Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
UG Courses Wef (2007-08)
Загружено:
Ganpat Lal SharmaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UG Courses Wef (2007-08)
Загружено:
Ganpat Lal SharmaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AGRON - 111
PRINCIPLES OF AGRONOMY AND AGRICULTURAL METEOROLOGY
3(2+1)
Theory: Meaning and Scope of Agronomy; National and International Agricultural Research Institutes and Agricultural Universities of India; Agroclimatic zones of India and Rajasthan. Classification of crops; Tillage; Sowings; Planting geometry; Crop stand establishment and its effects on growth and yield; Cropping systems; Harvesting, threshing and winnowing Agrometeorology, weather and climate, micro-climate, weather elements; Earths atmosphere: composition and structure; solar radiation: nature, properties, depletion, solar constant and energy balance; Atmospheric temperature: factors affecting, horizontal and vertical distribution variations, global warming; Air pressure: Variations; Wind: Factors affecting cyclones and anticyclones and general circulation; Atmospheric humidity: vapor pressure and saturation, process of condensation, formation of dew, fog, mist, snow, rain and hail; Formation and classification of clouds; Introduction to monsoon ; Basics of weather forecasting. Practical: Study of tillage implements; Practice of ploughing and puddling; Study of seeding equipments and different methods of sowing; Study of manures, green manure crops; Seed & fertilizers calculations; Study of intercultivation equipments and practice; Study of fertilizer application methods and practice; Participation in on going field operations at Instructional Farm; Site selection for Agromet observatory and installation of instruments; Measurement of Atmospheric and Soil temperature; Measurement of rainfall, evaporation, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure, solar radiation and wind direction and velocity; Study of weather forecasting and synoptic charts. Suggested Readings: 1. Lal, D.S.2005. Climatology, Sharda Pustak Bhawan, Allahbad 2. Sahu, D.D.2003. Agrometeorology and Remote Sensing: Principles and Practices, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur 3. Varshneya, M.C. and Balakrishana, Pillai, P.2003. Textbook of Agricultural Meteorology, ICAR, New Delhi 4. Balasubramaniyan, P. and Palaniappan, S.P.2001. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur 5. Reddy, S.R. 2004. Principles of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana 6. Reddy, S.R.2000. Principles of Crop Production, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana 7. ICAR. 2006. Handbook of Agriculture, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi 8. iksjoky] ch- ,y-] flag] iq"isUnz ,oe~ 'kekZ] Mh- Mh- 2000- lL; foKku ds ewy rRo] ds- ih- izdk'ku] mn;iqj
AGRON -121 Theory:
WEED MANAGEMENT
2 (1+1)
Weeds: Introduction, harmful and beneficial effects, classification, propagation, dissemination and persistence; Weed biology and ecology: crop weed association, crop weed competition and allelopathy; Concepts of weed prevention, control and eradication; Methods of weed control: physical, cultural, chemical and biological; Integrated weed management; Herbicides: advantages and limitations of herbicide use in India; Classes of herbicides, formulations, methods of application; Introduction to Adjuvants and their use in herbicides; Introduction to selectivity of herbicides; Weed management in major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, fibre and forage crops; Problematic weeds and their control viz.Parthenium hysterophorus, Cynodon dactylon, Orobanche and Striga . Practical: Identification of weeds; Survey of weeds in crop fields and other habitats; Preparation of weed herbarium; Determination of weed density and intensity; Physical weed control; Calculations on weed control efficiency and weed index; Herbicide label information; Computation of herbicide doses; Study of herbicide application equipment and calibration; Demonstration of methods of herbicide application; Preparation of list of commonly available herbicides; Study of phytotoxicity symptoms of herbicides in different crops and weeds; Biology of weeds; Economics of weed control practices; Tours and visits of problem areas. Suggested Readings: 1. Gupta, O.P.2005. Weed Management: Principles and Practices (2nd Ed.), Agribios (India), Jodhpur. 2. Gupta, O.P.2002. Modern Weed Management, Agribios (India), Jodhpur. 3. Rao, V.S. 2000. Principals of Weed Science (2nd Ed.), Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi. 4. Saraswat, V.N., Bhan, V.M. and Yaduraju, N.T.2003. Weed Management, ICAR, New Delhi.
AGRON - 122 Theory:
WATER MANAGEMENT
3(2+1)
Importance of water in plants; Irrigation: definition and objectives; Water resources and irrigation development in India and Rajasthan; Forms of soil water and soil moisture constants; Methods of soil moisture determination, evapotranspiration and crop water requirement; Scheduling of irrigation; Methods of irrigation: surface, sprinkler and drip irrigation; Irrigation efficiency and water use efficiency; Irrigation water quality and its management; Conjunctive use of water; Water management of different crops viz. rice, wheat, maize, sugarcane, and important pulses and oilseed crops; Agricultural drainage. Practical: Determination of bulk density by field method; Determination of soil moisture content by gravimetric method, tensiometer, electrical resistance block and neutron moisture meter; Determination of field capacity by field method; Determination of permanent wilting point; Measurement of irrigation water through flumes and weirs; Calculation of irrigation water requirement (Problems); Demonstration of irrigation methods viz. surface, sprinkler and drip methods; Calculation of irrigation efficiency; Acquaintance and upkeep of sprinkler and drip irrigation systems; Visit to farmers field and cost estimation of drip irrigation system; Determination of EC, pH, and Ca ++ + Mg++ of irrigation water Suggested Readings:
