Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
U 340
Загружено:
yosergeyИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
U 340
Загружено:
yosergeyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH-16
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General
The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure Control (See page CH-21) Shift Control in Uphill/Downhill Traveling (See page CH-22) Shift Timing Control Flex Lock-up Clutch Control (See page CH-23) Lock-up Timing Control Engine Torque Control N to D Squat Control Diagnosis (See page CH-24) Fail-Safe (See page CH-24) Function D Controls the pressure that is applied directly to B1 brake and C1 clutch by actuating the solenoid valves (ST, SLT) in accordance with the ECM signals. D The solenoid valve SLT minutely controls the clutch pressure in accordance with the engine output and driving conditions. Actuates the solenoid valve SLT to control the line pressure in accordance with information from the ECM and the operating conditions of the transaxle.
Controls to restrict the 4th upshift or to provide appropriate engine braking by using the ECM to determine whether the vehicle is traveling on uphill or downhill. The ECM sends current to the solenoid valve S1 and/or S2 based on signals from each sensor and shifts the gear. Controls the solenoid valve SLU, provides an intermediate mode between the ON/OFF operation of the lock-up clutch, and increases the operating range of the lock-up clutch to ensure fuel economy. The ECM sends current to the solenoid valve SLU based on the signals from each sensor and engages or disengages the lock-up clutch. Temporarily retards the engine ignition timing to restrict the output torque, thus ensuring the shift feel during up or down shifting. When the shift lever is shifted from the N to D position, the gear is temporarily shifted to the 3rd and then to the 1st to reduce vehicle squat. When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. Even if a malfunction is detected in the sensors or solenoids, the ECM effects fail-safe control to prevent the vehicles drivability from being affected significantly.
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-17
2. Construction
The configuration of the electronic control system in the U340E automatic transaxle is as show in the following chart. SENSORS MASS AIR FLOW METER
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
ACTUATORS VG NE S2 VTA1 SOLENOID VALVE S2 S1 SOLENOID VALVE S1
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
VTA2 VPA VPA2 THW SLT SOLENOID VALVE SLT
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH SHIFT LOCK ECU SPEED SENSOR NT ATF TEMPERATURE SENSOR STOP LIGHT SWITCH COMBINATION METER D Vehicle Speed Signal
ST
SOLENOID VALVE ST
P, R, N D, 2, L 3 NT THO1 STP SPD IGT1 X IGT4 IGF SPARK PLUGS ESA IGNITON COIL with IGNATER ECM SLU SOLENOID VALVE SLU
CAN H, CAN L SKID CONTROL ECU* COMBINATION METER SPEED SENSOR* DLC3 TC
00SCH78Y
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
*: Models with ABS System
CH-18
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
3. Layout of Main Components
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Stop Light Switch
ECM
Ignition Switch D Key Interlock Solenoid DLC3
Shift Lock ECU D P Detection Switch D 3 Range Position Switch
Solenoid Valve SLU
Speed Sensor NT Solenoid Valve SLT ATF Temperature Sensor Solenoid Valve S2 Solenoid Valve S1 Solenoid Valve ST
00RCH01Y
Park/Neutral Position Switch
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-19
4. Construction and Operation of Main Components
ATF Temperature Sensor D The ATF temperature sensor is installed in the lower valve body for direct detection of the fluid temperature. D The ATF temperature sensor is used for correction of clutch and brake pressures to keep smooth shift quality every time.
Lower Valve Body
ATF Temperature Sensor
247CH24
Speed Sensor NT The speed sensor NT detects the input speed of the transaxle. The forward clutch (C1) drum is used as the timing rotor for this sensor. Thus, the ECM can detect shift timing of the gears and appropriately control the engine torque and hydraulic pressure in response to the various conditions.
