Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
PCM Modulation
Загружено:
Sougata DasИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PCM Modulation
Загружено:
Sougata DasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Communicatron Techniques (9116)
EXPERIMENT No.6
1.0 Title:
To generate and interprets peM wave. Also to observe demodulated output.
1
2.0 Prior Concept: ^"
'j
Pulse modulation technique, sampling theorem, encoding, decoding, quantization.
3.0 New Concept: I
Proposition 1: PCM
peM is a technique of modulation in which the analog signal sampled and convered to fixed
length, serial binary numbers for transmission. The binary number values are according to
amplitude of the analog signal.
Proposition 2: Sampling
It is a first step in peM generation, which involves conversion of continuous analog signal into
discrete signal at regular intervals according to sampling theorem.
Proposition 3: Quantization
It is the process of rounding of the values of sample. In this process total amplitude range, which
signal may occupy is divided in to number of standard level called quantum levels.
Proposition 4: Encoding
Encoding is process converting quantized signal in to sequence of D's and 1 's depending to the
code used.
Concept Structure
9
- u __
Regular Interval Pulses
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION. Mumbai. b4
Communication Techniques (9116) Exeriment NO.6
4.0 Learning Objectives:
Intellectual skill:
To understand PCM modulation and demodulation.
MotorSkm;
Ability to adjust the instrument according to requirements.
e
Ability to observe and draw the wave form at diferent pOints in circuit
Ability to observe original analog signal after detection.
5.0 Apparatus:
Experimental kit, power supply (O-5V), function generator, CRO, etc.
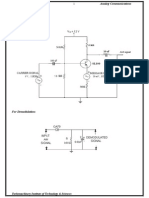
6,0 Circuit Diagram:
Modulating
signal
PCM Modulator
Anti-Aliasing samPle Quantizer
'
filter hold circuit
=
h
.
.----
L
-
P
-
M
-
-
Line waveform A D C
peM O/P
generator
rCM Demodulator
P
.
i
ecoder
De-Quantizer
L PF
tg signal
PCM I
= .
Student shalt draw circuit diagram of rCM modulator and demodulator available in the
laborator.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumbai. UU
Communication Techniques (9116)
~~~~**~~~~~ ~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~
7.0 Stepwise Procedure:
For PCM modulation.
1. Connect the experimental circuit diagram to the mains.
2. Apply modulating signal AC or DC.
3. Observe input and output wave form on CRO.
G
For pulse code demodulation.
1. Connect experimental kit to the mains.
2. Observe the demodulated output on CRO.
8.0 Obserations:
Teacher shall deSign observation table as per available experiment set (sample table given
below). Obtain different waveforms on CRO according to diferent input provided from pulse
code generator and draw one waveform each for modulation and demodulation on graph paper
indicating the corresponding input on the graph paper.
Observation table for PCM modulation
Sr. lo. ' Anal0uliP in volts
I
PCM (binary) O/P '
1
.
!
2
I
3
!
I
4
|
i
5
i
9.0 Conclusions:
:
In this system waveform are sampled at ....... .............. . . . . (regular I non continuous)
intervals.
Information regardi ng the sample is transmitted only at the sample ti mes wi th
.. ......................... (synchronizing I unsynchronizing pulses)
Student shall write the conclusion on the basis of amplitude of analog signal under the guidance
of teacher
10.0 Questions:
Teacher shall see that the student attempts the allotted question immediately afer
performing the experiment.
Write answers to Q. Q ..... Q .... Q .... (Teacher shall allot questions).
1. What is the advantage of PCM?
2. What is quantization?
3. Define quantization error.
4. Give the application of PCM.
5. Determine the Nyquist sample rate for a maximum analog input frequency of a 4 KHz, 10
KHz.
6. What is the disadvantage of PCM?
7. What is sampling theorem?
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCTION. Mumbal.