1. Lenka, D.1999. Irrigation and Drainage. Kalyani Publishers, L.D.H., New Delhi.
2. Michael, A.M.1987. Irrigation: Theory and Practice, Vikas Publishing House, New Delhi. 3. Mishra, R.D. and Ahmed, M. 1987. Manual on Irrigation Agronomy, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. 4. Parihar, S.S., and Sandhu B.S.1987. Irrigation of Field Crops Principles and Practices, ICAR, New Delhi. 5. Reddy, S.R. 2000. Principles of Crop Production, Kalyani Pub. , New Delhi.
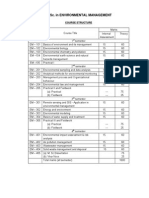
ENVS - 121
ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES
3(2+1)
Unit 1: The Multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies: Environmental studies: Definition, nature and Scope; Need for public awareness, measures to create awareness for healthy environment. Unit 2:Natural Resources: Renewable and non-renewable sources: National resources: Definition, types and conservation; Forest resources: Use and over exploitation, deforestation, case study, Timber extraction, mining, dams and their effects on forests and tribal people; Water resources: Uses and over utilization of surface and ground water, floods, drought, conflicts over water, dams benefits and problems; Mineral resources: Use and exploitation, environmental effects of extracting and using mineral resources, case studies; Food resources: World food problems, changes caused by agriculture and overgrazing, effects of modern agriculture, fertilizer-pesticide problems, water logging, salinity, case studies; Energy resources: Growing energy needs, renewable and non-renewable energy sources use of alternate energy sources. Case studies; Land resources: Land as a resource, land degradation, man induced landslides, soil erosion and desertification; Role of an individual in conservation of natural resources. Equitable use of resources for sustainable lifestyles. Unit 3. Ecosystem: Concept of ecosystem; Structure and function of an ecosystem, Producers, consumers and decomposers; Energy flow in the ecosystem. Ecological succession; Food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids; Introduction, types, characteristics features, structure and function of Forest ecosystem; Grassland ecosystem,; Desert ecosystem and Aquatic ecosystems. Unit 4:Biodiversity and its conservation: Biodiversity definition and types; Biogeographical classification of India; Value of biodiversity: consumptive use, productive use, social ethical, and aesthetic and option value; Biodiversity at global, national and local levels; India as a mega-diversity nation, Hot-spots of biodiversity; Threats to biodiversity: habitat loss, poaching of wildlife, man-wildlife conflicts; Endangered and endemic species of India; Conservation of biodiversity: In-situ and Ex-situ conservation of biodiversity. Unit5: Environmental pollution: Definition, causes, effects and control measures of: Air pollution, Water pollution, Soil pollution and Marine pollution, Noise pollution, Thermal pollution and Nuclear hazards; Solid waste management: Causes, effects and control measures of urban and industrial wastes; Role of an individual in prevention of pollution. Pollution case studies; Disaster management: floods, earthquake, cyclone and landslides. Unit 6:Social issues and the environment: From unsustainable to sustainable development. Urban problems related to energy; Water conservation, rainwater harvesting, and watershed management; Resettlement and rehabilitation of people; its problems and concerns, Case studies; Environmental ethics: Issues and possible solutions; Climatic change, global warming, acid rain ozone layer depletion, nuclear accidents and holocaust, Case studies; Wasteland reclamation. Consumerism and waste products; Environment Protection Act, Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, Wildlife Protection Act. Forest Conservation Act; Issues involved in enforcement of environmental legislation; Public awareness.
