Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form3 V 4.0
Загружено:
sEcZxОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form3 V 4.0
Загружено:
sEcZxАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cisco Networking Academy
Close Window
Assessment System Exam Viewer - ERouting Final Exam - CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)
Below you will find the assessment items as presented on the exam as well as the scoring rules associated with the item. Cisco Networking Academy content is copyrighted and the unauthorized posting, distribution or sharing of this exam content is prohibited. 1 Using default settings, what is the next step in the router boot sequence after the IOS loads from flash? Perform the POST routine. Search for a backup IOS in ROM. Load the bootstrap program from ROM. Load the running-config file from RAM. Locate and load the startup-config file from NVRAM. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 5 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 1.1.4 Router Boot-up Process A network administrator is in charge of two separate networks that share a single building. What device will be required to connect the two networks and add a common connection to the Internet that can be shared? hub
router access point Ethernet switch Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 1.1.1 Routers are Computers Which two router component and operation pair are correctly described? (Choose two.) DRAM - loads the bootstrap
RAM - stores the operating system Flash - executes diagnostics at bootup NVRAM - stores the configuration file ROM - stores the backup configuration file POST - runs diagnostics on hardware modules Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 4 and Option 6 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.1.2 Router CPU and Memory
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
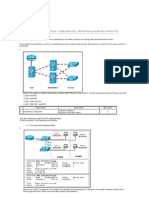
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are properly configured with default configurations and are running the OSPF routing protocol. The network is fully converged. A host on the 192.168.3.0/24 network is communicating with a host on the 192.168.2.0/24 network. Which path will be used to transmit the data? The data will be transmitted via R3-R2. The data will be transmitted via R3-R1-R2. The traffic will be load-balanced between two paths one via R3-R2, and the other via R3-R1-R2. The data will be transmitted via R3-R2, and the other path via R3-R1-R2 will be retained as the backup path. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
3.3.3 Load Balancing
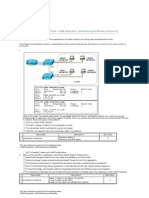
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R3 use different routing protocols with default administrative distance values. All devices are properly configured and the destination network is advertised by both protocols. Which path will be used to transmit the data packets from PC1 to PC2? The packets will travel via R2-R1. The packets will travel via R2-R3. The traffic will be load-balanced between two paths via R2-R1 and via R2-R3. The packets will travel via R2-R3, and the other path via R2-R1 will be retained as the backup path. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
3.3.3 Load Balancing
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. How many routes are both level 1 and qualify for use as an ultimate route? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 8.1.3 Level 1 Routes In a lab test environment, a router has learned about network 172.16.1.0 through four different dynamic routing processes. Which route will be used to reach this network? D 172.16.1.0/24 [90/2195456] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:09, Serial0/0/0
O 172.16.1.0/24 [110/1012] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:22, Serial0/0/0 R 172.16.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0/0 I 172.16.1.0/24 [100/1192] via 192.168.200.1, 00:00:09, Serial0/0/0 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
5.5.2 Propagating the Default Route in RIPv1
Refer to the exhibit. The results of the show ip route command are displayed in the graphic for Router R2. Which route will be selected for a packet with a destination address of 10.1.4.1? route to 0.0.0.0/0 route to 10.1.0.0/22 route to 10.1.0.0/23 route to 10.1.0.0/24 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas:
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.5.2 Modifying Static Routes
Which statement is true regarding routing metrics? All routing protocols use the same metrics. EIGRP uses bandwidth as its only metric. Routers compare metrics to determine the best route. The larger metric generally represents the better path. Observable Description 2 points for Option 3 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
correctness of response
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 3.3.1 Purpose of a Metric 10 A router has learned two equal cost paths to a remote network via the EIGRP and RIP protocols. Both protocols are using their default configurations. Which path to the remote network will be installed in the routing table? the path learned via EIGRP
the path learned via RIP the path with the highest metric value both paths with load balancing Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 9.1.8 Administrative Distance 11 You have been asked to explain converged networks to a trainee. How would you accurately describe a converged network? A network is converged when all routers have formed an adjacency.
A network is converged immediately after a topology change has occurred. A network is converged when all routers flush the unreachable networks from their routing tables. A network is converged after all routers share the same information, calculate best paths, and update their routing tables. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 3.2.3 Distance Vector and Link State 12 Which three statements about routing protocols are true? (Choose three.) EIGRP supports unequal cost load balancing.