Communication Techniques (9116) Experiment No, 1
1.0 Title:
EXPERIMENT No. 7
To generate and interpret ASK signal by using digital to analog modulation
technique.
2.0 Prior Concept:
Digital to analog cOiion or digital to analog modulation.
3.0 New Concept:
Proposition 1: ASK (Amplitude Shif Keying)
DJA is the process of changing one o the characteristic of an analog signal based on the
information in a digital signal.
('0' and 1's)
Concept Structure
I
L--
\
; ASK
J
.
Proposition 2:
\
Digital
To
Analog
Modulation
hl/:
PSK
ASK is that type o digital to analog modulation, in which the strength of the carrier signal (analog
signal) i s varied to represent binary 1 or O. Both frequency and phase remain constant while the
amplitude changes.
Student shall write the concept structure
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumbal. 61
Communrcation Techniques (9116)
~~--* ~~--* ~--. ~~-~-*
4.0 Learning Objectives:
Intellectual skills:
To understand the digital to analog modulation and amplitude shif keying.
Motor Skills:
Ability to obsere the (analog) carrier signal before modulation and record the observation.
Ability to observe the change in amplitude or strength afer modulation and record the
observation.
5.0 Apparatus:
Experimental kit, power supply (O-5V), function generator, eRO, etc.
6.0 Circuit Diagram:
7.0
8.0
10k
10k
W
(
(
Stepwise Procedure:
16
12
4053
1
4
2:1
Analo
mux
13
7 11
8
Vss
.".
J.
1K
ASK
oupu
10K
|
4K
.
4
C1
1
.-
I^}
1. Switch on the experimental kit, function generator and CRO.
4
8
7
1|D6|
6
2
3
5
+5
V
I
1
0l
.
J
..
2. Select a sine waveform 2Vpp and 1 KHz from signal /function generator and observe and
measure it on CRO.
3. Apply the above checked sine wave to input of ASK generator.
4. Connect CRO at output of 555(pin 3) and observe square wave (binar signal).
5. Observe the ASK output on CRO screen.
6. Trace the input and output waveforms of ASK generation on graph.
Observations:
:
Measured amplitude of analog signal at the input of ASK generator
.
. ..... , ............... v
Measured amplitudes of ASK output for binary 1 = a """." V, binary 0 = . + "4.. " .. ,, v.
Trac the input and output waveforms of ASK generator kit on graph.
~~~~~~~~~~
MAHAfASHTRA STATE BORD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION. Mumbai. 62
Communiction Tecniques (9116} Experiment No. 8
EXPERIMENT No. 8
1.0 Title:
To generate FSK signal and draw input! output waveforms.
2.0 Prior Concept:
Digital to analog modulation.
3.0 New Concept:
Proposition 1' Frequency shif keying (FSK)
In FSK (frequency shift keying) method of D/A modulation the frequency of the carrier signal is
varied according to infonnation keeping amplitude and phase constant.
CO' and ]'5)
Proposition Z.
Define bit rate and baud.
Concept //uCluO
to 0
l 1\'
______
Lg\!
'
.I\'- __
__
__
PY
`
PSK
I
-
- n - n J
Q P
-- - - - -
4.0 learning Objectives:
Intellectual skill:
To understand FSKgeneration.
Motor Skill:
Ability to observe the frequency of carrier signal before shifing.
Ability to observer the frequency change of carrier signal for JS and 0'5 and to record the
same.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BORD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumbai. 67
Communication Techniques (9116)
5.0 Apparatus:
Experimental power supply (O-5V), function generator, CRO, etc.
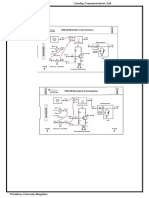
6.0 Circuit Diagram:
DC
J
|
|
[
Sq.wave to sine
,
C|B|D
,.
wae generation
L|0ronIc
8w||ch
"*..
FSK
put out
.
r
I (
)
|
'
r<. .. ,
I \
Sq.wave to sine
wave genertion
J
.
