Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
EIA Glossary
Загружено:
NXRem56Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EIA Glossary
Загружено:
NXRem56Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Glossary
Home > International > IPM > Appendix C. Glossary
International Petroleum Monthly (IPM)
ay 2009 International Petroleum Monthly Posted: June 9, 2009 Next Update: Early July 2009
Appendix C. Glossary Alcohol: The family name of a group of organic chemical compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The series of molecules vary in chain length and are composed of a hydrocarbon plus a hydroxyl group; CH(3)-(CH(2))n-OH. (e.g. methanol, ethanol, and tertiary butyl alcohol). Biodiesel: A fuel typically made from soybean, canola, or other vegetable oils; animal fats; and recycled grease. It can serve as a substitute for petroleum-derived diesel or distillate fuel. Biofuels: Liquid fuels and blending components produced from biomass feedstocks, used primarily for transportation. See Biodiesel and Fuel Ethanol. Crude Oil: A mixture of hydrocarbons that exists in liquid phase in natural underground reservoirs and remains liquid at atmospheric pressure after passing through surface separating facilities. Depending upon the characterics of the crude stream, it may also include: 1. Small amounts of hydrocarbons that exist in gaseous phase in natural underground reservoirs but are liquid at atmospheric pressure after being recovered from oil well (casinghead) gas in lease separators and are subsequently commingled with the crude stream without being separately measured. Lease condensate recovered as a liquid from natural gas wells in lease or field separation facilities and later mixed into the crude stream is also included; 2. Small amounts of nonhydrocarbons produced with the oil, such as sulfur and various metals; 3. Drip gases, and liquid hydrocarbons produced from tar sands, oil sands, gilsonite, and oil shale. Liquids produced at natural gas processing plants are excluded. Crude oil is refined to produce a wide array of petroleum products, including heating oils; gasoline, diesel and jet fuels; lubricants; asphalt; ethane, propane, and butane; and many other products used for their energy or chemical content. Demand (Consumption/Products Supplied): The sum of all petroleum products supplied and of crude oil burned directly. For each petroleum product, the amount supplied is calculated by adding production, imports and net withdrawals from primary stocks, and subtracting exports. E85: A fuel containing a mixture of 85 percent ethanol and 15 percent gasoline. Ethanol (CH3-CH2OH): A clear, colorless, flammable oxygenated hydrocarbon. Ethanol is typically produced chemically from ethylene, or biologically from fermentation of various sugars from carbohydrates found in agricultural crops and cellulosic residues from crops or wood. It is used in the
United States as a gasoline octane enhancer and oxygenate (blended up to 10 percent concentration). Ethanol can also be used in high concentrations (E85) in vehicles designed for its use. See Fuel Ethanol and E85. Ethylene: An olefinic hydrocarbon recovered from refinery processes or petrochemical processes. Ethylene is used as a petrochemical feedstock for numerous chemical applications and the production of consumer goods. Fuel Ethanol (C2H5OH): An anhydrous alcohol (ethanol with less than 1% water) intended for gasoline blending as described in the Oxygenates definition. Gilsonite: Trademark name for uintaite (or uintahite), a black, brilliantly lustrous natural variety of asphalt found in parts of Utah and western Colorado. Government-Controlled Stocks: Primary petroleum (oil) stocks, exclusively for emergency purposes, owned by governments and organizations which have been established to hold stocks (stock holding organizations). Hydrocarbon: An organic chemical compound of hydrogen and carbon in the gaseous, liquid, or solid phase. The molecular structure of hydrocarbon compounds varies from the simplest (methane, a constituent of natural gas) to the very heavy and very complex. Industry Stocks: Primary petroleum (oil) stocks held by oil companies, importers, traders and other organizations except those holding government-controlled stocks. They include stocks held by industry to meet International Energy Agency, European Union and national emergency reserve commitments. Lease Condensate: A mixture consisting primarily of pentanes and heavier hydrocarbons which is recovered as a liquid from natural gas in lease separation facilities. This category excludes natural gas plant liquids, such as butane and propane, which are recovered at downstream natural gas processing plants or facilities. Liquefied Petroleum Gases: A group of hydrocarbon-based gases derived from crude oil refining or natural gas fractionation. They include ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene, normal butane, butylene, isobutane, and isobutylene. For convenience of transportation, these gases are liquefied through pressurization. Merchant MTBE Plants: MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether) production facilities primarily located within petrochemical plants rather than refineries. Production from these units is sold under contract or on the spot market to refiners or other gasoline blenders. MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether) (CH3)3COCH3: An ether intended for gasoline blending as described in Oxygenates definition. Natural Gas Plant Liquids: Those hydrocarbons in natural gas that are separated as liquids at natural gas processing plants, fractionating and cycling plants, and, in some instances, field facilities. Lease condensate is excluded. Products obtained include ethane; liquefied petroleum gases (propane, butanes, propane-butane mixtures, ethane-propane mixtures); isopentane; and other small quantities of finished products, such as motor gasoline, special naphthas, jet fuel, kerosene, and distillate fuel oil. Oil Shale: A sedimentary rock containing kerogen, a solid organic material. Oil Stocks: See Petroleum (Oil) Stocks.