Speed Sensor NT
216CH12
Speed Sensor NT
CH-20
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
5. Clutch Pressure Control
Clutch to Clutch Pressure Control This control is used for shifting from the 3rd to 4th gear, and from the 4th to 3rd gear. It actuates solenoid valves ST and SLT in accordance with the signals from the ECM, and guides this output pressure directly to 4-3 shift timing valve and 3-4 shift timing valve in order to regulate the line pressure that acts on the B1 brake and C1 clutch. As a result, compact B1 and C1 accumulators without a back pressure chamber have been realized. Solenoid Valve SLT Accumulator Control Valve
3-4 Shift Valve
3-4 Shift Timing Valve
C1
4-3 Shift Timing Valve
Solenoid Valve ST B1
247CH25
Clutch Pressure Optimal Control The ECM monitors the signals from various types of sensors such as the speed sensor NT, allowing solenoid valve SLT to minutely control the clutch pressure in accordance with engine output and driving conditions. As a result, smooth shift characteristics have been realized.
Input Shaft Speed
Target rpm Change Ratio
Signals from Various Sensors Engine Speed Engine Torque Information ATF Temp.
Practical rpm Change Ratio
Time Engine
Speed Sensor NT SLT
Clutch/Brake Pressure Solenoid Drive Signal
Output Shaft Torque
Time
247CH26
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-21
6. Line Pressure Control
Through the use of the solenoid valve SLT, the line pressure is optimally controlled in accordance with the engine torque information, as well as with the internal operating conditions of the torque converter and the transaxle. Accordingly, the line pressure can be controlled minutely in accordance with the engine output, traveling condition, and the ATF temperature, thus realizing smooth shift characteristics and optimizing the workload in the oil pump.
Line Pressure
Throttle Valve Opening Intake Air Mass Engine Coolant Temp. Engine rpm Speed Sensor NT ATF Temp. Shift Position
Primary Regulator
Fluid Pressure
Solenoid Drive Signal
Current
Pump
Throttle Pressure Solenoid Valve SLT
232CH150
CH-22
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
7. Shift Control in Uphill/Downhill Traveling
General This control helps minimize the gear shifting when the driver operates the accelerator pedal while driving on a winding uphill or downhill road in order to ensure a smooth drive. Shift Control in Uphill Traveling When the ECM detects uphill travel, it prohibits upshifting to the 4th after downshifting to the 3rd. Shift Control in Downhill Traveling If a signal indicating that the driver has operated the brake pedal is input while the ECM detects downhill travel, it downshifts from the 4th to 3rd.
Uphill Corner
Without Control With Control
3rd
4th 3rd
3rd
4th 4th 3rd 4th
264CH06
Brake Operation
1) Uphill/Downhill Judgment The actual acceleration calculated from the speed sensor signal is compared with the reference acceleration (based on level road travel) stored in the ECM to determine uphill or downhill travel. Actual Acceleration < Reference Acceleration Reference acceleration Actual acceleration Smaller Greater Uphill Downhill
162CH10
Actual Acceleration > Reference Acceleration
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-23
8. Flex Lock-up Clutch Control
In addition to the conventional lock-up timing control, flex lock-up clutch control is used. This flex lock-up clutch control regulates the solenoid valve SLU as an intermediate mode between the ON/OFF operation of the lock-up clutch. The flex lock-up clutch control operates during acceleration, in the 3rd and 4th gears in the D range, and during deceleration, in the 3rd and 4th gears in the D range, and in the 3rd gear in the 3 range.
Engine Speed
ECM
Duty Ratio Time
Engine Speed Signal Speed Sensor NT Signal
Vehicle Speed
Throttle Position Sensor
Speed Sensor NT
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Lock-up Control Valve ATF Temperature Sensor Solenoid Valve SLU
00RCH02Y
Large
: Lock-up Operating Range : Flex Lock-up Operating Range Acceleration
Throttle Opening Angle
Deceleration
Vehicle Speed Flex Lock-up Operating Range
"
High
005CH04Y
Flex Lock-up Operation Gears in D and 3 Range A
Range Gear 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 1st 2nd 3rd Acceleration Flex Lock-up x x f f x x x Deceleration Flex Lock-up x x f f x x f
CH-24
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
9. Diagnosis
D When the ECM detects a malfunction, the ECM makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. Furthermore, the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) in the combination meter illuminates or blinks to inform the driver. D At the same time, the DTCs (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) are stored in the memory. The DTCs can be read by connecting the hand-held tester. For details, see the 06 Yaris Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM00R0U).
