Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cestodes
Загружено:
Siti NabilaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cestodes
Загружено:
Siti NabilaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
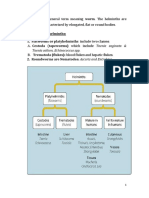
Type of cestodes Geog. Dist.
D. Latum Central Europe, Africa, N.America, Far East, Not Egypt Small int of man n fish eating mammals
S. Mansoni Far East, East Africa, North n South America Adults-small int of cats n dogs Plerocercoidamphibians, reptile, birds, man. Resemble D. Latum -shorter Uterus: not rosette shaped, more compact coils. Eggs:resemble D. Latum -smaller -conical operculum
T.Saginata Cosmopolitan, Ethiopia, Mexico, S. America, East n West Africa Small intestine of man.
T. Solium Cosmopolitanuncooked pig Rare in Islamic countries Small intestine of man.
E. Granulosus Cosmopolitan, cattle raising countries Small int of dogs n other carnivorous animal.
H.Nana Cosmopolitan, warm climates
D.Caninum Cosmopolitan
Habitat
Small int of man occasionally rodents
Tapeworm of dogs n cats Man accidentally infected.
Morph.
10 m, 3000-4000 segments Scolex: elongate, soon shaped w 2 long bothria. Mature segments: Broader than long Mid ventral gen.p ore Testes: multiple, dorsolateral Ovary: bilobed, post. V. glands : ventrolat Uterus:rosette shaped, darker, more coiled n packed w eggs Gravid: same morph as mature seg.
Pathogen.
-no of worms -competition for B12 -amount of
-drink water containing Cyclops w procercoid
4-10 m usually 5 m. 1000-2000 proglottids Scolex: Quadrate, Unarmed, 4 hemispherical suckers attach to prox jejunal mucosa. Mature seg: 300-400 testes Blind tubular uterus Bilobed ovary Vagina w term sphincter Gravid: greater no of lat side branches fr central stem Very active, detached singly fr parent worm n creeps out of anus without defecation. Change in motility n secretion of GIT. Reduced gastric secrt.
Differs w t.saginata in: -shorter, 3-8 m n less no f segments (1000) -Scolex: globular w a rosetellum w double rows of hooks -Ovary: trilobed -Gravid uterus; 713 main lat branches on each side.
Minute worm 3 to 6mm Scolex : pyriform w four suckers n 30 t0 36 hooks Neck: short Three proglottids Gravid: length of worm. Uterus : burst b4 evacuation of gravid
Smallest tape worm. Scolex: rhomboidal, 4 suckers, short rosetellum w 2030 spines in single row. Neck: long n slender , 100 segments, broader than long Mature: 3 globular testes in 1 line. Small lobed ovary, vit glands at the middle. Gravid: a sac like uterus w 80-100 eggs. Rupture liberating eggs in int.
Scolex; small rhomboidal, 4 deep cup shaped oval suckers, rosetellum w 7 rows of rose horn hooks. Neck: long n slender. Mature n gravid: longer than broad. Mature: double set of rep organ, 2 marginal gen pores on both sides, horse shoe shaped ovaries,vit glands dital to it. Gravid: longer than mature, net like uterus containing egg capsules each have 520 eggs
Slight irritation at the site of attachment Rare int
Well tolerated in large no. -allergic
Depends on no of worm. Mild symptomps: int disturb., indigestion,
metabolic by products absorbed by host
Clinical pic.
Asymptomatic. Diarrhea, abd pain, pernicious anemia, Intestinal obstruction.
Diagnosis
Eggs or segments in faeces
-eating raw tissues of frogs n snakes contain plerocercoid -apply ing frog tissues contain plerocercoid on inflamed tissue -site of the larvae Sub. Sparga.: Cyst like, itchy, migratory nosule, tender or not -peri. Eosinophilia ocular sparga: oedematous, itchy, painful w excs lacrimation, subconjunctival -retrobulbar: exopthalmus, corneal ulceration. Surgical removal n histopathoexam
obstruction
appetite loss.
Abd pain, nausea, inc or dec appetite/wght -Abd discomfort due to act crawling of gravid Complications: Worm-int obstr. Appendicitis n cholangitis.
-Abd discomfort, hunger pains, diarrhea, alt w constipation n loss of appetite.
Usually asymptomatic -headache, dizziness, anorexia, periodic pain n abd pain.
Treat.
Niclosamide:single dose (4 tablets) PZQ:10mg/kg
Prevent n control
-cooking of fish -freezing for 24 to 48 hrs at 18C -treat inf. Patients -res host: dogs n cats dewormed periodically.