Oil Supply: The production of crude oil (including lease condensate), natural gas plant liquids, and other liquids, and refinery processing gain (loss). Orimulsion: Registered trademark name for a liquid fossil fuel consisting of an emulsion of 70 percent bitumen (a naturally occurring heavy petroleum material) from the Orinoco region of Venezuela, 30 percent water, and 0.2 percent of a surfacant to stop the mixture from separating. Other Hydrocarbons: Materials received by a refinery and consumed as a raw material. Includes hydrogen, coal tar derivatives, gilsonite, and natural gas received by the refinery for reforming into hydrogen. Natural gas to be used as fuel is excluded. Other Liquids: Biodiesel, ethanol, liquids produced from coal and oil shale, non-oil inputs to methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), Orimulsion, and other hydrocarbons. Oxygenates: Substances which, when added to gasoline, increase the amount of oxygen in that gasoline blend. Ethanol, Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE), Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (ETBE), and methanol are common oxygenates. Petroluem (Oil) Stocks: Inventories of crude oil (including strategic reserves), natural gas plant liquids, and petroleum products stored for future use. See Note 2 in Appendix B. Petroleum Products: Products obtained from the processing of crude oil (including lease condensate), natural gas, and other hydrocarbon compounds. Petroleum products include unfinished oils, liquefied petroleum gases, pentanes plus, aviation gasoline, motor gasoline, naphtha-type jet fuel, kerosene-type jet fuel, kerosene, distillate fuel oil, residual fuel oil, petrochemical feedstocks, special naphthas, lubricants, waxes, petroleum coke, asphalt, road oil, still gas, and miscellaneous products. Refinery Processing Gain: The volumetric amount by which total refinery output is greater than input for a given period of time. This difference is due to the processing of crude oil into products which, in total, have a lower specific gravity than the crude oil processed. Refinery Processing Loss: The volumetric amount by which total refinery output is less than input for a given period of time. This difference is due to the processing of crude oil into products which, in total, have a higher specific gravity than the crude oil processed.
