Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit-V: Animal Physiology. 2
Загружено:
Sachikanta SharmaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit-V: Animal Physiology. 2
Загружено:
Sachikanta SharmaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UNIT-V: ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY.
1.
2.
Physiology deals with the functioning of an organism. Nutrition involves mode of procurement of nutrient and its utilization for various activities of the life.
Q. Describe the process of digestion of carbohydrates in human beings. Starch, lactose and sucrose are the major source of carbohydrates in human diet. Starch is a polysaccharide whereas lactose and sucrose are disaccharide present in milk and cane sugar respectively. 1. Digestion in mouth: When the food is chewed, it is mixed with saliva which contains starch hydrolyzing enzyme called salivary amylase(ptyalin). Ptyalin hydrolyses starch into maltose and isomaltose. The hydrolyzing activity of the ptyalin continue as long as for several hours after it enter the stomach before the food is completely mixed with gastric juice. Thus around 30-40% of starch are hydrolysed by ptyalin.The acidic pH of the gastric juice inhibit further activity of the ptylin. 2. Digestion in Duodenum: The partly digested food mixed with gastric uice is known as chime. It empties from the stomach into the duodenum where the food is mixed with pancreatic juice. It contains pancreatic amylase hydrolyses starch that have not been already digested into maltose, isomaltose and limit dextrins. STARCH pancreatic amylase MALTOSE + ISOMALTOSE + LIMIT DEXTRINS. 3. Digestion in small intestine: The intestinal juice contains disaccharide such as maltose, isomaltose, lactose, sucrose. They act on their corresponding substrate to produce monosaccharide. a). MALTOSE Maltase GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE b) ISOMALTOSE isomaltase GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE c). LACTOSE lactase GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE d). SUCROSE sucrase GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE e). LIMIT DEXTRINS limit dextrins GLUCOSE Thus, the overall digestion of carbohydrates produces monosaccharides that can be easily absorbed from the inner walls of the alimentary canal.
Parts of alimentary canal 1. buccal cavity 2. duodenum small intestine Secretions(enz ymes) Salivary amylase Pancreatic amylase Disaccharides substrate products
Starch salivary amylase maltose+isomaltose+limit dextrins Starch pancreatic amylase maltose+isomaltose+limit dextrins a). MALTOSE Maltase GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE b) ISOMALTOSE isomaltase GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE c). LACTOSE lactase GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE d). SUCROSE sucrase GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE e). LIMIT limit dextrins GLUCOSE
3.
Digestion of proteins: Q. Describe the process of protein digestion. Meat and the vegetables are the primary source of proteins in human diet. The protein hydrolyzing enzyme are collectively known as proteases. Generally they are produced in inactive In order to prevent intracellular digestion. Such inactive enzymes are known as proenzyme or zymozen. Digestion in stomach: Pepsin and rennin are the protein hydrolyzing enzyme present in the gastric juice. The inactive pepsinogen is converted into active pepsin by acidic pH of the gastric juice. Pepsinogen acidic pH pepsin (inactive) (active) Pepsin begins the digestion of protein in the stomach and hydrolyses into proteases, peptones and polypeptides. However, pepsin cannot hydrolyses milk protein, casein, unless they are converted into curd(calcium paracaseinate). i). Casein rennin paracasein
ii). Paracasein + Ca _______ calcium paracaseinate(curd) iii). Calcium paracaseinate pepsin peptones. Digestion of duodenum: The partly breakdown product of protein are mixed with pancreatic enzymes. The principle protein hydrolyzing enzyme present in pancreatic juice include trypsin, chymotrypsin and carbohydrates. The proteolytic enzymes are activated asTrypsinogen enterokinase trypsin. Chymotrypsinogen trypsin Chymotrypsin. Procarboxypeptidase trypsin carboxypeptidase Trypsin, Chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase hydrolyse breakdown product of protein into dipeptides and some into amino acids. PROTEASES + PEPTONES trypsin POLYPEPTIDES + AMINO ACIDS . Chymotrypsin Smaller peptides carboxypeptidase dipeptides + amino acids. . Digestion in Smal intestine: The intestinal juice contains dipeptidase that hydrolyze dipeptides into amino acids. The enzymes responsible for final hydrolysis of peptides into amino acids are amino polypeptidase and dipeptidase. Dipeptidase dipeptidase amino acids Amino peptidase Thus, the overall products of protein digestion are amino acids that can be easily absorbed by the cells lining the alimentary canal. Digestion of fat: 1. The most common fat of our diet are neutral fats also known as triglycerides. 