Unit 7: Human Population and the Environment: Population growth, variation among nations; Population explosion Family Welfare Programme; Environment and human health, Human Rights; Value education, HIV/ Aids; Women and Child Welfare; Role of Information Technology in Environment and human health, Case studies. Unit 8:Fieldwork: Visit to a local area to document environmental assetsriver/forest/grassland/hill/mountain; Visit to a local polluted site Urban/Rural/Industrial/Agricultural; Study of common plants, insects, birds; Study of simple ecosystems-pond, river, hill slopes, etc. Suggested Readings: 1. Bamaniya, B.R., Verma, L. N. and Verma A. 2005. Fundamentals of Environmental Studies, Yash Publishing House, Bikaner. 2. Rathore, N. S. and Singh, Pratap 2004. Environmental Studies, Himanshu Publishing House, New Delhi. 3. Choudhary, B.L. and Pandey, J. 2004. Environmental Studies, Apex Publishing House, Udaipur. 4. pkS/kjh] ch- ,y- ,oa ikaMs] ftrsUnz- 2004- i;kZoj.k
v/;;u] ,isDl ifCyf'kax gkml] mn;iqjA 5. dkSf'kd] vuqHkk ,oa dkSf'kd] lh- ih- 2005- i;kZoj.k v/;;u] U;w ,t bUVjus'kuy izk fyfeVsM] ubZ fnYyhA 6. tkxsfV;k] ch- ,y- vkSj iqjksfgr] iadt 2005- i;kZoj.k v/;;u] ,xzksVsd ifCyf'kax ,dsMeh] mn;iqjA
AGRON - 211 Theory:
FIELD CROPS-I (KHARIF)
3(2+1)
Study of following crops with reference to their importance; Origin; Geographic distribution and production in Rajasthan and India; Soil and climatic requirements; varieties; Cultural practices viz .Seed and sowing; Intercultural operations; Fertilizer, water and weed management; Plant protection measures; Harvesting and yield. Pearl millet, Sorghum, Maize, Rice, Groundnut, Soybean, Pigeonpea and Cotton. Study of package of practices of the following crops: Minor millets, Urdbean, Mothbean, Cowpea, Mungbean, Clusterbean, Sunflower, Sunnhemp, Castor, Sesame and Napier; Bio energy crops viz. Jatropha and Jojoba. Practical: Identification of seeds and crops of kharif season & others inputs; Seed bed preparation and sowing of kharif crops ; Calculations on seed rate; Effect of seed size on germination and seedling vigour of soybean/ groundnut; Preparation of seed material for sowing; Fertilizer application in various crops and study of Fertilizer experiments; Plant protection measures; Irrigation operation in various crops; Weed control in kharif crop and study of weed control experiments; Judging physiological maturity of various crops; Study of yield attributing characters and yield calculations in kharif crops; Crop harvesting and processing; Working out cost of production of two crops; Calculation of harvest index; Study of crop varieties and important agronomic experiments; Study of forage experiments. Suggested Readings: 1. Singh, Chhidda, Singh, Prem and Singh, Rajbir.2003. Modern Techniques of Raising Field Crops, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi. 2. Singh, S.S.1998. Crop Management Under Irrigated and Rainfed Conditions. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Singh, S.S.1993. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. Rathore, P.S. 2000. Techniques and Management of Field Crop Production, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur. Prasad, Rajendra 2002. Text Book of Field Crop Production, ICAR, New Delhi. ICAR. Handbook of Agriculture 2006. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
'kDrkor] eksgu flag ,oa O;kl] vHk; dqekj 2000. oSKkfud Qly izcU/ku] ;'k ifCyf'kax gkml] chdkusj
AGRON - 221 Theory:
FIELD CROPS-II (RABI)
3(2+1)
Study of following crops with reference to their importance; Origin; Geographic distribution and production in Rajasthan and India; Soil and climatic requirements; varieties; Cultural practices viz .Seed and sowing; Intercultural operations; Fertilizer, water and weed management; Plant protection measures; Harvesting and yield: Wheat, Barely, Rapeseed and mustard, Chickpea, Sugarcane, Potato and. Berseem, Lucerne Study of package of practices of the following crops: Linseed, Safflower, Sugarbeet, Lentil, Frenchbean, and Oats. An introduction to the importance and cultivation of Medicinal & aromatic plants viz. Isabgol, Opium poppy, Mentha, Lemon grass, Citronella and Palma rosa. Practical: Identification of seeds and crops of rabi season; Seed bed preparation and sowing of rabi crops; Calculations on seed rate; Preparation of seed material for sowing; Fertilizer application in crops and study of fertilizer experiments; Irrigation and plant protection measures; Weed flora and there control measure and study of weed control experiment; Judging physiological maturity of various crops; morphological characteristics of wheat, sugarcane, chickpea and mustard; Judging sugarcane maturity and quality test; Crop harvesting and processing; Calculation of harvest index, Working out cost of production of two crops; Crop distribution in the state and region, Important Agronomic experiments of rabi crops; Visit to research stations related to rabi crops. Suggested Readings: 1. Singh, Chhidda, Singh, Prem and Singh, Rajbir 2003. Modern Techniques of Raising Field Crops. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi. 2. Singh, S.S.1998. Crop Management Under irrigated and Rainfed Conditions Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi 3. Singh, S.S., 1993. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. 4. Rathore, P.S. 2000.Techniques and Management of Field Crop Production, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur. 5. Prasad, Rajendra 2002. Text Book of Field Crop Production, ICAR, New Delhi. 6. Prajapati, N.D., Purohit, S.S., Sharma, A.K. and Kumar, T. 2003. A Handbook of Medicinal Plants: A Complete Source Book, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur 7. ICAR, 2006 & 1980. Handbook of Agriculture, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
8. Kumar, N., Kader Md. Abdul, JBM, Rangaswami, P. and Irulappam, I. 1997. Introductin to Spices, Plantation Crops, Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Ltd., New Delhi
9. 'kDrkor] eksgu flag ,oa O;kl] vHk; dqekj 2000- oSKkfud Qly izcU/ku] ;'k ifCyf'kax gkml] chdkusj 10. pUnzk] ohjsUnz ,oa ikaMs;] eqdqy pUnz- 2004 tM+h cwfV;ksa dh [ksrh] Hkkjrh; d`f"k vuqla/kku ifj"kn~] ubZ fnYyh
AGRON - 311 Practical:
PRACTICAL CROP PRODUCTION-I (KHARIF CROPS)
1(0+1)
Crop planning; Raising field crops in multiple cropping systems: field preparation, seed treatment, sowing, Nutrient, water and weed management; Management of insect, pest and diseases of crops; Harvesting, threshing, drying, winnowing, storage and marketing of produce; Preparation of balance sheet including cost of cultivation, net return per student as well as per team of a group of student. Suggested Readings: 1. Yawalkar, K.S., Agarwal, J.P. and Bokde, S. 1992. Manures and Fertilizers, AgriHorticultural Pub. House, Nagpur. 2. Balasubramaniyan, P. and Palaniappan, S. P.2001. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur. Reddy, S. R., 2004. Principles of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana. Singh, S.S., 1993. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana.