Bu0er
..
Student shall drw circuit diagram of FSK generator available in the laboratory.
7.0 Stepwise Procedure:
o For modulation.
+
J. Give the power supply connecting to all the equipment required for this experiment.
2. Connect a DC power supply or some other appropriate equipment to bufer input to
represent the binary input.
3. Obsere the wave form at the each stage of block diagram.
4. Observer the FSK output on CRO screen and conform.
8.0 Observations:
$
The measured time of clock generator output (square wave) ... ...................... msec.
Measured time of sine wave without divider ......... ............ ... . . . .............. . . .. . . . ..... ,
Draw input and output waveform obsered on CRO on graph.
---- ... -.--..-
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumbai. 68
Communication Techniques (9116)
EXPERIMENT No.9
1.0 Title:
To generate and interpret of PSK signal by using digital to analog modulation
technique.
2.0 Prior Concepl:
Shift key methods types.
3.0 New Concepl:
Proposition J. PSK
ExerIment No. 9
QAM (quadrate amplitude modulation) is a form of digital modulation where the digital (binary)
information is present in both the amplitude and phase of transmitted carrier.
Proposition Z
Student to write definition of PSK
LDDC0DO|lUC|Ul0
0 0 0 0,
AS K
I
I
`
.
\
gEl
To
Analog
Modulation
P SK
_
Q
_
A
_
M
__
- - - - -
4.0 Learning Objectives:
Intellectual skill:
e To understand the concept of QAM and PSK generation.
Motor Skill:
Ability to obsere the difference in the phase of carrier befor and afer PSK generation and
record the obseration.
5.0 Apparats:
Experimental kit. power supply (O-5V), function generator, eRO, etc.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION. MumbaL 73
Communication Techniques (9116)
-... ... -
6.0 Circuit Diagram:
10k
mk
Pl
lK
V
16
PSK
4
6
12 14
0bl0\
2NDp
Tvh
<n
1 kHZ 40J
,\
4.1h
1|m0|
13 8 6
11
7
2
+ 3
IO.l./
ClT
'/
UU0H SH8U|8WCICU U80I8RO t 00H0I8OI 8V88D0 HH0 8DOI8O|y.
7.0 Stepwise Procedure:
lOI ROUU8OH
1. Give power connection to experiment kit.
""
.
2. Generate Get a sine wave of 2Vpp 1 KHz form signal generator with help of CRO.
3. Give the above measured sine wave to experiment kit
4. Connect output of 555 (pin 3) to (pinll) of 4053 to get binary input.
5. Observe the PSK output on CRO.
8.0 Observations: :
1) The measured amplitude of sine wave at pin number 12 and 13 is ......................... .
2) The observed phase of sine wave at pin no 12 and no 13 ........................... " ..... .
MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION, Mumb.i. 74
Вам также может понравиться
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsОт EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications LaboratoryДокумент25 страницDigital Communications Laboratorysunny756Оценок пока нет
- Aparna GupatДокумент24 страницыAparna GupatAkshat SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsДокумент50 страницDigital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsNeel SarkarОценок пока нет
- Ade Lab ManualДокумент47 страницAde Lab ManualSANIYYA AAFREENОценок пока нет
- 15ECL76 ManualДокумент35 страниц15ECL76 Manual1BO20EC026 TOLSTOY DAYCODS AОценок пока нет
- UCK304E ElectricalExperiments Experiment2 Lab FileДокумент7 страницUCK304E ElectricalExperiments Experiment2 Lab Filey.komurcu921Оценок пока нет
- MTech (DCN) DEC-I ManualДокумент34 страницыMTech (DCN) DEC-I ManualMallikarjun DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Digital Comminication COMPLETEДокумент25 страницDigital Comminication COMPLETEAkanksha DixitОценок пока нет
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual PDFДокумент61 страницаAdvanced Communication Lab Manual PDFRachel BartonОценок пока нет
- Cad For Electronics Lab Kec-653Документ59 страницCad For Electronics Lab Kec-653Aviral VarshneyОценок пока нет
- Amplitude Modulation and DemodulationДокумент22 страницыAmplitude Modulation and DemodulationSivagnanam NamasivayamurthyОценок пока нет
- Bapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451Документ30 страницBapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451nithyamnvОценок пока нет
- Pulse Position ModulaДокумент3 страницыPulse Position ModulaAlejandro Javier BerardiОценок пока нет
- Mahalakshmi: Unit - Iv - Storage and Display DevicesДокумент18 страницMahalakshmi: Unit - Iv - Storage and Display Devicestareq omarОценок пока нет
- Behavioral and Physical Modeling of An Incremental Rotary EncoderДокумент4 страницыBehavioral and Physical Modeling of An Incremental Rotary EncoderLÊ ĐẠI HIỆPОценок пока нет
- Advance Communication Lab Manual 1.1.13Документ72 страницыAdvance Communication Lab Manual 1.1.13rockettekcor50% (2)
- III/IV B.Tech (ECE) Sixth Semester: Ec361 - Digital Communication LabДокумент66 страницIII/IV B.Tech (ECE) Sixth Semester: Ec361 - Digital Communication LabBalu HanumanthuОценок пока нет
- VHDL ProjectДокумент10 страницVHDL ProjectSalma MohamedОценок пока нет
- WMC LAB Manual - 2022Документ98 страницWMC LAB Manual - 2022U20EC131SANKALP PRADHAN SVNITОценок пока нет
- Communication LabДокумент34 страницыCommunication LabSingam DonОценок пока нет
- Analog and Digital Electronics Lab Manual (17CSL37) : Department of Computer Science and EngineeringДокумент61 страницаAnalog and Digital Electronics Lab Manual (17CSL37) : Department of Computer Science and Engineeringvadla77Оценок пока нет
- Digital CommunicationДокумент45 страницDigital CommunicationgsathyascewОценок пока нет
- Pulse Code Modulation & Time Division MultiplexingДокумент11 страницPulse Code Modulation & Time Division MultiplexingSalem AllamОценок пока нет
- Circuit Diagram:: Turbomachinery Institute of Technology & SciencesДокумент59 страницCircuit Diagram:: Turbomachinery Institute of Technology & SciencesSubhashini MurugesanОценок пока нет
- AC Lab Manual2017 PDFДокумент35 страницAC Lab Manual2017 PDFSharmila KrishnaswamyОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual-1Документ61 страницаLab Manual-1039-21 RAKESH SОценок пока нет
- BPSK PDFДокумент3 страницыBPSK PDFSyam SundarОценок пока нет
- Phase Shift Keying: ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыPhase Shift Keying: ObjectivesSyam SundarОценок пока нет
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual - 15ECL76Документ89 страницAdvanced Communication Lab Manual - 15ECL76Surendra K V62% (13)
- Apparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputДокумент5 страницApparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputAdwait BorikarОценок пока нет
