Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Also Known As Software Quality Control
Загружено:
nandini0528Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Also Known As Software Quality Control
Загружено:
nandini0528Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Also known as software quality control.
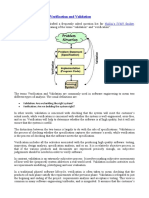
Validation checks that the product design satisfies or fits the intended usage (high-level checking) i.e., you built the right product. This is done through dynamic testing and other forms of review. According to the Capability Maturity Model (CMMI-SW v1.1),
Verification: The process of evaluating software to determine whether the products of a given development phase satisfy the conditions imposed at the start of that phase. [IEEESTD-610]. Validation: The process of evaluating software during or at the end of the development process to determine whether it satisfies specified requirements. [IEEE-STD-610]
In other words, validation ensures that the product actually meets the user's needs, and that the specifications were correct in the first place, while verification is ensuring that the product has been built according to the requirements and design specifications. Validation ensures that you built the right thing. Verification ensures that you built it right. Validation confirms that the product, as provided, will fulfill its intended use. From testing perspective:
Fault - wrong or missing function in the code. Failure - the manifestation of a fault during execution. Malfunction - according to its specification the system does not meet its specified functionality.
Within the modeling and simulation community, the definitions of validation, verification and accreditation are similar:
Validation is the process of determining the degree to which a model, simulation, or federation of models and simulations, and their associated data are accurate representations of the real world from the perspective of the intended use(s).[1] Accreditation is the formal certification that a model or simulation is acceptable to be used for a specific purpose.[1] Verification is the process of determining that a computer model, simulation, or federation of models and simulations implementations and their associated data accurately represents the developer's conceptual description and specifications.[1]
[edit] Related concepts
Both verification and validation are related to the concepts of quality and of software quality assurance. By themselves, verification and validation do not guarantee software quality; planning, traceability, configuration management and other aspects of software engineering are required.
[edit] Classification of methods
In mission-critical systems where flawless performance is absolutely necessary, formal methods can be used to ensure the correct operation of a system. However, often for non-mission-critical systems, formal methods prove to be very costly[citation needed] and an alternative method of V&V must be sought out. In this case, syntactic methods are often used.[citation needed]
[edit] Test cases
Main article: Test case A test case is a tool used in the process. Test cases are prepared for verification: to determine if the process that was followed to develop the final product is right. Test case are executed for validation: if the product is built according to the requirements of the user. Other methods, such as reviews, are used when used early in the Software Development Life Cycle provide for validation.
[edit] Independent Verification and Validation
Verification and validation often is carried out by a separate group from the development team; in this case, the process is called "Independent Verification and Validation", or IV&V.
[edit] Regulatory environment
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit 1:basic of Software TestingДокумент32 страницыUnit 1:basic of Software TestingMayur NarsaleОценок пока нет
- Deepraj Bhosale 181105016: Stqa Assignment-2 181105042Документ7 страницDeepraj Bhosale 181105016: Stqa Assignment-2 181105042AadilОценок пока нет
- Department of Computing Adama Science and Technology UniversityДокумент31 страницаDepartment of Computing Adama Science and Technology Universitybirhanu berihunОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Mode Real World System ValidationДокумент5 страницConceptual Mode Real World System ValidationGideon YegonОценок пока нет
- Quality Control Quality Assurance: Q60) Difference Between QA & QC?Документ4 страницыQuality Control Quality Assurance: Q60) Difference Between QA & QC?Somanath RugeОценок пока нет
- Testing NotesДокумент31 страницаTesting NotesanilОценок пока нет
- Stqa Assignment-2: Explain QA Activities in Waterfall Process With The Help of Neat DiagramДокумент7 страницStqa Assignment-2: Explain QA Activities in Waterfall Process With The Help of Neat DiagramAadilОценок пока нет
