Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Siva
Загружено:
Shashank_Pande_1611Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Siva
Загружено:
Shashank_Pande_1611Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Introduction to the new mainfame: z/OS basics Chapter 1: The new mainframe
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Chapter 1 objectives
Be able to:
List ways in which the mainframe of today challenges the traditional thinking on centralized computing versus distributed computing Explain how businesses make use of mainframe processing power, the typical uses of mainframes, and how mainframe computing differs from other forms of computing Outline the major types of workloads for which mainframes are best-suited Name five jobs or responsibilities related to mainframe computing List four mainframe operating systems.
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Key terms in this chapter
application programmer architecture batch processing compatibility e-Business EBCDIC high availability infrastructure mainframe online processing
platform production control punched card RAS scalability server farm system administrator system operator system programmer transaction processing
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Evolving architecture
CMOS HW S/360 S/370 S/370XA 31 bits ESA/390 Parallel Sysplex z/Architecture 64 bits
1964
1970
1980
1990
2000
2004
MVT, PCP MFT SW
MVS - VTAM
MVS/XA
MVS/ESA OS/390
USS TCP/IP
z/OS
Linux CICS VM DB2 WebSphere z/VM
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Mainframes in our midst
Mainframes: Are prevalent, yet hidden from public eye Not often publicized stable, reliable, dependable. Contrast with other forms of computing, such as PCs. Present opportunities for college graduates in a variety of technical fields.
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
What is a mainframe? A mainframe is a computing system that businesses use to host the commercial databases, transaction servers, and applications that require a greater degree of security and availability than is commonly found on smaller-scale machines. The power of a mainframe provides computing speed and capacity, enabling it to perform high volumes of processing. The mainframe can process a mixed workload of jobs from different time zones and of different types.
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Mainframe facts
Who uses mainframes?
Most Fortune 1000 companies use a mainframe environment 60% of all data available on the Internet is stored on mainframe computers
Why mainframes?
Large-scale transaction processing
Thousands of transactions per second
Support thousands of users and application programs Simultaneously accessing resources Terabytes of information in databases Large-bandwidth communications
There are more CICS transactions processed daily than Web pages served
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Factors contributing to mainframe use RAS -- reliability, availability, serviceability Security Scalability Centralized control Workload management Partitioning / virtualization Continuing compatibility Evolving architecture Application enablement, complexity, variety Potential for thousands of users
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Typical mainframe workloads
Application Program
Batch job
Input Data
Process data to perform a particular task Output Data
Application Program Query Reply Access shared data on behalf of online user
Online (real time) transaction
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Typical batch use
Residence
CREDIT CARD
Branch offices
1234 5678 9012
VALID FROM GOOD THRU
XX/XX/XX XX/XX/XX XX/XX/XX PAUL FISCHER PAUL FISCHER
Account balances bills, etc
Main office 5
Processing reports 7
Reports Statistics,
4 summaries,
exceptions
Partners and clients exchange information
Mainframe
Processing batch jobs Reports
2 1
Reports
Backup s 3
Data update
Tape Storage 10
Sequential data sets
Disk Storage
Production Control System Operator databases
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Typical online use
ATMs
Account activities
SNA or TCP/IP network
4
Requests
Branch offices
Branch office automation systems
2 3
Office automation systems
Mainframe
Accesses database
queries and updates
Central office Business analysts Inventory control Disk storage controller
Stores database files
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Roles in the mainframe world
Roles
Application Developer Production Control Analyst
Operator End User
System Programmer
System Administrator
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Mainframe operating systems z/OS z/VM VSE Linux for zSeries z/TPF
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Introduction to the new mainframe
Summary
The New Mainframe:
Plays a central role in the daily operations of the worlds largest organizations and the daily lives of most people. Is known for its reliability, security, and enormous processing capabilities. Is designed for processing large scale workloads and serving thousands of users and transactions concurrently. Is managed by highly skilled technical support staff. Runs a variety of operating systems.
