Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Student Copy 16 Lecture
Загружено:
vpetro250Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Student Copy 16 Lecture
Загружено:
vpetro250Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
7/14/2011
Acid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria
Chapter 16
Common ion effect:
The presence of a common ion ____________ the ionization of a weak acid or a weak base. Consider mixture of CH3COONa (strong electrolyte) and CH3COOH (weak acid).
CH3COONa (s) CH3COOH (aq)
1
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Na+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
2
Consider mixture of salt NaA and weak acid HA. NaA (s) HA (aq) [H+] = Na+ (aq) + A- (aq) H+ (aq) + A- (aq) Ka [HA] [A-] Ka = [H+][A-] [HA]
Buffer solution is a soln of: 1. 2.
[HA] -log [H+] = -log Ka - log [A-] -log [H+] [A-] = -log Ka + log [HA] pH = pKa + log pKa = -log Ka
3
A buffer soln has the ability to resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of either acid or base. Consider an equal molar mixture of CH3COOH and CH3COONa [conjugate base] [acid] Add strong acid H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) Add strong base OH- (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) CH3COOH (aq) CH3COO- (aq) + H2O (l)
4
[A-] pH = pKa + log [HA]
HCl HCl + CH3COO-
H+ + ClCH3COOH + ClTitration:
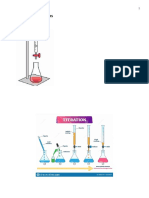
Titrations
Equivalence point Indicator
Slowly add base to unknown acid UNTIL The indicator changes color ( )
7/14/2011
Strong Acid-Strong Base Titrations Alternative Method of Equivalence Point Detection NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) OH- (aq) + H+ (aq) H2O (l) + NaCl (aq) H2O (l)
monitor pH
Weak Acid-Strong Base Titrations CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) CH3COOH (aq) + OH- (aq) At equivalence point (pH > 7): CH3COO- (aq) + H2O (l) OH- (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) CH3COONa (aq) + H2O (l) CH3COO- (aq) + H2O (l)
Strong Acid-Weak Base Titrations HCl (aq) + NH3 (aq) H+ (aq) + NH3 (aq) NH4+ (aq) + H2O (l) NH4Cl (aq) NH4Cl (aq) NH3 (aq) + H+ (aq)
At equivalence point (pH < 7):
10
Acid-Base Indicators
HIn (aq) H+ (aq) + In- (aq) [HIn] 10 Color of acid (HIn) predominates [In-] [HIn] 10 Color of conjugate base (In-) predominates [In-]
Solutions of Red Cabbage Extract
pH
11 12
7/14/2011
The titration curve of a strong acid with a strong base.
Which indicator(s) would you use for a titration of HNO2 with KOH ?
13
14
Solubility Equilibria
AgCl (s) Ksp = [Ag+][Cl-] MgF2 (s) Ag2CO3 (s) Ca3(PO4)2 (s) Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
Ksp is the solubility product constant Ksp = [Mg2+][F-]2 Ksp = [Ag+]2[CO32-] Ksp = [Ca2+]3[PO43-]2
Mg2+ (aq) + 2F- (aq) 2Ag+ (aq) + CO32- (aq) 3Ca2+ (aq) + 2PO43- (aq)
Dissolution of an ionic solid in aqueous solution: Q < Ksp Q = Ksp Q > Ksp
15 16
Molar solubility (mol/L): Solubility (g/L):
17
18
7/14/2011
The Common Ion Effect and Solubility
What is the molar solubility of AgBr in (a) pure water and (b) 0.0010 M NaBr?
