Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ec Mo Unemployment
Загружено:
Martin HuangИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ec Mo Unemployment
Загружено:
Martin HuangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Macroeconomic Objectives UNEMPLOYMENT
UNEMPLOYME NT
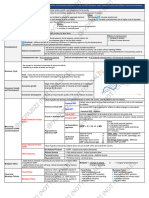
Types and Causes Note that some level of unN will always be present in an economy at the level we know as full employment. This natural rate of unN is also known as equilibrium unN. Below are the four main types of unN you should be aware of. Frictional Structural Arises when people are in Arises due to between jobs exists even 1. Changes in the structure when the economy is at full of the economy employment. 2. Mismatch between 1. Imperfect labour market skill/location of the labour operations force and those required 2. Immobility of workers for new jobs - Changes in pattern of demand/supply Policy Options Expansionary demand management policies Generally only works for demand-deficient unN as these policies increase AD Fiscal policy G on supply-side policies AD Income tax more incentive to be employed Monetary policy i/r Im AD [xcrp to increase demand for exports or to decrease amount of foreign labour] weak Conflicts Supply-side policies increase the productive capacity of the economy Improving employability: through education, retraining etc. (e.g. WDA in Singapore) Improving incentives for people to search and accept N (e.g. through tax/benefit reforms) Sustaining EG in the LR constantly creates new jobs
Classical 1. Monopoly power causing wages to be above market clearing level - Role of unions Consequences
Demand-deficient (cyclical) Involuntary unemployment 1. Due to lack of AD for goods 2. Associated with transitions of the economy through the business cycle
In general solving demand-deficient unN would have demand-pull inflationary pressures demand and costs pressures. Also, a low rate of unemployment may result in a current account deficit. External Decreased FDI unN FDI Especially in the case of structural unN labour force is deskilled, companies tend to pull out [unN M CP, current account this point is ] rather weak
Internal Ye < Y f unN output, G, NY all unN SOL runShort Loss of potential output that could have been produce if unemployed were employed less goods for consumption SOL for unemployed forced to consumer less due to lower YD Loss of output and profits: unN limits the outward shift of the PPC Structural unN inward shift of the PPC due to quantity of labour falling Long run Deskilling skills becoming obsolete PEG is affected in the LR PPC moves out less quickly Lower PEG unN dissavings S supply of loanable funds i/r Im K stock PEG (outward shift of PPC limited)
Income redistribution The Y-gap worsens as structural/seasonal unN tends to happen to people from lower Y groups Fiscal costs to governments In welfare states, G as unN benefits are paid out. Tax revenues both directly (as zero Y earners do not pay income tax) and indirectly (zero Y earners consume less and thus pay less taxes on C). Inefficiency as an economy is producing within the PPC Negative social effects like strikes, crimes and suicide.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ms20 - MacroeconomicsДокумент2 страницыMs20 - MacroeconomicsSeokjin KimОценок пока нет
- F2F W10 - ReviewДокумент9 страницF2F W10 - Reviews3976142Оценок пока нет
- Econ Review ProjectДокумент5 страницEcon Review ProjectNing GuangОценок пока нет
- AP Macro Cram Chart 2021Документ1 страницаAP Macro Cram Chart 2021weronikaОценок пока нет
- Types of Unemployment A) Seasonal UnemploymentДокумент6 страницTypes of Unemployment A) Seasonal Unemploymentabadi gebruОценок пока нет
- ECON1102 Macroeconomics ConceptsДокумент4 страницыECON1102 Macroeconomics ConceptsDikshit KashyapОценок пока нет
- Economics Reviewer - 3.3 MacroEconomic ObjectivesДокумент16 страницEconomics Reviewer - 3.3 MacroEconomic ObjectivesCK OngОценок пока нет
- Econs Monetary Policy TableДокумент11 страницEcons Monetary Policy Tableregine sunОценок пока нет
- Acroeconomic IMS: U NY SДокумент11 страницAcroeconomic IMS: U NY SHitisha agrawalОценок пока нет
- Reading 11 - Understanding Business CyclesДокумент33 страницыReading 11 - Understanding Business CyclesAllen AravindanОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three: Macro Economics: 1. Business CycleДокумент9 страницChapter Three: Macro Economics: 1. Business CycleTewodros TadesseОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - HandoutДокумент48 страницMacroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - Handoutdenny_sitorusОценок пока нет
- 44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2Документ12 страниц44-45. Demand and Supply Side Causes of Unemployment 2ryan sharmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ13 страницChapter 9ffffffОценок пока нет
- Sessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelДокумент143 страницыSessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelAbhay SahuОценок пока нет
- MacroДокумент6 страницMacrocorvids75% (4)
- SRJC JC2 H1 Econs / 2018 / Workbook - Economic GrowthДокумент25 страницSRJC JC2 H1 Econs / 2018 / Workbook - Economic GrowthXian LongОценок пока нет
- 總體經濟學 12Документ63 страницы總體經濟學 12王佑丞Оценок пока нет
- Recession Tips for EmployeesДокумент35 страницRecession Tips for EmployeesRegina Sharon PalletiОценок пока нет
- Economics Duran and LachicaДокумент1 страницаEconomics Duran and LachicaAaron Daniel DuranОценок пока нет
- New Pol Econ - Chapter 2Документ8 страницNew Pol Econ - Chapter 2Maureen OlvisОценок пока нет
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationДокумент3 страницы08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayОценок пока нет
- AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND DEMAND SHIFTSДокумент102 страницыAGGREGATE SUPPLY AND DEMAND SHIFTSPriyankaОценок пока нет
- Ammu Inflation & Unemployment English NotesДокумент5 страницAmmu Inflation & Unemployment English NotesAnimated TamashaОценок пока нет
- Ap Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study GuideДокумент23 страницыAp Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study Guideapi-243723152100% (1)
- BEC Notes Chapter 2Документ7 страницBEC Notes Chapter 2cpacfa100% (10)
- l1 Ec Rsheets b2Документ1 страницаl1 Ec Rsheets b2eloise.vernierОценок пока нет
- End Term Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыEnd Term Cheat SheetnupurОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14Документ32 страницыChapter 14bhavesh TanwaniОценок пока нет
- Ec Mo InflationДокумент2 страницыEc Mo InflationRellop NayОценок пока нет
- JP Mac MicДокумент43 страницыJP Mac MicJP MishraОценок пока нет
- Keynesian vs. Classical Income ModelДокумент70 страницKeynesian vs. Classical Income ModelNitish KhatanaОценок пока нет
- Economic Assignment 2Документ7 страницEconomic Assignment 2Prateek_Ghai_303Оценок пока нет
- Laws of Demand and Supply: 4 Phases of The Business CycleДокумент3 страницыLaws of Demand and Supply: 4 Phases of The Business CyclejazОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics AS-AD ModelДокумент3 страницыMacroeconomics AS-AD ModelMija DiroОценок пока нет
- Copia de Principles of Economics, Chapter 21 SummaryДокумент3 страницыCopia de Principles of Economics, Chapter 21 SummaryMariaDeLosAngelesPachecoRuizОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Aims and Issues Cheat SheetДокумент7 страницMacroeconomic Aims and Issues Cheat SheetAjathShatruRajuОценок пока нет
- Understanding Aggregate Demand and SupplyДокумент52 страницыUnderstanding Aggregate Demand and SupplyM Shubaan Nachiappan(Student)Оценок пока нет
- Advantages of Supply Side PoliciesДокумент1 страницаAdvantages of Supply Side PoliciesGupi PalОценок пока нет
- India's Slowdown: What It Is and What Can Be DoneДокумент6 страницIndia's Slowdown: What It Is and What Can Be DonePrisha BhatiОценок пока нет
- Link Between Resources, Income, EmploymentДокумент43 страницыLink Between Resources, Income, EmploymentPARVEENОценок пока нет
- ECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetДокумент2 страницыECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetCarla MissionaОценок пока нет
- Injections and WithdrawalsДокумент2 страницыInjections and WithdrawalsDynafrom100% (3)
- The circular flow of income and macroeconomic indicatorsДокумент9 страницThe circular flow of income and macroeconomic indicatorsjjkjljОценок пока нет
- Thiếu Hụt Ngân Sách Nhà NướcДокумент71 страницаThiếu Hụt Ngân Sách Nhà Nướccocghe2Оценок пока нет
- 7 As-AdДокумент34 страницы7 As-AdThảo Vân Nguyễn ThịОценок пока нет
- S.Y.B.com Semester III Business Economics Module 2Документ37 страницS.Y.B.com Semester III Business Economics Module 2dharmojiraotyОценок пока нет
- Lecture2020 SSP 9757Документ30 страницLecture2020 SSP 9757Sebastian ZhangОценок пока нет
- 7- aggregate demand and supply_student [Compatibility Mode]Документ21 страница7- aggregate demand and supply_student [Compatibility Mode]Hà Trang NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Fighting RecessionДокумент42 страницыWeek 2 Fighting Recessiondaisyruyu2001Оценок пока нет
- Spotting economics in everyday lifeДокумент4 страницыSpotting economics in everyday lifeneo leeОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics A2 UpdatedДокумент51 страницаMacroeconomics A2 UpdatedmatthewvanherzeeleОценок пока нет
- 5 Inflation Unemployment BCДокумент39 страниц5 Inflation Unemployment BCSara BatoolОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - The MacroeconomyДокумент10 страницUnit 9 - The MacroeconomyNaomiОценок пока нет
- IG Business Chapter 24Документ34 страницыIG Business Chapter 24JoyceeОценок пока нет
- OP Jindal Lecture Series Overview by RaguramJi RajanДокумент18 страницOP Jindal Lecture Series Overview by RaguramJi RajanAnkit KumarОценок пока нет
- Session 3 & 4 Aggregate Demand and Multiplier ModelДокумент64 страницыSession 3 & 4 Aggregate Demand and Multiplier ModelPrateek BabbewalaОценок пока нет
- Session 17 - Fiscal PolicyДокумент54 страницыSession 17 - Fiscal PolicyLakshmi Harshitha mОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Policy Objectives and Tools in Open vs Closed EconomiesДокумент12 страницMacroeconomic Policy Objectives and Tools in Open vs Closed EconomiesLoliОценок пока нет
- Profit Maximisation at MR MC: An Open Source Education ProjectДокумент6 страницProfit Maximisation at MR MC: An Open Source Education ProjecthelixateОценок пока нет
- GP - Types of AqДокумент18 страницGP - Types of Aqhelixate100% (4)
- Economics - National Income and Balance of Payments AccountsДокумент2 страницыEconomics - National Income and Balance of Payments Accountshelixate100% (1)
- Math - IntegrationДокумент4 страницыMath - Integrationhelixate100% (2)
- Economics - Resource AllocationДокумент3 страницыEconomics - Resource Allocationhelixate100% (5)
- Chemistry - Mole Concept and Atomic Structures RevisionДокумент2 страницыChemistry - Mole Concept and Atomic Structures RevisionhelixateОценок пока нет
- Nitrogen Compounds RevisionДокумент2 страницыNitrogen Compounds RevisionhelixateОценок пока нет
- Math - Series & SequencesДокумент4 страницыMath - Series & Sequenceshelixate100% (3)
- Economics - Market StructuresДокумент5 страницEconomics - Market Structureshelixate67% (3)
- GP - Essay Questions Collection From Past PrelimsДокумент8 страницGP - Essay Questions Collection From Past Prelimshelixate100% (16)
- Economics - Macroeconomic Problems & Management 1Документ3 страницыEconomics - Macroeconomic Problems & Management 1helixate100% (1)