RIP cannot be configured to allow classless routing. OSPF elects designated routers on multiaccess links. RIP does not advertise a route beyond a hop count of 15. EIGRP uses broadcast traffic to establish adjacencies with its neighbors. OSPF can convergence more quickly because it can find a feasible successor in its topology table when a successor route goes down. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 1, Option 3, and Option 4 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 3
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
3.2.2 IGP and EGP
13
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. What are two of the routes added to the routing table of R1? (Choose two.) R 172.16.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.3.0, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.2.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/1 R 192.168.9.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 R 192.168.100.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0 Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 2 and Option 4 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
5.3.3 Verifying RIP: debug ip rip
14
Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured the interfaces on the Router, but upon inspection discovers that interface FastEthernet0/1 is not functioning. Which action will most likely correct the problem with FastEthernet0/1? A clock rate should be added to the interface configuration. The subnet mask should be added to the interface configuration. An interface description needs to be added to the interface configuration. The no shutdown command needs to be added to the interface configuration. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.2.2 Basic Router Configuration
15
Refer to the exhibit. A device is required to complete the connection between router R1 and the WAN. Which two devices can be used for this? (Choose two.) a CSU/DSU device a modem an Ethernet switch a hub a bridge
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Observable 1 correctness of response
Description Option 1 and Option 2 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required.
Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 2.2.5 Examining Router Interfaces 16 Which port should a terminal emulator be connected to in order to access a router without network connectivity? T1
serial console FastEthernet Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 3 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.1.5 Router Interfaces
17
Refer to the exhibit. Which two facts can be derived from this output? (Choose two.) Three network devices are directly connected to Router2. The serial interface between Router2 and Router3 is up. Router1 and Router3 are directly connected. Six devices are up and running on the network. Layer 3 functionality between routers is configured properly. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 1 and Option 2 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 2.3.4 Using CDP for Network Discovery 18 Which component is typically used to connect the WIC interface of a router to a CSU/DSU? V.35 cable
RJ-45 adapter crossover cable straight-through cable Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.2.5 Examining Router Interfaces
19
Refer to the exhibit. All interfaces are addressed and functioning correctly. The network administrator runs the tracert command on host A. Which two facts could be responsible for the output of this command? (Choose two.) The gateway for Host A is missing or improperly configured. The gateway for Host B is missing or improperly configured. The entry for 192.168.1.0/24 is missing from the routing table of R1. The entry for 192.168.1.0/24 is missing from the routing table of R2. The entry for 192.168.2.0/24 is missing from the routing table of R1. The entry for 192.168.2.0/24 is missing from the routing table of R2. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 4 and Option 5 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.7.2 Troubleshooting a Missing Route
20
Refer to the exhibit. The command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/0 is run on router R2. What are the two results of this command? (Choose two.) A static route will be updated in the routing table. The traffic from the Internet will be directed to R2. The traffic from the source network 172.16.0.0/22 will be blocked. The route will be specified as the default route for all networks not defined in the routing table. All the broadcasts will be forwarded via the S0/0/0 interface of R2. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 1 and Option 4 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.7.3 Solving the Missing Route
21
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. Although R2 is configured correctly, host A is unable to access the Internet. What are two static routes that can be configured on R1, either of which would enable Internet connectivity for host A? (Choose two.) ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Fa0/0 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Fa0/1 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.2 ip route 209.165.202.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1 Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 2 and Option 4 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 2.7.3 Solving the Missing Route 22 In which situation would a default static route be recommended? when connecting an edge router to the Internet
when variable length subnet masking is in effect when there is more than one valid route for a destination network when a destination network has a larger mask than any routes in the routing table Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.6.2 Default Static Route
23
Refer to the exhibit. A ping from R1 to 10.1.1.2 is successful, but a ping from R1 to 192.168.2.0 fails. What is the cause of this problem? There is no gateway of last resort at R1. The serial interface between the two routers is down.