-Surgical removal -Inj ethyl alcohol w procaine in ocular sparga. -PZQ if inoperable -drinking h20 w suspected Cyclops must b filtered or boiled -x use as poultices -x eat raw tissues
Most difficult to diagnose in first 3 mnths. -Gravid seg in faeces Niclosamide PZQ
-stool- gravid segments
Eggs in stool
Gravid in stool Rarely egg capsules
Niclosamide PZQ
Niclosamide (57D)-adult worm PZQ- cysticercoids n adult
PZQ
X eat raw/undercooked beef -carcasses w int cysticerci condemned/boiled. Light inf-freexe at -
-Periodic deworming of cats n dogs. -Dusting of dogs w insecticides to kill fleas.
of snakes n frogs
18C for 5 days Early detect n treat.
LIFE CYCLE D. LATUM Eggs : -faeces of inf person Immature, ovoid, operculated, yellowish brown, 65x45 u. -reach fresh water -mature: 2 weeks -liberate coracidium S. MANSONI Eggs : -faeces of of cats n dogs -water hatch T.SAGINATA Eggs: -mature T.SOLIUM Gravid segments: Pass w defecation on soils E.GRANULOSUS Eggs: Faeces of dogs H.NANA ,Eggs : infective 2 thin shells, inner shell has two knobs w arise 4-8 filaments -man inf by ingestion or autoinfection. -oncospheres hatch in stomach or small int, penetrate the villi n metamorphose into cysticercoids Migrate into lumen of int, attach to mucosa n mature 1st int host: Cyclops 1st int host: Cattle -on reaching duodenum oncosphere hatch n penetrate int wall to mesenteric venules then lymph, gen circ to the muscle. Cysticercus Bovis 1st int host: Pigs n hogs -eggs pass to duodenum or jejunum Int juice n gastric juice disintegrates the eggs -oncosphere penetrate int wall to mesenteric venules n troughout the bosy. -filtered between muscles -Cyst Cellulosae 1st int host: Sheep, cattle, camel, horses, goats, oxen, hogs n accidentally by man -hatch in duodenuoncosphere penetrates int wall, mesenteric venules, lodged in various organ. Hydatid cyst -Bone: no capsule, confined by dense osseous tissue, 1st int host: Fleas n floor beetles -larvae ingest eggs cysticercoid 1st int host: Ctenocephalides canis or c.felis (cat n dog fleas in larval stage) Pulex irritans( human) -oncosphere hatch n penetrate the int of the insects n migrate to their haemocoele n develop into cysticercoids -man infected when ingest insects in D.CANINUM Egg capsules -ingested by larval stages of cat n dogs fleas n human fleas
1st int host: Cyclops within 12 hrs -Penetrate by hook to the body cavity Procercoid larva 2nd int host Fresh water fish -between the muscle Plerocercoid Larvae or Sparganum (inf stage)
2nd int host ; Frogs, lizards, snakes n birds -penetrates int wall n migrates to tissues Plerocercoid Larva *Human Drink h20 containing Cyclops.
Procercoid penetrates int wall n bcomes plerocercoid, released in his int n again migrate to various tissues Def Host: Attach to mucous memb of small int n grow to adult(5-6 weeks) Def host Def host Ingest by cats n dogs Man Adult worm -ingesting inf meat containing cyst bovis(inf stage) -scolex invaginates n fixes to the mucosa n the necks forms segments
*Human -Ingest the eggs n presence of larval stage (cysticercosis)
irregular branching shape, poor laminated layer
food
Def host Man Consume unperfectly cooked pig meat containing cyst (inf stage) -in stomach the cyst wall is digested n the head evaginate upper small int and attached by suckers -adult
Def host: Dogs n carnivores -eat cyst w scolices which develops into adult
Def Host Rodents ingests the insects. Cysticercoids larva attaches to int wall n mature
DISEASES Disease Definition Method of inf Cysticercosis Cond in which the larval stage of T. Soelium cyst. Cellulosae is present in the tissues of man who acts as int host -ingest food or drinks contaminated w eggs -Ext autoinf: He ingests eggs pass in his own faeces -Int autoinfect: reverse peristalsis carry the egg to stomach or duodenum n hatch releasing oncosheres -Gastric juice followed by int juice causes hatching of the eggs -By hooklets n lytic secretions penetrate int wall too mesenteric bv n troughout the body -Subcutaneous tissue n muscle followed by eyes, brain, liver n lungs -develop into Cysticerci -cellular reaction : neutrophils, eosino, lympho. n round cells -fibrous encapsulation Hidatid Disease Presence