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsДокумент28 страниц15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarОценок пока нет
- ASK Generation & DetectionДокумент3 страницыASK Generation & DetectionSyam SundarОценок пока нет
- EC2307-New Digital Communication Lab Manual Odd 2011Документ53 страницыEC2307-New Digital Communication Lab Manual Odd 2011chenthiltrОценок пока нет
- Department of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Документ57 страницDepartment of E.C.E.: Digital Communications Lab Manual Autonomous Pvp-12Ravi JaiswalОценок пока нет
- DC Manual Final PDFДокумент25 страницDC Manual Final PDFAsma FirdouseОценок пока нет
- Digital Communication (EC 691) Lab Manual Protected PDFДокумент62 страницыDigital Communication (EC 691) Lab Manual Protected PDFPoulami RoyОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент50 страницLab ManualAniket BhowmikОценок пока нет
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual-15ECL76 FinalДокумент41 страницаAdvanced Communication Lab Manual-15ECL76 FinalRakesh. KrОценок пока нет
- DC Lab ManualДокумент43 страницыDC Lab ManualSowmya KharviОценок пока нет
- Analog & Digital Student Lab ManualДокумент150 страницAnalog & Digital Student Lab ManualMaheshwaran Mahi100% (1)
- Digital Communications: Lab Manual (Student Copy)Документ78 страницDigital Communications: Lab Manual (Student Copy)dhileepan DilipОценок пока нет
- D C Lab ManualДокумент76 страницD C Lab ManualHanzo HenshiОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications Practical File PDFДокумент44 страницыDigital Communications Practical File PDFAshi Saxena100% (1)
- EC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswersДокумент83 страницыEC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswerssunandaalurОценок пока нет
- Jnanavikas Institute of Technology: Mr. Shubas S.RДокумент74 страницыJnanavikas Institute of Technology: Mr. Shubas S.RAbhishek nОценок пока нет
- Emi Lab Manual PDFДокумент39 страницEmi Lab Manual PDFMadhusudhanan RamaiahОценок пока нет
- Digital CommunicationДокумент47 страницDigital CommunicationAnjana KvОценок пока нет
- MN Lab ManualДокумент58 страницMN Lab ManualManjunath MohiteОценок пока нет
- Analog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyДокумент60 страницAnalog Circuits Lab Manual: Atria Institute of TechnologyTháHäKâduvàyîLzОценок пока нет
- NEW Advanced Communication Laboratory ManualДокумент54 страницыNEW Advanced Communication Laboratory Manualkeerthans_150% (4)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1От EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Guitar Strumming PatternsДокумент1 страницаGuitar Strumming PatternsSougata DasОценок пока нет
- PNP-64 Thermal PrinterДокумент8 страницPNP-64 Thermal PrinterSougata DasОценок пока нет
- 12 Bar Blues Turnaround - Mac OS X 10.10.5 Quartz PDFContext - 001849Документ1 страница12 Bar Blues Turnaround - Mac OS X 10.10.5 Quartz PDFContext - 001849Sougata DasОценок пока нет
- STM32 Cube WBGetting StartedДокумент36 страницSTM32 Cube WBGetting StartedSougata DasОценок пока нет
- GRIDCONNECT Modbus GatewayДокумент69 страницGRIDCONNECT Modbus GatewaySougata DasОценок пока нет
- Op Amp Precision Design-DC ErrorsДокумент14 страницOp Amp Precision Design-DC ErrorsSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Atmega Bench Power SupplyДокумент31 страницаAtmega Bench Power SupplySougata Das100% (2)
- Practical Countermeasures For PV Inverter Failure Modes - Powerex Tech BriefДокумент1 страницаPractical Countermeasures For PV Inverter Failure Modes - Powerex Tech BriefSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Hand Wound Output Transformers Using SILK Winding TechniquesДокумент3 страницыHand Wound Output Transformers Using SILK Winding TechniquesSougata DasОценок пока нет
- How To Wind Your Own Audio TransformersДокумент6 страницHow To Wind Your Own Audio TransformersSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Edn 15429-101404di 1000V Output From OPAMPДокумент6 страницEdn 15429-101404di 1000V Output From OPAMPSougata DasОценок пока нет
