Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
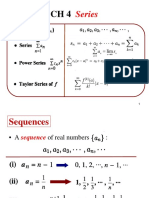
Series
Загружено:
Ansikhan KingkhanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Series
Загружено:
Ansikhan KingkhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Series Cheatsheet
Denitions
Basic Series
Innite Sequence: sn Limit/Convergence of a Sequence: limn sn = L Innite Serie: (Partial sums) Sn = Geometric Serie:
n k=1
MacLaurin Serie If f a function innitely differentiable,
f (n) (0) n x n! n=0 Taylors Formula with Remainder x between c and x such that
n
sn = s1 + s2 + + sn + a(1 rn ) 1r
f (x) =
k=0
f (k) (c) (x c)k + Rn (x) k! f (n+1) (x ) (x c)n+1 (n + 1)!
ark1 = Sn = a + ar + ar2 + + arn1 =
Rn (x) =
Positive Series
Positive Serie: If all the terms sn are positive. Integral Test: If f (n) = sn , continuous, positive, decreasing: Comparison Test: an and bn where ak < bk (k m)
an bn
Applications
Application: Showing Function/Taylor-Series Equivalence sn converges 1. If 2. If exists,
1
f (x)dx converges.
n+
lim Rn (x) = 0
bn converges, so does an an diverges, so does bn an converges bn converges.
Application: Approximating Functions or Integrals Rn (x0 ) < K Binomial Serie (1 + x)r = 1 +
+ n=1
Limit Comparison Test:
an and
bn such that limn
Convergence
Alternating Serie: (1)n+1 an = a1 a2 + a3 a4 + a5 |sn | is convergent. sn is convergent but not absolutely convergent. < 1: absolutely convergent 1: (no conclusion) > 1 or +: diverges < 1: absolutely convergent 1: (no conclusion) > 1 or +: diverges fn (x) f (x) <
r(r 1)(r 2) (r n + 1) n x n!
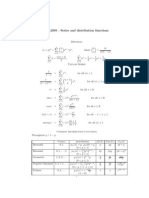
Common Series
ex = x2 x3 xn =1+x+ + + n! 2! 3! n=0
Absolute Convergence: If Conditional Convergence: If
Ratio Test: If limn | sn+1 | = sn
1 = xn = 1 + x + x2 + x3 + + 1 x n=0
ln(1 + x) =
(1)n1
n=0
xn 1 1 1 = x x2 + x3 x4 + n 2 3 4
Root Test: If limn
|sn | =
sin x =
(1)n x2n+1 x3 x5 x7 =x + + (2n + 1)! 3! 5! 7! n=0 (1)n x2n x2 x4 x6 =1 + + (2n)! 2! 4! 6! n=0 x2n+1 x3 x5 x7 =x+ + + + (2n + 1)! 3! 5! 7! n=0 x2n x2 x4 x6 =1+ + + + (2n)! 2! 4! 6! n=0
Uniform Convergence: If > 0, m such that for each x and every n m,
cos x =
Power Series
Power Serie:
+ n=0
sinh x = an (x c)n = a0 + a1 (x c) + a2 (x c)2 +
cosh x =
Power Serie About Zero:
+ n=0
an xn = a0 + a1 x + a2 x2 +
Taylor Serie If f a function innitely differentiable,
f (n) (c) (x c)n n! n=0
Author: Martin Blais, 2009. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution - Non-Commercial - Share-Alike license.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- Math Formulas: Arithmetic and Geometric Series: NotationДокумент4 страницыMath Formulas: Arithmetic and Geometric Series: Notationtdzida26Оценок пока нет
- Calculus BookletДокумент6 страницCalculus Bookletangie81Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Power SeriesДокумент19 страницChapter 3 - Power SeriesAlex TanОценок пока нет
- Section 26: - Review of Power SeriesДокумент12 страницSection 26: - Review of Power SeriesPalash SiddamsettiwarОценок пока нет
- PP 14Документ2 страницыPP 14monu991Оценок пока нет
- Review of CH 4 (2nd Part) Power SeriesДокумент15 страницReview of CH 4 (2nd Part) Power Serieslzyabc597Оценок пока нет
- Math Stats Booklet 1Документ20 страницMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoОценок пока нет
- 11p8 PDFДокумент14 страниц11p8 PDFltt00218925293045Оценок пока нет
- Power SeriesДокумент1 страницаPower SeriesjingalingtingОценок пока нет
- Numerical Series: 7. Solved ProblemsДокумент22 страницыNumerical Series: 7. Solved ProblemsMarian LupulescuОценок пока нет
- Calculus FormulasДокумент1 страницаCalculus FormulasKimberly WaltersОценок пока нет
- Power Series ExpДокумент42 страницыPower Series ExpkunjuОценок пока нет
- Calculus FormulaДокумент2 страницыCalculus FormulaleeshiОценок пока нет
- List MF9: MATHEMATICS (8709, 9709) Higher Mathematics (8719) STATISTICS (0390)Документ8 страницList MF9: MATHEMATICS (8709, 9709) Higher Mathematics (8719) STATISTICS (0390)Muhammad FarhanОценок пока нет
- Formulae Sheet: Some Trigonometric FormulasДокумент1 страницаFormulae Sheet: Some Trigonometric FormulasceprostieОценок пока нет