of larval stage of E. Granulosus in the tissue of man resulting in cystic disease due to unilocular and osseous cyst -ingest eggs of E. Granulosus By: soil, dogs, furs, skeening of foxes In liver (70%), lung (20%), brain, eyes, bone, spleen, spinal cords, kidney Hydatid cyst -surround by fibrous tissue made by immunological response Cyst wall proper -outer milky Non-nucleated laminal layer -innner nucleated laminal layer : a. brood capsule: protoscolices-mature-infective b. daughter cyst: attached or free Hydatid Sand : daughter cyst n free scolices Damage : -mechanical -bones- no capsule : bony invasion n fracture Leakage: allergic manifestations, anaphylactic n scolices disseminate to other organ Clinical pic - No of cysticerci, organs , n viability -subcutaneous tissue n muscle: muscle pain, subcutaneous nodules -brain:epilepsy, focal paralysis, encephalitis n psychic disturb. -eyes: periorbital pain, opacities in the vitreous, glaucoma, blindness -heart: arrythmia n heart block Incubation period: 2 to 20 years b4 signs n symp develop Cyst in liver -painless enlarge. Of abdomen n right hypochondrial pain. Lungs: cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis Eye: Blindness Brain: brain tumor Osseous hydatid cyst: fractures Fate: heales spontaneously, calcified, 2ry inf, metastasis, anaphylactic reaction. -ELISA -Eosinophilia (20 to25%) -Immunoelectrophoresis -Never cyst puncture -Freezing cyst wall -Surgical removal -Abendazole
Pathology n pathogenesis
Diagnosis
Treatment
-biopsy of subcutaneous nodules -x-ray to see calcified lesion in brain n muscle - CSF: Eosinophilia -ELISA -Immunoelectrophoresis -Excision of cysts -PZQ
Prevention
-Corticosteroid -Hospitalization in neurocystocercosis -Niclosamide has no role -Early treat of inf person to reduce autoinf or othr infection -x defecate in soil -inf meat freezed at -15c for 3 days at least -sanitary disposal of human faeces n pig sties far away from houses
-strict personal hygiene -supervise n warns persons working in fur manufactures -control abattoirs Pet n working dogs examined periodically n treated if infected . -kill stray dogs
Вам также может понравиться
- Case Taking Proforma - Respiratory SystemДокумент7 страницCase Taking Proforma - Respiratory SystemK Haynes Raja100% (11)
- Scott Foresman Science Grade 4Документ8 страницScott Foresman Science Grade 4rofi modiОценок пока нет
- Cestodes (Table)Документ3 страницыCestodes (Table)Marelle M. Yamzon87% (15)
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueДокумент76 страницAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- Tapeworms: Diphyllobothrium Latum-Fish Tapeworm Taenia Saginata - Beef Tapeworm Taenia Solium - Pork TapewormДокумент21 страницаTapeworms: Diphyllobothrium Latum-Fish Tapeworm Taenia Saginata - Beef Tapeworm Taenia Solium - Pork TapewormSumit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Taenia SoliumДокумент7 страницTaenia Soliumn41995639Оценок пока нет
- HelminthsДокумент35 страницHelminthsBr1nfoОценок пока нет
- Platyhelminthes: Hazel Anne L. Tabo Olgga A. HaraДокумент79 страницPlatyhelminthes: Hazel Anne L. Tabo Olgga A. HaraHara OgheeОценок пока нет
- Cestoda TapewormДокумент45 страницCestoda TapewormNandra Adryan0% (1)
- Pha6114 CestodesДокумент34 страницыPha6114 CestodesLisaОценок пока нет
- Cyclophyllidean CestodesДокумент92 страницыCyclophyllidean CestodesPauline AñesОценок пока нет
- Taenia SoliumДокумент10 страницTaenia SoliumDorothyОценок пока нет
- Tables - CestodesДокумент8 страницTables - CestodesSid Loverholic50% (4)
- Selma CestodesДокумент23 страницыSelma CestodesAhmed EisaОценок пока нет
- Helminthology Platyhelminthes CestodesДокумент46 страницHelminthology Platyhelminthes CestodesTutde SedanaОценок пока нет
- Prof. DR Fahim ShaltoutДокумент55 страницProf. DR Fahim ShaltoutSumit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Class Cestodes-Tape WormДокумент46 страницClass Cestodes-Tape WormRediat GossayeОценок пока нет
- Parasitology - CestodesДокумент23 страницыParasitology - CestodesJeth Roque GalleneroОценок пока нет
- Cestodes 2023Документ46 страницCestodes 2023Ming YanОценок пока нет
- Cestodes Parasitology NotesДокумент5 страницCestodes Parasitology NotesKat SunicoОценок пока нет