AGRON - 312 Theory:
FARMING SYSTEMS AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
2(1+1)
Farming systems: definition, principles, scope and components; IFS models for wetland, irrigated, and dryland situations; Components of Farming systems; Interactions among components of different enterprises; Resource management under constrained situations; Low cost and non monetary inputs particularly for wasteland and problematic soils. Sustainable agriculture: Introduction, definition, goal and current concepts; Indices of sustainability; Emerging issues fro present day technologies; Factors affecting ecological balance; Ameliorative measures and management practices for sustainable agriculture viz. soil, water sources, rain water and integrated pest management; Land degradation and conservation of natural resources; LEISA, LEIA & HEIA; Irrigation problems, waste lands and their development. Practical: Preparation of cropping scheme for irrigated situations; Preparation of cropping scheme for dryland situations; Study of existing farming systems in nearby villages; Preparation of integrated farming system model for wetlands; Preparation of integrated farming system model for drylands; Preparation of enriched Farm Yard Manure; Preparation of Vermicompost; Visit to urban waste recycling unit; Study of profitable utilization of agricultural wastes; Visit to poultry and dairy units to study resource allocation, utilization and economics; Visit to an organic farm to study various components and utilization; Study of degraded lands. Suggested Readings: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Panda, S.C.2004. Cropping Systems and Farming Systems, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur Sharma, Arun K. 2002. A Handbook of Organic Farming, Agrobios (India) Ltd., Jodhpur Balasubramaniyan, P. and Palaniappan, S.P. 2004. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur. Shukla, Rajeev K. 2004. Sustainable Agriculture, Surbhee Publications, Jaipur Palaniappan, S.P.1985. Cropping Systems in the Tropics: Principles and Management, Wiley Easter Ltd. and TNAU, Coimbatore. Reddy S. R. 2004. Principles of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana. Palaniappan, S.P. and Sivaraman, K. 1996. Cropping system in Tropics, New International Pvt. New Delhi.
xkSre] vkj.lh. ,oa flag] iatkc-1997- fVdk [ksrh] Hkkjrh; d`f"k vuqlU/kku ifj"kn] ubZ fnYyh
AGRON - 313
ORGANIC FARMING
3 (2+1)
Theory: Introduction, concept, relevance in present context and future prospects; Organic production requirements; Principles, objectives and components of organic farming; Biological intensive nutrient management-organic manures, composting, vermicomposting, green manuring, recycling of organic residues, biofertilizers; Soil improvement and amendments; Integrated diseases and pest management use of biocontrol agents, biopesticides pheromones, trap crops, bird perches; Weed management; Quality considerations, certification, labeling and accreditation processors, marketing, exports. Practical: Aerobic and anaerobic methods of compost making, , Techniques of treating legume seeds with Rhizobium culture, Use of Azotobacter, Azospirillum and PSB culture in field crops; Raising of crops organically through nutrient, diseases and pest management; vermicomposting; vegetable and ornamental nursery raising; macro quality analysis, grading, packaging, post harvest management; Visit to organic farm. Suggested Readings: 1. Dhama, A.K. 1999. Organic Farming, Agro Botanica, Bikaner 2. Sharma, Arun K.2002. A Handbook of Organic Farming, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur 3. Palaniappan, S.P. and Anandurai, K.1999. Organic Farming Theory and Practice, Scientific Pub. Jodhpur 4. Thapa, U and Tripathy, P. 2006. Organic Farming in India: Problems and Prospects, Agrotech, Publising Academy, Udaipur. 5. 'kekZ] v:.k ds- 2005. tSfod [ksrh & fl)kUr] rduhd o
mi;ksfxrk] ,xzksck;ksl bf.M;k] tks/kiqj
AGRON - 321 Practical:
PRACTICAL CROP PRODUCTION-II (RABI CROPS)
1(0+1)
Crop planning; Raising field crops in multiple cropping systems: field preparation, seed treatment, sowing, Nutrient, water and weed management; Management of insect, pest and diseases of crops; Harvesting, threshing, drying, winnowing, storage and marketing of produce; Preparation of balance sheet including cost of cultivation, net return per student as well as per team of a group of student. Suggested Readings: 1. Yawalkar, K.S., Agarwal, J.P. and Bokde, S. 1992. Manures and Fertilizers, Agri-Horticultural Pub. House, Nagpur. 2. Balasubramaniyan, P. and Palaniappan, S. P.2004. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Agrobios (India), Jodhpur. Reddy, S. R. 2002. Principles of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana. Singh S.S. 1993. Principles and Practices of Agronomy, Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana.
