Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mikey 1stshift Clinicalanatomy
Загружено:
Michael Jeffrey M. MillaresИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mikey 1stshift Clinicalanatomy
Загружено:
Michael Jeffrey M. MillaresАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 Shift Shifting Exam Reviewer
st
Anatomy
2007 Mikey
Clinical Anatomy
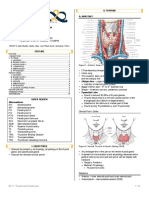
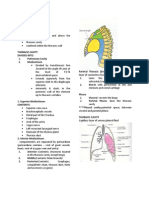
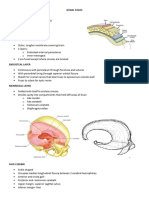
SCALP Loose areolar tissue dangerous layer of the scalp due to the presence of emissary vein. Bleeding is profuse due to high vascularity plus the fact that the vessels cannot retract or constrict because of the surrounding fibrous tissue. SKULL Anterior Fontanel former site indicated by bregma. Estimates hydration during infancy. Posterior Fontanel former site indicated by lambda. Pterion contains anterior branch of middle meningeal artery Skull Fractures Linear most frequent Depressed inner table is more fractured than the outer table Basal Skull o Anterior cranial fossa - involves frontal, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal sinuses; bleeding into nose and mouth. CSF leakage from nose (tear in meninges); anosmia loss of smell. o Middle cranial fossa bleeding of CSF from the ear o Posterior fossa cranial nerve damage; bruising over mastoid region. Sutural Landmarks Bregma Lambda Lambdoid Coronal Pterion Metopic
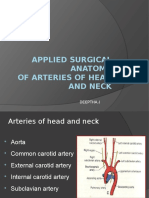
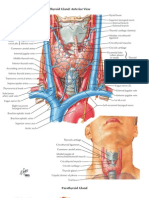
Malocclusion displacement of the bone fragments. Muscles of mastication (TIM) Temporalis, Masseter, Internal Pterygoid. Opponents: External pterygoid, Digastric, Mylohyoid, Geniohyoid. Clonic chattering of teeth, Tonic Trismus, lockjaw Angular vein (at the sides of the nose) dangerous area of the face; external nose. Bells Palsy unable to close their lips and eye on the affected side. Injury to facial nerve. Langers Lines surgical incisions must be made along these lines. Sialolith calcified deposit blocking the parotid duct. NECK Zone I submandibular and submental nodes Zones II IV lymph nodes along jugular vein (deep to the SC, upper, mid, and lower neck) Zones V nodes that lie posterior to the SCM. Commonly enlarged with viral infections. Zone VI between the carotid sheaths; drain larynx and thyroid gland. Thyroid Epithyroideum true capsule Perithyroideum false capsule; opened in thyroidectomy; derived from the pretracheal fascia. External Laryngeal Nerve injury to this nerve causes hoarseness. Monotonous voice due to paralysis of cricothyroid muscle; Closely related to superior thyroid artery. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve injury causes aphonia (Bilateral); passes near inferior thyroid artery. Enlarged Goiter Dyspnea trachea Dysphagia esophagus Enophthalmus prolonged pressure on adjacent cervical sympathetic chain Thyroid gland moves with swallowing because the suspensory ligament of Berry binds the gland to the sides of the cricoid cartilage.
