Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Shaft Current Supressor Application of Static Excitation
Загружено:
Juan Fernando UbeiraИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Shaft Current Supressor Application of Static Excitation
Загружено:
Juan Fernando UbeiraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ANSI C50.
13 offer guidelines as indicated in Table 2 that show the permissible short time overload current plotted against time. When excitation support is being considered, the following additional questions must be addressed. What is the generator short circuit current capability and permissible time allowed? Is the switchgear designed to handle the possible sustained P short circuit .U. current? Is sufficient machine data available to design the excitation system? What is the maximum allowable overcurrent time? Has there been proper consideration of relay coordination and tripping?
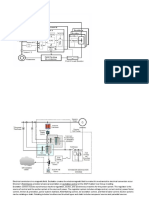
SHAFT VOLTAGE ON CYLINDRICAL TYPE TURBINE GENERATORS Cylindrical rotor generators may have a voltage that exists between a rotating shaft and the stationary parts of the turbine-generator. Voltages, if sufficiently high, can produce a current between the rotor and the stationary parts to ground by way of the insulated bearing. See Figure 15.
Figure 15: Shaft Voltage Suppression These voltages are called shaft voltages. If not minimized, they can dramatically shorten the operating life of the insulated bearings. Shaft voltages are caused by magnetic irregularities in the generator long shaft and appear most commonly on high speed cylindrical generators. In these applications, it has been found that bearing deterioration (pitting) originates from electrostatic discharges. The electrostatic discharges can be caused by a number of noise sources. One of the sources can be the switching thyristors in the static exciter power rectifier bridge.
16
One solution to this problem involves adding a grounding brush seated at the end of the shaft that connects to ground. Stray currents will flow through the grounding brush rather than through the insulated bearing. This system, however, requires regular maintenance checks to ensure good surface contact. Today, resistor and capacitor snubber circuits are used to send high frequency noise to ground. See Figures 2 and 4. The snubber circuit consist of a symmetrical resistor and capacitor network connected across the field with a center tap to ground. The snubber circuit responds to high frequency noise generated by the power thyristors. The snubber circuit provides a low impedance circuit path that shunts high frequency currents caused by the thyristors to ground. PACKAGED EXCITATION SYSTEMS Many power plants today are totally automated because of their isolated locations. In these applications, the excitation system must be responsive to remote commands from the supervisory station. Due to their remote location, the basic static exciter/regulator package is usually equipped with other excitation accessories. Today, these accessories are enabled by software that allows easy implementation. The additional functions to ensure the continuity of power and integrity of the system during system disturbances. A system develops from a basic static exciter/regulator to one that includes excitation limiters, power factor controller, semiconductor failure indicators and remote control based upon the needs of the generator and its importance to the mill. See Figure 16 and Figure 1.
Figure 16: Static Exciter Cabinet
17
Вам также может понравиться
- Industrial Power System Protection Series - Differential ProtectionДокумент9 страницIndustrial Power System Protection Series - Differential Protectionlakthant7967Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Power Systems: 1.1: A.C Transmission SystemДокумент23 страницыIntroduction To Power Systems: 1.1: A.C Transmission Systemkar1740Оценок пока нет
- Protection Of: AlternatorДокумент27 страницProtection Of: AlternatorDev KumarОценок пока нет
- Hartmann 2019Документ23 страницыHartmann 2019juanОценок пока нет
- Static Excitation System-AMTECHДокумент24 страницыStatic Excitation System-AMTECHsssduduОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 QuestionsДокумент8 страницChapter 7 QuestionsNicole Irene Dela Pena67% (3)
- ExcitationДокумент12 страницExcitationDdumbaОценок пока нет
- Protection of Alternators and TransformersДокумент19 страницProtection of Alternators and TransformersGabriel UdokangОценок пока нет
- Evaluating Motor and Transformer Inrush CurrentsДокумент4 страницыEvaluating Motor and Transformer Inrush CurrentsMind of BeautyОценок пока нет
- Understanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsДокумент12 страницUnderstanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsArni 2020Оценок пока нет
- Double Fed Induction Generator (Dfig)Документ5 страницDouble Fed Induction Generator (Dfig)sravanОценок пока нет