10. Fail-Safe
This function minimizes the loss of operability when any abnormality occurs in each sensor or solenoid.
"
Fail-Safe Control List A Malfunction Part Function During a vehicle speed signal malfunction, the 4th upshift is prohibited. During a speed sensor NT signal malfunction, the 4th upshift is prohibited. During a ATF temperature sensor malfunction, the 4th upshift is prohibited. During a solenoid valves SLT or SLU malfunction, the 4th upshift is prohibited. During a water temperature sensor, knock sensor, or throttle position sensor malfunction, the 4th upshift is prohibited. During a malfunction in the solenoid valve S1 or S2, the current to the faulty solenoid valve is cut off and control is effected by operating the normal solenoid valves. Shift control is effected as described in the table below, depending on the failed solenoid valve. When solenoid valve S1 is abnormal Solenoid valve S1 x x x x S2 ON # OFF OFF OFF ON Gear When solenoid valve S2 is abnormal Solenoid valve S1 ON ON OFF OFF S2 x x x x Gear When solenoid valves S1 and S2 are abnormal Solenoid valve S1 x x x x S2 x x x x Gear
Vehicle Speed Signal Speed Sensor NT ATF Temperature Sensor Solenoid Valve SLT or SLU Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor, Knock Sensor, or Throttle Position Sensor
Solenoid Valve S1 or S2
When all solenoid valves are normal Solenoid valve S1 ON ON OFF OFF S2 ON OFF OFF ON Gear
1st 2nd 3rd 4th
3rd 3rd 3rd 4th
2nd 2nd 3rd 3rd
3rd 3rd 3rd 3rd
CH-10
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
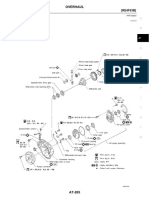
JPLANETARY GEAR UNIT 1. Construction
D A CR-CR type planetary gear is used in the planetary gear unit, which is located on the input shaft. This planetary gear is a type of the planetary gear unit that joins the front and rear planetary carriers to the front and rear ring gears. As a result, the unit has been made significantly simple and compact. D A centrifugal fluid pressure canceling mechanism is used in the C1 clutch, which is applied when shifting from the 3rd to 4th.
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C2
C1
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
216CH07
B1
B2
2. Function of Component
Component C1 C2 C3 B1 B2 B3 F1 F2 Forward Clutch Direct Clutch Reverse Clutch OD & 2nd Brake 2nd Brake 1st & Reverse Brake No. 1 One-Way Clutch No. 2 One-Way Clutch Function Connects input shaft and front planetary sun gear. Connects intermediate shaft and rear planetary carrier. Connects intermediate shaft and rear planetary sun gear. Lock the rear planetary sun gear. Prevent rear planetary sun gear from turning counterclockwise. Lock the front planetary ring gear and rear planetary carrier. Prevents rear planetary sun gear from turning counterclockwise. Prevents front planetary ring gear and rear planetary carrier from turning counterclockwise. These gears change the route through which driving force is transmitted, in accordance with the operation of each clutch and brake, in order to increase or reduce the input and output speed.