Copyright IBM Corp., 2005. All rights reserved.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Beginners Guide To The Post Installation Configuration of SAP Access Control PDFДокумент123 страницыA Beginners Guide To The Post Installation Configuration of SAP Access Control PDFBob SmythОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- XLR UserDemoДокумент27 страницXLR UserDemoSobhy GendykhelaОценок пока нет
- Operating SystemДокумент28 страницOperating SystemKunalОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- TpsДокумент14 страницTpsRohith JayaramОценок пока нет
- SchedulingДокумент252 страницыSchedulingSnehal BhattОценок пока нет
- OSY Notes Vol 1 - Ur Engineering FriendДокумент68 страницOSY Notes Vol 1 - Ur Engineering FriendSameer TembhareОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- CPOB - DocumentationДокумент18 страницCPOB - DocumentationNatanaelHendrySantosoОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Vin PlusДокумент20 страницVin PlusNamrata ShettiОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Natural Performance Considerations: by Andreas Schütz Software AG August 2000 9th Natural User Conference BostonДокумент12 страницNatural Performance Considerations: by Andreas Schütz Software AG August 2000 9th Natural User Conference BostonjuliobernardОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The ICT Lounge: Section 7.7: Types of ProcessingДокумент6 страницThe ICT Lounge: Section 7.7: Types of ProcessingMahmoud A.RaoufОценок пока нет
- Internal Control in The Computer Information System Chap 27 Aud 5 FINALДокумент37 страницInternal Control in The Computer Information System Chap 27 Aud 5 FINALJay LloydОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Sap SD - Sap SD Interview Questions With AnswersДокумент22 страницыSap SD - Sap SD Interview Questions With AnswersAbhinavkumar PatelОценок пока нет
- BDC LSMW CustomerДокумент13 страницBDC LSMW CustomerRavi kishore G100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Period End Process For OPM OrgsДокумент7 страницPeriod End Process For OPM OrgstenalisОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- EBS 122 Cum RCD VCPДокумент291 страницаEBS 122 Cum RCD VCPRajesh BalbaleОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- vt59.2708-21282868044 626785678961539 7501882681118986219 n.pdfMXT122-Learning-Module - PDF NC Cat 110&cДокумент73 страницыvt59.2708-21282868044 626785678961539 7501882681118986219 n.pdfMXT122-Learning-Module - PDF NC Cat 110&cFabrigasBennetОценок пока нет
- DIY Exercise 13-1 - Create A Batch Job To Process RecordsДокумент4 страницыDIY Exercise 13-1 - Create A Batch Job To Process Recordssurendra54Оценок пока нет
- Jde 910 Accounts ReceivableДокумент612 страницJde 910 Accounts ReceivableazizirfanОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- BDC DocumentДокумент3 страницыBDC DocumentMayur GBОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Dispute Management With SAP FSCMДокумент20 страницDispute Management With SAP FSCMdurgaaus100% (1)
- Informatica MDM CourseДокумент3 страницыInformatica MDM CoursesunilchopseyОценок пока нет
- Solutions 10-1 and 10-7Документ7 страницSolutions 10-1 and 10-7Seth936276772Оценок пока нет
- Control-M Concepts GuideДокумент50 страницControl-M Concepts Guideksaw11100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Erpi AdminДокумент428 страницErpi Adminmohamed-mof100% (1)
- Lecture 01Документ41 страницаLecture 01Jooo loОценок пока нет
- BDC Interview QuestionsДокумент5 страницBDC Interview Questionsవంశీ యుОценок пока нет
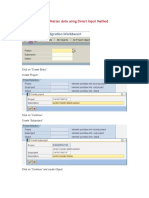
- Uploading Vendor Master Data Using Direct Input Method: Go To Transaction LSMWДокумент42 страницыUploading Vendor Master Data Using Direct Input Method: Go To Transaction LSMWChaituОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter Four Common Business Applications of Information TechnologyДокумент14 страницChapter Four Common Business Applications of Information TechnologyHayelom Tadesse GebreОценок пока нет
- SAP BASIS Introductory Training Program - Day 2Документ68 страницSAP BASIS Introductory Training Program - Day 2luongdkОценок пока нет
- Sterling Connect Direct Z-OS Users GuideДокумент234 страницыSterling Connect Direct Z-OS Users GuideVictor SerranoОценок пока нет