- Verification and ValidationДокумент4 страницыVerification and ValidationZamm ZammОценок пока нет
- The Difference Between Verification and Validation: NASA's IV&V FacilityДокумент4 страницыThe Difference Between Verification and Validation: NASA's IV&V FacilityZamm ZammОценок пока нет
- Syit Se Unit4Документ28 страницSyit Se Unit4HARRYОценок пока нет
- Verification/Validation/Certification: AbstractДокумент11 страницVerification/Validation/Certification: AbstractsivasakthitecegmailcОценок пока нет
- Department of Computing Adama Science and Technology UniversityДокумент31 страницаDepartment of Computing Adama Science and Technology Universitybirhanu berihunОценок пока нет
- Manual Testing Interview QuestionДокумент25 страницManual Testing Interview QuestionANIL KUMAR SAMALОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 PSHДокумент23 страницыUnit 1 PSHRaviraj ChoudhariОценок пока нет
- Software Testing Class 2Документ34 страницыSoftware Testing Class 2mujahadahОценок пока нет
- 112 Manual Testing Interview Questions Answers 1656817516 2Документ1 399 страниц112 Manual Testing Interview Questions Answers 1656817516 2Anurag JainОценок пока нет
- 112 Manual Testing Interview Questions & AnswersДокумент26 страниц112 Manual Testing Interview Questions & AnswersSuresh KonatalaОценок пока нет
- Basic Form of Testing Process: Verification and ValidationДокумент29 страницBasic Form of Testing Process: Verification and ValidationBudanam TejaswiniОценок пока нет
- Software Verification and ValidationДокумент21 страницаSoftware Verification and Validationumama amjadОценок пока нет
- Quality ManagementДокумент49 страницQuality ManagementnnoumanОценок пока нет
- Validation NotesДокумент13 страницValidation Notesjothi LОценок пока нет
- SE Chapter05 Conventional Methods For Software Engineering Student Copy1Документ16 страницSE Chapter05 Conventional Methods For Software Engineering Student Copy1Getachew ShambelОценок пока нет
- V & V Model1Документ7 страницV & V Model1ShivamОценок пока нет
- Software TestingДокумент16 страницSoftware TestingAhmad AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Manual Testing Interview QuestionsДокумент31 страницаManual Testing Interview QuestionsrameshОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент11 страницIntroductionltl9999Оценок пока нет
- Testing and Quality AssuranceДокумент5 страницTesting and Quality AssuranceBulcha MelakuОценок пока нет
- Software Quality AssuranceДокумент30 страницSoftware Quality Assuranceaishdesai31Оценок пока нет
- Testing LatestДокумент17 страницTesting LatestMd. Fahim SahrierОценок пока нет
- Verification and Validation TestingДокумент5 страницVerification and Validation TestingNida AhmedОценок пока нет
- 110+ Manual Testing Interview Questions For Freshers and ExpertsДокумент43 страницы110+ Manual Testing Interview Questions For Freshers and ExpertsKrishan ThakurОценок пока нет
- Manual PitanjaДокумент35 страницManual PitanjaKatarina MilojevicОценок пока нет
- Unit - Iv: Software TestingДокумент36 страницUnit - Iv: Software TestingHASAN KAMRAN (RA2011033010059)Оценок пока нет
- SE - UNIT3 Part2 PDFДокумент83 страницыSE - UNIT3 Part2 PDFPrathamesh KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Verification and Validation: Unit-VДокумент23 страницыVerification and Validation: Unit-Vgau_1119Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Software TestingДокумент37 страницUnderstanding Software Testingemmarvelous11Оценок пока нет
- Software Testing by Yogesh KhairnarДокумент13 страницSoftware Testing by Yogesh KhairnarYOGESH KHAIRNARОценок пока нет
- Why Do We Test Software?Документ38 страницWhy Do We Test Software?Phalguna SatishОценок пока нет
- Manual Testing Interview Questions 1704361238Документ187 страницManual Testing Interview Questions 1704361238DrushtidesaiОценок пока нет
- Introduction ToTestingДокумент23 страницыIntroduction ToTestingSatish PuthranОценок пока нет
- 11 Steps of Testing ProcessДокумент10 страниц11 Steps of Testing ProcessCheryl SanchisОценок пока нет
- Project Testing Plan - Guidelines: PurposeДокумент3 страницыProject Testing Plan - Guidelines: PurposepmpcvilleОценок пока нет
- Verification and ValidationДокумент3 страницыVerification and ValidationVineet ErankiОценок пока нет
- Basic-Software-Testing - 28 03 2015Документ29 страницBasic-Software-Testing - 28 03 2015Tapas GhoshОценок пока нет
- Software Test Life Cycle PPTXДокумент68 страницSoftware Test Life Cycle PPTXMr Sathesh Abraham Leo CSEОценок пока нет
- DocДокумент8 страницDocSripriya Venkatesh PrasadОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Software TestingДокумент42 страницыIntroduction To Software TestingRoxanaОценок пока нет
- TestingДокумент34 страницыTestingPSIEBELОценок пока нет
- Software Quality Assurance and QA IssuesДокумент21 страницаSoftware Quality Assurance and QA IssuesLij Melkam AbuhayОценок пока нет