FACE Common Facial Fractures Le Fort I horizontal fracture of the maxilla; upper jaw becomes movable. Le Fort II entire central part of the face becomes movable. Le Fort III The maxilla and zygomatic bones are separated from the rest of the skull. Antrum of Highmore biggest cavity of maxillary bone. Common Sites of Fracture of the Mandible Coronoid process Neck of the mandible Angle of the mandible Body of the mandible
UPPER EXTREMITIES Flattening shoulder Impacted fracture about anatomical neck Dislocation of the head of humerus from glenoid cavity Atrophy of deltoid muscle Erbs birth palsy Muscular Dystrophy Axillary nerve damage
Clavical Fractures Indirect when one falls and tries to break the fall by extending the upper extremity; inner fragment remains unchanged; outer fragment is pulled downward. Direct fragments are driven inwards; compresses subclavian artery, brachial plexus. Axillary Vessels Formed by the vena comites of the brachial artery and the basilic vein. Adhered to the upper part of the costo-coacoid membrane (prevents its collapse) Close to the heart, inspiratory movement induce air embolism Median Nerve most injured; Musculocutaneous least injured. Brachial Plexus Upper trunk most commonly injured; exposed Erbs Palsy rupture of the upper trunk Klumpkes Paralysis injury of the lower trunk Forcibly pulled outward arm evulsion of roots from the cord Types of Dislocations subglenoid; subcoracoid (most common); subclavicular; subspinous (very rare) Kochers Method very slow external rotation of humerus; a movement directly forward of the elbow; rapid internal rotation. Hippocratic method foot is used as fulcrum. Surgical neck of humerus most commonly fractured. Cephalic vein upper part of arm used in introducing a catheter for determination of central venous pressure. Medial cubital/Median vein intravenous injections because: they are large and prominent; superficial; least movable; least subject to variations. Volkmans Ischemic fibrosis of muscles of the anterior compartment of the forearm from tight bandages over the elbow in the fully flexed position. Colles Fracture compression fracture above the wrist (dinner fork) Ulna is more often fractured by direct violence; hair on the dorsum of the proximal phalanges are directed towards the ulna; Sweat glands are numerous in the palm; rich supply of Pacinian corpuscles Ulnar Nerve C8&T1; muscles paralyzed: flexor carpi ulnaris, medial half of the FDP, medial two lumbricals, all interossei and the adductor pollicis. Hand resembles a claw. Median Nerve inability to approximate the 5 fingers. Compressed at the wrist in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Radial Nerve paralysis of triceps, anconeus, extensors of the wrist (wrist drop). Injured if humerus breaks. Failure to extend the digits (Trigger test). Infections: Carbuncles found in dorsum of hand and fingers due to presence of hair follicles and sweat glands Felon infection involving closed spaces of the terminal phalanx (osteomyelitis if not treated early) Paronchia (run around) infection with abscess formation under the root of the nail. Tenosynovitis tendon sheath infection. Usually flexor tendon. Palmar Abscesses mid-palmar = normal concavity of the palm becomes convex. Thenar = normal concave curve between the thumb and index finger is convex.
Вам также может понравиться
- X ANATOMY HEAD AND NECKДокумент16 страницX ANATOMY HEAD AND NECKArijeet77Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and NeckДокумент21 страницаAnatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and NeckTracie YW100% (1)
- Gross Anatomy CheatsheetДокумент302 страницыGross Anatomy CheatsheetNobody2015100% (1)
- SecretДокумент72 страницыSecretTravis JungleОценок пока нет
- Behind The Knife ABSITE Podcast CompanionДокумент270 страницBehind The Knife ABSITE Podcast CompanionMuhammad Zeeshan87% (30)
- Head and NeckДокумент63 страницыHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- Anatomy Quest.Документ9 страницAnatomy Quest.Ade AlcarazОценок пока нет
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewДокумент119 страницPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaОценок пока нет
- Head & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFДокумент113 страницHead & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFPranavОценок пока нет