2. Triglycerides consists of glycerol and three fatty acids. 3. In addition, our diet also contain phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol ester. 4. Digestion of fats mainly occur in the intestine. However, a small amount of short chain triglyceride of butter-fat origin is digested in the stomach by gastric lipase. 5. Essentially all the digestion of fats occur in the small intestine as follows: a). Emulsification: 1. The conversion of large globules into small sizes so that water soluble enzymes can act on the globular surfaces is known as emulsification. It is the first step in fat digestion. 2. This can be achieved by the activity of bile which is a secretion of liver. 3. Bile contains bile salts and carboxy terminals of the bile salts are highly soluble in water whereas sterol portion are soluble in fats. The fat soluble portion of bile salts dissolves in the surface layer of the fat globule thereby decreasing surface tension of the fat, on agitation the fat globules can be easily broken down into many minute particles. b). Digestion of fats by pancreatic lipase: 1. The most important fat hydrolyzing enzyme is pancreatic lipase. The lipase are water soluble and can act only on the emulsified fat to produce monoglycerides, fatty acids and glycerol as the end product. 2. The end products are absorbed from the inner walls of the alimentary canal. Absorption of fats: 1. The hydrolysis of triglyceride is a highly reversible process and the end products of digestion needs to be removed rapidly. 2. Bile salts has a capacity to form micelles and during triglyceride digestion, monoglycerides and free fatty acids are dissolved in the fatty portion of the micelles. 3. The bile salt micelles also act as a transport medium to carry the monoglycerides and fatty acids to the brush border epithelial cells. 4. Since monoglycerides and fatty acids are soluble in lipids are absorbed by simple diffusion inside the muccosal cell. 5. The free fatty acids are reconstituted into triglyceride in the endoplasmic reticulum, once form the triglyceride aggregates into globules with cholesterol, phospholipid into globules. Each globules is coated with protein and are known as chylomicron which are transported into lymphatic vessels called lacteals. Q. Name the enzyme which hydrolyses starch into maltose. Salivary amylase hydrolyses starch into maltose. Q. Starch ptyalin Maltose. State the function of liver. The functions of liver are stated as below:
a). Bile secretion . b) Storage of fat. c). Breakdown of RBC. d). Iron storage. e). Vitamin A synthesis, urea synthesis. f). Primary site of detoxification. g). It is the sire of erythropoesis in foetus. Q. Name the true stomach in ruminant animal. Abomassum(the stomach of ruminant animal consists of four chambers). a). Rumen b). Reticulum c). Omasum d). Abomassum. * A ruminant is an animal with a complicated digestive system in which stmach has four several chambers. Rumen harbour bacteria and protozoa for fermentation of cellulose. The end products of the fermentation include carboxylic acid, carbondioxide and methane. The partially digested food called cud is passed to the second chamber reticulum where it is formed into pellets. It is then regurgitated and thoroughly chewed. This is called rumination or chewing the cud. The food is then reswallowed andn undergoes further fermentation. Eventually the partially digested food is passed through the first three chambers of the gut to reach the abomassum which is the true stomach. Further, food undergoes digestion usual mammalian digestive system. Q. Describe the role of HCl in digestion. Gastric juice is the principle secretion in the stomach. It contains HCl, mucus, two inactive enzyme pepsinogen and pro-rennin and small amount of gastric lipase. The hydrochloric acid plays the following role in digestion. 1. It produces an acidic ph(1-2.5) required for the activation of protein digesting enzyme. 2. It makes stomach content ideal for optimum activity of the stomach. 3. It kills harmful bacteria contaminated with the food and acts as a defence mechanism. 4. It denature many proteins and makes easier to digest. 