- Important Series in CalculusДокумент2 страницыImportant Series in CalculusBob leОценок пока нет
- Infinite Series Sequence:: S U, U,, UДокумент29 страницInfinite Series Sequence:: S U, U,, UAvinash SinghОценок пока нет
- Tests For Convergence: N N N N N A 1 R N 1 1 NДокумент2 страницыTests For Convergence: N N N N N A 1 R N 1 1 NytpukhhisОценок пока нет
- Cap1 Sol Calculus 1Документ45 страницCap1 Sol Calculus 1Brisc BiancaОценок пока нет
- University of Cambridge Department of Chemical Engineering DatabookДокумент40 страницUniversity of Cambridge Department of Chemical Engineering DatabookwaterdrinkОценок пока нет
- Examples02 Power SeriesДокумент12 страницExamples02 Power SeriesEmilОценок пока нет
- Series: N N N NДокумент52 страницыSeries: N N N Nlzyabc597Оценок пока нет
- 13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFДокумент11 страниц13.differentiation and Integration of Power Series PDFAtikah JОценок пока нет
- Extra Problems For Test 3 Math 2414Документ8 страницExtra Problems For Test 3 Math 2414tyler.mcclainОценок пока нет
- Seminar LimiteДокумент3 страницыSeminar LimiteGheorghePîrţacОценок пока нет
- Maths FormulaДокумент4 страницыMaths Formulamickey_disney93Оценок пока нет
- Stewart 8Документ3 страницыStewart 8alleblinkОценок пока нет
- Math Paper 3 Practice MSДокумент47 страницMath Paper 3 Practice MSRaahish KalariaОценок пока нет
- Tab LiceДокумент2 страницыTab LiceМилован МиљковићОценок пока нет
- Look-Up Table: Solving Differential EquationsДокумент10 страницLook-Up Table: Solving Differential Equationsgaurav_juneja_4Оценок пока нет
- 9.5 - Testing Convergence at EndpointsДокумент13 страниц9.5 - Testing Convergence at Endpointsasoni98Оценок пока нет
- SeriesДокумент2 страницыSeriesdevagyna_p_pandyaОценок пока нет
- Series TableДокумент1 страницаSeries TableTsatsaa TstsОценок пока нет
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetДокумент2 страницыAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Differentiation Cheat SheetДокумент15 страницDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboОценок пока нет
- 2003test2 mth240Документ2 страницы2003test2 mth240Urshia Likes CookiesОценок пока нет
- Sol 6 Fall 04Документ9 страницSol 6 Fall 04Daniel Cervantes CabreraОценок пока нет
- Math ReferenceДокумент24 страницыMath ReferenceSujib BarmanОценок пока нет
- Examples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Документ8 страницExamples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Shaibal AhmedОценок пока нет
- Analiza InfoДокумент36 страницAnaliza InfoButiri CristianОценок пока нет
- Tcu12 CRC SinglegДокумент2 страницыTcu12 CRC SinglegTyler BienhoffОценок пока нет
- 03 Truncation ErrorsДокумент37 страниц03 Truncation ErrorsArturo AvilaОценок пока нет
- Seven Power Series To Memorize: For MATH 123Документ1 страницаSeven Power Series To Memorize: For MATH 123Edgar FigueroaОценок пока нет
- Things+to+know+ Part+2 PDFДокумент2 страницыThings+to+know+ Part+2 PDFJohn ChenОценок пока нет
- Sol. Stein Cap 6 PDFДокумент9 страницSol. Stein Cap 6 PDFAline MeloОценок пока нет
- ECE 5650/4650 Tables For Exam I: Sequence Sum FormulasДокумент3 страницыECE 5650/4650 Tables For Exam I: Sequence Sum Formulasue06037Оценок пока нет
- Commonly Used Taylor SeriesДокумент4 страницыCommonly Used Taylor SeriesBob leОценок пока нет
- Series Tests 2Документ3 страницыSeries Tests 2Kyle KoofersОценок пока нет
- MATH 122: Calculus II: Section 8.7 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesДокумент19 страницMATH 122: Calculus II: Section 8.7 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesJosé MendozaОценок пока нет
- Convergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFДокумент7 страницConvergence of Taylor Series (Sect. 10.9) PDFTu ShirotaОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОт EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsОценок пока нет
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)От EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Оценок пока нет
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)От EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Оценок пока нет