Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SMS Call Flow
Загружено:
Kumar VivekИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SMS Call Flow
Загружено:
Kumar VivekАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
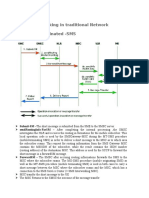
Assumptions: A and B both are Vodafone Delhi Subscribers (Ported In or normal). A is postpaid number.
Let us now go through signalling flow. 1) A sends an SMS to B. Mobile Originated Forward Short Message (MO-FSM) is send to STP/MNP with destination as SMSC address(SMSC GT). SMSC address is already stored in SIM. MO-FSM also contains B number to which SMS is sent. 2) MNP check its database attaches RN/LRN to B number and forward MO-FSM to SMSC. 3) SMSC acknowledges the MO-FSM by FSM Response to MSC. This three steps complete the MO leg of SMS Flow and handset receives an indication "SMS sent" at this point of flow. 4) Step4 marks the beginning of SMS terminating flow. SMSC checks this is our own RN/LRN removes RN from B number and sends Send Routing Info- Short Message (SRI-SM) to STP/MNP. This message can be directly send to HLR also that depends on network topology. 5) SRI-SM is forwarded to HLR with B number.
6) HLR responds SRI-SM Response with the VLR address where subscribers is currently registered and IMSI of B number. 7) On receiving VLR address now SMSC knows where to send MT-FSM. SMSC send MT-FSM to that particular VLR with B number IMSI and SMS data. Here after MSC tries to deliver this message to B Subscriber using standard MT SMS flow. 8) MSC/VLR acknowledge SMSC by MT-FSM response which contains status of MT SMS. i.e delivered or failed cause if SMS is not delivered to B number. This sums the SMS flow in case of MNP,our main motive was to highlight the difference between normal and MNP SMS Flow. Hope we fulfilled that and hope this post was informative for you.
Вам также может понравиться
- SMS BasicДокумент11 страницSMS Basicsrsnth100% (1)
- Basiccall Flow Part 2Документ14 страницBasiccall Flow Part 2Sneha JohnОценок пока нет
- SMSC Call FlowsДокумент12 страницSMSC Call FlowsAnkit Raina100% (1)
- GSM Call SetupДокумент6 страницGSM Call SetupArockiaruby RubyОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Networks (In) and CAMELДокумент11 страницIntelligent Networks (In) and CAMELnaggu1983Оценок пока нет
- Camel PPSДокумент82 страницыCamel PPSmugeshpv90Оценок пока нет
- SMS Flow - Aditya GhaiДокумент5 страницSMS Flow - Aditya Ghaiunme_11Оценок пока нет
- SMS Routing - Call FlowsДокумент8 страницSMS Routing - Call Flowsreemajain2210Оценок пока нет
- 2G SMS FlowДокумент37 страниц2G SMS FlowShaharyar KhanОценок пока нет
- 1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSДокумент7 страниц1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSdilipsharma04Оценок пока нет
- Digit AnalysisДокумент50 страницDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- Sigtran Connectuon by CiscoДокумент75 страницSigtran Connectuon by CiscoKomunitasGerakanCintaJagapuraОценок пока нет
- Location Update DescriptionДокумент12 страницLocation Update Descriptionpradeepkumarverma07Оценок пока нет
- GSM Call Path CourseДокумент75 страницGSM Call Path CourseHeraa FarooqОценок пока нет
- SmsДокумент4 страницыSmsmberege1991Оценок пока нет
- SGSN Commands Global Title TranslationДокумент4 страницыSGSN Commands Global Title TranslationChristopher NicholsОценок пока нет
- 13 International RoamingДокумент10 страниц13 International RoamingMahesh Kumar NigamОценок пока нет
- Learn SoRДокумент8 страницLearn SoRRasheedKhouliОценок пока нет