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
A default route is not configured on R1. The static route for 192.168.2.0 is incorrectly configured. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.7.3 Solving the Missing Route
24
Refer to the exhibit. A static route was configured on router R1 to forward packets to the remote networks. During a network upgrade, the network administrator configured RIPv2 on all routers in the network. What will router R1 do with a packet that is sourced from PC1 and destined for PC3? The packet will be forwarded out the Serial0/0/0 interface via the static route. The packet will be forwarded out the FastEthernet0/1 interface via the static route. The packet will be forwarded out the Serial0/0/0 interface via the route that is learned through RIP. The packet will be forwarded out the FastEthernet0/1 interface via the route that is learned through RIP. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
2.4.4 Resolving to an Exit Interface
25
Refer to the exhibit. Which summarization should R1 use to advertise its networks to R2? 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.0.0/24 192.168.0.0/22 192.168.1.0/22 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 3 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
6.3.1 Route Summarization
26
Refer to the exhibit. Routers 1 and 2 are directly connected over a serial link. Pings are failing between the two routers. What change by the administrator will correct the problem? Set the encapsulation on both routers to PPP. Decrease the bandwidth on Serial 0/1/0 on router 2 to 1544. Change the cable that connects the routers to a crossover cable. Change the IP address on Serial 0/1/0 on router 2 to 192.168.0.1/30. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.2.2 Basic Router Configuration
27
Refer to the exhibit. Which host has a combination of IP address and subnet mask on the same network as Fa0/0 of Router1? host A host B host C host D Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.2.1 Implementing Basic Addressing Schemes
28
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. What does the highlighted entry for network 172.30.0.0/16 indicate? Automatic summarization is enabled on R1. The routing table of R2 contains only classful networks. R2 will reject this update. The routing protocol that is configured on both routers is RIPv1. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 7.2.2 Auto-summary and RIPv2 29 Which subnetting scheme will accommodate a network of 10 LANs, each of which contains a minimum of 2000 hosts? 10.0.0.0/10
10.0.0.0/11 172.16.0.0/18 172.16.0.0/20 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 6.1.1 Classful IP Addressing 30 How will a router that is configured with a classless routing protocol determine the subnet mask that should be assigned to routes that are learned from neighboring classless routers? The subnet mask that is included in the routing updates will be used.
The subnet mask of the interface that receives the update will be used. The subnet mask that is specified in the network command will be used. The class of the network in the update will determine the subnet mask that is used. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
6.1.4 Classless Routing Protocol
31
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. When troubleshooting a network, it is important to interpret the output of various router commands. On the basis of the exhibit, which three statements are true? (Choose three.) The missing information for Blank 1 is the command show ip route. The missing information for Blank 1 is the command debug ip route. The missing information for Blank 2 is the number 100. The missing information for Blank 2 is the number 120. The missing information for Blank 3 is the letter R. The missing information for Blank 3 is the letter C. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 1, Option 4, and Option 6 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 3
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 3.5.1 Identifying Elements of the Routing Table 32 Which statement correctly describes a feature of RIP? RIP is a link-state routing protocol.
RIP uses only one metrichop count for path selection. Advertised routes with hop counts greater than 10 are unreachable. Messages are broadcast every 10 seconds. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
5.1.2 RIPv1 Characteristics and Message Format
33
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 is unable to access the Internet. What is the cause of the problem? An incorrect IP address is configured between the two routers. No static route is configured on Router2. A routing loop has occurred. No routing protocol is configured on either of the two routers.