5. The acid also loosens fibrous and the cellular components of the tissue. Q. How stomach is safe from the action of HCl? There are mechanisms that protect inner lining of the stomach and it is believed that acid in oxyntic cells of gastric glands is secreted near the edge of the cell rather than within the cell itself. Moreover, the freshly secreted acid is immediately diluted with the mucuc(produced by goblet cells). The mucus produced thus form a thick coat lining the walls of the stomach protecting from the damaging effect of HCl. In addition, goblet cells renew lining the stomach that cannot be penetrated by HCl. Q. What are gastric pits? These are long tubular gastric glands formed bny infolding of the epithelials. These are two specialized types of cells, parietal cells and chief cells. Parietal cells secrete HCl whereas chief cells secrete pepsinogen and pro-renin. Q. Why is bile juice important for digestion though it is not involved for digestion? Give three pints. Bile contains water, bile salts and bile pigments but no digestive enzymes. Bile salts are bicarbonates of glycocholate and taurocholate of sodium. It is however important for digestion of fats becausei). It increases the digestive action of lipase. ii). Sodium bicarbonates of bile neutralize acid in the gastric juice and makes chime alkaline necessary for action of proteolytic enzymes. iii). Bile salts emulsify large fat globules into small droplets(emulsification). Q. Give one difference between pepsin and trypsin. Pepsin is secreted by peptic or chief cells of the gastric gland whereas trypsin is secreted by pancreas. Pepsin works at an optimum acidic whereas trypsin works at an optimum ph. Q. Draw the transverse section of the alimentary canal. * Structure of alimentary canal. 1. A transverse section of alimentary canal(gut) has four distinct layers. a). Mucosa b) Sub-mucosa c). Muscularis Externa. d). Serosa Mucosa 1. It consists of the innermost layer of the gut. 2. It has three sub-layer-epithelium, lamina propia muscularis mucosa. 3. Epithelium secrete mucus. 4. Epithelium rests on basement membrane called lamina propia consisting of connective tissue. 5. Outside the lamina propia, there is a thin layer of smooth muscle called muscularis mucosa. Sub-mucosa 1. It is layer of connective tissue containg nerves, blood and lymph vessels, collagen and elastic fibre.
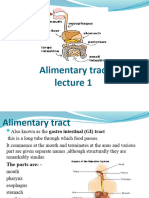
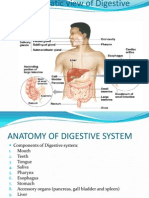
Muscularis externa. 1. It consists of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle. 2. It is responsible for wave like peristaltic movement of the gut wall which force food along. 3. Between circular and longitudinal muscle layer is auerbachs plexus. Plexus is a mass of nerve tissue which control peristaltis. 4. At a number of points along the gut, the circular muscles thickens into structures called sphincters. Cardiac sphincters are found at the junction of stomach and duodenum. Similarly, sphincters are present at caecal junction. Serosa 1. It is the outermost coat of the gut wall. 2. The serosa is covered by peritoneum. Q. Name the different pats of the alimentary canal. 1. mouth 2. buccal cavity 3. pharynx 4. Oesophagus 5. Stomach 6. Duodenum 7. Jejunum 8. Ileum 9. Colon 10. Rectum 11. Anus. Q. What are different parts of the stomach? Stomach is T-shaped organ. It has four main parts: 1. Cardiac part: it is present near the heart and lies in the opening of esophagus and stomach which is guarded by sphincter. 2. Fundus: It is commonly filled with air or gas.
3. 4.
Body: The main part of the stomach is body and has greater curvature.
Pyloric: It is the posterior part of the stomach and present near the opening part of the stomach into small intestine. Pyloric part often divided into pyloric entrum and pyloric canal. Pyloric canal opens into the duodenum. Q. State the function of stomach . 1. It stores food for sometime(the stomach stores food for 4-5 hrs). 2. Churning action of stomach mix food with acidic gastric juice. 3. Castles intrinsic factor necessary for absorption of vitamin B12 is produced. 4. It produces pepsinogen, pro-rennin, HCl, gastric lipase and gastric amylase. 5. Gastrin is a hormone secreted by gastric gland that promote secretion of gastric juice. 6. Inside the stomach, alcohol, aspirin, drugs, moderate amount of sugar and water are absorbed. Q. Define the following terms: a). Dental formula b). Diphyodont c). Heterodont d). Thecodont. a). Dental formula. The arrangement of teeth can be convenient expressed in the form of a dental formula. Dental formula gives number and types of teeth in half of the jaws. Dental formula for human being is 2123/2123*2 or 2[i2/2c1/1pm2/2m3/3] b). Diphyodont: Condition for having two sets of teeth, one is deciduous teeth(milk teeth), appear first and progressively replaced by another set called permanent teeth. c). Heterodont: Conditions having different types of tooth. Human beings have four basic kinds of tooth. They are incisors, canines, premolar and molars. d). Thecodont: Teeth are embedded in the socket of the jaw bone is known is known as thecodont. Q. Draw the generalized structure of a tooth. 1. The visible part of the tooth is known as crown. The crown is covered with enamel which is the hardest substance in the body and relatively resistant to decay. 2. The neck of the tooth is surrounded by gum. 3. The root remain embedded in the jaw bone. The body of the tooth is made up of dentine which is present beneath the enamel. 4. Inside the tooth, there is a pulp cavity that contains odontoplast, nerves, and blood vessels which provides nutrients to the living tissue of the tooth. 5. The root of the tooth is covered with cement, a substance similar to bone.