- Basic ISUP SCCP MAP MessagesДокумент10 страницBasic ISUP SCCP MAP MessagesmukeshrinkОценок пока нет
- SMPP SMS Call FlowДокумент1 страницаSMPP SMS Call Flowkataz2010Оценок пока нет
- SMSC 1Документ52 страницыSMSC 1Manivannan LoganathanОценок пока нет
- In in Mobile - CamelДокумент62 страницыIn in Mobile - CamelManish Das100% (1)
- 01-02 Short Message ServiceДокумент21 страница01-02 Short Message ServiceUmar MiskiОценок пока нет
- 2 Signaling Connection Control Part SCCPДокумент12 страниц2 Signaling Connection Control Part SCCPMohamed AbushamaОценок пока нет
- Missed Call SolutionДокумент2 страницыMissed Call Solutionsuman_123Оценок пока нет
- TN - SA001 - E1 - 0 Digital Number Analysis-76Документ70 страницTN - SA001 - E1 - 0 Digital Number Analysis-76CoachArun MishraОценок пока нет
- International Roaming For GSMДокумент43 страницыInternational Roaming For GSMAyan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Study Theme 3 CamelДокумент47 страницStudy Theme 3 CamelMohammed AnwarОценок пока нет
- 10 Slides SMSДокумент12 страниц10 Slides SMSTuan AnhОценок пока нет
- SMSCДокумент12 страницSMSCmutaisteveОценок пока нет
- Call FlowДокумент30 страницCall Flownaveedraza4213Оценок пока нет
- HLR Data BarringДокумент2 страницыHLR Data BarringSamSameleviОценок пока нет
- Mobile Application PartДокумент7 страницMobile Application Partomjaijagdish.rai100% (1)
- R R RR: R R RRRRRRR RRR RRR RRR RRR RRR RДокумент6 страницR R RR: R R RRRRRRR RRR RRR RRR RRR RRR RSravan DameraОценок пока нет
- Call FlowtДокумент2 страницыCall Flowtmrinalkantinath100% (1)
- Traffic CasesДокумент30 страницTraffic CasesNitin JainОценок пока нет
- Need For Global Title TranslationДокумент5 страницNeed For Global Title TranslationKalaarangan100% (2)
- BICC ProtocolДокумент41 страницаBICC ProtocolYoussouf DoumbiaОценок пока нет
- SMS Over LTE - HALДокумент63 страницыSMS Over LTE - HALAsit SwainОценок пока нет
- SMS DocumentДокумент80 страницSMS Documentvetonim47Оценок пока нет
- OWB600719 PS International RoamingДокумент25 страницOWB600719 PS International RoamingJuan Carlos RОценок пока нет
- MNP Call FlowДокумент2 страницыMNP Call FlowKyle DiopОценок пока нет
- Mobile Terminating Call DescriptionДокумент9 страницMobile Terminating Call Descriptionpradeepkumarverma07Оценок пока нет
- Technical Report On VAS OperationsДокумент14 страницTechnical Report On VAS OperationsSamSameleviОценок пока нет
- CAMEL Feature1Документ34 страницыCAMEL Feature1elson brito juniorОценок пока нет
- M3UA Message Classes and Types:: Management (MGMT) Messages Transfer MessagesДокумент8 страницM3UA Message Classes and Types:: Management (MGMT) Messages Transfer MessagesSaurabh BarabdeОценок пока нет
- In Call FlowДокумент11 страницIn Call FlowPrathyusha VijayОценок пока нет
- IMS Signaling: Sebastian Schumann Slovak TelekomДокумент49 страницIMS Signaling: Sebastian Schumann Slovak TelekomAshish ShuklaОценок пока нет
- BICC ProtocolДокумент8 страницBICC ProtocolsinansafaaОценок пока нет
- VOIP SIP PardeepДокумент85 страницVOIP SIP PardeepViswanathОценок пока нет
- Home Location RegisterДокумент30 страницHome Location RegistermushishinaОценок пока нет
- Tac2 Workshop GSM Network: Call FlowДокумент26 страницTac2 Workshop GSM Network: Call FlowAdinda Dendi IsnandarОценок пока нет
- Map Call Flow ImportantДокумент22 страницыMap Call Flow ImportantPham Thanh TamОценок пока нет
- Camel Call FlowДокумент0 страницCamel Call FlowVenky KondepudiОценок пока нет
- ATI Call FlowДокумент39 страницATI Call FlowVivek ShahОценок пока нет
- CALL Flow ProcedureДокумент54 страницыCALL Flow ProcedureSitraka ALAINОценок пока нет