AGRON - 322
INTRODUCTORY AGRICULTURE (ANCIENT HERITAGE, AGRICULTURAL SCENARIO AND GENDER EQUITY IN AGRICULTURE)
1(1+0)
Theory: Art, Science and business of crop production, Basic elements of crop production; Factors affecting crop production; History of Agricultural Development; Ancient India Agriculture in Civilization Era, Chronological Agricultural Technology development in India. Indian Agriculture, balance sheet, liabilities; Assets and Contrasting trends (DATA), Agricultural growth, Diversity in physiography, Soil groups, marine, livestock and water; Liabilities: Soil factors, weather factors, Economic ecology, dry and irrigation agriculture, value addition, requirements in new technology; Women in Agriculture: multifaceted roles and tasks, work stress factors, Nutritional and rural life standards, role in house hold design making, drudgery reduction for farm women, women friendly agricultural technology; Empowerment of women; Group dynamics for farm women, rural women; The nucleus of Agricultural Extension and Training. Suggested Readings: 1. ICAR, 2006. Handbook of Agriculture, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi 2. Morachan, Y.B. 1989. Crop Production and Management, Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi 3. Verma, S. 1992. Women in Agriculture (A Socio-economic Analysis), Concept Publication Company, New Delhi 4. Randhawa, M.S. 1980. A History of Agriculture in India Vol. I, ICAR, New Delhi 5. Randhawa, M.S. 1982. A History of Agriculture in India Vol. II, ICAR, New Delhi 6. Randhawa, M.S. 1983. A History of Agriculture in India Vol. III, ICAR, New Delhi 7. Randhawa, M.S. 1986. A History of Agriculture in India Vol. IV, ICAR, New Delhi 8. Choudhary, S.L. Sharma, G.S. And Nena, Y.L. (Ed.) 2000. Ancient and Medieval History of Indian Agriculture, Proceedings of the Summer School held from 28 May-17 June, 1999. Rajasthan College of Agriculture, Udaipur
Вам также может понравиться
- Global Climate ChangeОт EverandGlobal Climate ChangeSuruchi SinghОценок пока нет
- 1st Sem Syllabus For B.SC Agri For MPKVДокумент23 страницы1st Sem Syllabus For B.SC Agri For MPKVVIKRAM9350% (4)
- Kenya: A Natural Outlook: Geo-Environmental Resources and HazardsОт EverandKenya: A Natural Outlook: Geo-Environmental Resources and HazardsОценок пока нет
- TNSPCB degreestandards-EnvironmentalScienceДокумент4 страницыTNSPCB degreestandards-EnvironmentalSciencerexОценок пока нет
- AECCДокумент3 страницыAECCAkshay Negi JiОценок пока нет
- Environment and Society: Indicative Syllabus of Environmental EngineeringДокумент12 страницEnvironment and Society: Indicative Syllabus of Environmental EngineeringAshish VermaОценок пока нет
- 18AE656Документ2 страницы18AE656tupoОценок пока нет
- First Semester:: M.SC - Part - 1Документ22 страницыFirst Semester:: M.SC - Part - 1spooky200Оценок пока нет
- HORT 111 Fundamentals of Horticulture Credit Hours: 2 (1+1)Документ13 страницHORT 111 Fundamentals of Horticulture Credit Hours: 2 (1+1)AnuragОценок пока нет
- Environment Management Guwahati UniversityДокумент17 страницEnvironment Management Guwahati UniversityRahul DekaОценок пока нет
- Environmt Science SET SyllabusДокумент10 страницEnvironmt Science SET SyllabusRajat PatilОценок пока нет
- Biological and Environmental Hazards, Risks, and DisastersОт EverandBiological and Environmental Hazards, Risks, and DisastersRamesh SivanpillaiОценок пока нет
- University of Madras Syllabus: Ability Enhancement CompulsorycoursesДокумент4 страницыUniversity of Madras Syllabus: Ability Enhancement CompulsorycoursesSam PeterОценок пока нет
- 1EVS SyllabusДокумент3 страницы1EVS Syllabushollandw2001Оценок пока нет
- Paper: (100 MARKS) : Agriculture & ForestryДокумент13 страницPaper: (100 MARKS) : Agriculture & ForestrySarwan AliОценок пока нет
- Biodiversity and Climate Change Adaptation in Tropical IslandsОт EverandBiodiversity and Climate Change Adaptation in Tropical IslandsОценок пока нет
- Environmental Studies SyllabusДокумент5 страницEnvironmental Studies SyllabusShona ShonaОценок пока нет
- B.SC AgricultureДокумент56 страницB.SC AgricultureShravani SalunkheОценок пока нет
- Law-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES & DISASTER MANAGEMENTДокумент3 страницыLaw-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES & DISASTER MANAGEMENTNeeti JapraОценок пока нет