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Observable 1 correctness of response
Description 2 points for Option 3 0 points for any other option
Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 4.4.6 Split Horizon with Poison Reverse or Route Poisoning 34 Which mechanism helps to avoid routing loops by advertising a metric of infinity? route poisoning
split horizon hold-down timer triggered updates Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
4.4.6 Split Horizon with Poison Reverse or Route Poisoning
35
Refer to the exhibit. A packet enters Router1 with a destination IP of 172.16.28.121. Which routing table entry will be used to forward this packet to the destination address? 172.16.0.0/16 [1/0] via 192.168.0.1 172.16.0.0/20 [1/0] via 192.168.0.9 172.16.16.0/20 [1/0] via 192.168.0.17 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 3 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
8.2.2 Longest Match: Level 1 Network Routes
36
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are both configured with RIPv1. Beginning from global configuration mode, what comand or commands will eliminate RIP updates on the Ethernet segment of R2? R2# configure terminal R2(config)# router rip R2(config-router)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 R2# configure terminal
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
R2(config)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 R2# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 R2# configure terminal R2(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0 R2(config-if)# passive-interface FastEthernet0/0 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
5.3.4 Passive Interfaces
37
Refer to the exhibit. The routers in the exhibit are running the EIGRP routing protocol. What statement is true regarding how packets will travel from the 172.16.1.0/16 network to the 192.168.200.0/24 network? The router chooses the first path that it learned and installs only that route in the routing table. The router chooses the path with the lowest administrative distance and installs only that route in the routing table. The router chooses the highest routing ID based on the advertised network IP addresses and installs only that route in the routing table. The router installs all the equal cost paths in the routing table but sends packets out only one, holding the others in reserve in case the primary route goes down. The router installs all the equal cost paths in the routing table and performs equal cost load balancing to send packets out multiple exit interfaces. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 5 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
1.4.2 Best Path and Metric
38
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are directly connected via their serial interfaces and are both running the EIGRP routing protocol. R1 and R2 can ping the directly connected serial interface of their neighbor, but they cannot form an EIGRP neighbor adjacency. What action should be taken to solve this problem? Enable the serial interfaces of both routers. Configure EIGRP to send periodic updates. Configure the same hello interval between the routers.
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Configure both routers with the same EIGRP process ID. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
9.2.2 Autonomous Systems and Process IDs
39
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true based on the exhibited output? (Choose two.) All routes are stable. Each route has one feasible successor. The serial interface between the two routers is down. The administrative distance of EIGRP has been set to 50. The show ip eigrp topology command has been run on R1. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 1 and Option 5 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 9.5.2 Disabling Automatic Summarization 40 Which two statements are true about the EIGRP successor route? (Choose two.) It is saved in the topology table for use if the primary route fails.
It may be backed up by a feasible successor route. It is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to the destination. It is flagged as active in the routing table. After the discovery process has occurred, the successor route is stored in the neighbor table. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 2 and Option 3 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
9.4.1 DUAL Concepts
41
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. Which route will be removed from the routing table if manual EIGRP summarization is disabled the Serial0/0/0 interface of R3? 0.0.0.0/0 172.16.0.0/16 172.16.1.0/24 172.16.3.0/30 Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 9.2.6 Examining the Routing Table 42 When would the network administrator use the ip bandwidth-percent eigrp as-number percent command? when there is a low bandwidth connection
when the connection is on a shared medium when the connection is serial instead of Ethernet when the link is always busy Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 1 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 9.5.5 Fine-tuning EIGRP 43 Which statement correctly describes a feasible successor in EIGRP? It is a primary route that is stored in the routing table.
It is a backup route that is stored in the routing table. It is a primary route that is stored in the topology table. It is a backup route that is stored in the topology table. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
9.4.4 Topology Table: Successor and Feasible Successor
44
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is trying to determine why router JAX has no OSPF routes in its routing table. All routers are configured for OSPF area 0. From the JAX router, the administrator is able to ping its connected interfaces and the Fa0/1 interface of the ORL router but no other router interfaces. What is a logical step that the network administrator should take to troubleshoot the problem? Reboot the routers. Change the OSPF process ID on all of the routers to 0. Check to see if the cable is loose between ORL and JAX. Check to see if CDP packets are passing between the routers. Use show and debug commands to determine if hellos are propagating. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 5 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
10.1.6 Building the Link-State Packet
45
Refer to the exhibit. The hosts that are connected to R2 are unable to ping the hosts that are connected to R1. How can this problem be resolved? Configure the router ID on both routers. Configure the R2 router interfaces for area 0. Configure a loopback interface on both routers. Configure the proper subnet masks on the router interfaces. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
l 11.2.3 The network Command 46 What is the function of the OSPF LSU packet? used to confirm receipt of certain types of OSPF packets
used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers used to request more information about any entry in the BDR used to announce new OSPF information and to reply to certain types of requests Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l 11.1.3 OSPF Packet Types 47 All routers in a network are configured in a single OSPF area with the same priority value. No loopback interface has been set on any of the routers. Which secondary value will the routers use to determine the router ID? The highest MAC address among the active interfaces of the network will be used.