Planetary Gears
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-11
3. Transaxle Power Flow
Shift Lever Position P R N Gear Park Reverse Neutral 1st D 2nd 3rd 4th 1st 3 2nd 3rd 2 L f: Operation 1st Gear (D, 3 or 2 Position) 1st 2nd 1st Solenoid Valve S1 ON ON ON ON ON OFF OFF ON ON OFF ON ON ON S2 ON ON ON ON OFF OFF ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF ON f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f f C1 Clutch C2 C3 B1 Brake B2 B3 One-Way Clutch F1 F2
Rear Planetary Gear
F1
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C1
C2
C3
F1
B1
B2
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
248CH39
CH-12
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
2nd Gear (D or 3 Position)
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C2
C1
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
171CH06
B1
B2
3rd Gear (D or 3 Position)
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C2
C1
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
248CH40
B1
B2
4th Gear (D Position)
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C1
C2
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
248CH41
B1
B2
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 2nd Gear (2 Position)
CH-13
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C1
C2
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
171CH09
B1
B2
1st Gear (L Position)
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C2
C1
C3
F1
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
248CH42
B1
B2
Reverse Gear (R Position)
Rear Planetary Gear
F2
B3
Front Planetary Gear Counter Drive Gear
C1
C2
C3
F1
B1
B2
Intermediate Shaft (Input Shaft) Counter Driven Gear
248CH43
CH-14
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
4. Centrifugal Fluid Pressure Canceling Mechanism
There are two reasons for improving the conventional clutch mechanism: D To prevent the generation of pressure by the centrifugal force that applied to the fluid in piston fluid pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as chamber A) when the clutch is released, a check ball is provided to discharge the fluid. Therefore, before the clutch can be subsequently applied, it took time for the fluid to fill the chamber A. D During shifting, in addition to the original clutch pressure that is controlled by the valve body, the pressure that acts on the fluid in the chamber A also exerts influence, which is dependent upon revolution fluctuations. To address these two needs for improvement, a canceling fluid pressure chamber (hereafter referred to as chamber B) has been provided opposite chamber A. C1 Clutch
Chamber B
Chamber A
Piston
247CH21
By utilizing the lubrication fluid such as that of the shaft, the same amount of centrifugal force is applied, thus canceling the centrifugal force that is applied to the piston itself. Accordingly, it is not necessary to discharge the fluid through the use of a check ball, and a highly responsive and smooth shifting characteristic has been achieved. Centrifugal Fluid Pressure applied to the Chamber A Piston Target Fluid Pressure Chamber A (Piston Fluid Pressure) Fluid Pressure applied to Piston Clutch
Centrifugal Fluid Pressure applied to Chamber B Chamber B (Canceling Fluid Pressure)
157CH17
Shaft Side
Fluid pressure applied to piston
Centrifugal fluid pressure applied to chamber B
Target fluid pressure (Original clutch pressure)
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-15
JVALVE BODY UNIT
The valve body consists of the upper and lower valve bodies and 5 solenoid valves. The 5 solenoid valves are installed in the lower valve body for serviceability. Solenoid Valve SLU Upper Valve Body
Lower Valve Body Solenoid Valve SLT
Solenoid Valve S2 Solenoid Valve S1
"
Solenoid Valve ST
"
00RCH11Y
Upper Valve Body A
Lower Valve Body A 1-2 Shift Valve Accumulator Control Valve
Lock-up Coast Relay Low Coast Relay Valve Valve Modulator Valve 3-4 Shift 2-3 Shift Timing Valve Valve
Primary Regulator Valve
Secondary Reverse 4-3 Shift Regulator Solenoid Control Valve Timing Valve Valve Relay Valve
216CH10
4-3 Shift Timing Valve
3-4 Shift Valve
216CH11
"
Function of Solenoid Valve A Action For 2-3 shift valve control For 1-2 and 3-4 shift valve control For clutch to clutch pressure control For clutch engagement pressure control For line pressure control Function Shifts gears by switching the 2-3 shift valve and controlling the C2 clutch. Shifts gears by switching the 1-2 and 3-4 shift valves and controlling 2 clutches (C1 and C2) and 2 brakes (B1 and B2). Switches 3-4 and 4-3 shift valves. Controls the lock-up clutch. Controls the line pressure, secondary pressure, and accumulator back pressure.
Solenoid Valve S1 S2 ST SLU SLT
CH-6
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JDESCRIPTION
06 Yaris 1NZ-FE engine model with automatic transaxle uses the U340E automatic transaxle. This automatic transaxle is a compact and high-capacity 4-speed Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle).