- 05.11.02 Thyroid and ParathyroidДокумент10 страниц05.11.02 Thyroid and Parathyroidbo gum parkОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Nose and Sinus Paranasal, Case RhinosinusitisДокумент51 страницаAnatomy of The Nose and Sinus Paranasal, Case RhinosinusitisDera Seta SaputriОценок пока нет
- Neurosurgery Congenital Anomalies: Types & DefinitionsДокумент41 страницаNeurosurgery Congenital Anomalies: Types & DefinitionsMAYОценок пока нет
- The Head and Neck Lectures: Anas Ibrahim YahayaДокумент242 страницыThe Head and Neck Lectures: Anas Ibrahim YahayaBilkisu badamasiОценок пока нет
- eMRCS AnatomyДокумент158 страницeMRCS AnatomyNayem Hossain Hemu50% (2)
- Anaesthesia For Thyroid SurgeryДокумент19 страницAnaesthesia For Thyroid SurgeryPraveen Ramasamy0% (1)
- TMP - 21700-Basic Science Summary For The MRCS-2069613412Документ111 страницTMP - 21700-Basic Science Summary For The MRCS-2069613412Omar Sarahneh100% (5)
- First Aid Anatomy NotesДокумент15 страницFirst Aid Anatomy NotessethrbОценок пока нет
- High Yield EmbryologyДокумент5 страницHigh Yield EmbryologyKyle Derouen100% (1)
- External Carotid ArteryДокумент80 страницExternal Carotid Arterybaba bunnyОценок пока нет
- Head and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017Документ53 страницыHead and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017aaamirrrОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Cranial CavityДокумент35 страницIntroduction To Cranial CavityexoОценок пока нет
- Difficult Airway AlgorithmДокумент48 страницDifficult Airway AlgorithmshikhaОценок пока нет
- Pearls and Pitfalls in Head and Neck SurgeryДокумент225 страницPearls and Pitfalls in Head and Neck SurgeryMoustafa Amin AlyОценок пока нет
- Thyroidectomy Morbidities:: Preventions & InterventionsДокумент52 страницыThyroidectomy Morbidities:: Preventions & InterventionsAlfonso DanacОценок пока нет
- Arterial Suppply of Head&NeckДокумент89 страницArterial Suppply of Head&NeckPiyusha SharmaОценок пока нет
- Arteries of Head and NeckДокумент77 страницArteries of Head and NeckdeepthamagetОценок пока нет
- Neurosurgical EmergenciesДокумент25 страницNeurosurgical EmergenciesFarah Wahidah Abd RazakОценок пока нет
- Ajay YadavДокумент351 страницаAjay YadavTabish Javaid90% (10)
- Anatomy One LinersДокумент10 страницAnatomy One Linersridin007100% (2)
- Head N Neck-MCQsДокумент57 страницHead N Neck-MCQsbhargavi pasagadaОценок пока нет
- Basic Sinus AnatomyДокумент71 страницаBasic Sinus AnatomyTalal AlanzyОценок пока нет
- 4 6021775789463175331Документ163 страницы4 6021775789463175331Muhammad Farrukh ul IslamОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmic ENT sLE MCQДокумент10 страницOphthalmic ENT sLE MCQAsif Newaz100% (4)
- Correlative AnatomyДокумент19 страницCorrelative AnatomyLicensed to HealОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 3RD Semester by Apostle JohnДокумент28 страницAnatomy 3RD Semester by Apostle JohnOROKE JOHN EJEОценок пока нет
- Anatomy ReviewДокумент95 страницAnatomy ReviewGaby Ycaza Zurita100% (2)
- Anatomy Review Block 1Документ32 страницыAnatomy Review Block 1ngОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of External EarДокумент49 страницAnatomy of External EarInderdeep AroraОценок пока нет
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFДокумент3 страницы48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachОценок пока нет
- ENT Course 1-2-3 General, Rhino. OtoДокумент30 страницENT Course 1-2-3 General, Rhino. Ototaliya. shvetzОценок пока нет
- ENT CourseДокумент29 страницENT Coursetaliya. shvetzОценок пока нет
- HN Infections Pic 2011 11Документ35 страницHN Infections Pic 2011 11Oriza Aridilah FitraОценок пока нет
- MSK SummaryДокумент5 страницMSK SummaryRahla KhanОценок пока нет
- Cranial CavityДокумент49 страницCranial CavityEastma MeiliОценок пока нет
- Ana 211 The Brachial PlexusДокумент10 страницAna 211 The Brachial PlexusAmadi CedarОценок пока нет
- Clinical Correlates Block IIIДокумент23 страницыClinical Correlates Block IIIAshley BuchananОценок пока нет
- GRDA Intro NeckДокумент12 страницGRDA Intro NeckKingОценок пока нет
- VTH CNДокумент59 страницVTH CNdoktergigikoeОценок пока нет
- Head & Neck: Clinical AnatomyДокумент42 страницыHead & Neck: Clinical Anatomycheckmate100% (1)
- Blood SupplyДокумент10 страницBlood Supplysyed ahmedОценок пока нет
