Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Meaning of Data
Загружено:
yscheeИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Meaning of Data
Загружено:
yscheeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
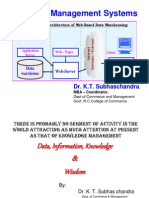
Meaning of data, information and knowledge
The terms information and knowledge are frequently used for overlapping concepts. The main difference is in the level of abstraction being considered. Data is the lowest level of abstraction, information is the next level, and finally, knowledge is the highest level among all three.[citation needed] Data on its own carries no meaning. For data to become information, it must be interpreted and take on a meaning. For example, the height of Mt. Everest is generally considered as "data", a book on Mt. Everest geological characteristics may be considered as "information", and a report containing practical information on the best way to reach Mt. Everest's peak may be considered as "knowledge". Information as a concept bears a diversity of meanings, from everyday usage to technical settings. Generally speaking, the concept of information is closely related to notions of constraint, communication, control, data, form, instruction, knowledge, meaning, mental stimulus, pattern, perception, and representation. Beynon-Davies uses the concept of a sign to distinguish between data and information; data are symbols while information occurs when symbols are used to refer to something. [14] [15] It is people and computers who collect data and impose patterns on it. These patterns are seen as information which can be used to enhance knowledge. These patterns can be interpreted as truth, and are authorized as aesthetic and ethical criteria. Events that leave behind perceivable physical or virtual remains can be traced back through data. Marks are no longer considered data once the link between the mark and observation is broken. [16] Raw data refers to a collection of numbers, characters, images or other outputs from devices to convert physical quantities into symbols, that are unprocessed. Such data is typically further processed by a human or input into a computer, stored and processed there, or transmitted (output) to another human or computer (possibly through a data cable). Raw data is a relative term; data processing commonly occurs by stages, and the "processed data" from one stage may be considered the "raw data" of the next. Mechanical computing devices are classified according to the means by which they represent data. An analog computer represents a datum as a voltage, distance, position, or other physical quantity. A digital computer represents a datum as a sequence of symbols drawn from a fixed alphabet. The most common digital computers use a binary alphabet, that is, an alphabet of two characters, typically denoted "0" and "1". More familiar representations, such as numbers or letters, are then constructed from the binary alphabet. Some special forms of data are distinguished. A computer program is a collection of data, which can be interpreted as instructions. Most computer languages make a distinction between programs and the other data on which programs operate, but in some languages, notably Lisp and similar languages, programs are essentially indistinguishable from other data. It is also useful to distinguish metadata, that is, a description of other data. A similar yet earlier term for metadata is "ancillary data."
The prototypical example of metadata is the library catalog, which is a description of the contents of books. Experimental data refers to data generated within the context of a scientific investigation by observation and recording. Field data refers to raw data collected in an uncontrolled in situ environment
Вам также может понравиться
- Information Knowledge Wisdom: DIKW PyramidДокумент2 страницыInformation Knowledge Wisdom: DIKW Pyramidcap tainОценок пока нет
- Meaning of Data, Information and Knowledge: For Data in Computer Science, See - For Other Uses, SeeДокумент4 страницыMeaning of Data, Information and Knowledge: For Data in Computer Science, See - For Other Uses, SeeLeila MoralesОценок пока нет
- It Module 3Документ53 страницыIt Module 3Neenu SukumarОценок пока нет
- Data - WikipediaДокумент37 страницData - WikipediaCollins AdionyeОценок пока нет
- DataДокумент6 страницDataAnonymous 2HTDgMtОценок пока нет
- Data Vs Information: KnowledgeДокумент7 страницData Vs Information: KnowledgeEASSAОценок пока нет
- Database Concepts With Emerging TrendsДокумент104 страницыDatabase Concepts With Emerging TrendsNikhil KasatОценок пока нет
- InformationДокумент1 страницаInformationPRINTDESK by DanОценок пока нет
- TLE4 Lesson 1 - Data vs. InformationДокумент11 страницTLE4 Lesson 1 - Data vs. Informationsirpencilbox100% (1)
- MIS BookДокумент174 страницыMIS BookLaury Phillips80% (5)
- Computer Data ProcessingДокумент10 страницComputer Data ProcessingKhuramzahoor CheemaОценок пока нет
- Management Information SystemДокумент26 страницManagement Information SystemRaghav WadhwaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To CompДокумент47 страницIntroduction To CompalemayehuОценок пока нет
- What Do You Mean by Data and Information ?: ComputerДокумент30 страницWhat Do You Mean by Data and Information ?: ComputertusherОценок пока нет