There will be no router ID until a loopback interface is configured. The highest IP address among the active FastEthernet interfaces that are running OSPF will be used. The highest IP address among the active interfaces will be used. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
11.2.4 OSPF Router ID
48
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting the OSPF network. The 10.10.0.0/16 network is not showing up in the routing table of Router1. What is the probable cause of this problem? The serial interface on Router2 is down. The OSPF process is not running on Router2. The OSPF process is configured incorrectly on Router1. There is an incorrect wildcard mask statement for network 10.10.0.0/16 on Router2. Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 4 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l l
11.2.5 Verifying OSPF 11.2.6 Examining the Routing Table
49
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Refer to the exhibit. If the router loopback interfaces, FastEthernet interfaces, and OSPF priorities are configured as shown, which router would win an OSPF DR election? A B C D Observable 1 correctness of response Description 2 points for Option 2 0 points for any other option Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
11.4.2 DR/BDR Election Process
50
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers that are configured for area 0 are unable to establish neighbor adjacency. Which two configuration changes should be made to resolve this problem? (Choose two.) Both the routers should be configured for the same router ID. The serial interface of both the routers must be configured in the same subnet. Both the routers should be configured as designated routers. Both the routers should be configured for the same process ID. The network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 command must be issued on both routers. Observable 1 correctness of response Description Option 2 and Option 5 are correct. 1 point for each correct option. 0 points if more options are selected than required. Max Value 2
This item references content from the following areas: CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts
l
11.2.5 Verifying OSPF
Reset View
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Cisco Networking Academy
Showing 1 of 1
Prev Page: 1
Next
Close Window
All contents copyright 2001-2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Privacy Statement and Trademarks.
mhtml:file://D:\CCNA Exploration\CCNA 2\CCNA 2 Final 3.mht
//
Вам также может понравиться
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GОт EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GОценок пока нет
- CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form2 V 4.0Документ19 страницCCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form2 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Документ20 страницCCNA 2 Exploration ERouting Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- ROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Документ12 страницROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (5)
- CCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form3 V 4.0Документ17 страницCCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form3 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- ROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Документ10 страницROUTE Chapter 5 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205Оценок пока нет
- DRSEnt Chapter 7 - CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise - Version 4.0Документ8 страницDRSEnt Chapter 7 - CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise - Version 4.0Jesusforgiveme100% (1)
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - SWITCH Chapter 7 - CCNP SWITCH (Version 6.0)Документ7 страницAssessment System: Take Assessment - SWITCH Chapter 7 - CCNP SWITCH (Version 6.0)sogunmola100% (1)
- ROUTE Chapter 1 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Документ5 страницROUTE Chapter 1 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (7)
- En ENetwork IPTM v4040Документ38 страницEn ENetwork IPTM v4040abdelhf1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Документ9 страницChapter 5 Exam - Ccnp-Tshoot Sp2016Eddie83100% (11)
- CCNA2Документ374 страницыCCNA2pinky_armsОценок пока нет
- E1 PTAct 10-7-1 InstructorДокумент3 страницыE1 PTAct 10-7-1 InstructorDamian SandakОценок пока нет
- Ccna 2Документ13 страницCcna 2Koen JansenОценок пока нет
- Cisco CCNP Semester 5 Moduel 6Документ8 страницCisco CCNP Semester 5 Moduel 6msleibi2003Оценок пока нет
- 1en DHomesb ILM v4030Документ148 страниц1en DHomesb ILM v4030Murash javaidОценок пока нет