171CH03
"
Specification A U340E 1NZ-FE 1st 2nd 2.847 1.552 1.000 0.700 2.343 4.237 6.4 (6.78, 5.63) Toyota Genuine ATF WS kg (lb) 68.5 (150.7)
Transaxle Type Engine Type
Gear Ratio
3rd 4th Reverse
Differential Gear Fluid Capacity*2 Fluid Type Weight
Ratio*1 Liters (US qts, Imp.qts)
(Reference)*3
*1: Counter Gear Ratio Included. *2: Differential Included. *3: Weight shows the figure with the fluid fully filled.
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-7
B1 C2
B2
F2
B3
Counter Drive Gear
C1
Input Shaft F1 Front Planetary Gear C3 Rear Planetary Gear
216CH05
Counter Driven Gear
"
Specification A C1 C2 C3 B1 B2 B3 F1 F2 Forward Clutch Direct Clutch Reverse Clutch OD & 2nd Brake 2nd Brake 1st & Reverse Brake No. 1 One-Way Clutch No. 2 One-Way Clutch The No. of Sprags The No. of Rollers The No. of Sun Gear Teeth The No. of Pinion Gear Teeth The No. of Ring Gear Teeth The No. of Sun Gear Teeth The No of Discs No. 4 3 2 2 3 4 16 15 46 21 85 32 21 75 52 53
Front Planetary Gear y
Rear Planetary Gear y
The No. of Pinion Gear Teeth The No. of Ring Gear Teeth The No. of Drive Gear Teeth The No. of Driven Gear Teeth
Counter Gear
CH-8
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
JATF (AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID) WS
D The ATF WS is used to reduce the resistance of the ATF and ensure fuel economy by reducing its viscosity in the practical operation range. At the high-temperature end, its viscosity is the same as that of the ATF Type T-IV, which ensures the durability of the automatic transaxle. D There is no interchangeability between the ATF WS and other types of ATFs (ATF Type T-IV, D-II). Viscosity Reduced Viscosity : ATF Type T-IV : ATF WS
High
High Service Tip
Temperature
259LSK03
D The color of the ATF level gauge used in the ATF WS has been changed to black. (Orange was used in the ATF Type T-IV on the previous model.) D If a vehicle with a transaxle filled with ATF WS is replenished with another type of ATF, the vehicle might not start off at extremely low temperatures.
JTORQUE CONVERTER
D This torque converter has optimally designed fluid passages and impeller configuration resulting in substantially enhanced transmission efficiency to ensure good starting, acceleration and fuel economy. D Furthermore, a hydraulically operated lock-up mechanism which cuts power transmission losses due to slippage at medium and high speeds is used.
"
Specification A 3-Element, 1-Step, 2-Phase (With Lock-up Mechanism) 2.0 Stator Pump Impeller
Turbine Runner Lock-up Clutch
Torque Converter Type Stall Torque Ratio
Input Shaft
One-way Clutch
216CH06
CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CH-9
JOIL PUMP
The oil pump is combined with torque converter, lubricates the planetary gear units and supplies operating pressure to the hydraulic control.