- PCB Drill ChartДокумент4 страницыPCB Drill ChartSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Phono Cartridge Impedance MatchingДокумент5 страницPhono Cartridge Impedance MatchingSougata DasОценок пока нет
- G1Документ90 страницG1Tanisha JindalОценок пока нет
- Falcon FiberOpticsДокумент17 страницFalcon FiberOpticsSougata Das100% (1)
- Line Interactive 450 W UPS STEVALДокумент4 страницыLine Interactive 450 W UPS STEVALSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Opto Triac MOC3020 AppNoteДокумент10 страницOpto Triac MOC3020 AppNoteSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Using The MC3PHACДокумент50 страницUsing The MC3PHACSougata DasОценок пока нет
- 250 MHZ RF GeneratorДокумент7 страниц250 MHZ RF GeneratorSougata DasОценок пока нет
- Create Todo List Ruby On RailsДокумент9 страницCreate Todo List Ruby On RailsaliaseelshareefОценок пока нет
- Standart PortsДокумент3 страницыStandart PortsAbhinayMylavarapuОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Switches and AccessoriesДокумент13 страницMagnetic Switches and AccessoriesMarko NedicОценок пока нет
- Os9 Bab60 1a SoftwДокумент80 страницOs9 Bab60 1a Softwgarysun585Оценок пока нет
- Get StartДокумент79 страницGet StartIamandei ElenaОценок пока нет
- File Net SysrefДокумент150 страницFile Net SysrefFernando NunesОценок пока нет
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing Question BankДокумент16 страницCs9251 Mobile Computing Question BankNivithaОценок пока нет
- Extreme Cat 6 Component-Rated Utp Quickport Jack: Product Specifications 61110-Xx6Документ2 страницыExtreme Cat 6 Component-Rated Utp Quickport Jack: Product Specifications 61110-Xx6Adi PurnomoОценок пока нет
- KeysДокумент3 страницыKeysjojo sosoОценок пока нет
- Session 04 - Homework-1Документ3 страницыSession 04 - Homework-1Thanh TranОценок пока нет
- Chat Log SampДокумент14 страницChat Log SampAnonymous SaLWoIgABHОценок пока нет
- MIDAS Resultant Force DiagramДокумент7 страницMIDAS Resultant Force DiagramBALRAJОценок пока нет
- Lab No.3 CCNДокумент2 страницыLab No.3 CCNMaham AkramОценок пока нет
- Structure of A SwitchДокумент25 страницStructure of A SwitchArijit MukhopadhyayОценок пока нет
- TourTrax ManualДокумент115 страницTourTrax ManualTim BramhamОценок пока нет
- Vloc3 Pro Sales Sheet VXMT MSP PDFДокумент2 страницыVloc3 Pro Sales Sheet VXMT MSP PDFCristhian CoariteОценок пока нет
- Cs Ps Core Network Planning Training CourseДокумент3 страницыCs Ps Core Network Planning Training Coursenima_farzad5718Оценок пока нет
- Wired CommunicationДокумент1 страницаWired CommunicationSushilShankerMishra100% (3)
- QNAPДокумент112 страницQNAPshaggerukОценок пока нет
- Wind River License Administrator Tools Guide 1.1Документ134 страницыWind River License Administrator Tools Guide 1.1patopickОценок пока нет
- Letter From Brian Glicklich To Twitter General Counsel Vijaya GaddeДокумент18 страницLetter From Brian Glicklich To Twitter General Counsel Vijaya GaddeBrian GlicklichОценок пока нет
- Jag Extreme ManualДокумент252 страницыJag Extreme ManualrancokilОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolДокумент5 страницCHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolAlexandrosAristeridisОценок пока нет
- Esp 32Документ17 страницEsp 32henry jhonsonОценок пока нет
- Computer ServicingДокумент30 страницComputer ServicingJhon Keneth NamiasОценок пока нет
- Arduino MatterДокумент7 страницArduino MatterChemudupati SunilОценок пока нет
- 11gR2 Node Addition Post Host ReimageДокумент5 страниц11gR2 Node Addition Post Host ReimageSaeed MeethalОценок пока нет
- ML 2165Документ210 страницML 2165बासुदेव अर्यालОценок пока нет
- SQL Temenos t24Документ14 страницSQL Temenos t24Ashwin LeonardОценок пока нет
- Khan y Kellner-Opositional Politics and The Internet PDFДокумент27 страницKhan y Kellner-Opositional Politics and The Internet PDFcanicanitaОценок пока нет