- CCNP Switch - Chapter 7Документ12 страницCCNP Switch - Chapter 7armani_delato100% (3)
- Final Discovery 3 100%Документ20 страницFinal Discovery 3 100%Trần Ngọc Ngàn100% (2)
- 4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsДокумент3 страницы4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDaniel OsorioОценок пока нет
- 3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationДокумент17 страниц3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí0% (2)
- CCNA Discovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final ExamДокумент17 страницCCNA Discovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final ExamJesusforgivemeОценок пока нет
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANДокумент5 страниц6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteОценок пока нет
- CCNP 3 Final Exam v6.0Документ23 страницыCCNP 3 Final Exam v6.02lkopp3n50% (2)
- At Tshoot 642-832Документ249 страницAt Tshoot 642-832_asdffgОценок пока нет
- Lab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseДокумент5 страницLab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseRano RenoОценок пока нет
- ENetwork Final Exam CCNA 1 4Документ22 страницыENetwork Final Exam CCNA 1 4Jay LeeОценок пока нет
- DHomesb Chapter 1 - CCNA DiscoveryДокумент6 страницDHomesb Chapter 1 - CCNA DiscoveryAbdullah Al HawajОценок пока нет
- CCNA Routing and Switching S3Документ16 страницCCNA Routing and Switching S3FiskoaujОценок пока нет
- 4 2 4 4Документ5 страниц4 2 4 4john67% (3)
- Lab 07 RIP ConfigurationДокумент12 страницLab 07 RIP Configurationmuhammad.mursleen025Оценок пока нет
- Lab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterДокумент8 страницLab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- Lab 4 Configure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN RoutingДокумент14 страницLab 4 Configure Router On A Stick Inter VLAN RoutingShara MerinОценок пока нет
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesОт EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Erouting Final Exam - AДокумент35 страницErouting Final Exam - Atschneider2Оценок пока нет
- ERouting Final Exam - CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) (rbm668)Документ19 страницERouting Final Exam - CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) (rbm668)rbm668Оценок пока нет
- CCNA2 Chapter 3 v2Документ3 страницыCCNA2 Chapter 3 v2im_terabyte2291Оценок пока нет
- Download: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Документ9 страницDownload: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Router_MaestroОценок пока нет
- 100% Correct: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Документ77 страниц100% Correct: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Oueslati FakherОценок пока нет
- Ccna Discovery4.0 Final 3rd ModuleДокумент13 страницCcna Discovery4.0 Final 3rd ModuleManmohan gargОценок пока нет
- CCNA Answers - CCNA Exam - CCNA ExamsДокумент32 страницыCCNA Answers - CCNA Exam - CCNA ExamsAldrin RimongОценок пока нет
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Документ19 страницCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCENT Practice Certification Exam1Документ31 страницаCCENT Practice Certification Exam1Test5804Оценок пока нет
- Practice Exam AnswersДокумент20 страницPractice Exam AnswersJay MulwaniОценок пока нет
- CCNA2 Final Exam 2013 - Version1 - ZeuxidisДокумент16 страницCCNA2 Final Exam 2013 - Version1 - ZeuxidisVelito GujamoОценок пока нет
- CCNA2 Final Mar 2010: CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam PracticeДокумент21 страницаCCNA2 Final Mar 2010: CCNA Cisco Routing Protocols and Concepts Final Exam Practicetuananh0788Оценок пока нет
- CCNA3 Practice FinalДокумент34 страницыCCNA3 Practice Finaldemon332Оценок пока нет
- Ccna Discovery4.0 Final 3rd ModuleДокумент12 страницCcna Discovery4.0 Final 3rd ModuleManmohan garg0% (1)
- CCNA 2 (v5.1 + v6.0) Final Exam Answers FullДокумент50 страницCCNA 2 (v5.1 + v6.0) Final Exam Answers Fullmuhammad hafis100% (1)
- 100% Correct: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Документ19 страниц100% Correct: Erouting Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Rodrigo DominguesОценок пока нет
- CCNA 2 v60 Final Exam Answers 2019 Routing Amp Switching EssentialsДокумент71 страницаCCNA 2 v60 Final Exam Answers 2019 Routing Amp Switching EssentialsMaría ArmijosОценок пока нет
- Scribd Explore Community Upload A Document: Search Books, Presentations, Business, Academics..Документ14 страницScribd Explore Community Upload A Document: Search Books, Presentations, Business, Academics..olive103Оценок пока нет