Driven Gear
Drive Gear
247CH20
Pump Body
Stator Shaft
Вам также может понравиться
- U 340Документ19 страницU 340ruslan1580Оценок пока нет
- U140E U241E Vac LocationsДокумент5 страницU140E U241E Vac LocationsPedroMecanicoОценок пока нет
- вакуум тест для JF016-017 PDFДокумент4 страницывакуум тест для JF016-017 PDFМихаил Болотин100% (1)
- 11005d1137975747 Diy Check Automatic Transmission Fluid Level 05tundratranoperДокумент5 страниц11005d1137975747 Diy Check Automatic Transmission Fluid Level 05tundratranoperJimmy Zegarra100% (1)
- Jactó 015eДокумент2 страницыJactó 015ehidraulic100% (3)
- CVT Transmission Parts k313 Automatic Transmission Valve BodyДокумент5 страницCVT Transmission Parts k313 Automatic Transmission Valve BodyRepuestos Maceira0% (1)
- CVTДокумент228 страницCVTenalso100% (1)
- Aw 03 72le Aw0373leДокумент195 страницAw 03 72le Aw0373leBrian AqifОценок пока нет
- Jatco JF017 Forma de Armado y DesarmadoДокумент18 страницJatco JF017 Forma de Armado y DesarmadoTransmisiones Vicab100% (4)
- Magneti Marelli Selespeed CFC328 (DUALOGIC) - Italian Robot - The AKPPro MagazineДокумент1 страницаMagneti Marelli Selespeed CFC328 (DUALOGIC) - Italian Robot - The AKPPro MagazineGregОценок пока нет
- Sonnax AW 6-Speed FWDДокумент37 страницSonnax AW 6-Speed FWDhornet22Оценок пока нет
- A 340 e 343Документ8 страницA 340 e 343Mauricio Exequiel Chavez100% (1)
- 464192534 вакуум тест для JF016 017 PDFДокумент4 страницы464192534 вакуум тест для JF016 017 PDF89539306889Оценок пока нет
- 3040LE Cable-CompleteДокумент13 страниц3040LE Cable-CompleteZafer IlhanОценок пока нет
- A750E ManualДокумент5 страницA750E ManualJehovanaОценок пока нет
- Critical Wear Areas & Vacuum Test Locations: Valve & Pump BodiesДокумент2 страницыCritical Wear Areas & Vacuum Test Locations: Valve & Pump BodiesAndersonОценок пока нет
- A43 PDFДокумент126 страницA43 PDFyermain100% (1)
- CRV Matic MCVA BZKA PDFДокумент8 страницCRV Matic MCVA BZKA PDFAlli Yanti50% (2)
- Front Wheel Drive Automatic Transmission VT2Документ6 страницFront Wheel Drive Automatic Transmission VT2Erin Lam100% (2)
- A 6 LF 1Документ2 страницыA 6 LF 1Mansor Alqaaf100% (1)
- 5HP18Документ39 страниц5HP18Leonard67% (3)
- Información de Transmisión CVT ToyotaДокумент151 страницаInformación de Transmisión CVT ToyotaMauricio Exequiel Chavez93% (15)
- 16K in PDFДокумент2 страницы16K in PDFossoskiОценок пока нет
- Jatco6speed Intro PDFДокумент49 страницJatco6speed Intro PDFleeroy381100% (1)
- CFT30 VacTestДокумент7 страницCFT30 VacTestOscar SerranoОценок пока нет
- (Hyundai I10 2007-) (Kia Morning 2011-, Picanto 2009-, Ray 2012-, Suria 2006-2011) 4 SPEED FWD With Lock Up (Electronic Control)Документ4 страницы(Hyundai I10 2007-) (Kia Morning 2011-, Picanto 2009-, Ray 2012-, Suria 2006-2011) 4 SPEED FWD With Lock Up (Electronic Control)EduRoiОценок пока нет
- K111 Continuously Variable Transaxle: DescriptionДокумент35 страницK111 Continuously Variable Transaxle: Descriptionhungchagia1100% (2)
- 6T40 Gen2 Zip in PDFДокумент10 страниц6T40 Gen2 Zip in PDFAlberto Del Rio Mejia100% (1)
- Assembly U241E TransmissionДокумент29 страницAssembly U241E TransmissionFirman SuryaОценок пока нет
- Manual 245 U140F 060Документ6 страницManual 245 U140F 060Nacho Arroyo100% (2)
- A960e Transmission SolenoidДокумент2 страницыA960e Transmission SolenoidDenis KonovalovОценок пока нет
- Vaccum Testing Info SonnaxДокумент34 страницыVaccum Testing Info SonnaxRobert Moreau100% (3)
- Aw03 PDFДокумент15 страницAw03 PDFamazonagirl19Оценок пока нет
- A4CF2Документ65 страницA4CF2Alex Maceira Graterol100% (2)
- U 140Документ163 страницыU 140mauricio_ch_91100% (6)
- Atra BulletinДокумент2 страницыAtra Bulletinossoski100% (3)
- A5SR1 Repair and Troubleshooting Guide For The 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox Kia Sorento 2008Документ205 страницA5SR1 Repair and Troubleshooting Guide For The 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox Kia Sorento 2008Leonardo Alves Fiusa100% (2)