- Scientific DataДокумент2 страницыScientific DataSon Chaeyoung MinariОценок пока нет
- Title: Powerful Basic Concepts of Database System Target Population: Second Year BSCS/ICT and First Year ACT Students III - OverviewДокумент6 страницTitle: Powerful Basic Concepts of Database System Target Population: Second Year BSCS/ICT and First Year ACT Students III - OverviewArnel CuetoОценок пока нет
- What Is A DatabaseДокумент14 страницWhat Is A DatabasebutooooОценок пока нет
- Information Is AnДокумент2 страницыInformation Is AnLevon GevorgyanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1-Introduction To ComputerДокумент10 страницChapter 1-Introduction To Computerhariye2225Оценок пока нет
- Chapter-1 Introduction To ComputerДокумент15 страницChapter-1 Introduction To ComputerTesfaye GemechuОценок пока нет
- Data Information Information SystemДокумент33 страницыData Information Information SystemMark Hyunn DicenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Introduction To Data ScienceДокумент56 страницChapter 2 - Introduction To Data ScienceSam ContactОценок пока нет
- Chapter One Introduction To Information Storage and RetrievalДокумент107 страницChapter One Introduction To Information Storage and Retrievalshegawcoc2015Оценок пока нет
- Data and InformationДокумент17 страницData and InformationAkhilesh BhuraОценок пока нет
- Database Management Systems: Dr. K.T. SubhaschandraДокумент42 страницыDatabase Management Systems: Dr. K.T. SubhaschandraMahesh NanjappaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Lecture SlidesДокумент49 страницChapter 2 Lecture Slidespeneal feleekОценок пока нет
- Data Information Knowledge WisdomДокумент7 страницData Information Knowledge Wisdomson phan100% (1)
- Module 1 - Information Processing Study GuideДокумент34 страницыModule 1 - Information Processing Study GuideChad-WayneChambersОценок пока нет
- Information System ManagementДокумент24 страницыInformation System Managementआदित्य त्रिपाठीОценок пока нет
- Data (Computing) - WikipediaДокумент29 страницData (Computing) - WikipediaNaniОценок пока нет
- Cos 242 Data Comm and NetworksДокумент71 страницаCos 242 Data Comm and NetworksasogwamariankeirukaОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Introduction To DataScience and AnalyticsДокумент10 страницModule 1 Introduction To DataScience and Analyticsivy100803Оценок пока нет
- Data Structures IntroductionДокумент82 страницыData Structures Introductionidk what im creating atmОценок пока нет
- Data Structures Introduction1Документ26 страницData Structures Introduction1idk what im creating atmОценок пока нет
- It NotesДокумент30 страницIt Notesydab gamesОценок пока нет
- Information Technology: International Advanced Level Scheme of Work Unit 1Документ11 страницInformation Technology: International Advanced Level Scheme of Work Unit 1MuneshОценок пока нет
- Sison, Winnie Rose B - Learning-Activity - 1Документ5 страницSison, Winnie Rose B - Learning-Activity - 1Winnie SisonОценок пока нет
- Data Ni VenzДокумент24 страницыData Ni Venzcharlesdave1159Оценок пока нет
- 3 Sem Dbms NotesДокумент104 страницы3 Sem Dbms NotesPrasad KalalОценок пока нет
- C CC C C C! " C: G M G) + M MДокумент15 страницC CC C C C! " C: G M G) + M MKutemwa Chutu Ng'ambiОценок пока нет
- Data Information WisdomДокумент42 страницыData Information WisdomBrian HerreraОценок пока нет
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsДокумент5 страницData Structures and AlgorithmsJulie ann ArenaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Information Systems: Please Turn Your Cell Phone OffДокумент32 страницыIntroduction To Information Systems: Please Turn Your Cell Phone OffKumar AnkurОценок пока нет
- Defining Knowledge, Information, DataДокумент3 страницыDefining Knowledge, Information, DataNabilah Mat YasimОценок пока нет
- Data Structures Course Module PDFДокумент37 страницData Structures Course Module PDFjonnathan mandelaОценок пока нет
- Unit 16 Database Resource Management: StructureДокумент13 страницUnit 16 Database Resource Management: StructureCamilo AmarcyОценок пока нет
- Database System 1: Instructor: Ahsan KhanДокумент32 страницыDatabase System 1: Instructor: Ahsan Khan654321ahsanОценок пока нет
- A.1.1 Outline The Differences Between Data and Information. What Is Data: Data Is A Raw and Unorganized Fact That Required To Be Processed To Make ItДокумент27 страницA.1.1 Outline The Differences Between Data and Information. What Is Data: Data Is A Raw and Unorganized Fact That Required To Be Processed To Make ItINDRANI GOSWAMIОценок пока нет
- Student - Aytan Garaisayeva Instruction - Leyla Jumayeva Major - Computer Science Subject - DatabaseДокумент2 страницыStudent - Aytan Garaisayeva Instruction - Leyla Jumayeva Major - Computer Science Subject - DatabaseAyten QaraisayevaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 CSITДокумент13 страницChapter 1 CSITTigist TilahunОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Database DesignДокумент18 страницFundamentals of Database DesignsureshОценок пока нет
- Note For Final ExamДокумент47 страницNote For Final ExamDawit MihiretОценок пока нет
- Etymology: Information Is Processed, Organized and StructuredДокумент4 страницыEtymology: Information Is Processed, Organized and Structuredvaibhav lanjewarОценок пока нет