- Parasite Lab 5 Helminths PDF (M)Документ18 страницParasite Lab 5 Helminths PDF (M)Ali RonaldoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 para Summer 2023-1Документ47 страницLecture 3 para Summer 2023-1محمود سليمانОценок пока нет
- Cestodes Raw Doc AnchetaДокумент53 страницыCestodes Raw Doc Anchetaaya basilioОценок пока нет
- Classification of Medically Significant NematodesДокумент134 страницыClassification of Medically Significant Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- Outline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesДокумент73 страницыOutline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesAsxe CeeОценок пока нет
- Taenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusДокумент5 страницTaenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusKervy Jay AgraviadorОценок пока нет
- Lecture 19 - Introduction of Cestoda - 221217 - 195804Документ33 страницыLecture 19 - Introduction of Cestoda - 221217 - 195804rama jehadОценок пока нет
- Ancylostoma DuodenaleДокумент17 страницAncylostoma DuodenaleZee FaaizaОценок пока нет
- Intestinal Cestode - Taenia SoliumДокумент26 страницIntestinal Cestode - Taenia SoliumRijane Tabonoc OmlangОценок пока нет
- NematodesДокумент9 страницNematodesJessa MayОценок пока нет
- Taenia Saginata and SoliumДокумент46 страницTaenia Saginata and SoliumKotilakshmanareddy TetaliОценок пока нет
- General Parasitology L7Документ17 страницGeneral Parasitology L7kayse abtidoonОценок пока нет
- CestodesДокумент83 страницыCestodesveralynn2011Оценок пока нет
- Cestode NotesДокумент26 страницCestode NotesJOSEPH NDERITUОценок пока нет
- Taenia SoliumДокумент43 страницыTaenia SoliumKhushbu Yadav100% (1)
- 2) CestodesДокумент58 страниц2) Cestodesmisgshlove1Оценок пока нет
- Class Cestoidea: - The Tape WormsДокумент97 страницClass Cestoidea: - The Tape Wormsgg getuОценок пока нет
- Echniococcus Granulosis: Submitted By: Arushi Patiyal B.Sc. (Hons) Microbiology 3 YearДокумент41 страницаEchniococcus Granulosis: Submitted By: Arushi Patiyal B.Sc. (Hons) Microbiology 3 YearArushi PatiyalОценок пока нет
- المحاضرة 4 مادة الطفيلياتДокумент8 страницالمحاضرة 4 مادة الطفيلياتdyabw6430Оценок пока нет
- Spirometra, Hymenolepis NanaДокумент5 страницSpirometra, Hymenolepis NanaJayricDepalobosОценок пока нет
- Cestodes: Tapeworms Complex Life Cycles Definitive HostДокумент86 страницCestodes: Tapeworms Complex Life Cycles Definitive HostMuhammad IdreesОценок пока нет
- CestodesДокумент34 страницыCestodesمصطفي خندقاويОценок пока нет
- Taenia of HumanДокумент14 страницTaenia of HumaninnocentjeevaОценок пока нет
- General Properties of CestodesДокумент42 страницыGeneral Properties of CestodesNicole NipasОценок пока нет
- The Intestinal NematodesДокумент107 страницThe Intestinal Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- Hydatid CystДокумент50 страницHydatid CystShashidhara Puttaraj100% (1)
- Cestodes NotesДокумент27 страницCestodes NotesShanmathiОценок пока нет
- Echinococcus: Santosh Kumar Yadav M.Sc. Clinical Microbiology Iom, TuthДокумент40 страницEchinococcus: Santosh Kumar Yadav M.Sc. Clinical Microbiology Iom, TuthMeenakshisundaram CОценок пока нет
- PARASITOLOGYДокумент77 страницPARASITOLOGYZac Bornilla RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Taenias IsДокумент56 страницTaenias Iseliwaja100% (1)
- C L A S S C e S T o I D e A: Envelope Are Called CoracidiaДокумент12 страницC L A S S C e S T o I D e A: Envelope Are Called CoracidiabebibobuОценок пока нет
- Cestoidea:: CharactersДокумент20 страницCestoidea:: CharactersConОценок пока нет
- Taenia SoliumДокумент8 страницTaenia SoliumJoshua Bien FuentesОценок пока нет
- L17-Taenia SpeciesДокумент7 страницL17-Taenia SpeciesMohammed RedhaОценок пока нет
- Medical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesДокумент54 страницыMedical Helminthology - Chordata and Roundworms - Human ParasitesMewa MahartaОценок пока нет
- TRIBLASTICAДокумент31 страницаTRIBLASTICAcircovaesterkaОценок пока нет
- Diphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Документ11 страницDiphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Sheana TmplОценок пока нет