- 08-Environmental ScienceДокумент8 страниц08-Environmental Sciencedarga iahОценок пока нет
- Environmental Studies (U1)Документ63 страницыEnvironmental Studies (U1)aryavats2005Оценок пока нет
- (Irrigation Management) Fundamentals of Agronomy 2Документ58 страниц(Irrigation Management) Fundamentals of Agronomy 2Pushkraj NimbalkarОценок пока нет
- Ge32 Environmental Science and EngineeringДокумент3 страницыGe32 Environmental Science and Engineeringஇரவிச்சந்திரன்Оценок пока нет
- Theory Notes AGRO 111 - 1to10Документ75 страницTheory Notes AGRO 111 - 1to10darshan pawarОценок пока нет
- Soil Health, Soil Biology, Soilborne Diseases and Sustainable Agriculture: A GuideОт EverandSoil Health, Soil Biology, Soilborne Diseases and Sustainable Agriculture: A GuideРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Soil Pollution: From Monitoring to RemediationОт EverandSoil Pollution: From Monitoring to RemediationArmando C. DuarteОценок пока нет
- Environmental PollutionДокумент10 страницEnvironmental PollutionSubhash ChandraОценок пока нет
- ET COurse3Документ2 страницыET COurse3technicalboot4999Оценок пока нет
- 16 Environmental StudiesДокумент4 страницы16 Environmental StudiesMalsawmkima Maski-aОценок пока нет
- EVS (Yuva)Документ88 страницEVS (Yuva)dasbaldev73Оценок пока нет
- AU Syllabus Foundation Course-AECC2-1Документ3 страницыAU Syllabus Foundation Course-AECC2-1Nivedita GoswamiОценок пока нет
- Env. Education Syllabus Completed BiotechnologyДокумент4 страницыEnv. Education Syllabus Completed BiotechnologyKala OpОценок пока нет
- Environmental StudiesДокумент2 страницыEnvironmental StudiesAnkit SinghОценок пока нет
- Climate Change Impacts on Soil Processes and Ecosystem PropertiesОт EverandClimate Change Impacts on Soil Processes and Ecosystem PropertiesОценок пока нет
- Code No: 28 Subject: Environmantal Science: Telangana State-State Eligibility Test (Ts - Set)Документ7 страницCode No: 28 Subject: Environmantal Science: Telangana State-State Eligibility Test (Ts - Set)Umair AnsariОценок пока нет
- Environmental Resilience and Transformation in times of COVID-19: Climate Change Effects on Environmental FunctionalityОт EverandEnvironmental Resilience and Transformation in times of COVID-19: Climate Change Effects on Environmental FunctionalityA.L. RamanathanОценок пока нет
- 28-Environmental ScienceДокумент10 страниц28-Environmental ScienceGSR World (Shravan)Оценок пока нет
- CHY1003 Environmental StudiesДокумент2 страницыCHY1003 Environmental StudiessureshОценок пока нет
- Soils and Landscape RestorationОт EverandSoils and Landscape RestorationJohn A. StanturfРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- HDJ Du e Ienv ImvДокумент6 страницHDJ Du e Ienv ImvHarsha VardhanОценок пока нет
- EVS Syllabus - Sem IIДокумент3 страницыEVS Syllabus - Sem IIRylan DsaОценок пока нет
- AECC Environmental StudiesДокумент2 страницыAECC Environmental StudiesSanket MoreОценок пока нет
- Soilless Culture: Theory and Practice: Theory and PracticeОт EverandSoilless Culture: Theory and Practice: Theory and PracticeMichael RavivОценок пока нет
- RGPV Syllabus 3rd Sem Biomedical EngineeringДокумент10 страницRGPV Syllabus 3rd Sem Biomedical Engineeringoliver senОценок пока нет
- Evs Notes ThksДокумент80 страницEvs Notes ThksSagnikОценок пока нет
- M.SC Agriculture Agronomy (Syllabus)Документ36 страницM.SC Agriculture Agronomy (Syllabus)Wjajshs UshdОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ7 страницUnit 1sandhyarani beheraОценок пока нет
- 10B11GE411Документ2 страницы10B11GE411Ayush PurohitОценок пока нет
- Evs NotesДокумент79 страницEvs Notesvishwa.tdmОценок пока нет
- EVS SyllabusДокумент3 страницыEVS Syllabusritwik kalitaОценок пока нет
- Soil Science, Agricultural and Environmental PerspectivesДокумент439 страницSoil Science, Agricultural and Environmental PerspectivesAndreas100% (1)
- Environmental Studies Syllabus - For All Faculties - 22.122020-1Документ4 страницыEnvironmental Studies Syllabus - For All Faculties - 22.122020-1The GeniusОценок пока нет
- Global Climate Change and Terrestrial InvertebratesОт EverandGlobal Climate Change and Terrestrial InvertebratesScott N. JohnsonОценок пока нет
- PreviewДокумент71 страницаPreviewLudmilla FerreiraОценок пока нет
- 0EVSAECC01Документ4 страницы0EVSAECC01205 Shavan SharmaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus BSC Agri PDFДокумент209 страницSyllabus BSC Agri PDFManisha ReddyОценок пока нет
