Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Causes and Effects of Cerebrovascular Disease
Загружено:
Terence ValdehuezaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Causes and Effects of Cerebrovascular Disease
Загружено:
Terence ValdehuezaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
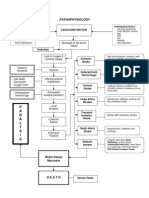
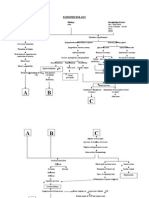
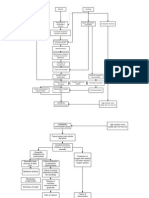
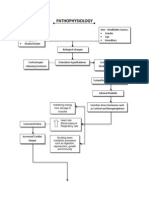
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE Definition: Cerebrovascular disease is a group of brain dysfunctions related to disease of the blood vessels supplying
the brain. Hypertension is the most important cause; it damages the blood vessel lining, endothelium, exposing the underlying collagen where platelets aggregate to initiate a repairing process which is not always complete and perfect.
PREDISPOSING FACTORS: - Age (48 years old) - Gender (Male)
PRECIPITATING FACTORS: - Hypertension - Obese (BMI: 33.51) - Increased cholesterol in diet
Obstruction of blood vessels
Decreased cerebral blood flow
Decreased O2 supply Stimulation of mitochondria Production of lactic acid Change in pH level (acidic) Anaerobic environment Decreased production of ATP by neurons Decreased depolarization Increase cellular death
Infarction
Medial aspect of one frontal lobe or both
Lateral hemisphere and deeper structures of frontal, parietal and temporal
Occipital lobe; anterior and medial portion of temporal lobe, thalamus involvement
Cerebral penducle; cerebellum and brainstem
Paralysis of foot/leg; impaired gait; problems in decision making or performing acts voluntarily; slowness of thought; urinary incontinence; cognitive and affective disorders
Contralateral hemiplegia (face and arm); aphasia; homonymous hemianopsia; altered consciousness; left- right confusion
Homonymous hemianopsia and other visual defects like color blindness; loss of central vision and visual hallucinations; memory deficits; loss of sensory modalities; spontaneous pain; aphasia
Oculomotor nerve palsy; visual disturbance such as diplopia; dystaxia; vertigo; dysphagia
Вам также может понравиться
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- Risk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент4 страницыRisk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeSherlyn KirisakiОценок пока нет
- Patho MIДокумент2 страницыPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of CVAДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaОценок пока нет
- Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic and Embolic DiseasesДокумент2 страницыModifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic and Embolic DiseasesJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Stroke PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Документ10 страницPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeОценок пока нет
- Stroke PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaОценок пока нет
- Stroke PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Pathophysiology CVAДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Pathophysiology CVAДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Документ1 страницаPathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1kristel_nicole18yaho60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of CVAДокумент7 страницPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVAДокумент10 страницSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Документ2 страницыNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- CVA PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Оценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryДокумент1 страницаPa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryGenel Joseph Jacildo Peñaflor100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Case On Intracranial HemorrhageДокумент17 страницCase On Intracranial HemorrhageLorebell100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of CVAДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeДокумент1 страницаSchematic Diagram of StrokeCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Pathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)Документ2 страницыPathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)PATHOSHOPPE100% (1)
- CKD PathoДокумент5 страницCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoОценок пока нет
- Case Study On CVAДокумент34 страницыCase Study On CVAGimcy Dela Fuente50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVAДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Anatomy Physiology Nervous System Brain Stroke Risk FactorsДокумент4 страницыAnatomy Physiology Nervous System Brain Stroke Risk FactorsKimsha ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Acute ischemic stroke monitoring and treatmentДокумент6 страницAcute ischemic stroke monitoring and treatmentMoonyeen Jann Casera Balic100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVAДокумент11 страницPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- A Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctДокумент38 страницA Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctKaycee Toling100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CKDДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology CKDReymon Mary JanineОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology TBIДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology TBIChester ManaloОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of Meningioma (Edited Version)Документ2 страницыPa Tho Physiology of Meningioma (Edited Version)Niño Villamarin71% (7)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Документ3 страницыPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- Pediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationДокумент39 страницPediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationRaghavendra DoddamaniОценок пока нет
- Perinatal AsphyxiaДокумент24 страницыPerinatal AsphyxiaZazzZaffaОценок пока нет
- Hie 200213194802Документ63 страницыHie 200213194802Thea DinoОценок пока нет
- Hypoxia Ischemic Encephalopathy and Congenital AnomaliesДокумент36 страницHypoxia Ischemic Encephalopathy and Congenital AnomaliesVarna MohanОценок пока нет
- Penyakit DegeneratifДокумент61 страницаPenyakit DegeneratifWidya Rizki AdzaniОценок пока нет
- Shock: Michael A. Puskarich Alan E. JonesДокумент9 страницShock: Michael A. Puskarich Alan E. JonesFarhanОценок пока нет
- Penyakit Degeneratif: Resti AraniaДокумент61 страницаPenyakit Degeneratif: Resti AraniaRobertus ElvantoraОценок пока нет
- Stroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular SyndromesДокумент49 страницStroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular Syndromesrabia khalidОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Management of PediatricДокумент48 страницManagement of PediatricIbrahimОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular PathologyДокумент182 страницыCardiovascular PathologyPavan chowdaryОценок пока нет
- Cerebro Vascular AccidentДокумент19 страницCerebro Vascular AccidentanshitaОценок пока нет
- Presented by DR Mohammed AtifДокумент42 страницыPresented by DR Mohammed AtifUmer HussainОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis Brain Dissorders: Marshell Tendean, MD Department of Internal Medicine Ukrida JakartaДокумент31 страницаAtherosclerosis Brain Dissorders: Marshell Tendean, MD Department of Internal Medicine Ukrida JakartaDeshielanny AlagumolyОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis Brain Dissorders: Marshell Tendean, MD Department of Internal Medicine Ukrida JakartaДокумент31 страницаAtherosclerosis Brain Dissorders: Marshell Tendean, MD Department of Internal Medicine Ukrida JakartaSekar LarasОценок пока нет
- CVD Infarct-HpniiДокумент3 страницыCVD Infarct-HpniilarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Shock 12-12-12Документ60 страницShock 12-12-12Dilip Kumar MОценок пока нет
- A Resolution Creating A Constitutional Commission For The Amendment of The Constitution of BukSU-LSGДокумент2 страницыA Resolution Creating A Constitutional Commission For The Amendment of The Constitution of BukSU-LSGTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- 2014Документ3 страницы2014Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Law Student Practice Rule Amendments AdoptedДокумент17 страницLaw Student Practice Rule Amendments AdoptedGJ LaderaОценок пока нет
- Oath of Office (Officers' Copy)Документ12 страницOath of Office (Officers' Copy)Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- 2014 Question # 3, (4%)Документ3 страницы2014 Question # 3, (4%)Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Marine mammals and fisherfolk challenge oil exploration in Tañon StraitДокумент13 страницMarine mammals and fisherfolk challenge oil exploration in Tañon StraitTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- NOTES Civil Procedure DeannWillard Riano PDFДокумент186 страницNOTES Civil Procedure DeannWillard Riano PDFEdmart Vicedo100% (1)
- Trust Receipts Law (PD 115)Документ5 страницTrust Receipts Law (PD 115)anailabucaОценок пока нет
- Suggested Answers To 2016 Remedial Law Bar ExamДокумент7 страницSuggested Answers To 2016 Remedial Law Bar ExamTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- A.M. No. 03-02-05-SCДокумент18 страницA.M. No. 03-02-05-SCTerence Valdehueza100% (1)
- Joseph E. Estrada, Petitioner, vs. Aniano DesiertoДокумент14 страницJoseph E. Estrada, Petitioner, vs. Aniano DesiertoTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- REMEDIAL EXAM BAR 2014Документ19 страницREMEDIAL EXAM BAR 2014Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- GДокумент8 страницGTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Bukidnon State University Law Students' Society OathsДокумент3 страницыBukidnon State University Law Students' Society OathsTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- REMEDIAL EXAM BAR 2014Документ19 страницREMEDIAL EXAM BAR 2014Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Military Abuse Case Decided by Writ of AmparoДокумент2 страницыMilitary Abuse Case Decided by Writ of AmparoTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Cañiza v. Court of Appeals Alamayri v. The PabalesДокумент15 страницCañiza v. Court of Appeals Alamayri v. The PabalesTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- 2014Документ10 страниц2014Terence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- General Considerations: Chapter OneДокумент1 страницаGeneral Considerations: Chapter OneTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Lawyer's Duty to Inform Clients of Case StatusДокумент4 страницыLawyer's Duty to Inform Clients of Case StatusTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Civil Liability Arising From DelictДокумент21 страницаCivil Liability Arising From DelictTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- A Law Each DayДокумент3 страницыA Law Each DayTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Torts - DigestДокумент8 страницTorts - DigestTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- A.M. No. 03-02-05-SCДокумент18 страницA.M. No. 03-02-05-SCTerence Valdehueza100% (1)
- IncorporationДокумент4 страницыIncorporationnijurokuОценок пока нет
- IncorporationДокумент4 страницыIncorporationnijurokuОценок пока нет
- Application of Civil Code provisions on effectivity of laws and waiver of rightsДокумент13 страницApplication of Civil Code provisions on effectivity of laws and waiver of rightsTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- ConcealmentДокумент15 страницConcealmentTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет
- Lacson v. ReyesДокумент2 страницыLacson v. ReyesMaya Julieta Catacutan-Estabillo67% (3)
- Torts - DigestДокумент6 страницTorts - DigestTerence ValdehuezaОценок пока нет