Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
VLSI Design
Загружено:
Vijitha KalassИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
VLSI Design
Загружено:
Vijitha KalassАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
VLSI Design (Unit-1) Lecture Notes strictly for internal circulation Page | 25 A photomask is constructed with chromium (chrome)
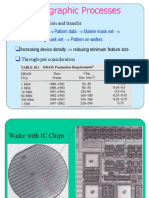
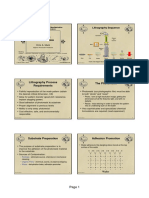
covered quartz glass. A UV light source isused to expose the photoresist. Figure:1 illustrates the lithography process. The photomask has chromewhere light should be blocked. The UV light floods the mask from the backside and passes through theclear sections of the mask to expose the organic photoresist (PR) that has been coated on the wafer. Adeveloper solvent is then used to dissolve the soluble unexposed photoresist, leaving islands of insolubleexposed photoresist. This is termed a negative photoresist. A positive resist is initially insoluble, and whenexposed to UV becomes soluble. Positive resists provide for higher resolution than negative resists, but areless sensitive to light. As feature sizes become smaller, the photoresist layers have to be made thinner. Thisis turn makes them less robust and more subject to failure. In turn, this can impact the overall yield of aprocess and the cost to produce the chip. Fig:1 Photomasking with a negative resist The photomask is commonly called a reticle and is usually smaller than the wafer, e.g., 2 cm on aside. A stepper moves the reticle to successive locations to completely expose the wafer.Projection printing is normally used, in which lenses between the reticle and wafer focus thepattern on the wafer surface. The reticle can be the same size as the area to be patterned (IX) or larger. Forinstance, 2.5X and 5X steppers with optical reduction have been used in the industry.The wavelength of the light source influences the minimum feature size that can be printed .In the1980s, mercury lamps with 436 nm or 365 nm wavelengths were used. Currently 193 nm argon-fluoridelasers are used for the critical layers down to the 90 nm node. In the future, 13.4 nm extreme ultraviolet(EUV) light sources may be used, but at present these sources are costly and require prohibitivelyexpensive reflective optics.Wavelengths comparable to or greater than the feature size cause distortion in the patternsexposed on the photoresist. Resolution enhancement techniques precompensate for this distortion so thedesired patterns are obtained. These techniques involve modifying the amplitude, phase, or direction of the incoming light. Optical proximity correction (OPC) makes small changes to the patterns on the masks tocompensate for these local distortions. 1.3 Well and Channel Formation Varying proportions of donor and acceptor impurities can be achieved using epitaxy, deposition, orimplantation. Epitaxy involves growing a single-crystal film on the silicon by subjecting the silicon wafersurface to an elevated temperature and a source of dopant material.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Levinson H J Principles of Lithography PDFДокумент524 страницыLevinson H J Principles of Lithography PDFXavier G TeslaОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Alternative Photographic ProcessesДокумент2 страницыAlternative Photographic ProcessesPham Ngoc TuanОценок пока нет
- Euv Lithography Vivek Bakshi PDFДокумент2 страницыEuv Lithography Vivek Bakshi PDFLawrenceОценок пока нет
- Euv Lithography Bakshi PDFДокумент2 страницыEuv Lithography Bakshi PDFMichaelОценок пока нет
- The Challenges of LithographyДокумент33 страницыThe Challenges of LithographyxellosdexОценок пока нет
- EUV LithographyДокумент26 страницEUV LithographyGabriel DonovanОценок пока нет
- DX DiagДокумент33 страницыDX DiagVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Wifi TetheringДокумент2 страницыWifi TetheringVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Irctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Документ1 страницаIrctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Vijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Caiib Macmillan Ebook Retail BankingДокумент41 страницаCaiib Macmillan Ebook Retail BankingVijitha Kalass100% (1)