- Damping of Sub Synchronous Resonance Using SSSC Based PWM Hysteresis ControllerДокумент9 страницDamping of Sub Synchronous Resonance Using SSSC Based PWM Hysteresis ControllerrajapandiyaОценок пока нет
- Generator: Over VoltagesДокумент10 страницGenerator: Over VoltagesKoushik BaruaОценок пока нет
- Wind Power 2008Документ11 страницWind Power 2008Dimas_pradethaОценок пока нет
- Ground Differential Protection Guide BaslerДокумент9 страницGround Differential Protection Guide BaslerBill CaiОценок пока нет
- User's Manual of Construction: Power Grid Corporation of India LimitedДокумент59 страницUser's Manual of Construction: Power Grid Corporation of India Limitedparamgagan100% (1)
- Excitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyДокумент12 страницExcitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyAmeer Hamza100% (1)
- Fig. 1a. Overlaid Plot of Voltage (Blue) and Rms Current (Red) of A Motor Start As A Function ofДокумент5 страницFig. 1a. Overlaid Plot of Voltage (Blue) and Rms Current (Red) of A Motor Start As A Function ofTapi SkОценок пока нет
- (ENGLISH) Material 1sp 2sem 1moduleДокумент63 страницы(ENGLISH) Material 1sp 2sem 1moduleКристина ШабалинскаяОценок пока нет
- Fuji Generators FER-14-01-01-1968Документ7 страницFuji Generators FER-14-01-01-1968alan.edwards7282Оценок пока нет
- Electric CalДокумент20 страницElectric CalRisky RiyanshОценок пока нет
- Marpower Week 5 To 8Документ8 страницMarpower Week 5 To 8Haeisy SimsuangcoОценок пока нет
- AC Generator and Motor ProtectionДокумент76 страницAC Generator and Motor ProtectionAtif Husayn100% (1)
- IEEE-FACTs & HVDC - Modern Countermeasures To BlackoutsДокумент10 страницIEEE-FACTs & HVDC - Modern Countermeasures To BlackoutsGustavo AguayoОценок пока нет
- Monthly Progress Report 20 May 20Документ25 страницMonthly Progress Report 20 May 20SBILALAHMEDОценок пока нет
- Understanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsДокумент12 страницUnderstanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsJose PradoОценок пока нет
- Speed Control of 3 Phase Ac Induction Motor Using Micro 2407Документ58 страницSpeed Control of 3 Phase Ac Induction Motor Using Micro 2407sundarspace100% (2)
- Monitoring of Generator Stator End - Winding Vibration How Reliable Are Existing Monitoring Systems?Документ9 страницMonitoring of Generator Stator End - Winding Vibration How Reliable Are Existing Monitoring Systems?Kevin Luis Perez QuirozОценок пока нет
- 109 Model Question Paper Power System PlaningДокумент23 страницы109 Model Question Paper Power System PlaningareejОценок пока нет
- Frequency RelayДокумент9 страницFrequency RelayLanya AramОценок пока нет
- 25asynchronous Machine Modeling Using Simulink Fed by PWM Inverter Copyright IjaetДокумент9 страниц25asynchronous Machine Modeling Using Simulink Fed by PWM Inverter Copyright IjaetPattrik SmartОценок пока нет
- Applications-Light Dimmer, Excitation System and Solar PV System in Phase Controlled ConvertersДокумент7 страницApplications-Light Dimmer, Excitation System and Solar PV System in Phase Controlled ConvertersSRAVAN KUMAR.M EEE100% (1)
- What Is Excitation System - Definition & Types of Excitation System - Circuit GlobeДокумент11 страницWhat Is Excitation System - Definition & Types of Excitation System - Circuit GlobeSabaMannan123Оценок пока нет
- NBVДокумент4 страницыNBVD SОценок пока нет
- Relays - Open ElectricalДокумент5 страницRelays - Open Electricalstalin63Оценок пока нет
- Transient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerДокумент78 страницTransient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerRagesh OdungattuОценок пока нет
- GCBДокумент10 страницGCBRavishankar.AzadОценок пока нет
- The Copperbelt University: School of TechnologyДокумент40 страницThe Copperbelt University: School of TechnologyMU Len GAОценок пока нет
- Full Paper P-031Документ9 страницFull Paper P-031SUBRATA BISWASОценок пока нет
- Generator ,-3Документ16 страницGenerator ,-3IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Electric Motor IT ReportДокумент9 страницElectric Motor IT ReportVincentОценок пока нет
- 5695 45 165 DC Motor Speed Control Using Magnetic AmplifierДокумент8 страниц5695 45 165 DC Motor Speed Control Using Magnetic AmplifierNexus GoddОценок пока нет
- Excitation SystemsДокумент15 страницExcitation SystemsSahiti DarikaОценок пока нет
- Substation Design DataДокумент10 страницSubstation Design DataSemifallen100% (1)
- Gen - Prot WcpyrtДокумент17 страницGen - Prot WcpyrtAshwinKumar GoswamiОценок пока нет
- Overview of Industrial Motor Control SystemsДокумент8 страницOverview of Industrial Motor Control Systemsiwuo4797Оценок пока нет
- Unit V 1. Define Matrix Converter and Mention It Application. Matrix Converter ConceptДокумент5 страницUnit V 1. Define Matrix Converter and Mention It Application. Matrix Converter Conceptsambu112Оценок пока нет
- File Name StamperДокумент35 страницFile Name StampersohaibazamОценок пока нет