- L13 - Diseases of LarynxI&IIДокумент90 страницL13 - Diseases of LarynxI&IINouf Al-orainiОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Embryology of The EarДокумент35 страницAnatomy and Embryology of The EarVictor EnachiОценок пока нет
- UW ObjectivesДокумент171 страницаUW ObjectivesCarolina Lopez0% (1)
- The Spinal - Cord: Dr. Budhi Suwarma, Sps FK UnjaniДокумент63 страницыThe Spinal - Cord: Dr. Budhi Suwarma, Sps FK UnjaniShiffaRamadhantiHОценок пока нет
- L 1 Scalp and FaceДокумент57 страницL 1 Scalp and FaceKashish GuptaОценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes SummaryДокумент16 страницBlue Boxes Summaryridin007Оценок пока нет
- Thoracic CavityДокумент6 страницThoracic CavityRubz JeanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Chest and LungsДокумент76 страницAnatomy of The Chest and LungsJeff GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Lateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideДокумент4 страницыLateral Ventricle: Number - Two in Number One On Each SideDr santoshОценок пока нет
- 3-4-5 Larynx Pharynx EsophagusДокумент25 страниц3-4-5 Larynx Pharynx Esophagustaliya. shvetzОценок пока нет
- Seminar Arterial Supply of Head and NeckДокумент73 страницыSeminar Arterial Supply of Head and NeckSANJU UDAYОценок пока нет
- Checklist 2Документ7 страницChecklist 2FranklinSappОценок пока нет
- 19 Spinal CordДокумент8 страниц19 Spinal Cordkarar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Branchial Pharyngeal Arches ConciseДокумент66 страницBranchial Pharyngeal Arches ConciseRitika Ahuja MalhotraОценок пока нет
- LMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesДокумент7 страницLMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesYuku BabyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 NotesДокумент4 страницыChapter 14 NotesRhianon Annie McDowellОценок пока нет
- Anatomy One Liners PDFДокумент12 страницAnatomy One Liners PDFAbida AhmedОценок пока нет
- Dent 730Документ15 страницDent 730Noelia FernandezОценок пока нет
- Dural FoldsДокумент3 страницыDural FoldsHello VintunnaraОценок пока нет
- The LarynxДокумент60 страницThe LarynxAbeer RadiОценок пока нет
- Anatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleДокумент4 страницыAnatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleJasmine TeoОценок пока нет
- A State in Which Body Lacks O or Defective Aeration of Blood - Mechanical Interference With RespirationДокумент99 страницA State in Which Body Lacks O or Defective Aeration of Blood - Mechanical Interference With RespirationVirendar Pal SinghОценок пока нет
- The Technique: of ThyroidectomyДокумент5 страницThe Technique: of Thyroidectomyعمر كمالОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesДокумент32 страницыMuscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesMaria Celina Lomboy SerapioОценок пока нет
- Oina MusclesДокумент73 страницыOina MusclesShen AndradeОценок пока нет
- NBDE Part 1 - 2010 Remembered QuestionsДокумент1 страницаNBDE Part 1 - 2010 Remembered QuestionsGEORGWHTОценок пока нет
- Trachea: Aguirre - Ecalnir - Maniego - VenturanzaДокумент41 страницаTrachea: Aguirre - Ecalnir - Maniego - VenturanzaCarlo ManiegoОценок пока нет
- Department of ZoologyДокумент27 страницDepartment of ZoologyAleenaОценок пока нет
- ENT-Laryngeal ParalysisДокумент26 страницENT-Laryngeal ParalysisRahul Kumar DiwakarОценок пока нет
- Gross Anatomy and Physiology of The Larynx: Samantha Soriano-Castañeda, MD, Fpso-Hns 10/30/2017Документ4 страницыGross Anatomy and Physiology of The Larynx: Samantha Soriano-Castañeda, MD, Fpso-Hns 10/30/2017Abi SulitОценок пока нет
- Thyroidectomy Vula AtlasДокумент15 страницThyroidectomy Vula AtlasyvonneОценок пока нет
- ThyroidectomyДокумент3 страницыThyroidectomyAnshuman Fotedar100% (1)
- Anatomical Steps of ThyroidectomyДокумент7 страницAnatomical Steps of ThyroidectomyJacobMsangОценок пока нет
- HemithyroidectomyДокумент2 страницыHemithyroidectomyShanthi ReddymasuОценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes SummaryДокумент16 страницBlue Boxes Summaryridin007Оценок пока нет
- 3 Ways To Examine The Larynx: PiriformДокумент10 страниц3 Ways To Examine The Larynx: PiriformbeautyОценок пока нет
- Superior Laryngeal Nerve InjuryДокумент11 страницSuperior Laryngeal Nerve InjuryBrilli Bagus DipoОценок пока нет
- Open Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Operative SurgeryДокумент16 страницOpen Access Atlas of Otolaryngology, Head & Neck Operative SurgeryMihai Ionut TanaseОценок пока нет