- Advance Software Engineering: Course Code: MCSE503Документ10 страницAdvance Software Engineering: Course Code: MCSE503Humaun KabirОценок пока нет
- Software TestingДокумент16 страницSoftware TestingRUET Persistenet TrioОценок пока нет
- Software Testing Principles and Concepts: By: Abel AlmeidaДокумент16 страницSoftware Testing Principles and Concepts: By: Abel Almeidaavanianand542Оценок пока нет
- Software Quality AssuranceДокумент7 страницSoftware Quality Assurancehina shahzadi100% (1)
- Basic Testing Qtn&ansДокумент4 страницыBasic Testing Qtn&ansapi-3772931Оценок пока нет
- Software TestingДокумент13 страницSoftware Testingrs7586792Оценок пока нет
- Glossaryof Software QATermsДокумент12 страницGlossaryof Software QATermsapi-3834072Оценок пока нет
- Verification and ValidationДокумент1 страницаVerification and ValidationPhanindrasai BoyapatiОценок пока нет
- Automated Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОт EverandAutomated Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОценок пока нет
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОт EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedОценок пока нет
- #854616 - Scdaemon Cannot Access Yubikey Using Ccid Driver Without PCSCD - Debian Bug Report LogsДокумент14 страниц#854616 - Scdaemon Cannot Access Yubikey Using Ccid Driver Without PCSCD - Debian Bug Report LogsGhygggОценок пока нет
- Responsive Web Design Tipsheet: Start SmallДокумент3 страницыResponsive Web Design Tipsheet: Start Smallsantosh kumarОценок пока нет
- Cisco ISE Ordering Guide 2020Документ31 страницаCisco ISE Ordering Guide 2020Yudi DjohanОценок пока нет
- TestNG Interview QuestionsДокумент5 страницTestNG Interview QuestionsPriyanka mestryОценок пока нет
- Scan A Hand ManualДокумент27 страницScan A Hand Manualsafin43Оценок пока нет
- Various Components of E-CommercedocxДокумент2 страницыVarious Components of E-CommercedocxRajeev Ranjan TiwariОценок пока нет
- BAC 223 A1 Task SheetДокумент5 страницBAC 223 A1 Task SheetAlan OpritaОценок пока нет
- Normalization of Database-Ass-2Документ31 страницаNormalization of Database-Ass-2Dhivya Bharathi pОценок пока нет
- Mold Design Using Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0Документ6 страницMold Design Using Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 4.0arachman297988Оценок пока нет
- Vulkan Tutorial PDFДокумент281 страницаVulkan Tutorial PDFabhijay25Оценок пока нет
- Amdahl's Law in The Multicore EraДокумент6 страницAmdahl's Law in The Multicore EraDmytro Shteflyuk100% (1)
- Fluid Sim P ManualДокумент0 страницFluid Sim P ManualJesús Adrian Sigala GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- Data MiningДокумент40 страницData MiningAbiali BohariОценок пока нет
- Frank J. Marshall - Marshall's Chess SwindlesДокумент157 страницFrank J. Marshall - Marshall's Chess SwindlesAnonymous FJQb6IОценок пока нет
- English Grade 6 FlipbookДокумент139 страницEnglish Grade 6 FlipbookDroidAbramTelan100% (1)
- C LanguageДокумент104 страницыC LanguageSagar Paul'gОценок пока нет
- Chapter TwoДокумент31 страницаChapter TwoBab KebedeОценок пока нет
- Chuletario ArduinoДокумент1 страницаChuletario Arduinohozze2Оценок пока нет
- Apollo Hospitals SRS by AkashДокумент14 страницApollo Hospitals SRS by AkashVishwa Sourab Brungi100% (2)
- IT2024-User Interface Design QuestionsДокумент5 страницIT2024-User Interface Design QuestionsKannan GopalrajОценок пока нет
- Source From The Menu. This Will Open A New Tab in Your BrowserДокумент20 страницSource From The Menu. This Will Open A New Tab in Your BrowserVhynnc Kaiser OdroniaОценок пока нет
- RELIABILITYrev2 Jan17 - Version 2Документ18 страницRELIABILITYrev2 Jan17 - Version 2Ainan SyabilОценок пока нет
- Using Oracle Data Integrator Stack Oracle Cloud MarketplaceДокумент74 страницыUsing Oracle Data Integrator Stack Oracle Cloud MarketplaceVamsi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- RFC IndexДокумент233 страницыRFC Indexumi1234Оценок пока нет
- How To Calculate The Output Energy or Power of A Solar Photovoltaic System, Excel PV Calculator To Estimate Solar Electricity OutputДокумент3 страницыHow To Calculate The Output Energy or Power of A Solar Photovoltaic System, Excel PV Calculator To Estimate Solar Electricity Outputsag14Оценок пока нет
- Tonehammer: All Rights Reserved © Tonehammer 2006 - 2010Документ20 страницTonehammer: All Rights Reserved © Tonehammer 2006 - 2010Nils Van der PlanckenОценок пока нет
- EoS Notice - PARTNER TAA TelephonesДокумент4 страницыEoS Notice - PARTNER TAA TelephonesasОценок пока нет
- System 20: Inline Sensors & MonitorsДокумент6 страницSystem 20: Inline Sensors & MonitorsJaimeEnriquePadillaPobleteОценок пока нет
- Advanced Programming Java - Course Outline ITДокумент3 страницыAdvanced Programming Java - Course Outline ITኢየሩሳሌም ገብረ ክርስቶስОценок пока нет
- IBM Annual Report 2016Документ164 страницыIBM Annual Report 2016AakasH TivariОценок пока нет