Вам также может понравиться
- Biochemistry of Carbohydrate DigestionДокумент10 страницBiochemistry of Carbohydrate DigestionWaseem Abbas ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Leaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyОт EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyОценок пока нет
- DigestionДокумент21 страницаDigestionAndersonОценок пока нет
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinДокумент64 страницыThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexОценок пока нет
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1От EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Gastro Section CДокумент11 страницGastro Section CNadja JamilahОценок пока нет
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormДокумент23 страницыHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- Analisis de Heces CompletoДокумент10 страницAnalisis de Heces CompletoIvonne SVОценок пока нет
- Lipid MetabolismДокумент52 страницыLipid MetabolismDr.P.NatarajanОценок пока нет
- CMFRI Digestive SystemДокумент7 страницCMFRI Digestive SystemNOORDIYANA MAT NOORDINОценок пока нет
- The Digestion ProcessДокумент7 страницThe Digestion ProcessKim Szydney RachoОценок пока нет
- Human PhysiologyДокумент43 страницыHuman PhysiologyBlowDatZaZaОценок пока нет
- Digestion SlideДокумент18 страницDigestion SlideezebelluciОценок пока нет
- Nutrition and DigestionДокумент8 страницNutrition and DigestionjeffchegzodОценок пока нет
- Digestion and AbsorptionДокумент6 страницDigestion and AbsorptionE.AshwinОценок пока нет
- Yr 10 WK 3 NoteДокумент5 страницYr 10 WK 3 Notesedrick ocheОценок пока нет
- Small Intestine and PancreasДокумент52 страницыSmall Intestine and PancreasLutfi AuliaОценок пока нет
- Absorption and The Products of Digestion1Документ55 страницAbsorption and The Products of Digestion1Abbie WhileyОценок пока нет
- Digestion of Starch in Human Body 1Документ12 страницDigestion of Starch in Human Body 1rbkavin10Оценок пока нет
- Handouts On Digestion and NutritionДокумент7 страницHandouts On Digestion and NutritionKaye Selene Raphaelle SyОценок пока нет
- Macronutrients SummaryДокумент2 страницыMacronutrients Summaryapi-259949424100% (1)
- Human digestion and small intestine absorptionДокумент29 страницHuman digestion and small intestine absorptionRaynaahОценок пока нет
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaДокумент37 страницUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- Poultry Digestive System GuideДокумент52 страницыPoultry Digestive System GuidegabrielwerneckОценок пока нет
- MODULE-1Документ24 страницыMODULE-1nutssdeez944Оценок пока нет
- Human PhysiologyДокумент41 страницаHuman PhysiologyBoris-Jeremie-Latyr GueyeОценок пока нет
- Digestion and Absorption - 101328Документ10 страницDigestion and Absorption - 101328Emmanuel IshiomaОценок пока нет
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandДокумент25 страницUman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandTahir AzizОценок пока нет
- Human Digestion PresentationДокумент35 страницHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoОценок пока нет
- Human PhysiologyДокумент39 страницHuman PhysiologyML6132021 KENG MING HUI CARMENОценок пока нет
- Digestion and Absorption of Lipids: A Comprehensive GuideДокумент28 страницDigestion and Absorption of Lipids: A Comprehensive GuideEng Matti Ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Digestive System Worksheet: Key Functions and OrgansДокумент5 страницDigestive System Worksheet: Key Functions and OrgansRJ CamarilloОценок пока нет
- Updated Presentation Note - 091343Документ3 страницыUpdated Presentation Note - 091343Joshua AladenikaОценок пока нет
- IP Pre-Worksheet GIДокумент6 страницIP Pre-Worksheet GIstormigirl017Оценок пока нет
- Calamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismДокумент13 страницCalamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismMelody DoriaОценок пока нет
- Digestive GlandДокумент22 страницыDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusОценок пока нет
- How a Cheese Sandwich is Digested from Mouth to ColonДокумент3 страницыHow a Cheese Sandwich is Digested from Mouth to ColonSherbet SpenceОценок пока нет
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss MylachalДокумент13 страницDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss MylachalBiju MylachalОценок пока нет
- Role of Digestive EnzymesДокумент8 страницRole of Digestive EnzymesvasaviОценок пока нет
- Digestive System - MCAT ReviewДокумент5 страницDigestive System - MCAT ReviewMano JayaramОценок пока нет
- 3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationДокумент13 страниц3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationAthirah SulaimanОценок пока нет
- Answer Key1 PDFДокумент4 страницыAnswer Key1 PDFsanthosh kumarОценок пока нет