- Electrical Grounding A Key Design Consideration For Subsea Booster Pumps and UmbilicalsДокумент7 страницElectrical Grounding A Key Design Consideration For Subsea Booster Pumps and UmbilicalsDiogo SilvaОценок пока нет
- 03 Definition - Classification of Power System Stability IEEE-CIGRE Joint Task Force On Stability Terms and DefinitionsДокумент63 страницы03 Definition - Classification of Power System Stability IEEE-CIGRE Joint Task Force On Stability Terms and DefinitionsRosa Elvira Montalvo MartínezОценок пока нет
- Excitation Systems of Synchronous MachinesДокумент15 страницExcitation Systems of Synchronous Machinesspark_star100% (1)
- HAL Project ReportДокумент19 страницHAL Project ReportPandu DonОценок пока нет
- Classification of FACTSДокумент8 страницClassification of FACTSEngr Imtiaz Hussain GilaniОценок пока нет
- A Review of Benefits of FACTS Devices in Power System: AbstractДокумент4 страницыA Review of Benefits of FACTS Devices in Power System: AbstractSaleemОценок пока нет
- Static Excitation SystemДокумент61 страницаStatic Excitation SystemSiva Kumar Tutika100% (8)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionОт EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesОт EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesОценок пока нет
- LCD TV: Service ManualДокумент51 страницаLCD TV: Service ManualvideosonОценок пока нет
- Advances in Bipolar Junction Transistor ModelingДокумент4 страницыAdvances in Bipolar Junction Transistor Modelingelectroamit123Оценок пока нет
- FT-817 Softw Adjustment Menu Tabela Com Valores DefaultДокумент6 страницFT-817 Softw Adjustment Menu Tabela Com Valores DefaultDaniel CoslovskyОценок пока нет
- 05 LT - SS1005 - E01 - 1 ZXSDR R8882 L268 Hardware Structure 31Документ31 страница05 LT - SS1005 - E01 - 1 ZXSDR R8882 L268 Hardware Structure 31Tharindu WijegoonasekaraОценок пока нет
- SCR3310v2.0 USB Smart Card ReaderДокумент2 страницыSCR3310v2.0 USB Smart Card ReaderDaniel DinisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03completeДокумент56 страницChapter 03completeMohammad SubhanОценок пока нет
- Theoretical Analysis of DC Link Capacitor Current Ripple Reduction in The HEV DC-DC Converter and Inverter System Using A Carrier Modulation MethodДокумент8 страницTheoretical Analysis of DC Link Capacitor Current Ripple Reduction in The HEV DC-DC Converter and Inverter System Using A Carrier Modulation MethodVanHieu LuyenОценок пока нет
- Bandwidth PDFДокумент5 страницBandwidth PDFaxelernesto2654Оценок пока нет
- Design and Fabrication of Automatic Railway Track Crack Detection SystemДокумент6 страницDesign and Fabrication of Automatic Railway Track Crack Detection SystemGRD Journals100% (1)
- Mipi DsiДокумент79 страницMipi Dsiback_to_batteryОценок пока нет
- 061 - ME8791, ME6702 Mechatronics - Important QuestionsДокумент7 страниц061 - ME8791, ME6702 Mechatronics - Important QuestionsSamsudeen AОценок пока нет
- Msa st300Документ2 страницыMsa st300SomvirОценок пока нет
- Sony DSR 300 CamcorderДокумент12 страницSony DSR 300 Camcorderdherm8orОценок пока нет
- Transformer: Professor Mohamed A. El-SharkawiДокумент87 страницTransformer: Professor Mohamed A. El-SharkawiImran AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Danfoss Fotocellen 2018Документ2 страницыDanfoss Fotocellen 2018veunderОценок пока нет
- Prima LC 32u16Документ45 страницPrima LC 32u16fuwenhuiОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Guide For PICsДокумент27 страницTutorial Guide For PICsJose Smith100% (1)
- SIM800 Series at Command Manual V1.05Документ367 страницSIM800 Series at Command Manual V1.05Oscar Aiza VeramendiОценок пока нет
- Tic 126Документ4 страницыTic 126Walter FabianОценок пока нет
- LPC2148 Microcontroller Architecture andДокумент50 страницLPC2148 Microcontroller Architecture andManikandan AnnamalaiОценок пока нет
- Walker Ultrasonic Wind Sensor2080Документ2 страницыWalker Ultrasonic Wind Sensor2080bobОценок пока нет
- Katalog Pretvarača ABB ACS800Документ60 страницKatalog Pretvarača ABB ACS800klozet85Оценок пока нет
- Sleek Performance.: SLIM 7 (14")Документ4 страницыSleek Performance.: SLIM 7 (14")RaditОценок пока нет
- Phương Pháp Dòng Mắc LướiДокумент20 страницPhương Pháp Dòng Mắc LướiKise RyotaОценок пока нет
- Question Text: Ammeter Is Connected Parallel in A Device. Select One: True FalseДокумент15 страницQuestion Text: Ammeter Is Connected Parallel in A Device. Select One: True FalseMelanie BuñalesОценок пока нет
- 01 06 ByVention V03 enДокумент166 страниц01 06 ByVention V03 enjeronimost100% (2)
- AWD-100-500-Datasheet Antenna ExpertДокумент1 страницаAWD-100-500-Datasheet Antenna Expertson nguyenОценок пока нет
- EXTRACT - Single-Supply Half and Full-Wave RectifierДокумент1 страницаEXTRACT - Single-Supply Half and Full-Wave RectifierElantoineОценок пока нет
- DRPCДокумент7 страницDRPCSelvaraj JohnОценок пока нет
- Manual Televisor 55UH615TДокумент68 страницManual Televisor 55UH615Thernando.ggОценок пока нет