- CestodesДокумент39 страницCestodesNachiket Vijay PotdarОценок пока нет
- Veterinary ParasitologyДокумент157 страницVeterinary ParasitologyPwaveno Bamaiyi75% (4)
- Diplydium CaninumДокумент12 страницDiplydium CaninumIslaam SabriОценок пока нет
- Diseases of Poultry - How to Know Them, Their Causes, Prevention and Cure - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerОт EverandDiseases of Poultry - How to Know Them, Their Causes, Prevention and Cure - Containing Extracts from Livestock for the Farmer and Stock OwnerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentОт EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentОценок пока нет
- PathologyДокумент2 страницыPathologySiti NabilaОценок пока нет
- Kerja TertangguhДокумент5 страницKerja TertangguhSiti NabilaОценок пока нет
- Kerja TertangguhДокумент5 страницKerja TertangguhSiti NabilaОценок пока нет
- Granulomatous Inflammation 4Документ57 страницGranulomatous Inflammation 4Siti NabilaОценок пока нет
- ST Rose of Lima Catholic SchoolДокумент30 страницST Rose of Lima Catholic SchoolKathy SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Autonomic NeuropathyДокумент20 страницAutonomic NeuropathyRegina CaeciliaОценок пока нет
- NCMC103 Prelims ReviewerДокумент13 страницNCMC103 Prelims ReviewerVeronica ShaneОценок пока нет
- Assam Hill Goat Production ND PerformanceДокумент5 страницAssam Hill Goat Production ND PerformanceShazzad Ul IslamОценок пока нет
- Nutrisi - Prof. Dr. Dr. Askandar, SP - PD-FINASIM - Dr. Sri Murtiwi, SP - PD-FINASIMДокумент23 страницыNutrisi - Prof. Dr. Dr. Askandar, SP - PD-FINASIM - Dr. Sri Murtiwi, SP - PD-FINASIMroviancahyaОценок пока нет
- Bleeding DisordersДокумент4 страницыBleeding DisordersRitz CelsoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Assignment: Properties of NicotineДокумент10 страницChemistry Assignment: Properties of Nicotineharshitha jagathieshОценок пока нет
- Gambaran Peran Tenaga Kesehatan SebagaiДокумент10 страницGambaran Peran Tenaga Kesehatan SebagaiNur Rahmy OktavianiОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Libros Transfusion PDFДокумент44 страницыCatalogo Libros Transfusion PDFmeds1313Оценок пока нет
- 2nd PU Practical Viva QuestionsДокумент10 страниц2nd PU Practical Viva QuestionsSadhvi CОценок пока нет
- 01a Calgary Cambridge Framework - BasicДокумент3 страницы01a Calgary Cambridge Framework - BasicJohn Sebastian Bittner SolisОценок пока нет
- Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis: DR Prathibha J PДокумент48 страницPsoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis: DR Prathibha J PjefferyОценок пока нет
- PTBD 2Документ4 страницыPTBD 2Alcntara AllenОценок пока нет
- Literature ReviewДокумент5 страницLiterature Reviewapi-609547856Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For Substance AbuseДокумент87 страницNursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For Substance AbuseZohrahLiaqatОценок пока нет
- Project Proposal DsaДокумент2 страницыProject Proposal DsaChristine Joy Pellos MacabeoОценок пока нет
- 20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisДокумент3 страницы20 Soal Latihan Report Text Dalam Bahasa InggrisDewi Lisna100% (1)
- Delivering and InsertionДокумент28 страницDelivering and Insertionomaryaya18Оценок пока нет
- En 100630253Документ10 страницEn 100630253Shuruq SanchezОценок пока нет
- CRISIL Industry Report - HospitalДокумент9 страницCRISIL Industry Report - Hospitalrahul.joisher2026Оценок пока нет
- C. Skills and Beneficial ToolsДокумент14 страницC. Skills and Beneficial ToolsVera AndryОценок пока нет
- II. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersДокумент98 страницII. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersarielleortuosteОценок пока нет
- Healthy Foods and The Body Parts They ResembleДокумент4 страницыHealthy Foods and The Body Parts They ResembleRobert AndujarОценок пока нет
- Phenacetin MsdsДокумент6 страницPhenacetin MsdstylerОценок пока нет
- Vinyl Chloride MonomerДокумент6 страницVinyl Chloride MonomerRizqia Putri ZakkaОценок пока нет
- A) MarasmusДокумент21 страницаA) Marasmusrathai0% (1)
- AEFI Surveillance and management-RVVДокумент19 страницAEFI Surveillance and management-RVVadi100% (1)