- Physics EquationsДокумент5 страницPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- GCE A Level Essay Questions by Year (1995-2006)Документ12 страницGCE A Level Essay Questions by Year (1995-2006)helixate86% (7)
- Math - Complex Numbers RefresherДокумент5 страницMath - Complex Numbers Refresherhelixate100% (2)
- Economics - Understanding The GovernmentДокумент2 страницыEconomics - Understanding The GovernmenthelixateОценок пока нет
- Math - Refresher Course (Graphing)Документ7 страницMath - Refresher Course (Graphing)helixate100% (2)
- Chemistry Cheat Sheet - Physical and Chemical PropertiesДокумент5 страницChemistry Cheat Sheet - Physical and Chemical PropertiesEdward LeeОценок пока нет
- Physics - DefinitionsДокумент2 страницыPhysics - Definitionshelixate100% (1)
- Chemistry - Physical Properties of Organic ChemistryДокумент3 страницыChemistry - Physical Properties of Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (3)
- Chemistry - PeriodicityДокумент6 страницChemistry - Periodicityhelixate100% (1)
- Physics - Definitions 2Документ18 страницPhysics - Definitions 2helixate100% (3)
- Chemistry - NBДокумент2 страницыChemistry - NBhelixate100% (1)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryДокумент1 страницаChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction SchemeДокумент19 страницChemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction Schemehelixate94% (16)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry MechanismsДокумент2 страницыChemistry - Organic Chemistry Mechanismshelixate100% (3)
- Chemistry - Group VIIДокумент2 страницыChemistry - Group VIIhelixateОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry and Energetics Concepts in 40 CharactersДокумент2 страницыOrganic Chemistry and Energetics Concepts in 40 CharactersEugene TayОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - BiochemistryДокумент3 страницыChemistry - BiochemistryhelixateОценок пока нет
- Kaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineОт EverandKaizen: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Continuous Improvement And Transforming Your Life With Self DisciplineРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (36)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyОт EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetОт EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetОценок пока нет
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingОт EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (97)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsОт EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (94)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesОт EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereОт EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyОт EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (227)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaОт EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaОценок пока нет
- The Hidden Habits of Genius: Beyond Talent, IQ, and Grit—Unlocking the Secrets of GreatnessОт EverandThe Hidden Habits of Genius: Beyond Talent, IQ, and Grit—Unlocking the Secrets of GreatnessРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (12)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenОт EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenОценок пока нет
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsОт EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОт EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОценок пока нет
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailОт EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (237)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistОт EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (37)
- Nudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentОт EverandNudge: The Final Edition: Improving Decisions About Money, Health, And The EnvironmentРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (92)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationОт EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (46)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomОт EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomОценок пока нет
- The Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldОт EverandThe Genius of Israel: The Surprising Resilience of a Divided Nation in a Turbulent WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- Poor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyОт EverandPoor Economics: A Radical Rethinking of the Way to Fight Global PovertyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (263)
- The Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerОт EverandThe Finance Curse: How Global Finance Is Making Us All PoorerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- How an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionОт EverandHow an Economy Grows and Why It Crashes: Collector's EditionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (102)
- Against the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskОт EverandAgainst the Gods: The Remarkable Story of RiskРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (352)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaОт EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldОт EverandThe Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (132)
- Oceans of Grain: How American Wheat Remade the WorldОт EverandOceans of Grain: How American Wheat Remade the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)















































![7- aggregate demand and supply_student [Compatibility Mode]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/723848507/149x198/42435e0249/1713335080?v=1)