- SSC Intensive Study Programme Syllabus Division For Revsion Tests MathematicsДокумент9 страницSSC Intensive Study Programme Syllabus Division For Revsion Tests MathematicsVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- EMP MotivationДокумент76 страницEMP MotivationVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- IBPS PO Mock Test (Answer) - 4: Profession City GenderДокумент5 страницIBPS PO Mock Test (Answer) - 4: Profession City GenderVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- BSC Academy: Mock-Test Paper-4Документ44 страницыBSC Academy: Mock-Test Paper-4Vijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Debit or CreditДокумент1 страницаDebit or CreditVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Balance Sheet As A PictureДокумент2 страницыBalance Sheet As A PictureVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- More Details About My ComputerДокумент2 страницыMore Details About My ComputerVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Wireless Keyboard & Mouse EmulatorДокумент84 страницыWireless Keyboard & Mouse EmulatorVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Meaning and Characteristics of Business CycleДокумент9 страницMeaning and Characteristics of Business CycleVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- 2.1 FDI Policy Framework in IndiaДокумент5 страниц2.1 FDI Policy Framework in IndiaVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Wireless Keyboard and MouseДокумент3 страницыWireless Keyboard and MouseVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Express in EnglishДокумент18 страницExpress in EnglishVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Laptop ProtectorДокумент47 страницLaptop ProtectorVijitha KalassОценок пока нет
- Lithographic Processes: Pattern Generation and TransferДокумент16 страницLithographic Processes: Pattern Generation and Transferanup_sky88Оценок пока нет
- EUVL Workshop Keynote - IMECДокумент2 страницыEUVL Workshop Keynote - IMECGary Ryan DonovanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Mems EA C415: Dr. N.N. SharmaДокумент14 страницIntroduction To Mems EA C415: Dr. N.N. SharmaArjit GoswamiОценок пока нет
- LithographyДокумент34 страницыLithographysona007Оценок пока нет
- Lithography Sequence: Lithography Process Requirements The PhotoresistДокумент3 страницыLithography Sequence: Lithography Process Requirements The PhotoresiststansilawОценок пока нет
- Bitumen of JudeaДокумент2 страницыBitumen of JudeaforonideoОценок пока нет
- EUV Lithography and Its Patterning Technology - Final - v2Документ38 страницEUV Lithography and Its Patterning Technology - Final - v2xellosdex100% (1)
- Ic Fabrication Technology Lab 2Документ5 страницIc Fabrication Technology Lab 2Vishnu VardhanОценок пока нет
- Photographic Printing - WikipediaДокумент9 страницPhotographic Printing - WikipediaLKMs HUBОценок пока нет
- 9,6 NM 9,03 Rad /S: Data 1Документ6 страниц9,6 NM 9,03 Rad /S: Data 1Agus PramonoОценок пока нет
- Euv Sources For Lithography PDFДокумент2 страницыEuv Sources For Lithography PDFChrisОценок пока нет
- HHДокумент18 страницHHtessyОценок пока нет
- Double Patterning LithographyДокумент1 страницаDouble Patterning Lithographyrashmi sОценок пока нет
- Micro and Smart SystemsДокумент22 страницыMicro and Smart SystemsGopinath ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Immersion Lithography Photomask and Wafer-Level MaДокумент34 страницыImmersion Lithography Photomask and Wafer-Level MaTao HouОценок пока нет
- LithographyДокумент17 страницLithographyRJ Singh100% (1)
- Lecture38 PDFДокумент2 страницыLecture38 PDFstansilawОценок пока нет
- Extreme Ultraviolet LithographyДокумент24 страницыExtreme Ultraviolet LithographyVishnu VardhanОценок пока нет
- CMOS VLSI Design 128Документ1 страницаCMOS VLSI Design 128Carlos SaavedraОценок пока нет
- CTR 040325Документ32 страницыCTR 040325denghueiОценок пока нет
- Mapper - Lithography in Nature BusinessДокумент1 страницаMapper - Lithography in Nature BusinessdewilibiawatiОценок пока нет
- Colortec c41 PDFДокумент2 страницыColortec c41 PDFBethОценок пока нет
- Lithography PresentationДокумент10 страницLithography PresentationNarendra AchariОценок пока нет
- Milestones ToolsДокумент25 страницMilestones ToolsThọ NguyễnОценок пока нет