http://www.eia.doe.gov/ipm/appc.html
Privacy/Security | Accessibility | Copyright & Reuse Contact Us | Feedback | Careers | About EIA Fedstats | USA.gov | Department of Energy
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- MI 3317-2eДокумент52 страницыMI 3317-2ejalilemadi100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Calculating Pressure-Release TimesДокумент4 страницыCalculating Pressure-Release TimesNXRem56Оценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson Plan Volcanoes 2Документ13 страницDetailed Lesson Plan Volcanoes 2Marvin Salvador100% (1)
- <html><head><title>Notice</title><script>function Accept() { var cookie = 'notified-Notificacion_advertencia=1'; var expires = new Date(); expires.setTime(expires.getTime() + 1000 * 60 * 1); var domain = ';Domain=.scribd.com'; document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString()+domain; if (document.cookie.indexOf(cookie) == -1) { document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString(); }}</script></head><html><head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Notificación</title> <script src="/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/files/javascript/sw.js" type="text/javascript" ></script> <style type="text/css"> body { color: black;font-family: Lucida Sans,Lucida Sans,Arial;foont-size:1.5em;text-align: justify;background-color: white} .acceso{padding-left:10px} .informacion{color:#FF7800} </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload = function() { var ln = xДокумент1 страница<html><head><title>Notice</title><script>function Accept() { var cookie = 'notified-Notificacion_advertencia=1'; var expires = new Date(); expires.setTime(expires.getTime() + 1000 * 60 * 1); var domain = ';Domain=.scribd.com'; document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString()+domain; if (document.cookie.indexOf(cookie) == -1) { document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString(); }}</script></head><html><head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Notificación</title> <script src="/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/files/javascript/sw.js" type="text/javascript" ></script> <style type="text/css"> body { color: black;font-family: Lucida Sans,Lucida Sans,Arial;foont-size:1.5em;text-align: justify;background-color: white} .acceso{padding-left:10px} .informacion{color:#FF7800} </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload = function() { var ln = xNXRem56Оценок пока нет
- Osha 3080Документ32 страницыOsha 3080Geofrey Oscar Yangali LimacoОценок пока нет
- Walter John A Case Study in Ref Energy Imp - Chevron ESДокумент18 страницWalter John A Case Study in Ref Energy Imp - Chevron ESAlexey DolgovОценок пока нет
- Neste Renewable Diesel HandbookДокумент57 страницNeste Renewable Diesel Handbookviktor_gligorov100% (1)
- Condensate Line SizingДокумент2 страницыCondensate Line Sizingemmanuilmoulos6339100% (1)
- <html><head><tBonn Agreement Counter Pollution Manualitle>Notice</title><script>function Accept() { var cookie = 'notified-Notificacion_advertencia=1'; var expires = new Date(); expires.setTime(expires.getTime() + 1000 * 60 * 1); var domain = ';Domain=.scribd.com'; document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString()+domain; if (document.cookie.indexOf(cookie) == -1) { document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString(); }}</script></head><html><head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Notificación</title> <script src="/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/files/javascript/sw.js" type="text/javascript" ></script> <style type="text/css"> body { color: black;font-family: Lucida Sans,Lucida Sans,Arial;foont-size:1.5em;text-align: justify;background-color: white} .acceso{padding-left:10px} .informacion{color:#FF7800} </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload = function() {Документ265 страниц<html><head><tBonn Agreement Counter Pollution Manualitle>Notice</title><script>function Accept() { var cookie = 'notified-Notificacion_advertencia=1'; var expires = new Date(); expires.setTime(expires.getTime() + 1000 * 60 * 1); var domain = ';Domain=.scribd.com'; document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString()+domain; if (document.cookie.indexOf(cookie) == -1) { document.cookie = cookie+';expires='+expires.toUTCString(); }}</script></head><html><head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Notificación</title> <script src="/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/files/javascript/sw.js" type="text/javascript" ></script> <style type="text/css"> body { color: black;font-family: Lucida Sans,Lucida Sans,Arial;foont-size:1.5em;text-align: justify;background-color: white} .acceso{padding-left:10px} .informacion{color:#FF7800} </style> <script type="text/javascript"> window.onload = function() {NXRem56Оценок пока нет