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form3 V 4.0Документ22 страницыCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form3 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 2 v60 Final Exam Answers 2019 Routing Amp Switching EssentialsДокумент76 страницCCNA 2 v60 Final Exam Answers 2019 Routing Amp Switching EssentialsSathyaa narayananОценок пока нет
- CCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Документ10 страницCCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Tanase CristianОценок пока нет
- CCNA 2:module 3: Options With Highlight Colours Are Correct AnswerДокумент3 страницыCCNA 2:module 3: Options With Highlight Colours Are Correct Answertrp2529100% (2)
- CCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Документ17 страницCCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form2 V 4.0Документ17 страницCCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form2 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Документ17 страницCCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form3 V 4.0Документ22 страницыCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form3 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA Discovery V 4.1 DHomesb Final Exam &100% Answers Forms A&B&CДокумент57 страницCCNA Discovery V 4.1 DHomesb Final Exam &100% Answers Forms A&B&CsEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form2 V 4.0Документ21 страницаCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form2 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- CCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0Документ19 страницCCNA 1 Exploration ENetwork Final Exam Form1 V 4.0sEcZxОценок пока нет
- Indonesia Form Paspor WNIДокумент4 страницыIndonesia Form Paspor WNIsEcZxОценок пока нет
- Kapitel 2 Svar - 2Документ6 страницKapitel 2 Svar - 2sEcZxОценок пока нет
- Paros User GuideДокумент13 страницParos User Guidenshuai100% (1)
- PQCДокумент77 страницPQCAnkit MittalОценок пока нет
- ENSC427 Team6 ReportДокумент22 страницыENSC427 Team6 ReportAnonymous TTVlXoОценок пока нет
- Basic Soil and Water RelationsДокумент2 страницыBasic Soil and Water RelationsFelizardo GuiananОценок пока нет
- AirFiber X UGДокумент76 страницAirFiber X UGJuan Carlos RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Arista ACP Thinmanager Ready Industrial Thin Client WhitepaperДокумент8 страницArista ACP Thinmanager Ready Industrial Thin Client Whitepaperali77sgОценок пока нет
- Section 3 Ele. RevisedДокумент40 страницSection 3 Ele. RevisedfiraolОценок пока нет
- Green ConstructionДокумент19 страницGreen ConstructionJohn ChristopherОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION Railway ReservationДокумент61 страницаINTRODUCTION Railway ReservationSanjiv GautamОценок пока нет
- Thesis 3 PDFДокумент40 страницThesis 3 PDFMohamed Abrar SALAMОценок пока нет
- AEG Ninja RulebookДокумент16 страницAEG Ninja RulebookJustin Walk Lee100% (1)
- 8255AДокумент3 страницы8255Ababa212Оценок пока нет
- DTDC ListДокумент102 страницыDTDC Listsaubhagsinh sodha100% (2)
- Dbms 2markДокумент13 страницDbms 2markdevmeczОценок пока нет
- ITECH1102 Networking & SecurityДокумент6 страницITECH1102 Networking & SecuritySarah EvanОценок пока нет
- Bid Docs Cladding WorksДокумент8 страницBid Docs Cladding WorksVholts Villa VitugОценок пока нет
- R.C.C Pier Design of BridgeДокумент42 страницыR.C.C Pier Design of BridgeMd BIN HASAN100% (1)
- Staad Example NewДокумент58 страницStaad Example Newsusarlasaicharan100% (1)
- IP InfoДокумент8 страницIP InfoAbadit AliОценок пока нет
- Hygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFДокумент55 страницHygene EPIHANIOU Faucets INT EN-1 PDFattikourisОценок пока нет
- Stronghold Crusader Multiplayer Demo ReadmeДокумент6 страницStronghold Crusader Multiplayer Demo ReadmeNara ZweiОценок пока нет
- MSP 430 F 2132Документ81 страницаMSP 430 F 2132rickseltОценок пока нет
- The Pink CityДокумент7 страницThe Pink CityKaur SimranОценок пока нет
- Catalogue Modulo En-20372 PDFДокумент32 страницыCatalogue Modulo En-20372 PDFflorinОценок пока нет
- EUROPA 2 - EuroconfortДокумент4 страницыEUROPA 2 - EuroconfortPeradОценок пока нет
- Austral DeckTechnical GuideДокумент31 страницаAustral DeckTechnical Guidebappy01_cuet9921100% (1)
- Saroj Bluebells RERA Area StatementДокумент10 страницSaroj Bluebells RERA Area StatementVeena SОценок пока нет
- Consumption StatementДокумент7 страницConsumption StatementRonnie SinghОценок пока нет
- Huawei U2000 Performance KPI On NMSДокумент5 страницHuawei U2000 Performance KPI On NMSfjbsantiagoОценок пока нет
- Report of Monument and PatternsДокумент23 страницыReport of Monument and PatternsMAHEEN FATIMAОценок пока нет
- Project A Civil Dire DawaДокумент46 страницProject A Civil Dire Dawaabel shimelesОценок пока нет