- Alimentary TractДокумент122 страницыAlimentary TractMosa MosaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System Final 1Документ34 страницыThe Digestive System Final 1Jam DabalosОценок пока нет
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionДокумент26 страницDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyОценок пока нет
- I) FEEDING AND DIGESTIONДокумент7 страницI) FEEDING AND DIGESTIONamarashah182Оценок пока нет
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesДокумент24 страницы6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesWILSON KosheyОценок пока нет
- Digestive System 2022-23Документ28 страницDigestive System 2022-23Fady Fady100% (1)
- Competitive Exams: Feeding: ExamraceДокумент3 страницыCompetitive Exams: Feeding: ExamraceManohar ReddyОценок пока нет
- Absorption in The Small IntestineДокумент2 страницыAbsorption in The Small IntestineSawan ShahОценок пока нет
- Human Anatomy Digestion AbsorptionДокумент2 страницыHuman Anatomy Digestion Absorptionjchu2919Оценок пока нет
- IB HL Biology Digestion ExtensionДокумент1 страницаIB HL Biology Digestion ExtensionChris WongОценок пока нет
- Digestion and Absorption in the GI TractДокумент7 страницDigestion and Absorption in the GI TractLeira Lee100% (1)
- Presentation 2Документ16 страницPresentation 2jamalhkeemОценок пока нет
- Digestion and Absorption: A Summary of the 5 StagesДокумент5 страницDigestion and Absorption: A Summary of the 5 StagesRocio Guadalupe Lopez BlandonОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Digestion and AbsorptionДокумент33 страницыUnit 8 Digestion and AbsorptionGlory MuedaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Nutrition (Part 1)Документ41 страницаChapter 6 - Nutrition (Part 1)Ema FatimahОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewДокумент117 страницGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- 12470616Документ1 страница12470616Sachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- 808 #16 Manual R2Документ6 страниц808 #16 Manual R2mr_vdgreefОценок пока нет
- 10 Axis Nomination FormДокумент2 страницы10 Axis Nomination FormSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- 14th Finance CommissionДокумент5 страниц14th Finance CommissionSarfaraj KhanОценок пока нет
- Oneric OncelotДокумент32 страницыOneric OncelotSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Celebrating Nowruz in AfghanistanДокумент3 страницыCelebrating Nowruz in AfghanistanSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Weekly Pocket PDF 2017 - February (1-10) by AffairsCloudДокумент11 страницCurrent Affairs Weekly Pocket PDF 2017 - February (1-10) by AffairsCloudchefdemilyОценок пока нет
- Bankruptcy Bill Xaam - inДокумент3 страницыBankruptcy Bill Xaam - inrravat111Оценок пока нет
- Discover Switzerland: Location & How To Reach There: Flora and FaunaДокумент1 страницаDiscover Switzerland: Location & How To Reach There: Flora and FaunaSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Public Sector Enterprises in India1Документ28 страницPublic Sector Enterprises in India1Sachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Application Form PDFДокумент1 страницаApplication Form PDFSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Design and Development of PEM Serial Data TRNMSNДокумент4 страницыDesign and Development of PEM Serial Data TRNMSNSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Growth 2015Документ90 страницGrowth 2015Sachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Gate SyllabusДокумент2 страницыGate SyllabusSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- River Dolphin India Bangladesh Nepal Pakistan Ganges BrahmaputraДокумент3 страницыRiver Dolphin India Bangladesh Nepal Pakistan Ganges BrahmaputraSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- LV013Документ14 страницLV013Sachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- EepromДокумент7 страницEepromSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Prepaid Energy MeterДокумент12 страницPrepaid Energy MeterSachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Goat PDFДокумент7 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The Goat PDFHannan MirzaОценок пока нет
- Nso Level2 Solution Class 7 Set 2Документ3 страницыNso Level2 Solution Class 7 Set 2Deb Kumar SarkarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 1Документ69 страницAnatomy 1ravinder malwalОценок пока нет
- Comparing Digestive Systems of Herbivores, Carnivores and Nectar FeedersДокумент2 страницыComparing Digestive Systems of Herbivores, Carnivores and Nectar FeedersCarol JamesОценок пока нет
- Spelling List 4Документ70 страницSpelling List 4BobbingtonionОценок пока нет
- Animal Nutrition Notes PDFДокумент24 страницыAnimal Nutrition Notes PDFCyrus BautistaОценок пока нет