- Agr 322 PDFДокумент149 страницAgr 322 PDFDiwakar KumarОценок пока нет
- Wheat: Global Scenario (2013-14) Country Area Production Yield % To World (Mha) (MT) (T/ha) ProductionДокумент8 страницWheat: Global Scenario (2013-14) Country Area Production Yield % To World (Mha) (MT) (T/ha) ProductionGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- SugarcaneДокумент12 страницSugarcaneGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- LentilДокумент5 страницLentilGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Rapeseed and MustardДокумент9 страницRapeseed and MustardGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- OatsДокумент3 страницыOatsGanpat Lal Sharma100% (1)
- Lucerne (Alfalfa) Botanical Name: Medicago Sativa L. Family: Fabaceae (Alt. Leguminosae) Subfamily: Faboideae Tribe: TrifolieaeДокумент5 страницLucerne (Alfalfa) Botanical Name: Medicago Sativa L. Family: Fabaceae (Alt. Leguminosae) Subfamily: Faboideae Tribe: TrifolieaeGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Linseed: Botanical Name: Linum Usitatissimum Linn. Family: Linaceae Chromosome Numaber: 2n 30Документ5 страницLinseed: Botanical Name: Linum Usitatissimum Linn. Family: Linaceae Chromosome Numaber: 2n 30Ganpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Field PeaДокумент5 страницField PeaGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Berseem (Egyptian Clover)Документ4 страницыBerseem (Egyptian Clover)Ganpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Cotton Economic ImportanceДокумент9 страницCotton Economic ImportanceGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Chickpea: Vulgaris) and Dry Peas (Pisum Sativum L.) - Chickpea Seeds Contain On Average 18-22% ProteinДокумент7 страницChickpea: Vulgaris) and Dry Peas (Pisum Sativum L.) - Chickpea Seeds Contain On Average 18-22% ProteinGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- English: Blond Psyllium, Spogel Seeds: Plantago Ovata ForskДокумент4 страницыEnglish: Blond Psyllium, Spogel Seeds: Plantago Ovata ForskGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- BarleyДокумент6 страницBarleyGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Soybean Economic ImportanceДокумент6 страницSoybean Economic ImportanceGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Fertilizers and Their UseДокумент24 страницыFertilizers and Their Usedvskiwi100% (1)
- Greengram & BlackgramДокумент9 страницGreengram & BlackgramGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Finger MilletДокумент4 страницыFinger MilletGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Groundnut Economic ImportanceДокумент6 страницGroundnut Economic ImportanceGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- 11 6 9 Ijas PDFДокумент5 страниц11 6 9 Ijas PDFGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Sunnhemp Botanical Name: Crotolaria Juncea Family: Fabaceae (Leguminoseae) Chromosome Number: 2n 16Документ3 страницыSunnhemp Botanical Name: Crotolaria Juncea Family: Fabaceae (Leguminoseae) Chromosome Number: 2n 16Ganpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- MOTH BEAN or DEW BEANДокумент3 страницыMOTH BEAN or DEW BEANGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Abiotic Stress in Plants - Mechanisms and AdaptationsДокумент440 страницAbiotic Stress in Plants - Mechanisms and AdaptationsarunshankerОценок пока нет
- SESAMEДокумент5 страницSESAMEGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Abiotic Stress in Plants - Mechanisms and AdaptationsДокумент440 страницAbiotic Stress in Plants - Mechanisms and AdaptationsarunshankerОценок пока нет
- Essential Oil-Bearing Grasses The Genus Cymbopogon Medicinal and Aromatic Plants - Industrial ProfilesДокумент1 страницаEssential Oil-Bearing Grasses The Genus Cymbopogon Medicinal and Aromatic Plants - Industrial ProfilesGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Book Acsesspublicati Physiologicalba FrontmatterДокумент13 страницBook Acsesspublicati Physiologicalba FrontmatterMarlon Manaya GarriguesОценок пока нет
- SafflowerДокумент48 страницSafflowerGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Biopestcides: Types and Applications: IJAPBC - Vol. 1 (4), Oct-Dec, 2012Документ8 страницBiopestcides: Types and Applications: IJAPBC - Vol. 1 (4), Oct-Dec, 2012Balaji RajendranОценок пока нет