- U340 441E DescriptionДокумент25 страницU340 441E Descriptionruslan1580Оценок пока нет
- U660e Zip inДокумент11 страницU660e Zip inGabriel Harper'100% (1)
- Honda CVT PDFДокумент3 страницыHonda CVT PDFWagner Augusto100% (1)
- U340 Manual PDFДокумент25 страницU340 Manual PDFOliverFrancoCruzAranibar100% (2)
- RE4F03BДокумент118 страницRE4F03Bossoski100% (1)
- Just Another: Play BallДокумент8 страницJust Another: Play BallAnonymous eExWojLxОценок пока нет
- Automatic Transaxle (F4A51)Документ194 страницыAutomatic Transaxle (F4A51)Dayro GeneyОценок пока нет
- MIL ON WITH DTC P0741, P0744, P0746, P0776, P0841, P0965, P2857, P2858, P2859, AND/OR P285A STORED, and May Have Hesitation And/Or Lack of PowerДокумент22 страницыMIL ON WITH DTC P0741, P0744, P0746, P0776, P0841, P0965, P2857, P2858, P2859, AND/OR P285A STORED, and May Have Hesitation And/Or Lack of Powerdamian berduscoОценок пока нет
- Ford Fnr5 TCC SlipДокумент2 страницыFord Fnr5 TCC SlipAlex Maceira Graterol100% (2)
- A 960eДокумент28 страницA 960elucasgratao100% (3)
- Technical Service Information3Документ4 страницыTechnical Service Information3JoseОценок пока нет
- 15 - Automatic TransaxleДокумент246 страниц15 - Automatic TransaxleesquisofОценок пока нет
- Operation: A340E A340F Automatic TransmissionДокумент7 страницOperation: A340E A340F Automatic TransmissionHugoE.Torres100% (3)
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) : Group 23Документ12 страницContinuously Variable Transmission (CVT) : Group 2308088338100% (1)
- A540 ToyotaДокумент7 страницA540 ToyotaporkfaceОценок пока нет
- A340-Le TransmissionДокумент24 страницыA340-Le TransmissionLuisGonzalezОценок пока нет
- 1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Документ11 страниц1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Jose Calle100% (1)
- Operation: Mechanical Operation Operating ConditionsДокумент7 страницOperation: Mechanical Operation Operating Conditionshybrid_motorsports_llcОценок пока нет
- Control System 1Документ34 страницыControl System 1Shrinivas Prabhu100% (4)
- The NAG1 (5-Speed) Automatic TransmissionДокумент4 страницыThe NAG1 (5-Speed) Automatic TransmissionEdBunge100% (1)
- Brake ControlДокумент212 страницBrake ControllogammicОценок пока нет
- 106-111 Ect and A-T IndicatorДокумент6 страниц106-111 Ect and A-T Indicatormyke pythoneОценок пока нет
- Ricoh mp301Документ72 страницыRicoh mp301cahernandezg1Оценок пока нет
- ZJ70D Drilling Rig Maintenance ManualДокумент55 страницZJ70D Drilling Rig Maintenance ManualQamar Shahzad100% (4)
- Vespa Service Manual 08-04-2021Документ322 страницыVespa Service Manual 08-04-2021Julio Borrero100% (1)
- Et BrakeДокумент22 страницыEt Brakecudalb georgeОценок пока нет
- System Information (Power Train) : Testing and AdjustingДокумент4 страницыSystem Information (Power Train) : Testing and AdjustingguayanecitroОценок пока нет
- Manual K50 Sectional Machine ManДокумент47 страницManual K50 Sectional Machine ManeliezerperezОценок пока нет
- Yuchai YC4DДокумент59 страницYuchai YC4DFerran Alfonso100% (13)
- Trucker Tipper Test ENG 2011-07Документ11 страницTrucker Tipper Test ENG 2011-07gruponuevageneracionОценок пока нет
- Transmissão 2007Документ72 страницыTransmissão 2007Fabricio Félix100% (1)
- Sample 40404Документ16 страницSample 40404Rahul RoyОценок пока нет
- Funcionamiento Convertido 960 FДокумент54 страницыFuncionamiento Convertido 960 FMiguel Huaman PolarОценок пока нет
- 1991 Johnson Evinrude EI 60 Loop V Models 150 175 Outboards Service Manual Page-3Документ1 страница1991 Johnson Evinrude EI 60 Loop V Models 150 175 Outboards Service Manual Page-3Anthony Shawn BateОценок пока нет
- Tractor Training PresentationДокумент55 страницTractor Training PresentationSantosh LokhandeОценок пока нет
- Eatonroadranger RTOF-14909MLLДокумент32 страницыEatonroadranger RTOF-14909MLLJavier Estrada ColindresОценок пока нет
- Automatic Transmission SystemДокумент34 страницыAutomatic Transmission SystemAsad Khan100% (3)