- Ebook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент34 страницыEbook Cultural Anthropology Canadian 2Nd Edition Robbins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFengagerscotsmangk9jt100% (7)
- FINAL ANSWER KEY FOR LIVESTOCK INSPECTOR EXAMДокумент11 страницFINAL ANSWER KEY FOR LIVESTOCK INSPECTOR EXAMNisha HariОценок пока нет
- MODULE 1B Organismal Biology-Animal BiologyДокумент253 страницыMODULE 1B Organismal Biology-Animal BiologyAlthea Angela BulaclacОценок пока нет
- Survey of Cattle Feed Channel and An Including Dealer District Network and Dairies and To Part 1Документ41 страницаSurvey of Cattle Feed Channel and An Including Dealer District Network and Dairies and To Part 1kundankumarsharmaОценок пока нет
- Class 7, CH 2 Nutrition in AnimalsДокумент4 страницыClass 7, CH 2 Nutrition in AnimalsAkkshara Kashyap 7-HОценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Документ33 страницыScheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Sitinorsyahidah JantanОценок пока нет
- Simple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagДокумент30 страницSimple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagMc Kjell Dagman RaveloОценок пока нет
- The Ruminant Digestive System Day 2Документ18 страницThe Ruminant Digestive System Day 2Yanyan PaydaОценок пока нет
- Alternative Feeds GuideДокумент128 страницAlternative Feeds GuideKadiwala Dairy Farm100% (1)
- Dairy Cattle Nutrition - The Basics: Dr. L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell UniversityДокумент49 страницDairy Cattle Nutrition - The Basics: Dr. L. E. Chase Department of Animal Science Cornell UniversityEarl Adam LambacoОценок пока нет
- Leafy Corn Silage Hybrids Promotional GuideДокумент24 страницыLeafy Corn Silage Hybrids Promotional GuideMargo Lee100% (1)
- Unit-V: Animal Physiology. 2Документ5 страницUnit-V: Animal Physiology. 2Sachikanta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Effect of Dietary Buffers on Milk Production and Physiology in Early LactationДокумент8 страницEffect of Dietary Buffers on Milk Production and Physiology in Early LactationNICOL GIORJINA LOPEZ HUILLCAОценок пока нет
- Size Matters A Review of The Effect of Pellet Size On Animal Behaviour and DigestionДокумент6 страницSize Matters A Review of The Effect of Pellet Size On Animal Behaviour and DigestionHerald Scholarly Open AccessОценок пока нет
- Agric JSS 1Документ54 страницыAgric JSS 1FolukeОценок пока нет
- Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle e 974Документ23 страницыNutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle e 974sicario.bingchillingОценок пока нет
- 0600 w16 QP 11 PDFДокумент16 страниц0600 w16 QP 11 PDFAhmed NaserОценок пока нет
- Digestive of RuminantsДокумент4 страницыDigestive of RuminantsRosel Gonzalo-AquinoОценок пока нет
- Voluntary Food Intake and Diet Selection in Farm Animals - J.M. Forbes - 2nd Ed - 2007 - (CABI)Документ462 страницыVoluntary Food Intake and Diet Selection in Farm Animals - J.M. Forbes - 2nd Ed - 2007 - (CABI)José Pedro Casagrande TrentínОценок пока нет
- Digestive System of GoatsДокумент4 страницыDigestive System of Goatssoliun2556100% (1)
- Babcock Institute For International Dairy Research and Development University of Wisconsin-MadisonДокумент4 страницыBabcock Institute For International Dairy Research and Development University of Wisconsin-MadisonHardiansah Faisal RitoPTK2020Оценок пока нет
- Agriculture TermsДокумент12 страницAgriculture TermsDaizie SancleyОценок пока нет
- Pig Production QuestionsДокумент7 страницPig Production QuestionsMrGilmartinОценок пока нет
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsОт EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeОт EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionОт EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsОт EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableОт EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilОт EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksОт EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingОт EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolОт EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolОценок пока нет
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsОт EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (90)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryОт EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (25)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementОт EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableОт EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableОценок пока нет
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeОт EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionОт EverandThe History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)