- Aromatic PlantsДокумент9 страницAromatic PlantsGanpat Lal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Hesc101 PDFДокумент16 страницHesc101 PDFBhaskar SharmaОценок пока нет
- Dionaea Cultivares RegistradosДокумент11 страницDionaea Cultivares RegistradosCarlos BriascoОценок пока нет
- 20 Best Plants For Cleaning Indoor Air 2021Документ4 страницы20 Best Plants For Cleaning Indoor Air 2021maria evangelistaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial1 2Документ1 страницаTutorial1 2chifunirokamangira9Оценок пока нет
- (Geographies of Imagination) Gary L Peters - American Winescapes - The Cultural Landscapes of America's Wine Country-Westview Press (1997)Документ241 страница(Geographies of Imagination) Gary L Peters - American Winescapes - The Cultural Landscapes of America's Wine Country-Westview Press (1997)Sergio RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Agri Easter Term Exam PaGRADE 7 Maths Multiple Choice TestperДокумент4 страницыGrade 7 Agri Easter Term Exam PaGRADE 7 Maths Multiple Choice Testpersaajid hafizОценок пока нет
- 1 - Mustafa E. KaracanДокумент2 страницы1 - Mustafa E. KaracanMustafa Ergin KaracanОценок пока нет
- Thesis For The Master's Degree in Chemistry: 60 Study PointsДокумент137 страницThesis For The Master's Degree in Chemistry: 60 Study Pointsmichael nwoyeОценок пока нет
- Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adult Elementary School H 2026180276531408185150a3 70193881Документ2 страницыIslcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adult Elementary School H 2026180276531408185150a3 70193881Ioana IvanОценок пока нет
- Vermicompost-Business ModelДокумент28 страницVermicompost-Business Modelrupali100% (2)
- African Violet Care FS 501Документ2 страницыAfrican Violet Care FS 501bobbeaОценок пока нет
- Summative 1 and 2 TLEДокумент7 страницSummative 1 and 2 TLEReyna CarenioОценок пока нет
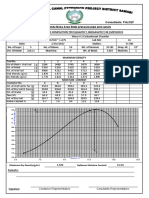
- Maximum Dry Density: (G/CC) Optimum Moisture ContentДокумент1 страницаMaximum Dry Density: (G/CC) Optimum Moisture ContentUmair khanОценок пока нет
- 29-Pesticides Compounds, Use and HazardДокумент109 страниц29-Pesticides Compounds, Use and HazardSeyha L. AgriFoodОценок пока нет
- Fisheries Potential of Pakistan Salma NusratДокумент34 страницыFisheries Potential of Pakistan Salma NusratTalha AhmedОценок пока нет
- Advance Reading - Chapin Castor Iddent - 19340015Документ2 страницыAdvance Reading - Chapin Castor Iddent - 19340015chapin castorОценок пока нет
- Synergisms Between Compost and Biochar For Sustainable Soil AmeliorationДокумент33 страницыSynergisms Between Compost and Biochar For Sustainable Soil AmeliorationasdfghjklОценок пока нет
- Sehala Seyemit Agriculture OfficeДокумент14 страницSehala Seyemit Agriculture OfficeBogale TemesgenОценок пока нет
- Lab (Feed Formulation)Документ4 страницыLab (Feed Formulation)Izukanji KayoraОценок пока нет
- Advantages and Disadvantages of IrrigationДокумент2 страницыAdvantages and Disadvantages of IrrigationAngelo EnoriaОценок пока нет
- Agriculture Water Demand Management in Pakistan A PDFДокумент8 страницAgriculture Water Demand Management in Pakistan A PDFstudy timeОценок пока нет
- Guancari SystemДокумент60 страницGuancari Systemmonisha kunjumonОценок пока нет
- Profile of Scientist/Research Worker: NameДокумент8 страницProfile of Scientist/Research Worker: NameArun T YltpОценок пока нет
- Bio FertilizerДокумент19 страницBio FertilizerDipshikha SarmaОценок пока нет
- Summary of PepsiCo Case StudyДокумент6 страницSummary of PepsiCo Case StudyAbdullah ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Anglian Water Annual Report and Accounts 2013Документ207 страницAnglian Water Annual Report and Accounts 2013shibor1231Оценок пока нет
- Updated SIBO Specific Diet Food GuideДокумент13 страницUpdated SIBO Specific Diet Food GuideBenОценок пока нет
- SEA - National Power Plan Development 2011-2020-EnДокумент269 страницSEA - National Power Plan Development 2011-2020-EnMinh Sang ĐoànОценок пока нет
- Introducción (Manual para El Cultivo de Frutales en El Trópico)Документ12 страницIntroducción (Manual para El Cultivo de Frutales en El Trópico)pepeОценок пока нет
- BackyardGardening (NSTP Project)Документ66 страницBackyardGardening (NSTP Project)Aireen Chavez100% (4)
- Omar M Moma Thesis Outline 2Документ20 страницOmar M Moma Thesis Outline 2Nor-Ton NB BatingkayОценок пока нет