- Ishift and Powertronioc Training PDFДокумент265 страницIshift and Powertronioc Training PDFsengottaiyan100% (3)
- CST H450K User ManualДокумент156 страницCST H450K User Manualvjvijay88100% (1)
- Corsa Owners Manual January 2016Документ265 страницCorsa Owners Manual January 2016TomОценок пока нет
- STIHL 021 023 025 Workshop Manual PDFДокумент52 страницыSTIHL 021 023 025 Workshop Manual PDFBoth JánosОценок пока нет
- Chelsea PTO 277 Series Parts ManualДокумент45 страницChelsea PTO 277 Series Parts Manualruben dario valle villalobosОценок пока нет
- Form1 Crankshaft DeflectionДокумент1 страницаForm1 Crankshaft DeflectionmakinaОценок пока нет
- Clutch Components - July'20Документ17 страницClutch Components - July'20Shubham GoelОценок пока нет
- G56 GTA User Manual V1.2Документ47 страницG56 GTA User Manual V1.2alexОценок пока нет
- L936 Wheel Loader Parts Catalog: Shandong Lingong Construction Machinery Co.,LtdДокумент287 страницL936 Wheel Loader Parts Catalog: Shandong Lingong Construction Machinery Co.,LtdVitor RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Audi Gear RatioДокумент3 страницыAudi Gear RatioIrina Veresinina100% (2)
- Automatic Transaxle PDFДокумент50 страницAutomatic Transaxle PDFdemos70100% (1)
- WSM - Maintenance Instruction Part - 1 Truk - en PDFДокумент120 страницWSM - Maintenance Instruction Part - 1 Truk - en PDFDul AdulОценок пока нет
- Bostitch: Operation and Maintenance ManualДокумент28 страницBostitch: Operation and Maintenance ManualAnonymous 2MRGC0w1Оценок пока нет
- Embragues de Freno Eaton Airflex - Uncoiler R4 (8CB250-142096JB) PDFДокумент40 страницEmbragues de Freno Eaton Airflex - Uncoiler R4 (8CB250-142096JB) PDFCesarFTAОценок пока нет
- Grinding Mills With Dual Pinnion DrivesДокумент20 страницGrinding Mills With Dual Pinnion Drivesjazzfan52Оценок пока нет
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionОт EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AОт EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AОценок пока нет
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersОт EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CОт EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CОценок пока нет
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisОт EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionОт EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedОт EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)От EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (12)
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesОт EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsОт EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsОценок пока нет
- Laminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataОт EverandLaminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataОценок пока нет
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseОт EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (51)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsОт EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongОценок пока нет
- Machinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionОт EverandMachinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionОценок пока нет
- Safety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationОт EverandSafety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Gas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsОт EverandGas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- Electrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeОт EverandElectrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsОт EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Working Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsОт EverandWorking Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Mechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringОт EverandMechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)