pH and Solubility
The presence of a common ion decreases the solubility. Insoluble bases dissolve in acidic solutions Insoluble acids dissolve in basic solutions
remove add
Mg(OH)2 (s)
Mg2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) At pH less than 10.45
Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]2 = 1.2 x 10-11 Ksp = (s)(2s)2 = 4s3 4s3 = 1.2 x 10-11 s = 1.4 x 10-4 M [OH-] = 2s = 2.8 x 10-4 M pOH = 3.55 pH = 10.45
Lower [OH-] OH- (aq) + H+ (aq) H2O (l) Increase solubility of Mg(OH)2 At pH greater than 10.45 Raise [OH-] Decrease solubility of Mg(OH)2
20
Complex Ion Equilibria and Solubility
A complex ion Co2+ (aq) + 4Cl- (aq) CoCl2- (aq) 4
Effect of Complexation on Solubility AgNO3 + NaCl Add NH3
The formation constant or stability constant (Kf):
2[CoCl4 ] [Co2+][Cl-]4
2+ Co(H2O)6
CoCl24
Kf =
HCl
Kf
stability of complex
21
Ag(NH3)2+ AgCl
22
23
24
7/14/2011
Qualitative Analysis of Cations
Flame Test for Cations
lithium
25
sodium
potassium
copper
26
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Student Copy HW 13BДокумент2 страницыStudent Copy HW 13Bvpetro250Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Student Copy HW 14AДокумент4 страницыStudent Copy HW 14Avpetro250Оценок пока нет
- Student Copy HW 15AДокумент3 страницыStudent Copy HW 15Avpetro250Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 22 IsmДокумент14 страницChapter 22 Ismvpetro250Оценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Exam 1 Review SheetДокумент3 страницыExam 1 Review Sheetvpetro250Оценок пока нет
- Tuesday, July 05, 2011 9:25 PM: Unfiled Notes Page 1Документ3 страницыTuesday, July 05, 2011 9:25 PM: Unfiled Notes Page 1vpetro250Оценок пока нет
- Tuesday, July 05, 2011 6:54 PM: Unfiled Notes Page 1Документ3 страницыTuesday, July 05, 2011 6:54 PM: Unfiled Notes Page 1vpetro250Оценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsДокумент31 страницаIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsvpetro250Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Grade 5 - Investigatory ResearchДокумент17 страницGrade 5 - Investigatory ResearchPrimosebastian TarrobagoОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Chapter 9 Material ChangesДокумент6 страницChapter 9 Material ChangesFitria Istikomah DewiОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- MS SCI PS Unit 2 Chapter 7 Acids Bases and SolutionsДокумент36 страницMS SCI PS Unit 2 Chapter 7 Acids Bases and SolutionsgaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3 Acid and Base TitrationДокумент17 страницExperiment 3 Acid and Base TitrationRadhwanОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Product Analysis.Документ7 страницProduct Analysis.Jazzie D. CamañanОценок пока нет
- Pharmacuetics For The Students of Pharmacy Technicians (Category-B)Документ45 страницPharmacuetics For The Students of Pharmacy Technicians (Category-B)Naina's kitchencookingvediosОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Iwa 281 Lab 2Документ28 страницIwa 281 Lab 2Lp NgОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Cabbage ChemistryДокумент3 страницыCabbage ChemistryNeilОценок пока нет
- Grade 12 TH A WorksheetДокумент7 страницGrade 12 TH A Worksheetabdimoh7522Оценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Mccord H06 Buffers - Titrations SolutionsДокумент12 страницMccord H06 Buffers - Titrations SolutionsLois KimОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Techniques in Food Analysis Manual-4Документ109 страницTechniques in Food Analysis Manual-4JyothiОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Asam BasaДокумент75 страницAsam BasaRani PuspitaОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Uf Sem 1201314Документ9 страницUf Sem 1201314Dalton ChanОценок пока нет
- TITRATIONДокумент50 страницTITRATIONDawn WRein LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 - Acids, Bases, and Salts Powerpoint (Updated1)Документ46 страницUnit 8 - Acids, Bases, and Salts Powerpoint (Updated1)Rithik Visu100% (1)
- Enzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food LabДокумент21 страницаEnzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food Labmasre semagnОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 1 TitrimetryДокумент3 страницыLab Report 1 TitrimetryJoevelyn ValdezОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Unit 2 Assignment 1Документ32 страницыChemistry Unit 2 Assignment 1tamjidbhuiyan4075Оценок пока нет
- Red Cabbage Grade 9Документ12 страницRed Cabbage Grade 9Pia PlaysОценок пока нет
- 029 3105 Bunga Rombel1 Tugaske01Документ81 страница029 3105 Bunga Rombel1 Tugaske01Corinne SandersОценок пока нет
- QB - Ch10 - Eng 222Документ196 страницQB - Ch10 - Eng 222羅天佑Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Titration Guide MS - PG1682EN PDFДокумент36 страницTitration Guide MS - PG1682EN PDFCJ PrettyОценок пока нет
- Science Worksheet - SolutionДокумент15 страницScience Worksheet - SolutionZainul ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Word Version STUDENT NOTES PH (Titration) Curves and IndicatorsДокумент12 страницWord Version STUDENT NOTES PH (Titration) Curves and IndicatorsQuan nguyen minhОценок пока нет
- CHM 1061 Chemistry Lab ManualДокумент74 страницыCHM 1061 Chemistry Lab ManualTushar PatelОценок пока нет
- Double Indicator Titration Single FlaskДокумент3 страницыDouble Indicator Titration Single FlaskEricka PerezОценок пока нет
- Soil PH and Soil Acidity PDFДокумент16 страницSoil PH and Soil Acidity PDFManuel EscobarОценок пока нет
- CHM 222 Complexometric Titration PDFДокумент38 страницCHM 222 Complexometric Titration PDFGlory Usoro100% (1)
- Piochem Catalogue PDFДокумент98 страницPiochem Catalogue PDFمحمد التابعيОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit7 Ionic EquilibriaДокумент5 страницSem1 Unit7 Ionic Equilibriashehdilanun50% (2)