- Unit-4: Information SystemsДокумент63 страницыUnit-4: Information SystemsASHISH KUMARОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Information System 2nd Year Unite 3Документ16 страницFundamentals of Information System 2nd Year Unite 3Alehegn EskeziaОценок пока нет
- Walls2017 DemolitionforsustainableconstructionRGДокумент6 страницWalls2017 DemolitionforsustainableconstructionRGStefan GhidiuОценок пока нет
- Food Defense Self-Assessment FormДокумент4 страницыFood Defense Self-Assessment FormLynn GeiseОценок пока нет
- The Age of Exploration/Age of Discovery: Countries InvolvedДокумент6 страницThe Age of Exploration/Age of Discovery: Countries InvolvedRocky RayoОценок пока нет
- Genesis NP Application Manual US NP AM 003 - 0111 PDFДокумент16 страницGenesis NP Application Manual US NP AM 003 - 0111 PDFcalejandrotgОценок пока нет
- DPC6HG Aa00 G0000 ZS001 - 001 - 01Документ6 страницDPC6HG Aa00 G0000 ZS001 - 001 - 01rajitkumar.3005Оценок пока нет
- Proses Manufaktur: Machining Operation and Machine ToolsДокумент34 страницыProses Manufaktur: Machining Operation and Machine ToolsLyndaОценок пока нет
- RhinoGold 4.0 - Level 1 - Tutorial 014P - Half Channel RingДокумент2 страницыRhinoGold 4.0 - Level 1 - Tutorial 014P - Half Channel RingJulio mendoza100% (2)
- Literature MyДокумент5 страницLiterature MysandipparekhОценок пока нет
- IELTS Writing - Bar ChartДокумент2 страницыIELTS Writing - Bar ChartTrí Võ PhạmОценок пока нет
- Mechanical ComprehensionДокумент14 страницMechanical Comprehensiondanielhealy100% (6)
- SCA0424R500 560 620SpecSheet SAU2016-8-R500 R560 R620 6x4 WEBДокумент4 страницыSCA0424R500 560 620SpecSheet SAU2016-8-R500 R560 R620 6x4 WEBChristopherОценок пока нет
- Man Pa-4000Документ18 страницMan Pa-4000JOEY76BYОценок пока нет
- Chapter ONE Full PDFДокумент125 страницChapter ONE Full PDFAzimSyahmiОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Step 2 Comprehend Intellectual Property: Valuation and Negotiation of TechnologyДокумент16 страницUnit 1 - Step 2 Comprehend Intellectual Property: Valuation and Negotiation of TechnologyGiovanny MicОценок пока нет
- Trailler On JettyДокумент4 страницыTrailler On JettyFuad Andaru BaskaraОценок пока нет
- 6090 Uv Printer Operation Manual - BlackДокумент26 страниц6090 Uv Printer Operation Manual - BlackSonia NaickerОценок пока нет
- Print Master ProjectДокумент62 страницыPrint Master ProjectVipin PouloseОценок пока нет
- Mobilgrease XHP 460Документ3 страницыMobilgrease XHP 460Jaime Miloz Masle JaksicОценок пока нет
- Traditional Healer in Carletonville, Germiston, Johannesburg, Krugersdorp South Africa+27782669503Документ139 страницTraditional Healer in Carletonville, Germiston, Johannesburg, Krugersdorp South Africa+27782669503mama shifahОценок пока нет
- EEPW3142 QP Version-AДокумент8 страницEEPW3142 QP Version-A3nathОценок пока нет
- Electrical Equipment in Hazardous LocationsДокумент41 страницаElectrical Equipment in Hazardous LocationsSAYEDОценок пока нет
- 10039030M00 - PB560 System Final Test Procedure PDFДокумент12 страниц10039030M00 - PB560 System Final Test Procedure PDFDaniel MarquesОценок пока нет
- Fully Automated Luxury CommunismДокумент8 страницFully Automated Luxury CommunismNicoleta MeruțiuОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Braking System of Mine WindersДокумент53 страницыMechanical Braking System of Mine WindersAJEET YADAV100% (6)
- Clearvista UrgentДокумент2 страницыClearvista UrgentkevinОценок пока нет
- Linguistic Determinism & Linguistic RealismДокумент1 страницаLinguistic Determinism & Linguistic RealismTünde KovácsОценок пока нет
- Ze Gcs04a20-Eng 247-270Документ24 страницыZe Gcs04a20-Eng 247-270ikrima BenОценок пока нет
- Women in LeadershipДокумент17 страницWomen in LeadershipSodfa EttafakshiОценок пока нет
- Boostherm DWV 01 2017 ENДокумент6 страницBoostherm DWV 01 2017 ENCarlos LehmanОценок пока нет
- Summary of The 48 Laws of Power: by Robert GreeneОт EverandSummary of The 48 Laws of Power: by Robert GreeneРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (233)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (24)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (80)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОценок пока нет
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosОт Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (207)
- Codependent No More: How to Stop Controlling Others and Start Caring for YourselfОт EverandCodependent No More: How to Stop Controlling Others and Start Caring for YourselfРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (88)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryОт EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (44)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (328)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsОт EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (722)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (253)
- Rewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryОт EverandRewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (157)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossОт EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingОт EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingОценок пока нет
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)