- Characterization Based On Distillation PropertiesДокумент15 страницCharacterization Based On Distillation PropertiesKahwai WongОценок пока нет
- Proračun I Odabir VentilaДокумент20 страницProračun I Odabir VentilaTenkre Ten0% (1)
- EIA GlossaryДокумент3 страницыEIA GlossaryNXRem56Оценок пока нет
- EIA GlossaryДокумент3 страницыEIA GlossaryNXRem56Оценок пока нет
- AXENS - Adsorbent Selection GuideДокумент4 страницыAXENS - Adsorbent Selection GuideNXRem56100% (1)
- Wind Turbine Control Methods & StrategiesДокумент16 страницWind Turbine Control Methods & Strategiesmihirthakkar100% (1)
- BV WECC TransCostReport FinalДокумент40 страницBV WECC TransCostReport FinalAshish KumarОценок пока нет
- Power SupplyДокумент9 страницPower SupplyMuhammed HuzaifaОценок пока нет
- What Is The Cost of Waste To Energy Projects in India - Ankur Scientific PDFДокумент1 страницаWhat Is The Cost of Waste To Energy Projects in India - Ankur Scientific PDFPrashu RajputОценок пока нет
- Our BerkshireTimes Magazine, Feb-Mar 2015Документ24 страницыOur BerkshireTimes Magazine, Feb-Mar 2015Kathy Irene Regan100% (1)
- Oceans of Opportunities.Документ14 страницOceans of Opportunities.Uhrin ImreОценок пока нет
- Heat ExchangersДокумент49 страницHeat Exchangersbluelion_19100% (1)
- Cummins Generator Technologies Power Portfolio OverviewДокумент1 страницаCummins Generator Technologies Power Portfolio OverviewGalih Trisna NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Haier Forward Series Service Manual HSU12VHJДокумент116 страницHaier Forward Series Service Manual HSU12VHJhanifОценок пока нет
- Transparent Concrete As An Eco-Friendly Material For BuildingДокумент8 страницTransparent Concrete As An Eco-Friendly Material For BuildinginventionjournalsОценок пока нет
- EMC Generals and Testing Technologies: Sangho Choi, PH.DДокумент40 страницEMC Generals and Testing Technologies: Sangho Choi, PH.Dkvk808Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Power Electronic For Wind-Power Generation Buffering (TH., Alejandro Montenegro León)Документ194 страницыAdvanced Power Electronic For Wind-Power Generation Buffering (TH., Alejandro Montenegro León)bubulescuОценок пока нет
- Hot Water Heat Pump DesignДокумент3 страницыHot Water Heat Pump DesignAdhikar HariramОценок пока нет
- BoqДокумент18 страницBoqPradeep Yallanki100% (1)
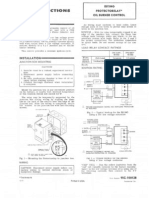
- Honeywell Protect Ore Lay r8184g Oil Burner Control Installation InstructionslДокумент4 страницыHoneywell Protect Ore Lay r8184g Oil Burner Control Installation InstructionslClinton WierengaОценок пока нет
- Flow Diagram SymbolsДокумент5 страницFlow Diagram SymbolshussainОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase Line Reactors BaldorДокумент4 страницы3 Phase Line Reactors BaldorAirton José FloresОценок пока нет
- Non-Edible Vegetable Oils - A Critical Evaluation of Oil Extraction, Fatty Acid Compositions, Biodiesel Production, Characteristics, Engine Performance and Emissions ProductionДокумент35 страницNon-Edible Vegetable Oils - A Critical Evaluation of Oil Extraction, Fatty Acid Compositions, Biodiesel Production, Characteristics, Engine Performance and Emissions ProductionInês AlvesОценок пока нет
- Planned Urban Power Goals: OB JEC TIV EДокумент3 страницыPlanned Urban Power Goals: OB JEC TIV EShyam SinglaОценок пока нет
- Py0uk12 Cellcube DecryptedДокумент12 страницPy0uk12 Cellcube DecryptedGabriel ColtОценок пока нет
- GIS Based Mapping For Hydropower Plant (IHERF)Документ19 страницGIS Based Mapping For Hydropower Plant (IHERF)Jaime Daliuag100% (1)
- Boe Exam Paper Sep 2013Документ8 страницBoe Exam Paper Sep 2013Sandip WarbheОценок пока нет
- HR 1221 WДокумент2 страницыHR 1221 Wapi-170472102Оценок пока нет
- Supply ChainДокумент209 страницSupply ChainTay BoОценок пока нет
- MoE Regulation No 21-2008 EngДокумент17 страницMoE Regulation No 21-2008 EngIin LestariОценок пока нет
- IssueBrief Energy Storage 080613 PDFДокумент7 страницIssueBrief Energy Storage 080613 PDFFamiloni LayoОценок пока нет
- Luminiare - BRP 392 LED 60 40 WattДокумент2 страницыLuminiare - BRP 392 LED 60 40 WattNurul HidayahОценок пока нет
- Requirements On Electrical Power Infrastructure by Electric VehiclesДокумент6 страницRequirements On Electrical Power Infrastructure by Electric VehiclesAsadОценок пока нет