits?question questionОценок пока нет
- Mastering IELTS: A Practical Approach for Non-Native SpeakersОт EverandMastering IELTS: A Practical Approach for Non-Native SpeakersОценок пока нет
- Ielts GuideДокумент22 страницыIelts GuideVishnu Lal100% (3)
- PTE Guide L3 PDFДокумент48 страницPTE Guide L3 PDFFran GRОценок пока нет
- Test ReviewДокумент12 страницTest Reviewapi-423339155Оценок пока нет
- IELTS Info CompendiumДокумент21 страницаIELTS Info Compendiumdd.tsi.krОценок пока нет
- Get Ready For IELTS Reading Pre-Intermediate A2 (RED) PDFДокумент136 страницGet Ready For IELTS Reading Pre-Intermediate A2 (RED) PDFKẹo Bông100% (13)
- PTEG GuideL4Документ46 страницPTEG GuideL4scofield03Оценок пока нет
- Information For Candidates: Introducing IELTS To Test TakersДокумент9 страницInformation For Candidates: Introducing IELTS To Test TakersClaudio Bautista AguilarОценок пока нет
- Information For Candidates: Introducing IELTS To Test TakersДокумент8 страницInformation For Candidates: Introducing IELTS To Test TakersMirsamidОценок пока нет
- IELTS Preparation Course in AdelaideДокумент3 страницыIELTS Preparation Course in AdelaideUnicorn Academy AustraliaОценок пока нет
- IELTS - OverviewДокумент1 страницаIELTS - OverviewPakaims ChakwalОценок пока нет
- About IELTSДокумент2 страницыAbout IELTSRaghavendra charyОценок пока нет
- IELTS Mastery: The Ultimate Guide to Scoring High on the International English Language Testing SystemОт EverandIELTS Mastery: The Ultimate Guide to Scoring High on the International English Language Testing SystemОценок пока нет
- IELTS Listening: How to improve your IELTS band score: How to Improve your IELTS Test bandscoresОт EverandIELTS Listening: How to improve your IELTS band score: How to Improve your IELTS Test bandscoresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Project Ielts BookДокумент10 страницProject Ielts BookBhishan officialОценок пока нет
- Mastering the TOEFL: A Complete Guide for Non-Native English SpeakersОт EverandMastering the TOEFL: A Complete Guide for Non-Native English SpeakersОценок пока нет
- IELTS Speaking - How to improve your bandscore: How to Improve your IELTS Test bandscoresОт EverandIELTS Speaking - How to improve your bandscore: How to Improve your IELTS Test bandscoresОценок пока нет
- Expressions of Quantity Countable and Uncountable NounsДокумент19 страницExpressions of Quantity Countable and Uncountable Nounsanon_182037896Оценок пока нет
- Language Hub Advanced Syllabus 120 HrsДокумент13 страницLanguage Hub Advanced Syllabus 120 HrsMustafaОценок пока нет
- Tsuki Ga Michibiku Isekai Douchuu - Vol 07Документ187 страницTsuki Ga Michibiku Isekai Douchuu - Vol 07Paula AlencarОценок пока нет
- 0580 w18 Ms 21 PDFДокумент5 страниц0580 w18 Ms 21 PDFHilmar AlfianОценок пока нет
- European Standard EN 1530-2: 2002 Has The Status of A DIN StandardДокумент100 страницEuropean Standard EN 1530-2: 2002 Has The Status of A DIN StandardAslan100% (1)
- Reviewer Rizal WorksДокумент6 страницReviewer Rizal WorksDianeОценок пока нет
- Object Oriented Modeling and Decision SupportДокумент23 страницыObject Oriented Modeling and Decision SupportUm SitthaОценок пока нет
- To The Top 2 Test 2 PDFДокумент4 страницыTo The Top 2 Test 2 PDFÁgi Szabó86% (7)
- Numerical PythonДокумент116 страницNumerical Pythonoundhakar100% (1)
- Direct Speech - Punctuation PracticeДокумент5 страницDirect Speech - Punctuation PracticeRachel AlexОценок пока нет
- A Summary of The Nature of Philosophical InquiryA Summary of Robert JohannДокумент3 страницыA Summary of The Nature of Philosophical InquiryA Summary of Robert JohannJemar TapilotОценок пока нет
- Culture and International BusinessДокумент36 страницCulture and International BusinesskboadОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Practice QuestionsДокумент6 страницEnglish Grammar Practice QuestionsZnabu MehariОценок пока нет
- Federated Group PDF Free Download Barron S New Sat Flash Cards 3rd Edition 500 Flash Cards To Help You Achieve AДокумент3 страницыFederated Group PDF Free Download Barron S New Sat Flash Cards 3rd Edition 500 Flash Cards To Help You Achieve AHabib T0% (1)
- The Coinage of Lydia and Persia, From The Earliest Times To The Fall of The Dynasty of The Achaemenidae / by Barclay V. HeadДокумент67 страницThe Coinage of Lydia and Persia, From The Earliest Times To The Fall of The Dynasty of The Achaemenidae / by Barclay V. HeadDigital Library Numis (DLN)Оценок пока нет
- Eric BirlingДокумент5 страницEric BirlingalexiamanlapazОценок пока нет
- The Grammar Gameshow: BBC Learning EnglishДокумент4 страницыThe Grammar Gameshow: BBC Learning EnglishuncorreopararegistroОценок пока нет
- Macro and Micro Lesson Planning - ESL Library BlogДокумент6 страницMacro and Micro Lesson Planning - ESL Library Blogsubhas9804009247100% (1)
- Old FrisianДокумент10 страницOld FrisianBengisu SakaryaОценок пока нет
- Empower Unit Overview A22Документ4 страницыEmpower Unit Overview A22Ilkin RəsulzadəОценок пока нет
- Facultad de Ciencias de La Salud: Escuela Profesional de EnfermeríaДокумент3 страницыFacultad de Ciencias de La Salud: Escuela Profesional de EnfermeríaMirian CubasОценок пока нет
- MINGGU 5 (29-31 JANUARI 2014) Isnin 29 JAN 2014 Perkara Rancangan PengajaranДокумент5 страницMINGGU 5 (29-31 JANUARI 2014) Isnin 29 JAN 2014 Perkara Rancangan PengajaranAzad Iqram NadmilailОценок пока нет
- Libro Libre 2nd Edition July 2021 UpdateДокумент415 страницLibro Libre 2nd Edition July 2021 UpdateAmalia Cantisan-KostersОценок пока нет
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Informal CommunicationДокумент4 страницыAdvantages and Disadvantages of Informal Communicationmisael gizacheОценок пока нет
- The Battle of Maldon 991Документ6 страницThe Battle of Maldon 991Александра ГринОценок пока нет
- A New Translation of Kjolmen Inscription First EditionДокумент16 страницA New Translation of Kjolmen Inscription First EditionGeorgi MishevОценок пока нет
- InglesprimariaДокумент762 страницыInglesprimariaelenaОценок пока нет
- DevOps - Q Ans AДокумент76 страницDevOps - Q Ans AVijay BalanОценок пока нет
- 7 Phrasal Verbs For Everyday LifeДокумент12 страниц7 Phrasal Verbs For Everyday LifeAira Frances BagacinaОценок пока нет
- 15 Jill Mowbray-JSAA2013Документ12 страниц15 Jill Mowbray-JSAA2013Александра ПалагинаОценок пока нет